| C H A P T E R 3 |
|
Configuring and Maintaining |
This chapter includes instructions for configuring and maintaining the DMM. The following topics are covered:
When the DMM is installed, the following configuration files are generated:
See the Sun Net Connect 3.2.1 Customer Operations Guide for more information on configuring and maintaining the monitored system and editing the proxy configuration file parameters and default settings.
After you install the DMM on your system, the following DMM information is available on the Sun Control Station:
Perform the following steps to view the Data Manager Status:
1. Log in to the Sun Control Station by opening a browser window and typing the following:
If you do not want to use the SSL connection, type the following URL:
http://IP_address_of_server:8080/sdui/
2. At the Login page, type the user name and password. The default username is admin and the default password is admin.
After you log in, you should change the password. See the Sun Control Station CC Edition Administration Guide for the procedure for resetting the password.
3. Click Login. The Sun Control Station home page appears.
If you have a Sun Net Connect monitored system that has a direct Internet connection to Sun and would like to re-direct it to the DMM, you need to change the monitored system's proxy configuration file to point to the DMM or uninstall Sun Net Connect and do a new installation.
Perform the following steps on the Sun Net Connect monitored system that you want to redirect to the DMM:
1. As the root user, open the /etc/opt/SUNWsrspx/srsproxyconfig.cfg file on the monitored system.
2. Edit the SEND_BASE_URL to point to the DMM IP address.
For example, http://dmm-ip:8000
4. Type the following to find the srsproxy process that is running and stop it so that it rereads the configuration file:
5. Verify that srsproxy is running under a new process id by typing:
6. Check the system messages log (syslog) file for warnings. It is located in the /var/adm/messages file. Verify that a line containing the phrase ...srsproxy started appears.
The following secure sockets layer (SSL) parameters are available in the srsproxyconfig.cfg file:
You can change the settings for message encryption on your monitored system and DMM system by editing the SSL_CIPHERS parameter. The SSL_ENABLED parameter must be set to "true" for the SSL_CIPHERS level to be activated.
FIGURE 3-1 is an example of a configuration where peer-to-peer authentication is always required, but message encryption is turned off within the network. In this example, changing the SSL_CIPHERS parameter to "null" and the SSL_ENABLED parameter to "false" on the monitored systems allows unencrypted data to flow within the network. On the DMM, the SSL_CIPHERS parameter is set to "default" and the SSL_ENABLED parameter is set to "true", so all data is encrypted with a 128-bit cipher before it leaves the network.
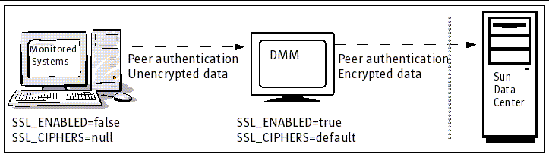
By default, SSL_CIPHERS is set to 128-bit encryption. The parameter is not visible in the configuration file, but you can add the parameter and change the setting to "null" or "high".
Perform the following steps to manually add SSL_CIPHERS to the configuration file:
1. Log in to the monitored system as the user you specified during installation.
|
Note - The DMM uses the Internet to connect to the Sun Net Connect Data Center. To protect data, message encryption on the DMM should not be set to "null". |
2. Open the /etc/opt/SUNWsrspx/srsproxyconfig.cfg file in a text editor.
The following is an example of a configuration file:
CONFIG_NAME=ncsystem
CUSTOMER_ID=123
TYPE=PROXY
HEARTBEAT_FREQ=300
SEND_BASE_URL=http://123.456.789.123
BULK_MESSAGE_SIZE=8192
BANDWIDTH_ID=52
HTTP_PROXY=
HTTP_PROXY_USERPWD=
HTTP_PROXY_PORT=
DISK_STORE_BASE=/var
DISK_STORE_SIZE=20
MAINTENANCE_MODE=OFF
UPLOAD_RETRY_INT=180
UPLOAD_RETRY_MAX=5
SEND_RETRY_INT=120
SEND_RETRY_MAX=5
SSL_ENABLED=true
SSL_CERT_FILE=/etc/opt/SUNWsrspx/CustomerCert.pem
SSL_CA_FILE=/etc/opt/SUNWsrspx/SRSCACert.pem
SSL_CERT_REDIRECT=
AUTO_UPDATE_ENABLED=Y
FALLBACK_CONFIG_URL=
SOCKS_RUNNER=
3. Add the SSL_CIPHERS parameter and setting to the srsproxyconfig.cfg file. The options are "null", "default", and "high". See Edit the Message Encryption Level for option definitions.
