Configuring File BC WSDL Attributes
To configure a JBI component to access web services, you specify both service
level WSDL elements and binding level WSDL elements.
Service Level WSDL Elements
Service level WSDL elements allow you to specify the “connectivity” information to a
file system. The File address extensibility element is the File Binding Component service
level WSDL element.
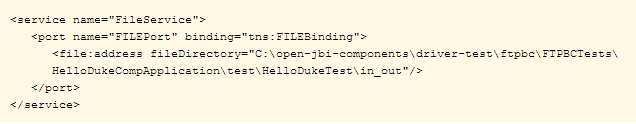
The service element specifies the connectivity to the file system using the File
address element file:address. The properties of address further allows you to specify a
path to a directory and then to specify whether the path is a
absolute path or a relative path.
File Address Element
When you create a WSDL file for a BPEL project in the
NetBeans IDE, the new WSDL Document wizard generates the address service definition. You can
then edit the properties of address service to specify the path.
The following table describes the properties available for this service:
|
|
|
|
|---|
fileDirectory |
Defines the directory path
in the file system to read from or write to. Defines the directory path
in the file system to read from or write to. If the
relativePath property is false, then fileDirectory represents an absolute path. If relativePath property
is true, then fileDirectory represents a path relative to the path specified in
the pathRelativeTo property. |
Required |
/home/joe/data |
relativePath |
Specifies whether the directory specified in the fileDirectory property is
a relative path. |
Optional |
true |
pathRelativeTo |
Defines the base directory for the directory defined by fileDirectory.
Select one of the three possible values:
|
Optional |
User Home |
lockName |
Specifies the lock
file name which is created under the target directory specified by fileDirectory. Inbound
readers use the lock to synchronize their concurrent access to the target directory. |
Optional |
filebc.lck |
seqName |
Specifies
the name of the file where the current value of the persistence backed
sequence number is stored. The file resides in the target directory specified
by fileDirectory. |
Optional |
filebc.seq |
workArea |
Specifies the temp directory name where UUID tagged input files wait to be
further processed. It is a functioning “staging area” for inbound processing, and is
relative to the target directory specified by fileDirectory. |
Optional |
filebc_tmp |
recursive |
Specifies whether inbound polling or
on demand read searches the subdirectories of the base directory specified by fileDirectory, |
Optional |
false |
recursiveExclude |
When
recursive is true, specifies, as a regular expression, subdirectories and files to exclude
from processing when performing inbound polling or on demand reads. |
Optional |
not_my_interests_ [0–9]+ |
|
The following example illustrates the WSDL service element:
Binding Level WSDL Elements
Binding level WSDL elements allow you to define the file “transport” specific information
for operations and messages. The File Binding Component binding level WSDL elements include
the File binding, operation, and message extensibility elements.
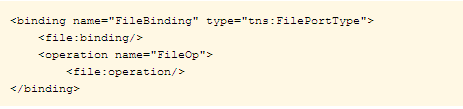
File Binding Element
The file binding extensibility element allows the association of a binding to be
file protocol specific. The message format and protocol for the File Binding
Component is always a file that is supported on the native file system.
When you create a WSDL file for a BPEL project in the
NetBeans IDE, the New WSDL Document wizard generates the file binding definition, which
includes a name you specify and a type that is generated by the
wizard.
The following example illustrates the File binding element:

File Operation Element
The file operation element defines the supported operations. For the File Binding Component
the operations that can be supported are one-way and request-response.
The following example illustrates the File operation element:
File Message Element
The File message element extends the binding element to specify properties associated with
reading input files or writing output files in the file system. In the
NetBeans IDE, select the properties for a file:messages() element to specify the behavior
for the message.
The following table describes the message properties available for reading from or writing
to the file system.
Table 1 Message Properties to Read/Write to a File System
|
|
|
|
|---|
Use |
Specifies whether a message (or message part) is literal
or encoded. If encoded is specified, then you must also specify the encoder using the
encodingStyle() property. |
Required |
Literal (Default) |
fileName |
Defines the file name relative to the specified directory
to read from or write to. If fileNameIsPattern() and fileNameIsRegex are both false, this attribute specifies
an actual file name. If fileNameIsPattern() is true, this attribute specifies a pattern marker used for
filtering input files from the directory, or a file name format to write
to the directory. If fileNameIsRegex() is true, this attribute specifies a regular expression used for
filtering input files from the directory, or a file name format to write
to the directory. |
Required |
data.xml (Default) |
fileNameIsPattern |
Indicates whether or not the fileName() attribute designates a filename pattern. |
Optional |
false |
fileNameIsRegex |
Indicates whether
or not the fileName() attribute designates a regular expression. |
Optional |
false |
recordDelimiter |
Defines the record delimiter when
multiple records are present. The value of this attribute is considered only
if multipleRecordsPerFile() is true. If no value is specified for this
attribute but maxBytesPerRecord() is defined when reading a file, it is assumed
that each record is of fixed length with the length being the value
defined for maxBytesPerRecord(). Otherwise, the default record delimiter is the linefeed character. |
Optional |
\r\n |
pollingInterval |
Defines the polling
interval that the File Binding Component searches for input files in the specified
directory. The polling interval is specified in milliseconds and has a default value
of 1000ms. This attribute has no effect for writing. |
Required |
1000 (Default) |
fileType |
Specifies whether the
file is a text file or binary file. |
Optional |
text (Default) |
encodingStyle |
Specifies the encoding type
associated with the message (or message part). This also defines the encoder type
responsible to process the encoded data. |
Optional |
customencoder-1.0 |
part |
The abstract WSDL configuration for message can have
one or more parts. The part() property references one of the parts that
is named in the abstract WSDL configuration. |
Optional |
Part1 |
addEOL |
Defines whether newline characters (EOL characters) should
be appended to the outbound message or to each record incase of multiple records.
