Chapter 9 Open Telecommunications Platform Administration
This chapter provides the procedures for administering the Open Telecommunications Platform 1.1.
The following topics are discussed:
-
Enabling and Disabling the OTP System Management Service and Provisioning Service
-
Changes to OTP High Availability Framework for Enterprise Installation Services Compliance
OTP Topologies
This section provides an overview of the N*N and Pair+N clustered OTP system topologies supported by OTP. A topology is the connection scheme that connects the clustered OTP hosts to the storage platforms used in the cluster.
N*N
The N*N topology allows every shared storage device in the cluster to connect to every OTP host in the cluster. This topology allows highly available applications to failover from one node to another without service degradation. When failover occurs, the new node can access the storage device using a local path instead of the private interconnect.
The following figure illustrates an N*N configuration where all four OTP hosts connect to shared storage.
Figure 9–1 N*N Topology
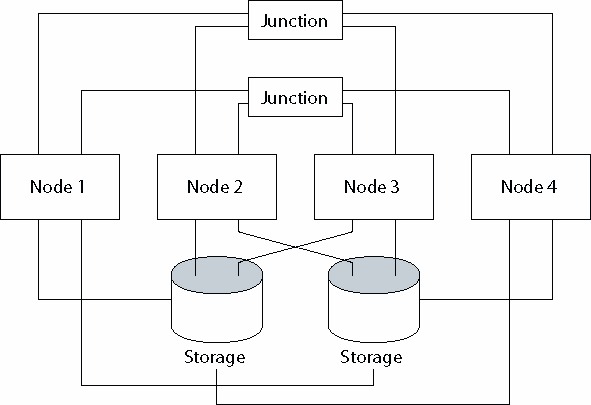
The following procedures are supported in N*N topology.
Pair+N
The pair+N topology includes a pair of OTP hosts directly connected to shared storage and an additional set of OTP hosts that use the cluster interconnect to access shared storage. The additional OTP hosts have no direct connection to the shared storage.
The following figure illustrates a pair+N topology where two of the four OTP hosts (Node 3 and Node 4) use the cluster interconnect to access the storage. This configuration can be expanded to include additional OTP hosts that do not have direct access to the shared storage.
Figure 9–2 Pair+N Topology
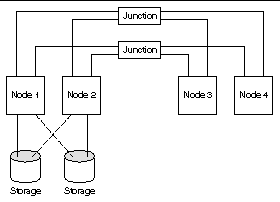
The following procedures are supported in pair+N topology.
For further information about clustered OTP system topology, see Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS.
Enabling and Disabling the OTP System Management Service and Provisioning Service
This section provides the procedures for enabling and disabling the system management service and the provisioning service on a single OTP host.
 To Enable and Disable the OTP System Management Service
Using the Command Line
To Enable and Disable the OTP System Management Service
Using the Command Line
The following steps enable and disable the OTP System Management Service only on the target host and not on the entire cluster.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the OTP host.
-
Use the serviceManagement script with the n1sm option to enable and disable the OTP System Management Service.
 To Enable and Disable the OTP Application Provisioning
Service Using the Command Line
To Enable and Disable the OTP Application Provisioning
Service Using the Command Line
Note –
-
If the OTP application provisioning service is running in the high availability mode, the provisioning service is enabled or disabled on all hosts in the cluster.
-
If the OTP Application Provisioning Service is not running in the High Availability mode, the OTP Application Provisioning Service is enabled or disabled only on the target host.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the OTP host.
-
Use the serviceManagement script with the n1sps option to enable and disable the OTP Application Provisioning Service.
 To Enable and Disable the OTP System Management and
Provisioning Services Using the Graphical User Interface
To Enable and Disable the OTP System Management and
Provisioning Services Using the Graphical User Interface
-
The following steps enable and disable the OTP System Management Service only on the target host and not on the entire cluster.
-
The graphical user interface cannot be used to disable the provisioning service on the host on which it is running. In other words, if the service is running on otpclient01, you cannot use the graphical user interface on otpclient01 to disable the provisioning service. Instead, use the command line interface to disable the provisioning service.
