Configuring Queues
Queues are containers for different categories of jobs. Queues provide the corresponding resources for concurrent execution of multiple jobs that belong to the same category.
In N1 Grid Engine 6, a queue can be associated with one host or with multiple hosts. Because queues can extend across multiple hosts, they are called cluster queues. Cluster queues enable you to manage a cluster of execution hosts by means of a single cluster queue configuration.
Each host that is associated with a cluster queue receives an instance of that cluster queue, which resides on that host. This guide refers to these instances as queue instances. Within any cluster queue, you can configure each queue instance separately. By configuring individual queue instances, you can manage a heterogeneous cluster of execution hosts by means of a single cluster queue configuration.
When you modify a cluster queue, all of its queue instances are modified simultaneously. Within a single cluster queue, you can specify differences in the configuration of queue instances. Consequently, a typical setup might have only a few cluster queues, and the queue instances controlled by those cluster queues remain largely in the background.
Note –
The distinction between cluster queues and queue instances is important. For example, jobs always run in queue instances, not in cluster queues.
When you configure a cluster queue, you can associate any combination of the following host objects with the cluster queue:
-
One execution host
-
A list of separate execution hosts
-
One or more host groups
Note –
To enable a queue to operate correctly in a parallel environment, you must associate the queue with the PE. This association enables more control of the resources and lets you assign specific queues to handle the parallel workload.
Use the queue_conf(5) attribute pe_list to identify the suited PEs. Then, to link the PE and queues, use either the QMON utility or the following form of the qconf command:
# qconf -mq <queue_name> |
A host group is a group of hosts that can be treated collectively as identical. Host groups enable you to manage multiple hosts by means of a single host group configuration. For more information about host groups, see Configuring Host Groups With QMON.
When you associate individual hosts with a cluster queue, the name of the resulting queue instance on each host combines the cluster queue name with the host name. The cluster queue name and the host name are separated by an @ sign. For example, if you associate the host myexechost with the cluster queue myqueue, the name of the queue instance on myexechost is myqueue@myexechost.
When you associate a host group with a cluster queue, you create what is known as a queue domain. Queue domains enable you to manage groups of queue instances that are part of the same cluster queue and whose assigned hosts are part of the same host group. A queue domain name combines a cluster queue name with a host group name, separated by an @ sign. For example, if you associate the host group myhostgroup with the cluster queue myqueue, the name of the queue domain is myqueue@@myhostgroup.
Note –
Queue domain names always include two @ signs, because all host group names begin with an @ sign..
Jobs do not wait in queue instances. Jobs start running immediately as soon as they are dispatched. The scheduler's list of pending jobs is the only waiting area for jobs.
Configuring queues registers the queue attributes with sge_qmaster. As soon as queues are configured, they are instantly visibly to the whole cluster and to all users on all hosts belonging to the grid engine system.
For further details, see the queue_conf(5) man page.
Configuring Queues With QMON
On the QMON Main Control window, click the Queue Control button. The Cluster Queues dialog box appears.
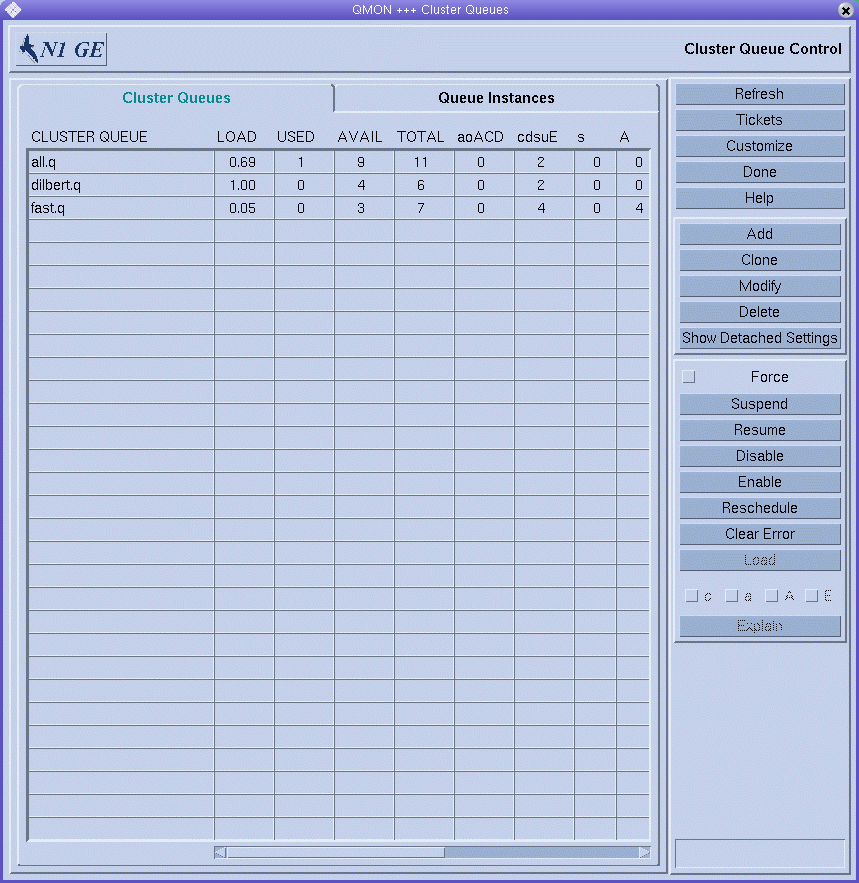
The Cluster Queues dialog box and its facilities for monitoring and manipulating the status of cluster queues and queue instances are described in Monitoring and Controlling Queues With QMON in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 User’s Guide.
