|
Local Patch Server |
This chapter describes Local Patch Server, henceforth referred to as LPS. By using an LPS on your intranet, you can supply patches to your local client systems and minimize the Internet traffic between your client systems and the SunTM patch server. The LPS caches any patches that are downloaded from its patch source, such as the Sun patch server, another LPS, or a local collection of patches.
The system you choose to act as the local patch server must be running at least the SolarisTM 9 Operating System and have at least the Entire Solaris Software Group installed. If your system runs the Solaris 9 OS, it must also have the Sun Control Station CC Edition software installed, which includes the Sun Patch Manager 2.0 product.
This chapter covers the following topics:
This section describes how to install and uninstall the LPS software. It also describes how to verify that the LPS software has been installed.
A Solaris 9 system or a Solaris 10 system that has the Sun Patch Manager 2.0 software installed can be used as an LPS on your intranet.
Before you can use the system as an LPS, you must have the LPS software configured and enabled. You must also configure your local client systems to obtain patch data from your LPS.
The Local Patch Server module is part of the Sun Control Station CC Edition product for the Solaris 9 OS. On a Solaris 9 system, you must have at least the Entire Solaris Software Group (SUNWCall) installed for the installer to succeed.
On a Solaris 10 system, you must have at least the Developer Solaris Software Group (SUNWCprog) installed. Then, you must download and install the LPS module after you install the Sun Control Station CC Edition software.
|
You can also verify that the LPS module is installed in another way. First, log in to the LPS as the root user and check that the SUNWpsvru package and the SUNWpsvrr package have been installed. If the packages are not found in the pkginfo output, you must install them.
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
1. Open the Sun Control Station application from a browser window by typing:
If you do not want to use the SSL connection, type the following URL:
http://IP-address-of-server:8080/sdui/
The Sun Control Station Login page appears.
2. Type the user name and the password in the fields.
The default user name and password are admin.
After you log in for the first time, change the password. See the Sun Control Station CC Edition Administration Guide for information about how to change passwords.
The Sun Control Station main page appears.
3. From the navigation bar, click Local Patch Server, and then click Status to open the LPS Status page.
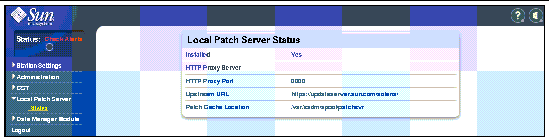
|
You can use the Module Manager of the control station software to uninstall the LPS module. You can also uninstall the LPS software in these ways:
1. As the root user, log in to the LPS system.
2. Run the Module Manager program.
# /scs/sbin/moduleMgr.pl -n lps
The following package is currently installed:
SUNWlpsui Local Patch Server Module for Solaris
Do you want to remove this package? [y,n,?,q]
3. Remove the LPS module by typing y.
When the remove operation completes, the following message appears:
Removal of SUNWlpsui was successful...
You can configure a chain of patch servers on your intranet. The last link in the chain of local servers can point to the Sun patch server or to a local collection of patches. By using this chain of servers, a patch download request from your client system to its primary patch server can be forwarded to other servers in the chain in an attempt to fulfill the request.
If your client system's primary server cannot locate a patch, the server makes the same request of the next server in the chain to determine whether the patch is stored there. If the patch is found, it is downloaded to the client system. If the patch is not found, the request continues along the chain until the patch is found or the last server in the chain is reached.
For example, your company has a patch server that obtains patches directly from the Sun patch server. Each office in your company has its own patch server that obtains patches from the company patch server.
Each local patch server in the chain stores the patches found on another server in the chain based on the download request. So, a patch that is not initially found on your local server will be downloaded to your local server and stored before being downloaded to the client system. Each system in a chain of local patch servers might increase the amount of time it takes to download patches to your client system.
Patch Manager can create an ordered list of patches that you can save to a text file and use to perform patch operations. The local patch server obtains patches from its source of patches on a per-request basis. You do not need to stock your patch server with patches before you can use it.
You might use a patch list to apply the same set of patches to systems that have the same hardware and software configurations. Or, you might create a patch list file that contains all pertinent security patches and use the patch list to apply those security patches to one or more systems.
You can create a file that contains an ordered patch list using the smpatch command in any of these ways:
If you modify a patch list and the patches are available on your system, use the smpatch order command to put the list in an order suitable for applying patches. Otherwise, use the smpatch analyze command, which also produces an ordered list of patches.
