Requestable Attributes
When users submit a job, a requirement profile can be specified for the job. Users can specify attributes or characteristics of a host or queue that the job requires in order to run successfully. The grid engine software maps these job requirements onto the host and queue configurations of the cluster and therefore finds suitable hosts for a job.
The attributes that can be used to specify the job requirements are related to one of the following:
-
The cluster, for example, space required on a network shared disk
-
Individual hosts, for example, operating system architecture
-
Queues, for example, permitted CPU time
The attributes can also be derived from site policies such as the availability of installed software only on certain hosts.
The available attributes include the following:
-
Queue property list – See Displaying Queues and Queue Properties
-
List of global and host-related attributes – See Assigning Resource Attributes to Queues, Hosts, and the Global Cluster in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 Administration Guide
-
Administrator-defined attributes
For convenience, however, the administrator commonly chooses to define only a subset of all available attributes to be requestable.
The currently requestable attributes are displayed in the Requested Resources dialog box, which is shown in the following figure.
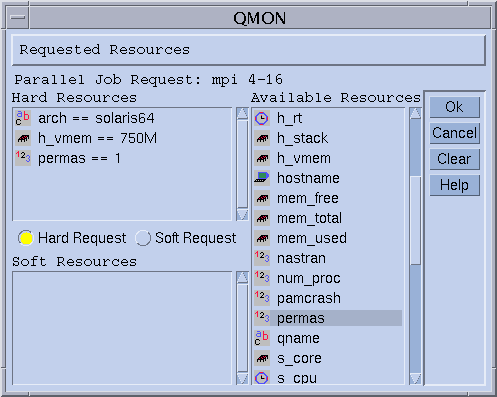
Use the QMON Submit Job dialog box to access the Requested Resources dialog box. Requestable attributes are listed under Available Resources.
Displaying a List of Requestable Attributes
To display the list of configured resource attributes, from the command line type the following command:
% qconf -sc |
The grid engine system complex contains the definitions for all resource attributes. For more information about resource attributes, see Chapter 3, Configuring Complex Resource Attributes, in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 Administration Guide. See also the complex format description on the complex(5) man page.
Sample output from the qconf -sc command is shown in Example 2–2.
Example 2–2 Complex Attributes Displayed
gimli% qconf -sc #name shortcut type relop requestable consumable default urgency #---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- arch a RESTRING == YES NO NONE 0 calendar c STRING == YES NO NONE 0 cpu cpu DOUBLE >= YES NO 0 0 h_core h_core MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 h_cpu h_cpu TIME <= YES NO 0:0:0 0 h_data h_data MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 h_fsize h_fsize MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 h_rss h_rss MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 h_rt h_rt TIME <= YES NO 0:0:0 0 h_stack h_stack MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 h_vmem h_vmem MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 hostname h HOST == YES NO NONE 0 load_avg la DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 load_long ll DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 load_medium lm DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 load_short ls DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 mem_free mf MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 mem_total mt MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 mem_used mu MEMORY >= YES NO 0 0 min_cpu_interval mci TIME <= NO NO 0:0:0 0 np_load_avg nla DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 np_load_long nll DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 np_load_medium nlm DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 np_load_short nls DOUBLE >= NO NO 0 0 num_proc p INT == YES NO 0 0 qname q STRING == YES NO NONE 0 rerun re BOOL == NO NO 0 0 s_core s_core MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 s_cpu s_cpu TIME <= YES NO 0:0:0 0 s_data s_data MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 s_fsize s_fsize MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 s_rss s_rss MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 s_rt s_rt TIME <= YES NO 0:0:0 0 s_stack s_stack MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 s_vmem s_vmem MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 seq_no seq INT == NO NO 0 0 slots s INT <= YES YES 1 1000 swap_free sf MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 swap_rate sr MEMORY >= YES NO 0 0 swap_rsvd srsv MEMORY >= YES NO 0 0 swap_total st MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 swap_used su MEMORY >= YES NO 0 0 tmpdir tmp STRING == NO NO NONE 0 virtual_free vf MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 virtual_total vt MEMORY <= YES NO 0 0 virtual_used vu MEMORY >= YES NO 0 0 # >#< starts a comment but comments are not saved across edits -------- |
The column name is identical to the first column displayed by the qconf -sq command. The shortcut column contains administrator-definable abbreviations for the full names in the first column. The user can supply either the full name or the shortcut in the request option of a qsub command.
The column requestable tells whether the resource attribute can be used in a qsub command. The administrator can, for example, disallow the cluster's users to request certain machines or queues for their jobs directly. The administrator can disallow direct requests by setting the entries qname, hostname, or both, to be unrequestable. Making queues or hosts unrequestable implies that feasible user requests can be met in general by multiple queues, which enforces the load balancing capabilities of the grid engine system.
The column relop defines the relational operator used to compute whether a queue or a host meets a user request. The comparison that is executed is as follows:
User_Request relop Queue/Host/... -Property |
If the result of the comparison is false, the user's job cannot be run in the queue or on the host. For example, let the queue q1 be configured with a soft CPU time limit of 100 seconds. Let the queue q2 be configured to provide 1000 seconds soft CPU time limit. See the queue_conf(5) and the setrlimit(2) man pages for a description of user process limits.
The columns consumable and default affect how the administrator declares consumable resources. See Consumable Resources in Sun N1 Grid Engine 6.1 Administration Guide.
The user requests consumables just like any other attribute. The grid engine system internal bookkeeping for the resources is different, however.
Assume that a user submits the following request:
% qsub -l s_cpu=0:5:0 nastran.sh |
The s_cpu=0:5:0 request asks for a queue that grants at least 5 minutes of soft limit CPU time. Therefore, only queues providing at least 5 minutes soft CPU runtime limit are set up properly to run the job. See the qsub(1) man page for details on the syntax.
Note –
The grid engine software considers workload information in the scheduling process only if more than one queue or host can run a job.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