To add a new cluster queue, click Add.
To modify an existing cluster queue, select it from the Cluster Queue list, and then click Modify.
The Clone button enables you to import all parameters of an existing cluster queue. You select the queue you want to clone from a list of existing queues.
When you click Add, the Queue Configuration – Add dialog box appears. When you click Modify, the Modify queue-name dialog box appears. When the Queue Configuration dialog box appears for the first time, it displays the General Configuration tab.
Figure 2–1 Queue Configuration– General Configuration Tab
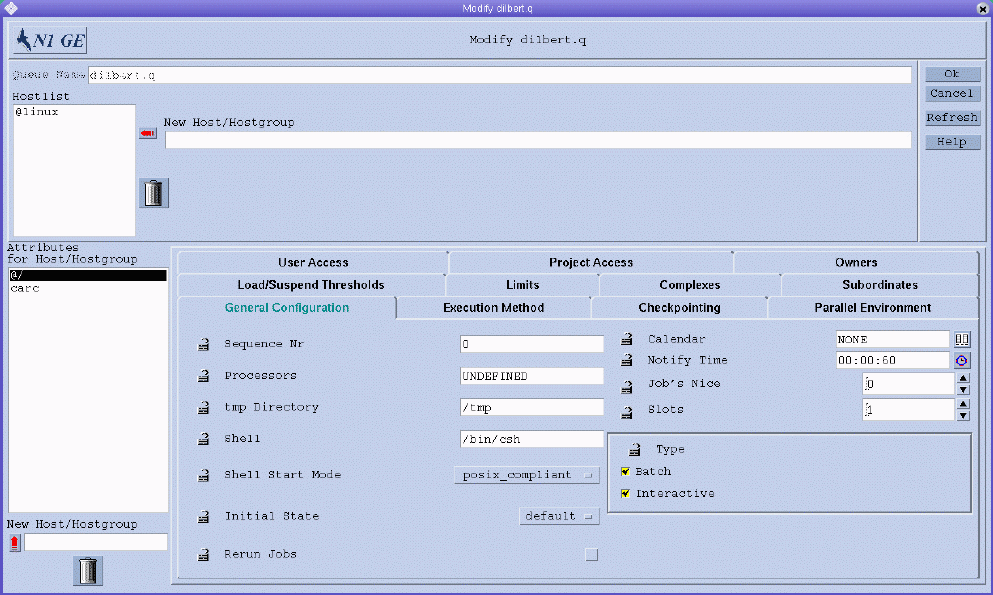
If you are modifying an existing queue, the name of the queue is displayed in the Queue Name field. The hosts where the queue instances reside are displayed in the Hostlist field.
If you are adding a new cluster queue, you must specify a queue name and the names of the hosts on which the queue instances are to reside.
In the Hostlist field, you can specify the names of individual hosts. You can also specify the names of previously defined host groups. Queue instances of this cluster queue will reside on all individual hosts and on all members of the host groups you specify, including all members of any host subgroups. For more information about host groups, see Configuring Host Groups With QMON.
The following 11 tabs for specifying parameter sets are available to define a queue:
-
General Configuration – see Configuring General Parameters
-
Execution Method – see Configuring Execution Method Parameters
-
Checkpointing – see Configuring the Checkpointing Parameters
-
Parallel Environment – see Configuring Parallel Environments
-
Load/Suspend Thresholds – see Configuring Load and Suspend Thresholds
-
Limits – see Configuring Limits
-
Complex – see Configuring Complex Resource Attributes
-
Subordinates – see Configuring Subordinate Queues
-
User Access – see Configuring User Access Parameters
-
Project Access – see Configuring Project Access Parameters
-
Owners – see Configuring Owners Parameters
To set default parameters for the cluster queue, select @/ in the Attributes for Host/Hostgroup list, and then click the tab containing the parameters that you want to set.
Default parameters are set for all queue instances on all hosts listed under Hostlist. You can override the default parameter values on a host or a host group that you specify. To set override parameters for a host or a host group, first select the name from the Attributes for Host/Hostgroup list. Then click the tab containing the parameters that you want to set. The values of the parameters that you set override the cluster queue's default parameters on the selected host or host group.
To set a host-specific parameter, you must first enable the parameter for configuration. Click the lock icon at the left of the parameter you want to set, and then change the parameter's value.