This attribute has no effect for reading |
Optional |
false |
removeEOL |
Defines whether newline characters
(EOL characters) should be removed before processing. or be removed for each record
incase of multiple records. This attribute has no effect for writing |
Optional |
false |
maxBytesPerRecord |
Defines the maximum number
of bytes to be read per record. If only a single record
is present, this attribute defines the total number of bytes to be read.
This attribute has no effect for writing. |
Optional |
1024 |
multipleRecordsPerFile |
Specifies whether the file to read
from or write to contains multiple records or should be considered a single
payload. |
Optional |
false |
archive |
Specifies whether a message is archived after it is read for processing by
the File Binding Component. When true, the message is moved to the
directory specified by archiveDirectory. When a file is processed, the File Binding
Component renames the file to input_file_name_processed() or input_file_name_error(), depending on the success of the
operation. If the archive() property is true, the file is then moved to the
archiveDirectory and a UUID is appended to the file name. |
Optional |
true |
archiveDirectory |
If the archive() property
is set to true(), archiveDirectory() specifies the directory to which processed (read) messages
will be moved. Filenames for archived messages are tagged with a UUID to
avoid file name collision in the archive directory. If the archiveDirIsRelative() property
is true(), then the directory specified here is a relative directory. The parent
directory is the directory specified in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address()
element. |
Optional |
true |
archiveDirIsRelative |
Indicates whether the directory specified in archiveDirectory() is an absolute directory
or a relative directory. If true(), the parent directory is the
directory specified in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address() element. |
Optional |
true |
protect |
Indicates if overwrite protection
is required before writing messages to a file. When true(), existing files of
the same name will be moved to the directory specified by protectDirectory before the
current message is written. When false(), the files of the same
name will be overwritten. |
Optional |
true |
protectDirectory |
If the protect property is set to true, protectDirectory
specifies the directory to which files will be moved to prevent them from
being overwritten. Filenames for protected messages are tagged with a UUID to avoid
file name collision in the protect directory. If the protectDirIsRelative() property is
true(), then the directory specified here is a relative directory. The parent directory
is the directory specified in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address() element. |
Optional |
false |
protectDirIsRelative |
Indicates
whether the directory specified in protectDirectory() is an absolute directory or a
relative directory. If true(), then the parent directory is the directory specified
in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address() element. |
Optional |
true |
stage |
Indicates if staging is enabled.
If set to true(), then messages are first written to the directory specified
by stagingDirectory. When the message is completely written to the staging directory, then
it is moved to the target directory for the message. Filenames
for staged messages are tagged with a UUID to avoid file name collision
in the staging directory. |
Optional |
false |
stageDirectory |
If the stage property is set to true,
stageDirectory() specifies the directory to which files will first be written before being
moved to the target directory for the message. If the stageDirIsRelative() property
is true, then the directory specified here is a relative directory. The parent
directory is the directory specified in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address()
element. |
Optional |
false |
stageDirIsRelative |
Indicates whether the directory specified in stageDirectory is an absolute directory
or a relative directory. If true, then the parent directory is
the directory specified in the fileDirectory() property for the file:address() element. |
Optional |
true |
|
File Name Patterns
File name patterns are used as a name filter for inbound message processing
and as a name generator for outbound message processing. The multiple processing
threads that make up the runtime File Binding Component fall into two types:
-
Inbound Processors: Message consumers that poll an input directory at a specified interval for a specific file name.
-
Outbound Processors: Message provisioners that write messages to an output directory by a specific file name.
Literal File Name
Input and output file names can be literal, or use a pattern.
-
Input: If the input file name is a literal, the inbound processor polls the input directory for a file by that name, and the content of the file is converted to a normalized message.
-
Output: If the output file name is a literal, the outbound processor writes the denormalized message to a file by that name.
Pattern File Name
In most cases, the file names specified for inbound or outbound processing are
patterns. File name pattern is a proprietary mechanism of the File Binding Component.
-
Inbound: When used by the inbound processor, the pattern serves as a filter. That is, if a file name matches the pattern, it is selected by the inbound processor and its content is read, normalized, and sent.
-
Outbound: When used by the outbound processor, the pattern serves as concrete name generator. That is, the special pattern symbols, such as %d(), %u(), %t(), and %{seq_name}(), that appear in the file name pattern specified as output file, will be expanded. The symbols are substituted with their current value and derive a concrete file name, to which the denormalized message is written.
When you set fileNameIsPattern() on a message property, you can specify patterns for generating
filenames for outbound messages or for reading filenames for inbound messages.
Application Variables in File Name Patterns
You can use application variables together with file name patterns to specify paths.
The following example shows how to use an application variable when specifying a
path name to a file that uses the %d pattern marker:
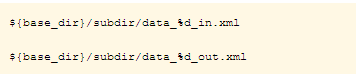
This example specifies a directory defined by the application variable base_dir. The application
variable is defined as a File Binding component runtime property. If base_dir is
defined as /duke/home, then this example reads or writes the following files: