| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Sun Storage 2500-M2 Arrays Hardware Release Notes, Release 6.10 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Sun Storage 2500-M2 Arrays Hardware Release Notes, Release 6.10 |
1. Sun Storage 2500-M2 Arrays Hardware Release Notes
Supported Disk Drives and Tray Capacity
Array Expansion Module Support
Supported Host Bus Adaptors (HBAs)
Supported FC and Multilayer Switches
ALUA/TPGS Multipathing with VMware
Procedure for ESX4.1U2 and ESXi5.0
Procedure for ESX4.1U3 and ESXi5.0U1
SAS Host Ports on the Sun Storage 2540-M2
Log Events With smartd Monitoring Enabled
Kernel Panics During Controller Firmware (CFW) Download
Kernel Panics During Controller Firmware Download
Network Interface on Device eth0 Fails to Come Online When Booting a Host
Tasks Aborts Are Logged During a Controller Firmware Upgrade
Unable to Add More Than 117 Volumes to the Oracle Virtual Machine (OVM) Manager Database
After an NVSRAM Download, a Controller Reboots a Second Time when the NVSRAM is Activated
Input/Output (I/O) Errors Occur when Disconnection of Devices from a SAS Switch Is Not Detected
Host Operating System Logs "Hung Task" During a Path Failure
Data is Misread when a Physical Drive Has an Unreadable Sector
The following are restrictions and known issues applicable to this product release.
In a single path data connection, a group of heterogeneous servers is connected to an array through a single connection. Although this connection is technically possible, there is no redundancy, and a connection failure will result in loss of access to the array.
 | Caution - Because of the single point of failure, single path data connections are not recommended. |
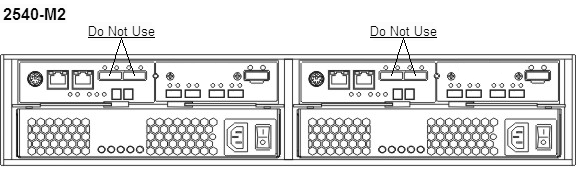
Although SAS host ports are physically present on the Sun Storage 2540-M2 array controller tray, they are not for use, not supported, and are capped at the factory. The following figure shows the location of these ports. The Sun Storage 2540-M2 only supports Fibre Channel host connectivity.
Bug 15693183 (7014293) – When volumes are mapped to a Linux host with smartd monitoring enabled, on either a Sun Storage 2500-M2 or 6780 array, it is possible to receive “IO FAILURE” and “Illegal Request ASC/ASCQ” log events. This bug has been observed on SLES 11.1, but occurs also on other Linux platforms and versions.
Workaround – Either disable smartd monitoring or disregard the messages. This is an issue with the host OS.
Operating System
Oracle OVM 3.0.3
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you re-install the OVM manager on the host using the same ID as the previous installation. ISO file systems that were imported with the previous OVM manager are now renamed with their UUIDs rather than their friendly names. This makes it difficult to identify the ISO file systems.
Workaround
None.
Operating System
Oracle OVM 3.0.3 with the generic SCSI plug-in
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you un-map a volume on an OVM server. The OVM manager continues to show the volume along with those that are still mapped to the server. When you try to assign one of the affected volumes to a virtual machine, you see this error message:
disk doesn't exist
Workaround
After you un-map the volumes, use the OVM manager to remove those volumes from the storage database on the server.
Operating System
Oracle OVM 3.0.3 with the generic SCSI plug-in
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Problem or Restriction
In the OVM user interface, only one drive at a time can be selected for deletion.
Workaround
None.
Operating System
Oracle Linux 5.7 with UEK kernel release 2.6.32-200.13.1.el5uek
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you upgrade CFW. The kernel panics on an attached host when downloading the CFW and shows the following message:
Kernel panic - not syncing: Fatal exception BUG: unable to handle kernel NULL pointer dereference at 0000000000000180 IP: [<ffffffff8123450a>] kref_get+0xc/0x2a PGD 3c275067 PUD 3c161067 PMD 0 Oops: 0000 [#1] SMP last sysfs file: /sys/block/sdc/dev
Workaround
To avoid this problem, do not perform a CFW upgrade on a storage array that is attached to hosts running the affected operating system version. If the problems occurs, power cycle the host.