The Refresh button loads the settings of other objects that were modified while the Queue Configuration dialog box was open.
Click OK to register all queue configuration changes with sge_qmaster and close the dialog box. Click Cancel to close the dialog box without saving your changes.
Configuring General Parameters
To configure general parameters, click the General Configuration tab. The General Configuration tab is shown in Figure 2–1.
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Sequence Nr. The sequence number of the queue.
-
Processors. A specifier for the processor set to be used by the jobs running in that queue. For some operating system architectures, this specifier can be a range, such as 1-4,8,10, or just an integer identifier of the processor set. See the arc_depend_*.asc files in the doc directory of your N1 Grid Engine 6.1 software distribution for more information.
 Caution –
Caution – Do not change this value unless you are certain that you need to change it.
-
tmp Directory. Temporary directory path.
-
Shell. Default command interpreter to use for running the job scripts.
-
Shell Start Mode. The mode in which to start the job script.
-
Initial State. The state in which a newly added queue comes up. Also, the state in which a queue instance is restored if the sge_execd running on the queue instance host gets restarted.
-
Rerun Jobs. The queue's default rerun policy to be enforced on jobs that were aborted, for example, due to system crashes. The user can override this policy using the qsub -r command or the Submit Job dialog box. See Extended Job Example in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 User’s Guide.
-
Calendar. A calendar attached to the queue. This calendar defines on-duty and off-duty times for the queue.
-
Notify Time. The time to wait between delivery of SIGUSR1/SIGUSR2 notification signals and suspend or kill signals.
-
Job's Nice. The nice value with which to start the jobs in this queue. 0 means use the system default.
-
Slots. The number of jobs that are allowed to run concurrently in the queue. Slots are also referred to as job slots.
-
Type. The type of the queue and of the jobs that are allowed to run in this queue. Type can be Batch, Interactive, or both.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Execution Method Parameters
To configure execution method parameters, click the Execution Method tab. The Execution Method tab is shown in the following figure.
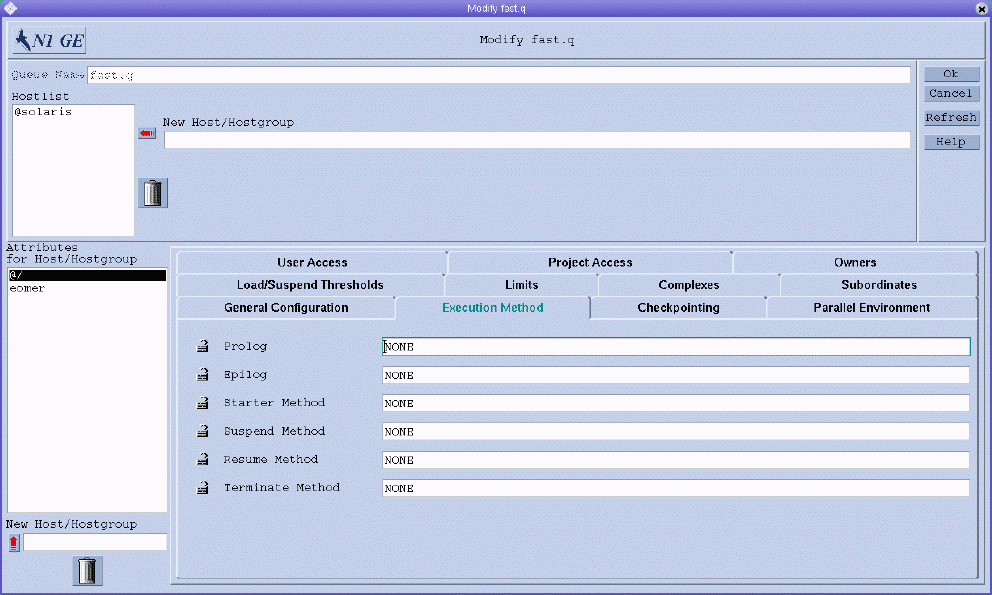
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Prolog. A queue-specific prolog script. The prolog script is run with the same environment as the job before the job script is started.
-
Epilog. A queue-specific epilog script. The epilog script is run with the same environment as the job after the job is finished.
-
Starter Method, Suspend Method, Resume Method, Terminate Method. Use these fields to override the default methods for applying these actions to jobs.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring the Checkpointing Parameters
To configure the checkpointing parameters, click the Checkpointing tab. The Checkpointing tab is shown in the following figure.
