| Previous Contents Index DocHome Next |
| iPlanet Application Server 6.0 Administration and Deployment Guide |
Chapter 12 Administering Multi-Server Applications
This chapter describes how to administer applications on multiple iPlanet Application Server (iAS) machines using iAS Administration Tool.The following topics are included in this chapter:
Hosting Applications Locally on Multiple Servers
iPlanet Application Server (iAS) Administration Tool allows you to simultaneously administer applications that are stored on multiple servers. Settings made to application components, such as Enterprise Java Beans (EJBs), distributed across multiple application servers are automatically updated across those servers. In addition, settings made to one iAS machine can be copied and applied to the other iAS machines in a group or the entire enterprise.Hosting Partitioned Applications on Multiple Servers
Using the administration tool, you can view each iAS machine in the enterprise and make changes to one or more servers at the same time.
To host applications on multiple iPlanet Application Server (iAS) machines, you can perform either of the following tasks:
Distribute applications or parts of applications across two or more servers to specialize request and application processing.
The more servers you have to work with, the greater your choice of application hosting configurations.Duplicate application components on two or more servers to increase application performance with load balancing.
The following table describes three common ways to host an application on multiple iAS machines:
Hosting Applications Locally on Multiple Servers
Hosting applications locally on multiple servers is the simplest of the three most common server configurations. In this configuration, you deploy the complete application on each iAS machine. If the application is already installed on an iAS machine, you can use the Deployment Tool to deploy the application to other servers.When you deploy an application locally, it means that session is neither backed up nor shared between iAS instances. In this scenario, you use a different web server for each iAS instance. Each iAS instance may (or may not) access a common database or other backend service (see following diagram). This configuration requires that you configure each web connector plug-in to forward requests to the appropriate iAS machine.
Alternatively, it is possible to deploy local applications across multiple iAS instances while sharing a common web server and LDAP server. This configuration functions much like the first example, except that there is a single web server, and all iAS instances share a common configuration through the same LDAP server. This configuration has the advantage in that load balancing can be done across multiple iAS instances whereas the prior example requires clients to access multiple different web servers. While this scenario is possible, it may or may not be suitable for your particular application.
Hosting Partitioned Applications on Multiple Servers
To partition an application, you must divide up the application components that make up an application. Application components are then hosted by separate iAS machines. Partitioning applications allows you to specialize the type of processing each iAS machine performs.For example, servlets responsible primarily for data access are I/O-intensive, while servlets responsible for performing calculations are CPU and active-memory intensive. To maximize your application's overall performance, you can partition the application to host these different types of servlets on separate iAS machines.
To configure a partitioned application, perform the following steps:
Deploy the complete application to all participating iAS machines using the iAS Deployment Tool.
While partitioning application components, if you want to view the server(s) where an application component is installed, perform the following steps:
Enable load balancing, which will allow each server to find application components hosted on other servers.
- You can view the applications and associated modules deployed to each registered iAS in the left pane of the Application window. Expand a server to see the deployed applications and then expanding an application folder to see the modules in an application.
- For more information on application deployment, see Chapter 2 "Deploying and Upgrading Applications."
Disable specific application components on a server-by-server basis.
- For more information on load balancing, see Chapter 13 "Balancing User-Request Loads."
- See
Open the Application window of iAS Administration Tool.
In the left pane of the Application window, expand the server whose application components you want to partition.
Open an application folder and then highlight a servlet icon for J2EE applications. For C++ applications, highlight an AppLogic icon .
- Deployed application components appear in the right pane of the Application window.
Select an application component in the right pane of the Application window.
Click the Servlet Component Properties (or Application Component Properties) button.
Click OK to dismiss the dialog box.
- A dialog box appears displaying the application servers where the component is installed. If the selected iAS machine is not listed, you must deploy the .ear file containing the necessary application components to that machine.
Disabling and Enabling Application Components
Disabling a component of your application (such as a servlet) stops users from accessing that component. Current requests are allowed to finish when a component is disabled, but no new requests are accepted until the component is re-enabled.To disable an application component, perform the following steps:
On the iAS Administration toolbar, click the Application button to open the Application window.
In the left pane of the Application window, double-click the server where the application component(s) to be disabled resides.
Expand the folder containing the application components to disable.
Expand the application folder to see the application modules.
Select the module that contains the application component(s) you want to disable.
In the right pane of the Application window, locate the component to disable.
- The right pane of the Application window shows each application component within the module.
Locate the component(s) to disable and click the Enabled checkbox to clear the checkbox.
Click Toggle Enabled if you want to enable or disable (toggle) all the application components in a group.
Click Apply Changes to save your changes to your iAS machine.
- To enable application components, click their corresponding Enabled checkboxes to select them.
Hosting and Deploying Applications for Load Balancing
Balancing application-request loads, or load balancing, differs from partitioning applications. Load balancing requires you to place one or more copies of an application component on multiple iAS machines rather than simply dividing an application's components among multiple servers (or partitioning the application). You then configure each server, allowing it to find application components on other servers.When you deploy an application, you must decide if you want to configure the application for load balancing and, if so, how you will configure it. Choose among the following load balancing configurations:
Balancing loads only between the servers in a production environment, if deploying to more than one iAS machine.