Operating System
Windows Server 2012 build 9200
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you attempt to install the BCM driver on a server. The driver installs, but the component reports one of the following errors:
This device is not configured correctly. (Code1) The system cannot find the file specified.
or
The drivers for this device are not installed. (Code 28) The system cannot find the file specified.
Workaround
None.
Operating System
Oracle Linux 5.8 with UEK kernel release 2.6.32-300.10.1.el5uek
Oracle Linux 6.2 with UEK kernel release 2.6.32-300.3.1.el6uek
Device Mapper MultiPath release 0.4.9-23.0.9.el5 and release 0.4.9-46.0.1.el6
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you upgrade controller firmware. A host with the affected kernel with UEK support experiences a devloss error for one of the world-wide port numbers (WWPNs) followed by a kernel panic.
Workaround
To avoid this problem, upgrade the host kernel to release 2.6.32-300.23.1.
If the problems occurs, power cycle the host.
Operating System
Oracle Linux 5.8 with UEK kernel release 2.6.32-300.10.1.el5uek
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs during a host boot process when a large number (112+) of volumes are mapped to the host.At the point in the boot process where the network interface should be brought online, the host displays the following message:
Bringing up interface eth0: Device eth0 has different MAC address than expected. [FAILED]
The network interface does not come online during the boot process, and cannot subsequently be brought online.
Workaround
To avoid this problem, reduce the number of volumes mapped to host with the affected version of Oracle Linux. You can map additional volumes to the host after it boots.
Operating System
Oracle Linux 5.8 with UEK kernel release 2.6.32-300.10.1.el5uek
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you have more than 128 volumes mapped to a host, both controllers reboot, and only one controller comes back online. Only the first 128 volumes mapped to the host are accessible to the host for input/output (I/O) operations after the reboot. During the controller reboot, there might be a delay before any of the volumes are accessible to the host. I/O timeouts occur when the host tries to communicate with the inaccessible volumes.
Workaround
You can avoid this problem by mapping no more that 128 volumes to a host with the affected operating system release. If the problem occurs, run the multipath command again after the controller comes back online.
Operating System
Red Hat Linux 6.2
SuSe Enterprise Linux 11.2
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Hosts attached through a SAS switch
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs during a controller firmware upgrade. The operating system logs task abort messages similar to those shown below.
May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.764601] sd 0:0:101:3: task abort: SUCCESS scmd(ffff88012383c6c0) May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.764606] sd 0:0:101:1: attempting task abort! scmd(ffff88022705c0c0) May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.764609] sd 0:0:101:1: CDB: Test Unit Ready: 00 00 00 00 00 00 May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.764617] scsi target0:0:101: handle(0x000c), sas_address(0x50080e51b0bae000), phy(4) May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.764620] scsi target0:0:101: enclosure_logical_id(0x500062b10000a8ff), slot(4) May 3 21:30:51 ictc-eats kernel: [118114.767084] sd 0:0:101:1: task abort: SUCCESS scmd(ffff88022705c0c0)
You might experience input/output (I/O) timeouts or read/write errors after the upgrade.
Workaround
If this problem occurs, restart input/output operations. the affected resources will come back online without further intervention.
Operating System
Oracle VM 3.0.3
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you attempt to add more that 117 volumes to the database of the OVM manager. When the OVM manager scans for the additional volumes, it returns the following error:
OSCPlugin.OperationFailedEx:'Unable to query ocfs2 devices'
Workaround
You can avoid this problem by deleting volumes from the OVM manager database when those volumes are no longer mapped to the OVM server.