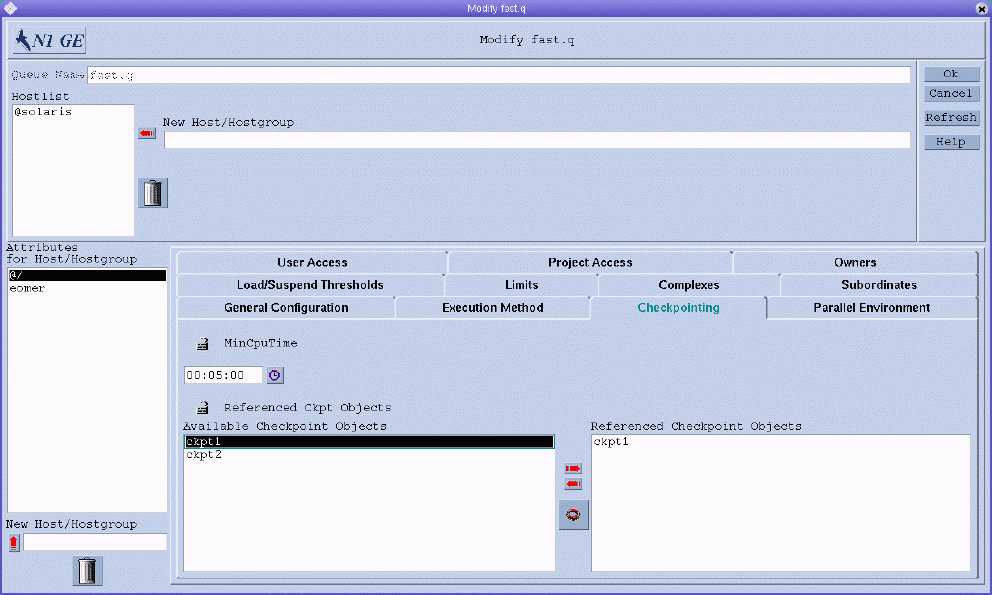
You can specify the following parameters:
-
MinCpuTime. The periodic checkpoint interval.
-
Referenced Ckpt Objects. A list of checkpointing environments associated with the queue.
To reference a checkpointing environment from the queue, select the name of a checkpointing environment from the Available list, and then click the right arrow to add it to the Referenced list.
To remove a checkpointing environment from the Referenced list, select it, and then click the left arrow.
To add or modify checkpointing environments, click the button below the red arrows to open the Checkpointing Configuration dialog box. For more information, see Configuring Checkpointing Environments With QMON.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Parallel Environments
To configure parallel environments, click the Parallel Environment tab. The Parallel Environment tab is shown in the following figure.
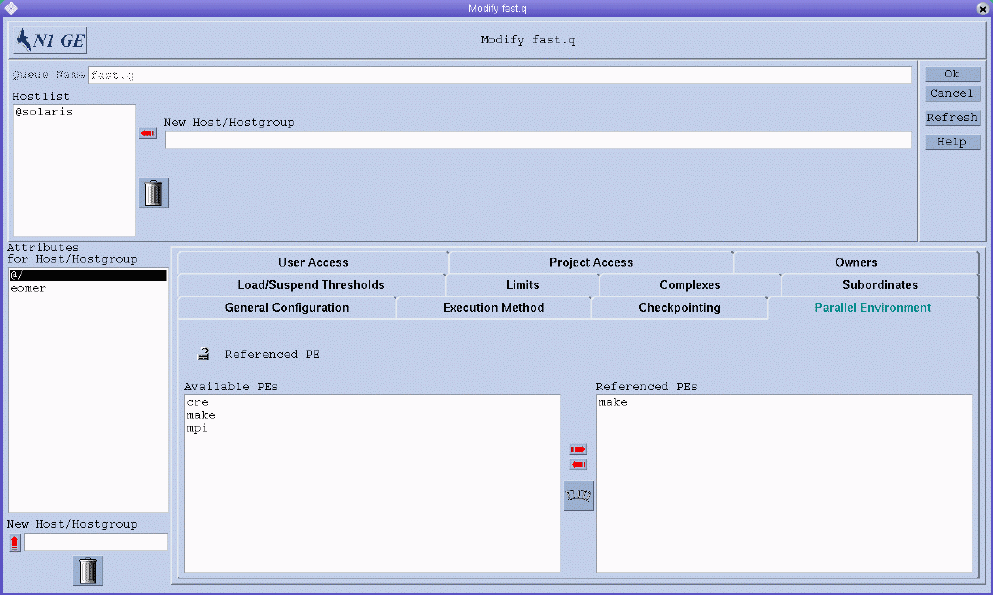
You can specify the following parameter:
-
Referenced PE. A list of parallel environments associated with the queue.
To reference a parallel environment from the queue, select the name of a parallel environment from the Available PEs list, and then click the right arrow to add it to the Referenced PEs list.
To remove a checkpointing environment from the Referenced PEs list, select it, and then click the left arrow.
To add or modify parallel environments, click the button below the red arrows to open the Parallel Environment Configuration dialog box. For more information, see Configuring Parallel Environments With QMON.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about this parameter.
Configuring Load and Suspend Thresholds
To configure load and suspend thresholds, click the Load/Suspend Thresholds tab. The Load/Suspend Thresholds tab is shown in the following figure.