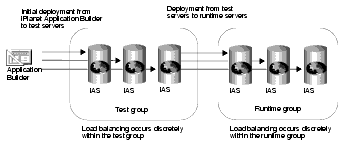
The following illustration depicts a load-balancing distribution as discussed in the Example 1:
Balancing application loads between existing production servers and new servers that you add to the enterprise.
- Example 1: You might have three iAS machines used for testing applications. Your production environment, where users' requests are actually processed, also consists of three iAS machines. Because the application components could be different between the two groups of servers, you do not want to enable application load balancing. Therefore, when you deploy an application from the test servers to the production servers, you should choose only to balance the loads between the destination servers.
Deploy the application locally to the server or servers (no load balancing).
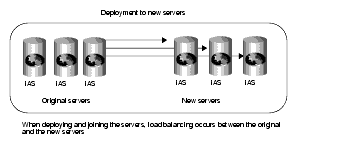
- Example 2: Suppose you scale the enterprise to include three more iAS machines in the production group, you can join all the servers in that group when deploying the applications from one of the existing production servers to the new servers. The application loads are then balanced between the existing servers and the new servers. (Scenario 2)
The next illustration depicts a joining of servers when adding new servers to a group and deploying an application to those servers with the join option as discussed in Example 2.
If you choose a local distribution during deployment, no application-request load balancing occurs between any of the servers.
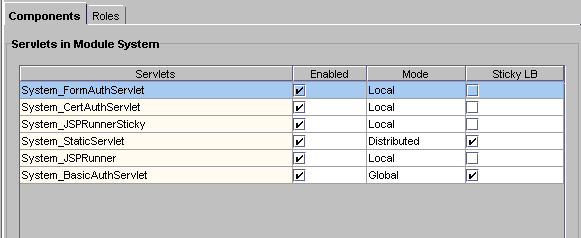
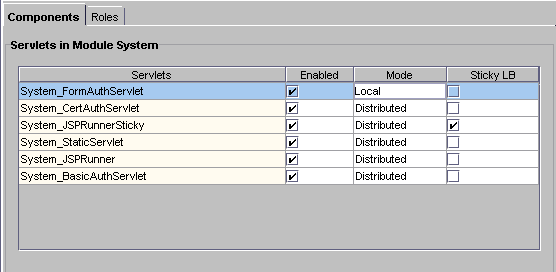
Changing Attributes of Distributed Application Components
When you change such attributes as enabled sticky load balancing for an application component that is distributed across multiple servers, those changes replicate themselves on the servers where that component is hosted. Changing the distribution level (local, distributed, and global) of installed application components is useful if you previously installed an application locally, but now want to distribute the application for load balancing. You can also disable load balancing by changing a distributed application to a local configuration on the specified server.If you change a component from a distributed or global state to a local state on one server, each server that hosts that component ceases to balance loads with the server where the distribution was set to local.
For example, an application component called ShopCart is distributed across servers A, B, and C. Should you decide to run ShopCart locally on server A, but continue to allow it to run in a distributed state across servers B and C, each server (A, B, and C) is automatically updated so that requests for ShopCart are no longer passed to server A from servers B and C. Instead, requests for ShopCart made to servers B or C are passed only between those two servers. All requests for ShopCart made to server A are processed only by server A.
To change the distribution level for an application component, perform the following steps:
Open the Application window of iAS Administration Tool.
In the left pane of the Application window, expand the server for which you want to change application settings.
Expand the application folder and select the servlet or AppLogic icon that contains the application components you want to modify.
In the right pane of the Application window, select each application component for which you want to change the distribution level as follows:
Local--The servlet or AppLogic runs on one iAS machine only
In the Mode column, change the distribution level.Distributed--The servlet or AppLogic runs on specified iAS machines
Global--The servlet or AppLogic runs anywhere in the enterprise.
If you are changing the distribution level for all components in the selected group, click Toggle Mode. All application components are updated simultaneously.
In the left pane, under Registered Servers, choose which iAS machines will participate in load balancing of the selected application component. The application component must be installed on each iAS machine participating in load balancing.If you are modifying the Mode from Local to Distributed or Global, you must modify the application properties to specify across which iAS machines load balancing is to occur.
If you are modifying the Mode from Distributed or Global to Local, there is nothing more you need to do.
- When you change an application component's Mode to Distributed all registered servers appearing in the left pane of the Application window are added to that application component's server list. You can access the server list by clicking the Application Component Properties button.
If you need to register additional application servers, go to the File menu and choose New, then choose Server.
Repeat these steps for each application component.
Click Apply Changes to save your changes to the iAS machine.
Previous Contents Index DocHome Next
Copyright © 2000 Sun Microsystems, Inc. Some preexisting portions Copyright © 2000 Netscape Communications Corp. All rights reserved.
Last Updated April 25, 2000