You can use patch lists as input to these commands:

|
Caution - The smpatch addcommand attempts to apply all the patches in the patch list, regardless of the policy for applying patches and patch dependencies. |
Your system can obtain patches from the following sources:
By default, your system obtains patches from the Sun patch server.
|
Note - If you want your system to obtain patches from a local patch server, you must first configure one. See Configuring Your Local Patch Server: Process Overview. |
1. Become an authorized user or assume a role that includes the Software Installation profile or the solaris.admin.patchmgr.* authorization.
The System Administrator profile includes the appropriate profiles.
2. Specify the URL of the patch source.
# smpatch unset patchpro.patch.source
# smpatch set patchpro.patch.source=http://server-name:3816/solaris/
# smpatch set patchpro.patch.source=file:/directory-name
directory-name can be a local file system or a remotely mounted file system.
# smpatch set patchpro.patch.source=file:/export/patches
# smpatch set patchpro.patch.source=file:/net/jupiter/export/patches
# smpatch set patchpro.patch.source=file:/cdrom/cdrom0
This process overview identifies the optional tasks that you can perform with the patchsvr setup command to configure a patch server on your intranet. See also the patchsvr(1M) man page.
1. Configure your LPS for the first time.
Before you can use your system as an LPS, do the following:
Configure client systems to specify your LPS as the source of patches.
See How to Initially Configure Your LPS.
2. (Optional) Obtain information about the configuration of your LPS.
This information can help you diagnose problems or view the configuration settings you specified.
See How to View Your LPS Configuration Settings.
3. (Optional) Change the configuration settings of your LPS.
By default, your LPS directly connects to the Internet and obtains patches from the Sun patch server.
If your patch management environment does not match the default, modify the configuration settings appropriately.
See How to Change Your LPS Configuration Settings.
Client systems are configured to obtain patches from the Sun patch server by default. You need an LPS in the following situations:
|
Note - Only a system that runs at least the Solaris 9 OS can be used as an LPS. |
To configure an LPS on your intranet and to begin using it to serve client systems, do the following:
1. Configure and start your LPS.
See How to Initially Configure Your LPS.
2. Configure your client systems to obtain patches from your LPS.
See How To Specify the Source of Patches.
After completing these steps, you are ready to have your client systems obtain patches from your LPS.
Your LPS needs to obtain patches and patch data from one of these sources:
To obtain a suitable patch CD from Sun, contact your Sun support representative.
After you set up the LPS, configure each of your client systems to communicate with that server. You are then ready to have your client systems obtain patches from your LPS.
Use the patchsvr command to configure and enable your LPS. See the patchsvr(1M) man page.
Before you can use a system as an LPS, ensure that these prerequisites are met:
A Solaris 9 system or a Solaris 10 system that runs the Patch Manager software is suitable to be a patch server on your intranet.
Obtain the LPS product from the Sun Download Center at http://wwws.sun.com/software/download.
|
Note - If your LPS uses a web proxy to connect to the Internet, you must specify information about the web proxy. See How to Change Your LPS Configuration Settings |
1. As the root user, log in to the system that you plan to use as your LPS.
2. Determine whether the SUNWpsvru package and the SUNWpsvrr package are installed on the system.
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
If the packages are not installed, you must install them before continuing this task.
Your LPS can point to a different source of patches. You can use this patch source to fulfill patch download requests that cannot be fulfilled by your LPS. By default, the source of patches for your LPS is the Sun patch server.
# patchsvr setup -p http://server-name:3816/solaris/
# patchsvr setup -p file:/directory-name
# patchsvr setup -p https://updateserver.sun.com/solaris/
The local collection of patches can be in a directory, on a CD, or on a remote file system.
5. (Optional) Enable your LPS so that it is started each time the system boots.
Each of these examples verify that the Sun Patch Manager 2.0 software is installed on the system.
Type the following to configure the first patch server, which will connect to the Sun patch server:
psvr1# pkginfo | grep SUNWpsvr
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
psvr1# patchsvr setup -x webproxy1:2010
psvr1# patchsvr setup -p https://updateserver.sun.com/solaris/
You also configure psvr2 to obtain patches from psvr1 by specifying the URL to the server, which is http://psvr1:3816/solaris/. After you configure psvr2, you must start it. You can also enable it for automatic restart when the system boots.
Type the following to configure the second patch server, which will get patches from the first patch server:
psvr2# pkginfo | grep SUNWpsvr
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
psvr2# patchsvr setup -p http://psvr1:3816/solaris/
Now that both of the patch servers are configured and started, you can configure client systems to use them.