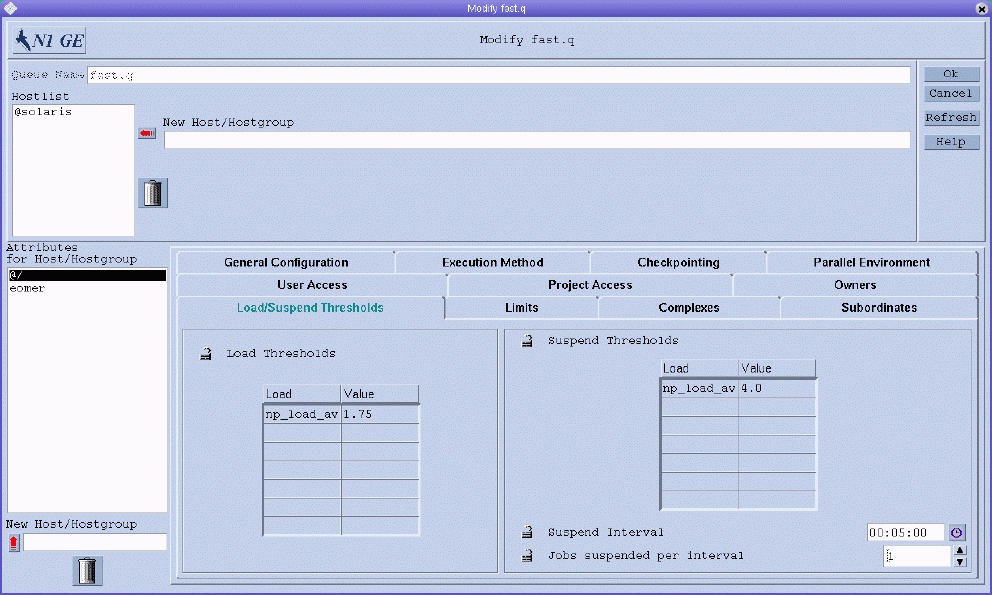
You can specify the following parameters:
-
The Load Thresholds and the Suspend Thresholds tables, which define overload thresholds for load parameters and consumable resource attributes. See Complex Resource Attributes.
In the case of load thresholds, overload prevents the queue from receiving further jobs. In the case of suspend thresholds, overload suspends jobs in the queue in order to reduce the load.
The tables display the currently configured thresholds.
To change an existing threshold, select it, and then double-click the corresponding Value field.
To add new thresholds, click Load or Value. A selection list appears with all valid attributes that are attached to the queue. The Attribute Selection dialog box is shown in Figure 1–2. To add an attribute to the Load column of the corresponding threshold table, select an attribute, and then click OK.
To delete an existing threshold, select it, and then type Control-D or click mouse button 3. You are prompted to confirm that you want to delete the selection.
-
Suspend interval. The time interval between suspension of other jobs in case the suspend thresholds are still exceeded.
-
Jobs suspended per interval. The number of jobs to suspend per time interval in order to reduce the load on the system that is hosting the configured queue.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Limits
To configure limits parameters, click the Limits tab. The Limits tab is shown in the following figure.
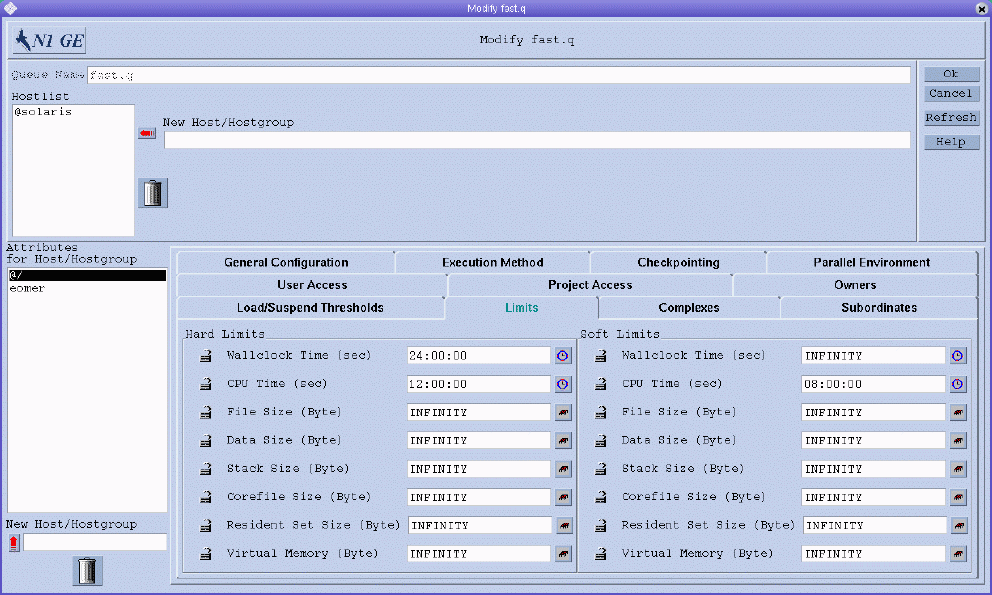
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Hard Limit and Soft Limit. The hard limit and the soft limit to impose on the jobs that are running in the queue.
To change a value of a limit, click the button at the right of the field whose value you want to change. A dialog box appears where you can type either Memory or Time limit values.
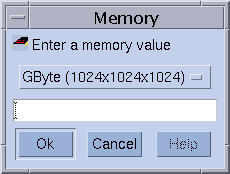
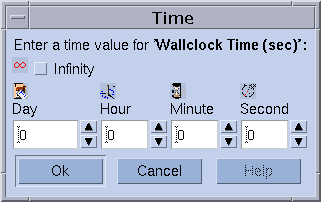
See the queue_conf(5) and the setrlimit(2) man pages for detailed information about limit parameters and their interpretation for different operating system architectures.
Configuring Complex Resource Attributes
To configure resource attributes, click the Complex tab. The Complex tab is shown in the following figure.
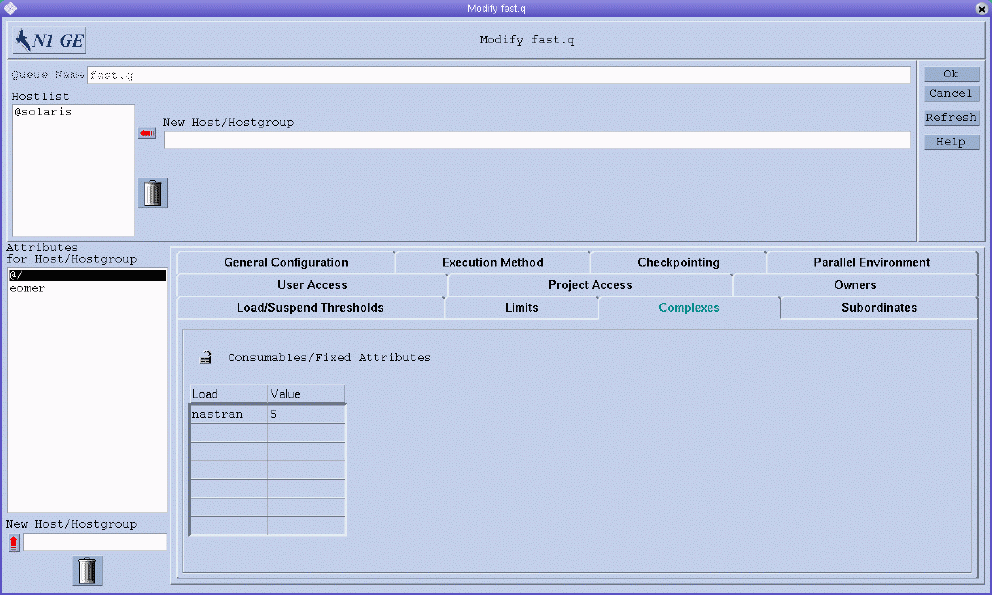
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Consumables/Fixed Attributes. Value definitions for selected attributes from the set of resource attributes that are available for this queue.
The available resource attributes are assembled by default from the complex.
Resource attributes are either consumable or fixed. The definition of a consumable value defines a capacity managed by the queue. The definition of a fixed value defines a queue-specific value. See Complex Resource Attributes for further details.
The attributes for which values are explicitly defined are displayed in the Consumable/Fixed Attributes table. To change an attribute, select it, and then double-click the corresponding Value field.
To add new attribute definitions, click Load or Value. The Attribute Selection dialog box appears with a list of all valid attributes that are attached to the queue. The Attribute Selection dialog box is shown in Figure 1–2.
To add an attribute to the Load column of the attribute table, select it, and then click OK.
To delete an attribute, select it, and then press Control-D or click mouse button 3. You are prompted to confirm that you want to delete the attribute.
See the queue_conf(5) page for detailed information about these attributes.
Use the Complex Configuration dialog box to check or modify the current complex configuration before you attach user-defined resource attributes to a queue or before you detach them from a queue. To access the Complex Configuration dialog box, click the Complex Configuration button on the QMON Main Control window. See Figure 3–1 for an example.
Configuring Subordinate Queues
To configure subordinate queues, click the Subordinates tab. The Subordinates tab is shown in the following figure.

Use the subordinate queue facility to implement high priority and low priority queues as well as standalone queues.
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Queue. A list of the queues that are subordinated to the configured queue.
Subordinated queues are suspended if the configured queue becomes busy. Subordinated queues are resumed when the configured queue is no longer busy.
-
Max Slots. For any subordinated queue, you can configure the number of job slots that must be filled in the configured queue to trigger a suspension. If no maximum slot value is specified, all job slots must be filled to trigger suspension of the corresponding queue.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring User Access Parameters
To configure user access parameters, click the User Access tab. The User Access tab is shown in the following figure.