-
Open a Web browser and go to URL https://OTP host:9090 where OTP host is either the IP address or the fully qualified name of the OTP host on which the resource group is active.
The OTP provisioning service log in screen appears.
-
Click OEM OTP.
-
Click Utility Plans.
-
Click OTP Service Management Control.
-
Click on OTP Service Management.
The OTP Service Management Plan page appears:
Figure 9–3 Service Management Plan Page
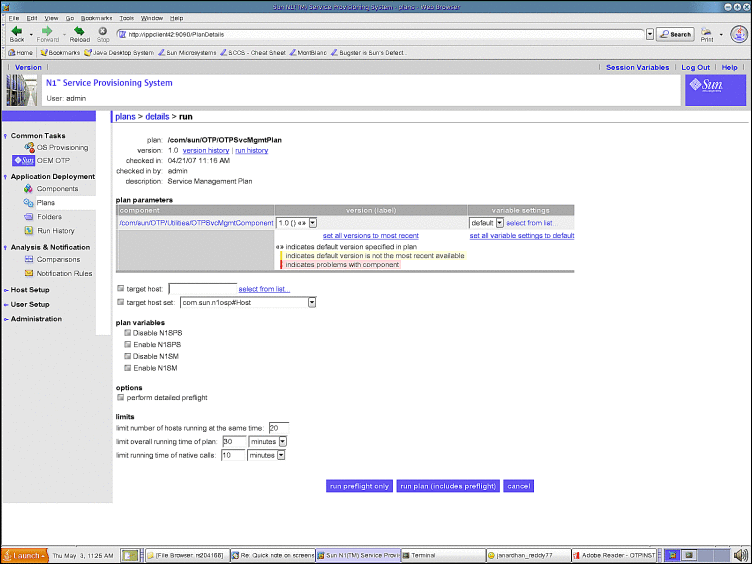
-
Type the host name on which you want to enable or disable the services in the target host field. Do not modify the target host set.
-
Choose the services you want to enable and disable.
-
Click the perform detailed preflight checkbox.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight)
Converting a Standalone OTP Host to a Clustered OTP Host
This section provides the procedure to convert a standalone OTP host to a clustered OTP host.
 To Convert a Standalone OTP Host to a Clustered OTP Host
To Convert a Standalone OTP Host to a Clustered OTP Host
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the external OTP installation server.
-
Copy /opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/templates/inputOTPSingleNode.dat /var/tmp/inputOTPSingleNode.dat.
-
Edit the /var/tmp/inputOTPSingleNode.dat file.
Specify the values for each keyword as described by Open Telecommunications Platform Plan Worksheets and the standalone OTP host Plan worksheet.
-
Convert the standalone OTP host to aclustered OTP host.
-
Using the command line, type:
/opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/deployOTPSingleNode -convertToManager /var/tmp/inputOTPSingleNode.dat
-
Using the graphical user interface:
-
Open a Web browser and go to URL https://OTP host:9090 where OTP host is either the IP address or the fully qualified name of the OTP host on which the resource group is active.
The OTP provisioning service log in screen appears.
-
Click OEM OTP.
-
Click Utility Plans.
-
Click Convert Standalone system to Clustered System.
-
Click Configure.
The Convert Single to Clustered page appears:
Figure 9–4 Convert Standalone OTP Host to Clustered OTP Host Page
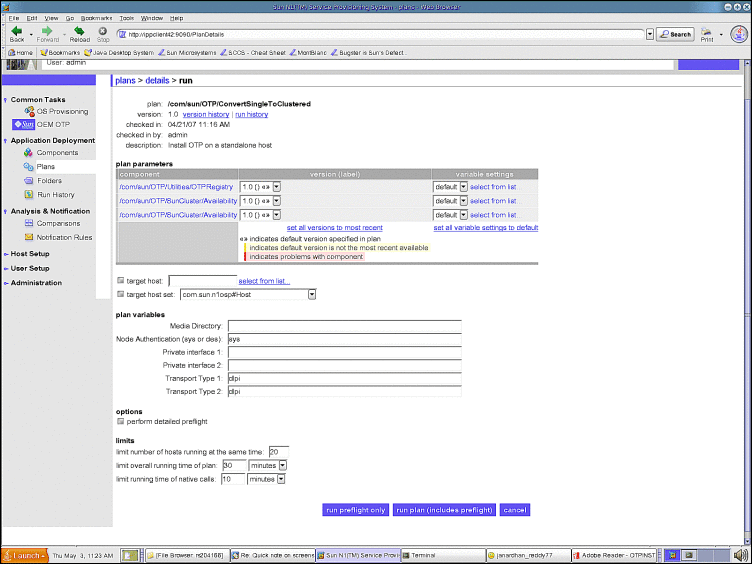
-
Type the name of the standalone OTP host that you want to convert to a clustered OTP host in the target host field. Do not modify the target host set.
-
In the Media Directory field, type the fully-qualified name of the NFS-mounted OTP installation directory.
For example: /net/otpsource.mycompany.com/otp1.1
-
In the Private interface 1 field, type the name of the private interface.
For example, ce0.
-
In the Private interface 2 field, type the name of the private interface.
For example, ce1.
-
Click the perform detailed preflight checkbox.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight)
-
-
-
Create the system shared storage as described in To Create Shared Storage on the Clustered OTP System.
-
Create a temporary mount point.
mkdir -p /var/tmp_otp
-
Mount the shared volume onto the temporary mount point.
mount /dev/md/sps-dg/dsk/d0 /var/tmp_otp
-
Bring the resource group offline.
scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y RG_system=false
scswitch -F -g otp-system-rg
-
Move the OTP contents from the local disk to the shared volume.
mv /var/otp/* /var/tmp_otp
umount /var/tmp_otp
-
Disable the resources in the following order.
scswitch -nj otp-spsms-rs
scswitch -nj otp-spsra-rs
scswitch -nj otp-sps-hastorage-plus
-
Modify the HAStoragePlus resource properties.
scrgadm -c -j otp-sps-hastorage-plus -x FilesystemMountPoints="/var/otp"
scrgadm -c -j otp-sps-hastorage-plus -x GlobalDevicePaths=/dev/md/sps-dg/dsk/d0
-
Enable the resources in the following order.
scswitch -ej otp-sps-hastorage-plus
scswitch -ej otp-spsra-rs
scswitch -ej otp-spsms-rs
-
Bring the resource group online.
scswitch -z -g otp-system-rg -h host name
-
Set the system property for the otp-system-rg resource group to true.
scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y RG_system=true
N*N Topology Administration
This section provides the procedures for adding new OTP host to an N*N clustered OTP system, and for repairing an OTP host within an N*N clustered OTP system.
The following topics are discussed:
Adding a Host to the Existing Cluster
This section provides the procedure for adding a host to an existing clustered OTP system.
 To Add a Host to the Existing Cluster
To Add a Host to the Existing Cluster
Before You Begin
Ensure that the sponsoring host (the first OTP host of the cluster) is added to the host list in the service provisioning service. See To Add Hosts to the External OTP Installation Server.
-
Install the Solaris OS on the new OTP host as described in Installing Solaris 10 Update 2 and the Remote Agent on the OTP Hosts.
-
Configure the Solaris OS on the new OTP host as described in Configuring Solaris 10 Update 2
-
Create a mount point /var/otp on the new OTP host.
# mkdir -p /var/otp
-
Add the following entry to the /etc/vfstab file.
/dev/md/sps-dg/dsk/d0 /dev/md/sps-dg/rdsk/d0 /var/otp ufs 2 no global,logging
-
Provision OTP on the new OTP host using either the graphical user interface or the command line interface.
-
Perform the following steps to provision OTP using the graphical user interface.
-
Set up high availability as described in Set Up the OTP High Availability Framework on the Additional OTP Hosts
-
Create the shared storage on the clustered OTP system as described in To Create Shared Storage on the Clustered OTP System.
-
Set up the OTP services on the host as described in Set Up OTP System Management and Provisioning Services on the Additional OTP Hosts
-
-
Perform the following steps to provision OTP through the command line interface.
-
Run the deployOTPMultiNode script with the -addNode option.
Type the command
/opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/deployOTPMultiNode -addNode /local-path/inputOTPMultiNode.dat
where local-path is the path to the file inputOTPMultiNode.dat.
-
Create metadb on the host and add the host to metaset as described in To Create Shared Storage on the Clustered OTP System.
-
Run the deployOTPMultiNode script with the -addNodeCont option.
Type the command
/opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/deployOTPMultiNode -addNodeCont /local-path/inputOTPMultiNode.dat
where local-path is the path to the file inputOTPMultiNode.dat.
Note –Quorum automatic configuration applies only to two-host clustered OTP systems. If you disable quorum automatic configuration on a two-host cluster by choosing no, you must manually configure the quorum for the two-host cluster and reset the cluster configuration as described in Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform on a Clustered OTP System.
For further information, see “Quorum and Quorum Devices” in Sun Cluster Concepts Guide for Solaris OS to understand the requirements for Quorum. Reconfigure the quorum as described in “Administering Quorum” in Sun Cluster System Administration Guide for Solaris OS.
You can use the scsetup(1M) utility to add a node to the node list of an existing quorum device. To modify a quorum device's node list, you must remove the quorum device, modify the physical connections of nodes to the quorum device you removed, then add the quorum device to the cluster configuration again. When a quorum device is added, scconf(1M) automatically configures the node-to-disk paths for all nodes attached to the disk.
-
-
-
Set the system property for the otp-system-rg resource group to false.
Type the command scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -h RG_system=false
-
Determine the current IPMP groups.
Type scrgadm -pvv | grep otp-lhn:NetIfList | grep value to list the current IPMP groups. For example:
# scrgadm -pvv | grep otp-lhn:NetIfList | grep value (otp-system-rg:otp-lhn:NetIfList) Res property value: sc_ipmp0@1 -
Determine the node ID value as follows:
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl3-ipp2 | grep ID (pcl3-ipp2) Node ID: 2
The IPMP group for the new node in this example would be sc_ipmp0@2
-
Add the IPMP group for the newly added host to the Logical Host Name resource.
Type the command
scrgadm -c -j otp-lhn -x NetIfList=list of IPMP groups
where list of IPMP groups is the current list of IPMP groups. For example:
# scrgadm -c -j otp-lhn -x NetIfList=sc_ipmp0@1,sc_ipmp0@2
-
Determine the current node list.
Type the command scrgadm -pvv | grep otp-system-rg | grep Nodelist. For example:
# scrgadm -pvv | grep otp-system-rg | grep Nodelist (otp-system-rg) Res Group Nodelist: pc13-ipp1
-
Add the host to the resource group.
# scrgadm -c -g resource-group -y nodelist
For example, add the host to the otp-system-rg resource group.
# scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y nodelist=pcl3-ipp1,pcl3-ipp2
-
Set the system property for the otp-system-rg resource group to true.
scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y RG_system=true
Repairing a Host in the Cluster
This section provides the procedure for repairing a failed host in a clustered OTP system. If a host fails in a multi-host cluster setup, the host has to be repaired. The host repair process involves the following two steps:
-
Remove the failed host from the cluster.
-
Add a host to the cluster as described in Adding a Host to the Existing Cluster.
 To Remove a Failed Host From the Cluster
To Remove a Failed Host From the Cluster
In this procedure, the host pcl17-ipp2 is removed from a two-host cluster configuration. The hosts are pcl17-ipp1 and pcl17-ipp2. Substitute your own cluster and host information.
Note –
If the host that is being removed is the first host in the cluster, back up the system management database as described in Backing Up The OTP System Management Service Database and Configuration Files so that the database can be restored to one of the remaining cluster hosts as described in Restoring the OTP System Management Service Database and Configuration Files to Another OTP Host.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the active host in the cluster.
If the cluster has more than two hosts:
-
Log in as root to an OTP host in the cluster.
-
Type /usr/cluster/bin/scstat -g | grep Online to determine which host in the cluster is active.
Make note of the host on which the resource group otp-system-rg is online.
For example:
# /usr/cluster/bin/scstat -g | grep Online Group: otp-system-rg pcl17-ipp2 Online Resource: otp-lhn pcl17-ipp2 Online Online - LogicalHostname online. Resource: otp-sps-hastorage-plus pcl17-ipp2 Online Online Resource: otp-spsms-rs pcl17-ipp2 Online Online Resource: otp-spsra-rs pcl17-ipp2 Online OnlineIn the above example, the active host is pcl17-ipp2.
-
Log in as root on the OTP host on which the resource group is active.
-
-
Add the cluster binaries path to your $PATH.
# PATH=$PATH:/usr/cluster/bin
-
Move all the resource groups and disk device groups to pcl17-ipp1.
# scswitch -z -g otp-system-rg -h pcl17-ipp1
-
Remove the host from all resource groups.
# scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y RG_system=false
# scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y Nodelist=pcl17-ipp1
Note –Nodelist must contain all the node names except the node to be removed.
-
If the node was set up as a mediator host, remove it from the set.
# metaset -s sps-dg -d -m pcl17-ipp2
-
Remove the node from metaset.
# metaset -s sps-dg -d -h -f pcl17-ipp2
-
Remove all the disks connected to the node except the quorum disk.
-
Check the disks connected to the node by typing the following command:
scconf -pvv |grep pcl17-ipp2|grep Dev
# scconf -pvv |grep pcl17-ipp2|grep Dev (dsk/d12) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d11) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d10) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d9) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d8) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d7) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp1, pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d6) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp1, pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d5) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp1, pcl17-ipp2 (dsk/d1) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp1, pcl17-ipp2
-
Remove the local disks.
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d8,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d9,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d10,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d11,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d12,localonly=false
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d8
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d9
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d10
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d11
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d12
-
Determine which disk is the quorum disk.
To determine which disk is the quorum disk, type the command scstat -q | grep "Device votes". For example:
# scstat -q | grep "Device votes" Device votes: /dev/did/rdsk/d1s2 1 1 Online
In this example, the quorum disk is dsk/d1
-
Remove the shared disks except for the quorum disk.
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d5,nodelist=pcl17-ipp2
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d6,nodelist=pcl17-ipp2
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d7,nodelist=pcl17-ipp2
-
Check that only the quorum disk is in the list.
# scconf -pvv |grep pcl17-ipp2|grep Dev
(dsk/d1) Device group node list: pcl17-ipp1, pcl17-ipp2
-
-
Shut down the failed node.
shutdown -y -g 0 -i 0
-
Place the failed node in maintenance state.
# scconf -c -q node=pcl17-ipp2,maintstate
-
Remove the private interconnect interfaces.
-
Check the private interconnect interfaces using the following command:
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl17-ipp2 | grep Transport
Transport cable: pcl17-ipp2:ce0@0 switch1@2 Enabled Transport cable: pcl17-ipp2:ce2@0 switch2@2 Enabled
-
Disable and remove the private interconnect interfaces.
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl17-ipp2:ce0,state=disabled
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl17-ipp2:ce2,state=disabled
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl17-ipp2:ce0
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl17-ipp2:ce2
-
Remove the private interfaces of the failed node.
# scconf -r -A name=ce0,node=pcl17-ipp2
# scconf -r -A name=ce2,node=pcl17-ipp2
-
-
Remove the quorum disk from the failed node.
-
For a two-node cluster, type the following commands:
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d1,nodelist=pcl17-ipp2
# scconf -c -q installmode
# scconf -r -q globaldev=d1
# scconf -c -q installmodeoff
-
For a three-host or more cluster, type the following commands:
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d1,nodelist=pcl17-ipp2
# scconf -r -q globaldev=d1
-
-
Add the quorum devices only to the nodes that will remain in the cluster.
# scconf -a -q globaldev=d[n],node=node1,node=node2
Where n is the disk DID number.
-
Remove the failed node from the node authentication list.
# scconf -r -T node=pcl17-ipp2
-
Remove the failed node from the cluster node list.
# scconf -r -h node=pcl17-ipp2
Perform this step from installmode (scconf -c -q installmode). Otherwise, you will get a warning about possible quorum compromise.
-
Use the following commands to verify whether the failed node is still in the cluster configuration.
# scconf -pvv |grep pcl17-ipp2
# scrgadm -pvv|grep pcl17-ipp2
If the failed node was successfully removed, both of the above commands return to the system prompt.
-
If the scconf command failed, command out will be similar to the following:
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl17-ipp2 Cluster nodes: pcl17-ipp1 pcl17-ipp2 Cluster node name: pcl17-ipp2 (ipp-node70) Node ID: 1 (ipp-node70) Node enabled: yes (ipp-node70) Node private hostname: clusternode1-priv (ipp-node70) Node quorum vote count: 0 (ipp-node70) Node reservation key: 0x462DC27400000001 (ipp-node70) Node transport adapters:
If the scrgadm command output is similar to the following, then Step 4 was not executed.
# scrgadm -pvv|grep pcl17-ipp2 (otp-system-rg) Res Group Nodelist: pc117-ipp1 pc117-ipp2
-
-
Change the RG_system property to true.
Type scrgadm -c -g otp-system-rg -y RG_system=true
Next Steps
Add the host to the cluster as described in Adding a Host to the Existing Cluster.
Pair+N Topology Administration
This section provides the procedures for adding a new OTP host to a Pair+N clustered OTP system, and for repairing an OTP host within a Pair+N clustered OTP system.
The following topics are discussed:
 To Add an OTP Host That Is Not Connected to Shared
Storage
To Add an OTP Host That Is Not Connected to Shared
Storage
-
Reinstall the Solaris 10 Update 2 operating system on the OTP host as described in Installing Solaris 10 Update 2 and the Remote Agent on the OTP Hosts.
-
Add the OTP host back into the cluster configuration as described in To Add a Host to the Existing Cluster
Note –As the OTP host will not be part of the resource group, steps to add the OTP host to the resource group need not be performed.
-
Install OTP on the OTP host.
-
To install OTP on the OTP hosts using the command line, see Chapter 4, Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform For the First Time Using the Command Line
-
To install OTP on the OTP hosts using the graphical user interface, see Chapter 5, Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform For the First Time Using the Graphical User Interface
-
To install OTP on the OTP hosts using a production standalone or clustered OTP system, see Chapter 6, Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform Using the Provisioning Service On an Existing OTP System
-
 To Repair an OTP Host That Is Not Connected to Shared
Storage
To Repair an OTP Host That Is Not Connected to Shared
Storage
In this procedure, pcl8-ipp2 is the OTP host that is being repaired. Substitute your own host information.
-
Check the disks connected to the OTP host that needs to be repaired.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp2 | grep Dev (dsk/d10) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp2 (dsk/d9) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp2
-
Remove the disks connected to the OTP host.
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d10,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d9,localonly=false
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d10
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d9
-
Place the OTP host to be repaired in maintenance state.
# scconf -c -q node=pcl8-ipp2,maintstate
-
Remove the transport information of the OTP host from cluster configuration.
-
Check the transport information.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp2 | grep Transport Transport cable: pcl8-ipp2:bge1@0 switch1@3 Enabled Transport cable: pcl8-ipp2:ce1@0 switch2@3 Enabled
-
Remove the related transport.
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp2:bge1,state=disabled
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp2:ce1,state=disabled
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp2:bge1
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp2:ce1
# scconf -r -A name=bge1,node=pcl8-ipp2
# scconf -r -A name=ce1,node=pcl8-ipp2
-
-
Remove the OTP host from authentication list.
# scconf -r -T node=pcl8-ipp2
-
Remove the OTP host from the host list.
# scconf -r -h node=pcl8-ipp2
-
Make sure that the OTP host is completely removed from the cluster configuration.
If you see any output for the following command, revisit the above steps to make sure all the steps are executed properly.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp2
-
Add the OTP host back into the cluster configuration as described in To Add an OTP Host That Is Not Connected to Shared Storage for more information.