For example, type the following: SSL_CIPHERS=null
5. Find the srsproxy process that is running and stop it so that it rereads the configuration file.
6. Verify that srsproxy is running under a new process id by typing:
7. Check the syslog file for warnings. It is located in the /var/adm/messages file. Verify that a line containing the phrase ...srsproxy started appears.
A Sun Net Connect software proxy alarm indicates that the proxy is not sending a status (heartbeat). This indicates that the monitored system is down, there is a failed connection between the monitored system and the DMM, or the connection between the DMM and the Sun Net Connect Data Center has been interrupted. By default, srsproxy error messages are sent to the /var/adm/messages file. See Redirecting Proxy Errors for the steps to redirect srsproxy error messages and Rolling Over a Redirected Proxy Syslog to roll the syslog file to maintain a manageable size.
The Net Connect proxy sends a heartbeat every five minutes. Sun Net Connect providers also send heartbeats and alarms that are displayed when those components go down.
If a Sun Net Connect monitored system is linked to the DMM, the Sun Net Connect proxy on the monitored system sends a proxy status (heartbeat) to the DMM every five minutes. If the connection is interrupted, a status is not sent to the DMM. When the DMM misses two consecutive heartbeats, the DMM sends a proxy alarm to Sun, as shown in FIGURE 3-2. If you configured the monitored system for notification, Sun sends you email or pager notification that the system is down. You also receive notification when the system is back up and the proxy sends a heartbeat. See the Sun Net Connect 3.2.1 Customer Operations Guide for the steps to set up notification of proxy status.
A Sun Net Connect monitored system has a number of providers that send heartbeats at different intervals to the Sun Net Connect proxy on the system. If a provider stops running, the proxy sends an alarm that is displayed on the Sun Net Connect Monitoring pages on the monitored system and sends email or pager notification, if you configured your system for notification.
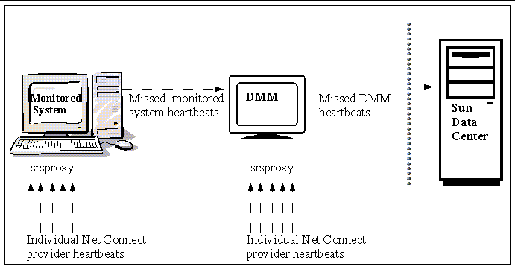
You can edit the heartbeat interval between Sun Net Connect monitored systems. For instructions on editing the monitored system's heartbeat interval, go to the "Configuration Maintenance" section in the Sun Net Connect 3.2.1 Customer Operations Guide. See DMM Maintenance Mode for information on temporarily disabling the heartbeat between your monitored system and DMM.
Perform the following steps to see if the network connection is working:
1. Log in to the monitored system as the root user.
2. Type the following command:
/opt/SUNWsrspx/bin/srspxrun -p
DMM Maintenance Mode is designed to block the incoming heartbeat while you perform maintenance on a monitored system. Set the Maintenance Mode to "on" to block proxy connection errors while you are updating the system configuration or hardware.
If you need to perform maintenance on a monitored system, you can disable incoming heartbeat monitoring on the DMM by changing the Maintenance Mode to "on". This setting disables heartbeat monitoring for all monitored systems attached to the DMM. Putting the DMM in maintenance mode blocks all heartbeats from incoming monitored systems but does not disable the DMM heartbeat.
See the Sun Net Connect 3.2.1 Customer Operations Guide for the steps to disable or edit individual provider heartbeats.
Perform the following steps to place the DMM in Maintenance Mode:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Change the maintenance the mode from "off" to "on", as shown below:
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/mlmc -p 8000 -m on
Perform the following steps to take the DMM out of Maintenance Mode and begin processing monitored system heartbeats:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Change the Maintenance Mode from "on" to "off".
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/mlmc -p 8000 -m off
3. Check the status of the Maintenance Mode.
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/mlmc -p 8000 -s
The system log (syslog) is located in the /var/adm/messages file. To keep the syslog to a manageable size, the log is automatically rolled.
|
Note - The debugging level affects the log file space and frequency of rollover. See Changing the DMM Log Priority Values for the steps to change your debugging level. |
You can redirect srsproxy errors from the /var/adm/messages file to another file. The file must be accessible and reside in a directory with read and write capabilities.
Perform the following steps to redirect srsproxy errors from /var/adm/messages:
1. As the root user, open the srsproxyconfig.cfg file on the monitored system in a text editor.
LOG_FILE=/var/tmp/srsproxy.log
Perform the following steps to roll over the new log file:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Move the log file to a new file extension.
# mv logfilename logfilename.1
By completing Step 3, the log is regenerated until the next rollover.
The DMM configuration file (dmmconfig.cfg), located in the /scs/modules/dmm/conf/ directory, contains the configuration file parameters downloaded with the DMM software.
