Assigning Resource Attributes to Queues, Hosts, and the Global Cluster
Resource attributes can be used in the following ways:
-
As queue resource attributes
-
As host resource attributes
-
As global resource attributes
A set of default resource attributes is already attached to each queue and host. Default resource attributes are built in to the system and cannot be deleted, nor can their type be changed.
User-defined resource attributes must first be defined in the complex before you can assign them to a queue instance, a host, or the global cluster. When you assign a resource attribute to one of these targets, you specify a value for the attribute.
The following sections describe each attribute type in detail.
Queue Resource Attributes
Default queue resource attributes are a set of parameters that are defined in the queue configuration. These parameters are described in the queue_conf(5) man page.
You can add new resource attributes to the default attributes. New attributes are attached only to the queue instances that you modify. When the configuration of a particular queue instance references a resource attribute that is defined in the complex, that queue configuration provides the values for the attribute definition. For details about queue configuration see Configuring Queues.
For example, the queue configuration value h_vmem is used for the virtual memory size limit. This value limits the amount of total memory that each job can consume. An entry in the complex_values list of the queue configuration defines the total available amount of virtual memory on a host or assigned to a queue. For detailed information about consumable resources, see Consumable Resources.
Host Resource Attributes
Host resource attributes are parameters that are intended to be managed on a host basis.
The default host-related attributes are load values. You can add new resource attributes to the default attributes, as described earlier in Queue Resource Attributes.
Every sge_execd periodically reports load to sge_qmaster. The reported load values are either the standard load values such as the CPU load average, or the load values defined by the administrator, as described in Load Parameters.
The definitions of the standard load values are part of the default host resource attributes, whereas administrator-defined load values require extending the host resource attributes.
Host-related attributes are commonly extended to include nonstandard load parameters. Host-related attributes are also extended to manage host-related resources such as the number of software licenses that are assigned to a host, or the available disk space on a host's local file system.
If host–related attributes are associated with a host or with a queue instance on that host, a concrete value for a particular host resource attribute is determined by one of the following items:
-
The queue configuration, if the attribute is also assigned to the queue configuration
-
A reported load value
-
The explicit definition of a value in the complex_values entry of the corresponding host configuration. For details, see Configuring Hosts.
In some cases, none of these values are available. For example, say the value is supposed to be a load parameter, but sge_execd does not report a load value for the parameter. In such cases, the attribute is not defined, and the qstat –F command shows that the attribute is not applicable.
For example, the total free virtual memory attribute h_vmem is defined in the queue configuration as limit and is also reported as a standard load parameter. The total available amount of virtual memory on a host can be defined in the complex_values list of that host. The total available amount of virtual memory attached to a queue instance on that host can be defined in the complex_values list of that queue instance. Together with defining h_vmem as a consumable resource, you can efficiently exploit memory of a machine without risking memory oversubscription, which often results in reduced system performance that is caused by swapping. For more information about consumable resources, see Consumable Resources.
Note –
Only the Shortcut, Relation, Requestable, Consumable, and Default columns can be changed for the default resource attributes. No default attributes can be deleted.
Global Resource Attributes
Global resource attributes are cluster-wide resource attributes, such as available network bandwidth of a file server or the free disk space on a network-wide available file system.
Global resource attributes can also be associated with load reports if the corresponding load report contains the GLOBAL identifier, as described in Load Parameters. Global load values can be reported from any host in the cluster. No global load values are reported by default, therefore there are no default global resource attributes.
Concrete values for global resource attributes are determined by the following items:
-
Global load reports.
-
Explicit definition in the complex_values parameter of the global host configuration. See Configuring Hosts.
-
In association with a particular host or queue and an explicit definition in the corresponding complex_values lists.
Sometimes none of these cases apply. For example, a load value might not yet be reported. In such cases, the attribute does not exist.
Adding Resource Attributes to the Complex
By adding resource attributes to the complex, the administrator can extend the set of attributes managed by thegrid engine system. The administrator can also restrict the influence of user-defined attributes to particular queues, hosts, or both.
User-defined attributes are a named collection of attributes with the corresponding definitions as to how the grid engine software is to handle these attributes. You can attach one or more user-defined attributes to a queue, to a host, or globally to all hosts in the cluster. Use the complex_values parameter for the queue configuration and the host configuration. For more information, see Configuring Queues and Configuring Hosts. The attributes defined become available to the queue and to the host, respectively, in addition to the default resource attributes.
The complex_values parameter in the queue configuration and the host configuration must set concrete values for user-defined attributes that are associated with queues and hosts.
For example, say the user-defined resource attributes permas, pamcrash, and nastran, shown in the following figure, are defined.
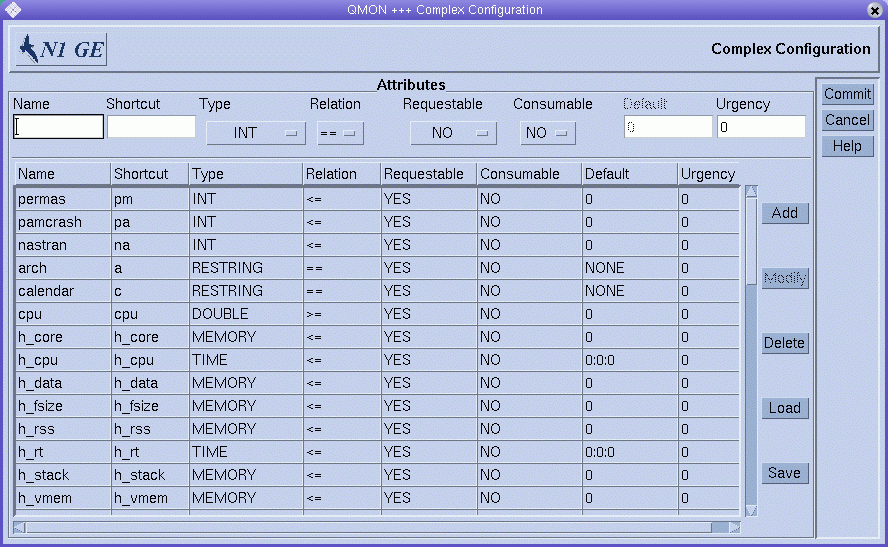
For at least one or more queues, add the resource attributes to the list of associated user-defined attributes as shown in the Complex tab of the Modify queue-name dialog box. For details on how to configure queues, see Configuring Queues and its related sections.
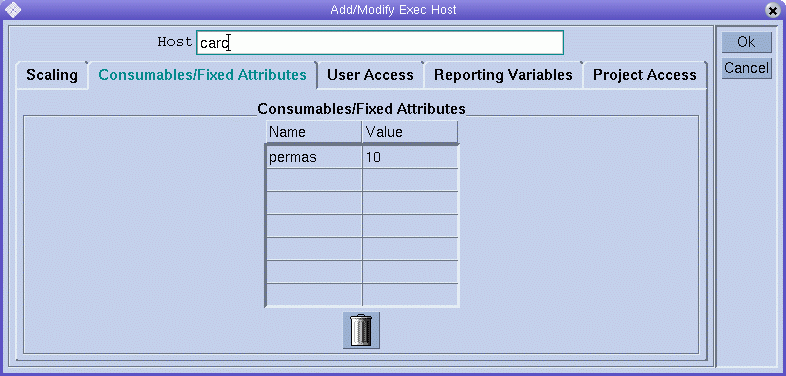
Then the displayed queue is configured to manage up to 10 licenses of the software package permas. Furthermore, the attribute permas becomes requestable for jobs, as expressed in the Available Resources list in the Requested Resources dialog box.
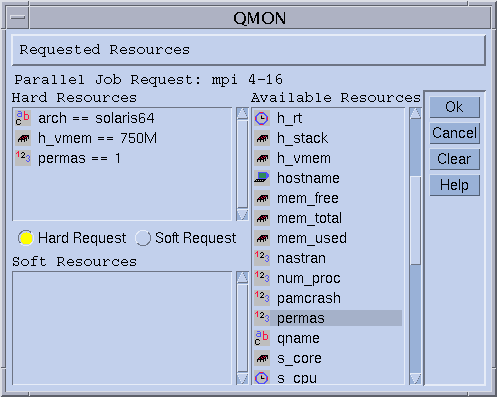
For details about how to submit jobs, see Chapter 3, Submitting Jobs, in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 User’s Guide.
Alternatively, the user could submit jobs from the command line and could request attributes as follows:
% qsub -l pm=1 permas.sh |
Note –
You can use the pm shortcut instead of the full attribute name permas.
Consequently, the only eligible queues for these jobs are the queues that are associated with the user-defined resource attributes and that have permas licenses configured and available.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