Note –As the OTP host will not be part of the resource group, steps to add the OTP host to the resource group need not be performed.
 To Repair an OTP Host That Is Connected
to Shared Storage
To Repair an OTP Host That Is Connected
to Shared Storage
In this procedure, pcl8-ipp3 is the OTP host that is being repaired. Substitute your own host information.
-
Move all the resource groups to another OTP host in the resource group list.
# scswitch -z -g otp-system-rg -h otherotphost
-
Remove the disks connected to the OTP host.
-
Check the disks connected to the OTP host.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp3 | grep Dev (dsk/d8) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp3 (dsk/d7) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp3 (dsk/d6) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp1, pcl8-ipp3 (dsk/d5) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp1, pcl8-ipp3 (dsk/d4) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp1, pcl8-ipp3 (dsk/d3) Device group node list: pcl8-ipp1, pcl8-ipp3
-
Remove the local disks.
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d8,localonly=false
# scconf -c -D name=dsk/d7,localonly=false
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d8
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d7
-
Remove the shared disks.
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d5,nodelist=pcl8-ipp3
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d6,nodelist=pcl8-ipp3
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d4,nodelist=pcl8-ipp3
-
-
Shut down the OTP host.
# shutdown -y -g 0 -i 0
-
Place the OTP host in maintenance mode.
# scconf -c -q node=pcl8-ipp3,maintstate
-
Remove the transport information.
-
Check the transport information.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp3 | grep Transport
Transport cable: pcl8-ipp3:bge1@0 switch1@2 Enabled Transport cable: pcl8-ipp3:ce1@0 switch2@2 Enabled
-
Remove the transport information.
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp3:bge1,state=disabled
# scconf -c -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp3:ce1,state=disabled
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp3:bge1
# scconf -r -m endpoint=pcl8-ipp3:ce1
# scconf -r -A name=bge1,node=pcl8-ipp3
# scconf -r -A name=ce1,node=pcl8-ipp3
-
-
Remove the quorum disk.
# scconf -r -D name=dsk/d3,nodelist=pcl8-ipp3
# scconf -r -q globaldev=d3
Note –If you perform this procedure on a three-host cluster, you will need to establish quorum before running the above procedure. Otherwise, you will get the following error:
# scconf -r -h node=pcl8-ipp3
scconf: Failed to remove node (pcl8-ipp3) - quorum could be compromised. scconf: All two-node clusters must have at least one shared quorum device.
-
Remove the host from the authentication list.
# scconf -r -T node=pcl8-ipp3
-
Remove the host from the host list.
# scconf -r -h node=pcl8-ipp3
-
Make sure that the OTP host is completely removed from the cluster configuration.
If you see any output for the following command, revisit the above steps to make sure all the steps are executed properly.
# scconf -pvv | grep pcl8-ipp3
-
Add the OTP host back into the cluster configuration as described in To Add a Host to the Existing Cluster for more information.
Changes to OTP High Availability Framework for Enterprise Installation Services Compliance
The main objective of the EIS installation standards is to produce a consistent, high-quality installation in an efficient way.
To make the OTP High Availability framework EIS compliant, the following steps must be performed. All these steps are not mandatory but they are recommended. The first five steps can be performed before setting up OTP. The last step can be performed after the OTP installation.
-
scsi-initiator-id must be defined in the Open Boot Prom (OBP).
-
Add all the cluster nodes and the logical hosts to the /etc/inet/hosts and /etc/inet/ipnodes files.
-
Do not configure cluster nodes as routers. Create the /etc/defaultrouter file manually before installing the OTP high availability framework.
-
If you use shared SCSI storage, add the following entries to the /etc/system file.
set sd:sd_io_time=30
set sd:sd_retry_count=3
set scsi_reset_delay=500
-
If you use the glm driver, add the following entry to the /kernel/drv/glm.conf file.
scsi-selection-timeout=64
-
If you do not install the SUNWescom package, disable the scsymon service.
# svcadm -v disable /system/cluster/scsymon-srv
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