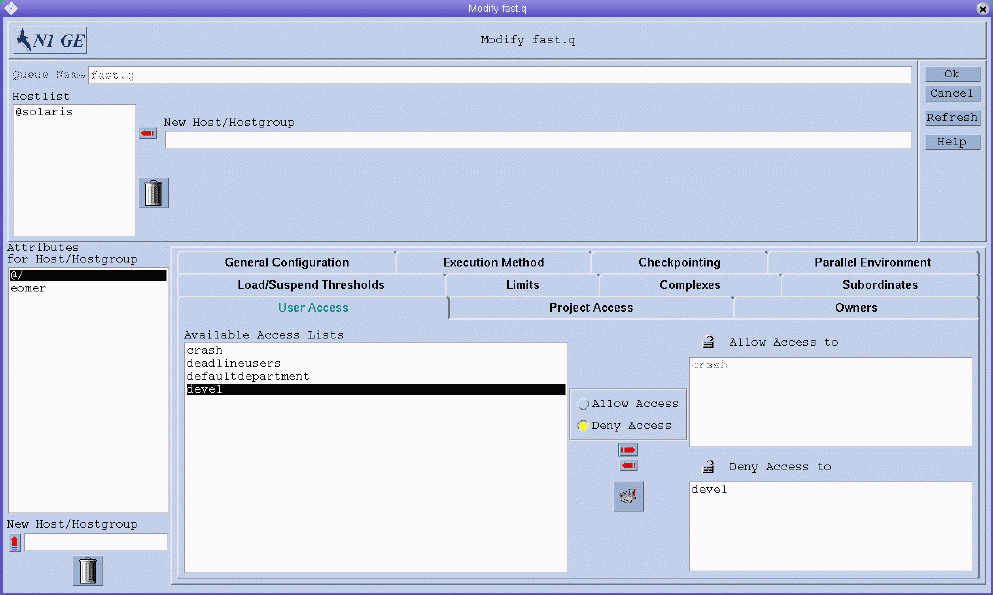
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Available Access Lists. The user access lists that can be included in the Allow Access list or the Deny Access list of the queue.
Users or user groups belonging to access lists that are included in the Allow Access list have access to the queue. Users who are included in the Deny Access list cannot access the queue. If the Allow Access list is empty, access is unrestricted unless explicitly stated otherwise in the Deny Access list.
To add or modify user access lists, click the button between the Available Access Lists and the Allow Access and Deny Access lists to open the User Configuration dialog box. For more information, see Configuring User Access Lists With QMON.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Project Access Parameters
To configure project access parameters, click the Project Access tab. The Project Access tab is shown in the following figure.
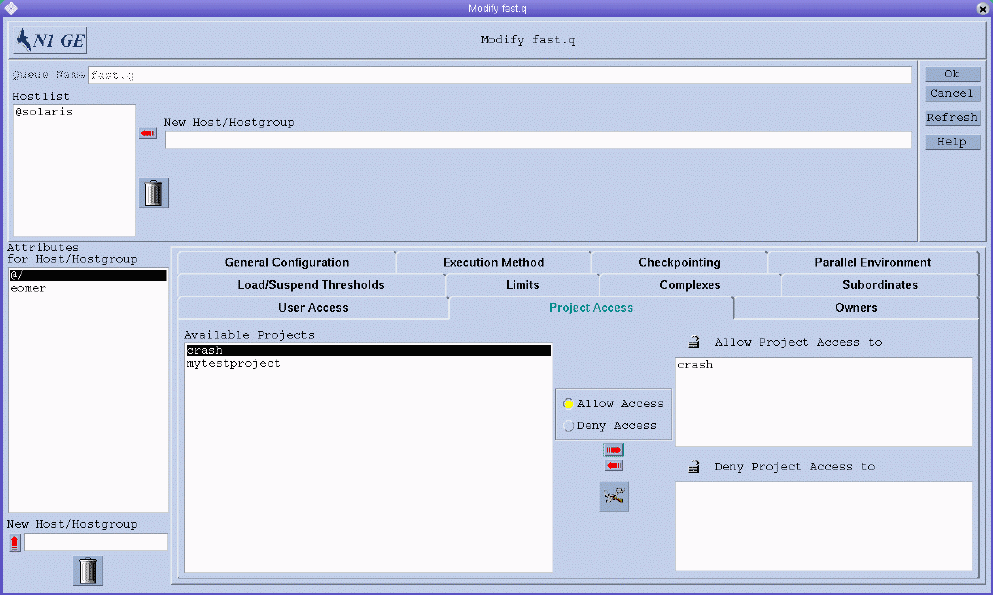
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Available Projects. The projects that are allowed access or denied access to the queue.
Jobs submitted to a project belonging to the list of allowed projects have access to the queue. Jobs that are submitted to denied projects are not dispatched to the queue.
To add or modify project access, click the button between the Available Projects list and the Allow Project Access and Deny Project Access lists to open the Project Configuration dialog box. For more information, see Defining Projects With QMON.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Owners Parameters
To configure owners parameters, click the Owners tab. The Owners tab is shown in the following figure.