Type the following to configure the LPS to get patches from the /export/patches directory:
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
# patchsvr setup -p file:/export/patches
Now that the patch server is configured and started, you can configure client systems to use it.
Type the following to configure the LPS to get patches from a CD:
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
# patchsvr setup -p file:/cdrom/cdrom0
Now that the patch server is configured and started, you can configure client systems to use it.
system SUNWpsvrr Patch Server Deployment (Root)
system SUNWpsvru Patch Server Deployment (Usr)
# patchsvr setup -p file:/net/mars/export/patches
Now that the patch server is configured and started, you can configure client systems to use it.
You can check the configuration settings of your LPS to diagnose problems or to understand your server's patch-related settings.
The information includes the following:
1. Log in to the LPS as the root user.
2. List your LPS configuration settings.
Patch source URL: https://updateserver.sun.com/solaris/
Cache location: /var/sadm/spool/patchsvr
To change the configuration settings of your LPS, you must first stop it. After you change the settings by using the patchsvr setup command, you must restart the LPS. See the patchsvr(1M) man page.
Perform the following steps to change a configuration setting:
1. As the root user, log in to the system that you plan to use as your LPS.
3. Change one or more configuration settings, one per command line.
For example, specify a web proxy, web-proxy-name, and a port number, port.
# patchsvr setup -x web-proxy-name:port
This example shows how to change some of your LPS configuration settings. The LPS communicates with the Internet by using a web proxy. First, you stop the LPS, then specify the host name, webproxy1, and the port number, 2010, of the web proxy.
Next, you specify the next LPS in the chain as your patch source. You configure two local patch servers to serve systems in two buildings. The psvr1 server obtains patches from the Sun patch server. The second server, psvr2, obtains patches from psvr1. You configure psvr2 to obtain patches from psvr1 by specifying the URL to the server, which is http://psvr1:3816/solaris/.
Shutting down Local Patch Server
# patchsvr setup -x webproxy1:2010
# patchsvr setup -p http://psvr1:3816/solaris/
This section describes common problems that you might encounter when using Sun Patch Manager 2.0 to analyze systems to determine the list of appropriate patches or to download the patches to the system.
Description: When you run the smpatch update command, one of the following error messages appears:
Cause: This problem might be caused by a network failure between the client and the patch server, or by the patch server being down.
Workaround: Ensure that patchpro.patch.source points to a valid patch source and check the condition of the network.
Description: The following error message appears when you run the smpatch analyze in remote mode against an LPS.
Type /? for help, pressing <enter> accepts the default denoted by [ ].
Please enter a string value for: password :: root-password Loading Tool: com.sun.admin.patchmgr.cli.PatchMgrCli from pserver-2
Login to pserver-2 as user root was successful.
Download of com.sun.admin.patchmgr.cli.PatchMgrCli from pserver-2 was successful.
Assessing patches for machine pserver-2. Please wait...
Patch analysis failed. com.sun.patchpro.util.CannotConnectException:
Cannot connect to retrieve patchprodb.zip: Server returned
HTTP response code: 500 for URL:
http://pserver-1:3816/solaris/.
Cause: You might see this error message if one of the following situations occur:
Workaround: Address these issues by doing the following:
Shutting down Local Patch Server
# patchsvr setup -p patch-source-url
Description: You configure an LPS to obtain patches from a CD mounted on the LPS. When you attempt to download patches from the CD, you see the following error message:
Downloading the recommended patches for machine host-name. Please wait...
Could not download patch. Error occurred while processing the download for this patch, patch-id, into /var/sadm/spool directory.
Error: No such file or directory.
Workaround: Ensure that Solaris Volume Manager is running properly on the LPS. If it is not, stop and restart the Solaris Volume Manager.
Description: You attempt to change the configuration settings of your LPS, but the changes are not reflected.
Workaround: Stop and restart the LPS.
Shutting down Local Patch Server
Description: You encounter other problems while using a patch management environment with one or more local patch servers.
Workaround: Perform the following steps:
1. Verify that the client system's configuration settings are correct.
2. Verify that the local patch server's configuration settings are correct.
3. View the /var/patchsvr/logs/catalina.out log and the /var/patchsvr/logs/localhost_log.date.txt log on the LPS.
4. View the system log file /var/adm/messages on the client system.
5. Run the snoop command on the client system or on the LPS to see if the data is being downloaded from the LPS to the client system. See the snoop(1M) man page.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.