Operating System
All
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when power is turned off and then back on to a controller-drive tray while there are failed volumes in the storage array. When the controllers reboot after the power cycle, they attempt to flush restored cache data to disk. If the controllers are unable to flush the cache data because of failed volumes, all of the volumes in the storage array remain in write-through mode after the controllers reboot. This will cause a substantial reduction in performance on input/output operations.
Workaround
None.
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.2 with DMMP and SteelEye LifeKeeper Clustering application
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when a cluster loses access to a file system resource. A message similar to the following appears in the cluster log:
Device /dev/mapper/mpathaa not found. Will retry wait to see if it appears. The device node /dev/mapper/mpathaa was not found or did not appear in the udev create time limit of 60 seconds Fri Apr 27 18:45:08 CDT 2012 restore: END restore of file system /home/smashmnt11 (err=1) ERROR: restore action failed for resource /home/smashmnt11 /opt/LifeKeeper/bin/lcdmachfail: restore in parallel of resource "dmmp19021 "has failed; will re-try serially END vertical parallel recovery with return code -1
You might experience I/O timeouts.
Workaround
If this problem occurs, restart I/O operations on the storage array.
Operating System
All
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware releases 7.80 through 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when a controller detects corruption in the signature of the NVSRAM loaded on the controller. The controller restores the NSVRAM from the physical drive, and then reboots.
Workaround
The controller recovers and continues normal operations.
Operating System
All
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you fail to follow standard procedures when replacing a controller. If you do not set a controller offline before you replace it, and the replacement controller has a difference firmware level from the remaining controller, the firmware mismatch is not properly detected.
Workaround
You can avoid this problem by following the standard procedure for replacing a controller. If this problem occurs, the replacement controller reboots after the exception and the storage array returns to normal operations.
Operating System
All
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Controllers attached to hosts through SAS switches
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when there is a heavy load of I/O operations between hosts and storage arrays that are connected through a SAS switch. The switch fails to notify the host when a volume is no longer available. A host experiences I/O errors or application timeouts.
Workaround
To avoid this problem, reduce some or all of the following factors:
The number of ports on the switch that are used or zoned
The number of volumes mapped to hosts through the switch
The throughput of I/O operations
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating systems with Device Mapper Multipath (DMMP)
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Controller-drive trays with SAS host connections
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you disconnect a SAS cable between a controller and a host. Even if you reconnect the cable before the normal failover timeout, the path fails and the controller fails over to the alternate.
Workaround
If this problem occurs, reconnect the cable. The path will be restored.
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating systems with Device Mapper Multipath (DMMP)
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when the maximum number of volumes (256) is mapped to a host. If you disconnect the cable between a controller and a host, and then reconnect the cable, I/O errors occur if the alternate controller becomes unavailable before the host can rediscover all of the volumes on the connection.
Workaround
After some delay, the host will rediscover all of the volumes and normal operations will resume.
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating systems with Device Mapper Multipath (DMMP)
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Hosts with 3 Gb/s SAS host bus adapters
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when you upgrade controller firmware during a heavy load of I/O operations. The host experiences I/O timeouts during firmware activation.
Workaround
Do not perform an online controller firmware upgrade while the system is under heavy I/O load. If this problem occurs, restart I/O operations on the host.
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.0 and later with multipath proxy (MPP) driver
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Hosts with SAS host bus adapters
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when there is a path failure through a host connection. The operating system logs a "Hung Task" message in /var/log/messages before the MPP driver marks the path failed and fails over to the alternate path.
Workaround
The logging of this message does not affect normal operation. You can disable the log message by entering the following command on the host command line:
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs
Operating System
Windows 2008 R2 Server (all editions) running Hyper‐V cluster with CSV
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when a backup operation of CSVs begins. The backup application talks to the VSS provider and initiates the backup operation. The creation of a snapshot volume or mounting of a snapshot volume fails. The backup application then tries to backup the CSVs instead of a snapshot of the CSVs. If the Retry option is set with lock, the application hosted on the CSVs or data written to or read from these volumes might throw an error. If the Retry option is set without lock, the backup skips files. This error occurs because the backup application and the application hosted on the CSVs or data being written to or read from the CSVs tries to "lock" the volume or file, which results in a conflict.