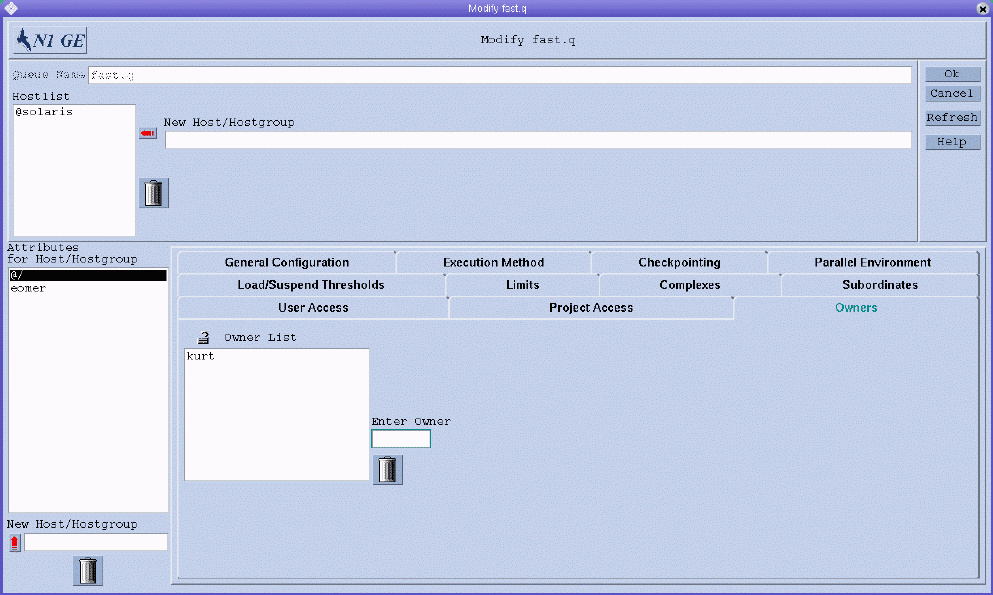
You can specify the following parameters:
-
Owner List. The list of queue owners.
Typically, users are set up to be owners of certain queue instances in order to allow them to suspend or disable jobs when they need to. For example, users might occasionally need certain machines for important work, and those machines might be strongly affected by jobs that are running in the background.
Queue owners can do the following:
Jobs that are suspended explicitly while a queue is suspended are not resumed when the queue is resumed. Explicitly suspended jobs must be resumed explicitly.
All possible user accounts can be added to the owner list. To delete a user account from the queue owner list, select it, and then click the trash can icon.
See the queue_conf(5) man page for detailed information about these parameters.
Configuring Queues From the Command Line
To configure queues from the command line, type the following command with the appropriate options:
# qconf options |
The qconf command has the following options:
-
The -aq option (add cluster queue) displays an editor containing a template for cluster queue configuration. The editor is either the default vi editor or an editor defined by the EDITOR environment variable. If cluster-queue is specified, the configuration of this cluster queue is used as template. Configure the cluster queue by changing the template and then saving it. See the queue_conf(5) man page for a detailed description of the template entries to change.
-
The -Aq option (add cluster queue from file) uses the file filename to define a cluster queue. The definition file might have been produced by the qconf -sq queue command.
-
The -cq option (clean queue) cleans the status of the specified cluster queues, queue domains, or queue instances to be idle and free from running jobs. The status is reset without respect to the current status. This option is useful for eliminating error conditions, but you should not use it in normal operation mode.
-
The -dq option (delete cluster queue) deletes the cluster queues specified in the argument list from the list of available queues.
-
The -mq option (modify cluster queue) modifies the specified cluster queue. The -mq option displays an editor containing the configuration of the cluster queue to be changed. The editor is either the default vi editor or an editor defined by the EDITOR environment variable. Modify the cluster queue by changing the configuration and then saving your changes.
-
The -Mq option (modify cluster queue from file) uses the file filename to define the modified cluster queue configuration. The definition file might have been produced by the qconf -sq queue command and subsequent modification.
-
The -sq option (show queue) without arguments displays the default template cluster queue, queue domain, or queue instance configuration. The -sq option with arguments displays the current configuration of the specified queues.
-
The -sql option (show cluster queue list) displays a list of all currently configured cluster queues.
The qconf command provides the following set of options that you can use to change specific queue attributes:
|
-aattr – Add attributes |
|
-Aattr – Add attributes from a file |
|
-dattr – Delete attributes |
|
-Dattr – Delete attributes listed in a file |
|
-mattr – Modify attributes |
|
-Mattr – Modify attributes from a file |
|
-rattr – Replace attributes |
|
-Rattr – Replace attributes from a file |
|
-sobjl – Show list of configuration objects |
For a description of how to use these options and for some examples of their use, see Using Files to Modify Queues, Hosts, and Environments. For detailed information about these options, see the qconf(1) man page.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