The following is an example of a configuration file:
CONFIG_NAME=dmm_A
TYPE=MID-LEVEL-MANAGER
CUSTOMER_ID=123
AUTO_UPDATE_ENABLED=Y
DMM_PORT=8000
HTTP_PROXY=my-HTTP-proxy-URL
HTTP_PROXY_PORT=8080
HTTP_PROXY_USERPWD=userid:password
COMM_URL=https://www.xxx.sun.com
COMM_BULK_THROTTLE=4
COMM_MESSAGE_THROTTLE=70
COMM_OUTBOUND_THROTTLE=20
COP_URL=persistent:///scs/data/dmm/data/clog
COP_BACKCHANNEL_URL=persistent:///scs/data/dmm/data/dmm-backchannel
COP_CONTROL_URL=persistent:///scs/data/dmm/data/dmm-control
COP_HEARTBEAT_URL=persistent:///scs/data/dmm/data/dmm-heartbeat
COP_SHMEM_URL=persistent:///scs/data/dmm/data/dmm-shmem
HEARTBEAT_THREAD_INTERVAL=150000
PULSE_THREAD_INTERVAL=300000
You can edit the config_name and HTTP proxy settings in the dmmconfig.cfg file. To edit the IP address, see Changing the DMM IP Address. To edit the DMM port, see Changing the Inbound Port Used by the DMM.
Perform the following steps to edit a value in the DMM configuration file:
1. As the root user, open the /scs/modules/dmm/conf/dmmconfig.cfg file.
2. Make your changes and save.
|
Note - If a value contains whitespace, place the value in quotation marks. For example, CONFIG_NAME="DMM A". |
3. Type the following to refresh the file and activate your changes:
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/stop_dmm.sh
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/reload_dmm_conf.sh
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/start_dmm.sh
Perform the following steps to stop or shut down the DMM:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Move the log file to a new file extension.
# mv logfilename logfilename.1
3. Stop the DMM by typing the following command:
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/stop_dmm.sh
If the Data Manager status shows that the DMM is not responding, you need to restart the DMM.
Perform the following steps to start the DMM:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Start the DMM by typing the following command:
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/start_dmm.sh
DMM output is stored in the log files located in the /scs/modules/dmm/logs directory. The DMM has the following log configuration files:
The following priority values are supported:
Each log file contains elements, or categories. Each category uses a separate priority value. In most cases, the default priority value is debug.
The following is a sample from the dmm-msg.log configuration file:
<category name="message.incoming">
<priority value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="incoming-flat-appender" />
</category>
<category name="message.outgoing">
<priority value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="outgoing-flat-appender" />
</category>
<category name="message.spoofed">
<priority value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="spoofed-flat-appender" />
</category>
<category name="com">
<priority value="info" />
<appender-ref ref="flat-appender" />
</category>
Perform the following steps to change the DMM log level in the message context files for debugging:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Open the configuration log file in a text editor:
Open the following Message Log Configuration file for message context files:
/scs/modules/dmm/webbase/webapps/msg/WEB-INF/classes/msg-log4j.xml
Open the following Cache Log Configuration file for the cache context file:
/scs/modules/dmm/webbase/webapps/msg/WEB-INF/classes/msg-log4j.xml
3. Change the category priority value. For example, change the priority value from "debug" to "info".
<category name="message.outgoing">
|
Note - The debugging level affects the size of your log file space and the frequency that your log file is rolled over. See System Messages Log Maintenance for details on the syslog. |
The monitored systems connect to the DMM using the DMM's IP address and port. If you change the IP address, you must redirect the monitored systems to the new DMM IP Address by performing the following steps:
1. Edit the SEND_BASE_URL on all monitored systems reporting to that DMM.See Direct an Existing Monitored System to the DMM for the steps to edit the SEND_BASE_URL on a Sun Net Connect monitored system.
2. Restart the monitored system proxy
3. Restart the DMM. When the DMM is restarted, a registration message that includes the new IP address is sent to Sun.
By default, the DMM uses port 8000 for incoming data and port 443 for outgoing data. The outgoing port cannot be configured.
Perform the following steps to edit the inbound port:
1. Log in to the system as root.
2. Open the /scs/modules/dmm/conf/dmmconfig.cfg file.
3. Change the DMM-port number.
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/stop_dmm.sh
5. Update the /scs/modules/dmm/webbase/conf/server.xml file.
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/reload_dmm_conf.sh
# /scs/modules/dmm/sbin/start_dmm.sh
Shared Shell and Shared Web use a dedicated SSL connection to Sun. However, when the DMM is used, you must open the connection to Sun using one of the following options:
See the Sun Net Connect 3.2.1 Customer Operations Guide for information on using remote access applications.
Copyright © 2005, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.