Users encounter this issue whenever there is a resource conflict between the backup operation and the application trying to perform write or read operations to the volume undergoing a backup operation.
Depending on the option the customers choose, the backup operation reports one of these conditions:
Skipped files
Application reports errors
Write or read operation to the volume under backup reports errors
Workaround
Run the backup operation at a time when the application is not doing write or read intensive work on the CSV undergoing backup.
Also, when using the option "Without Lock," files will be skipped and the user can then create another backup operation with the skipped files. For more information, see http://www.symantec.com/docs/TECH195868
Operating System
All
Hardware/Software/Firmware
Controllers with SAS host connections
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem rarely occurs when multiple hosts are connected by a quadfurcated cable to a single wide port on the controller. If the cable is disconnected, the controller reboots.
Workaround
The controller reboots and return to normal operations when the cable is reconnected.
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.x
Hardware/Software/Firmware
All controllers
Controller firmware release 7.84
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when issuing a read to a location where the length of the read includes an unreadable sector. The host operating system assumes that data up to the unreadable sector was read correctly, but this might not be the case. A bug has been opened with Red Hat: http://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=845135
Workaround
Replace any drives that have media errors.
Operating System
Solaris 10 VM
Hardware/Software/Firmware
ESXi 5.1 hosts in HA cluster configuration configured in fault tolerant mode with heavy I/O
Problem or Restriction
This problem occurs when the host fails while the host was running a secondary VM for a Solaris 10 (u10) guest. The message in the event log for that VM that reads as follows:
No compatible host for the Fault Tolerant secondary VM
When this problem occurs, the secondary VM for the guest is stuck in an Unknown status and cannot re‐enable Fault Tolerance for this VM. An attempt to disable and then re‐enable Fault Tolerance fails because it cannot relocate the secondary VM from a host that is not responding. Also Fault Tolerance cannot be completely turned off on the VM for the same reason.
The main problem is that the HA service reports that there are not enough resources available to restart the secondary VM. However, even after reducing all used resources in the cluster to a level so that there is an overabundance of resources, the HA service still reports that there are not enough and therefore no available host in the cluster on which to run the secondary VM. After the VM fails completely, however, the VM can be restarted and put into Fault Tolerance mode again.
The shutdown of the VM is something that always happens if a Fault Tolerance enabled VM is running unprotected without a linked secondary VM and the host on which the primary VM is running fails for any reason. The failure of the secondary VM in a node failure scenario for Solaris 10 guests can be regularly reproduced.
When a node failure happens, the customer sees that Solaris 10 guests can have issues restoring a secondary VM for Fault Tolerance enabled VMs. This is seen by reviewing the vSphere client in the cluster VM view as well as in the event log for the VM.
Workaround
In most cases, the customer can correct the problem by performing one of the following actions in the order shown. Perform one action and if that does not work, proceed to the next until the problem is resolved.
Disable and re-enable fault tolerance on the affected VM.
Turn off fault tolerance for the VM altogether and turn it back on.
Attempt to live vMotion the VM and try action 1 and action 2 again.
It is possible that either the host CPU model is not compatible with turning Fault Tolerance off and on for running VMs, or that, even after performing the previous action, a secondary VM still does not start. If the secondary VM does not start, the customer needs to briefly shut down the affected VM, perform action 2, and then restart the VM.
Page 38 of the Sun Storage 2500-M2 Arrays Hardware Installation Guide mistakenly refers to AIX and HP-UX as supported data host platforms. Disregard HP-UX and AIX referenced in the following note:
"The data host multipathing software for Red Hat Linux, HP-UX, AIX, and Windows platforms is Sun Redundant Dual Array Controller (RDAC), also known as MPP."