| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS HL7 Binding Component User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS HL7 Binding Component User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Oracle HL7 Binding Component User's Guide
About the HL7 Binding Component
The Health Level 7 Messaging Standard
HL7 Binding Component as a Consumer
HL7 Binding Component Features
Using the HL7 Binding Component Wizard
Accessing the HL7 Binding Component Wizard
To Access the Wizard by Creating a New File
To Access the Wizard by Creating a New Binding
To Access the Wizard by Creating a New WSDL Document
Configuring the HL7 Binding Component in the Wizard
To Configure the HL7 Binding Component in the Wizard
MLLP Version 2 Properties (Outbound Only)
HL7 Binding WSDL Extensibility Elements
Adding HL7 Extensibility Attributes From the WSDL Editor
To add Service Level HL7 Extensibility Attributes
Service Level HL7 Extensibility Elements
HL7 protocolproperties Element
HL7 communicationcontrols Element
Binding Level HL7 Extensibility Elements
Dynamically Configuring HL7 Endpoints
Dynamic Addressing Using Normalized Message Properties
Enabling Dynamic Endpoint Configuration
Using Normalized Message Properties in a BPEL Process
Using Predefined Normalized Message Properties in a BPEL Process
To Use Predefined Normalized Message Properties in a BPEL Process
General Normalized Message Properties
HL7 Binding Component Normalized Message Properties for Outbound Endpoints
HL7 Binding Component Normalized Message Properties for Inbound Endpoints
HL7 Binding Component Runtime Properties
Configuring the HL7 Binding Component Runtime Properties
To Edit HL7 Binding Component Runtime Properties
Defining an HL7 Binding Component Application Configuration
To Define the HL7 Application Configuration
Defining the Application Configuration Using Other Tools
Using Application Variables to Define Name/Value Pairs
Using Application Variables for Password Protection
Creating a Password Application Variable
Using HL7 Quality of Service (QoS) Features
Quality of Service (QoS) Properties
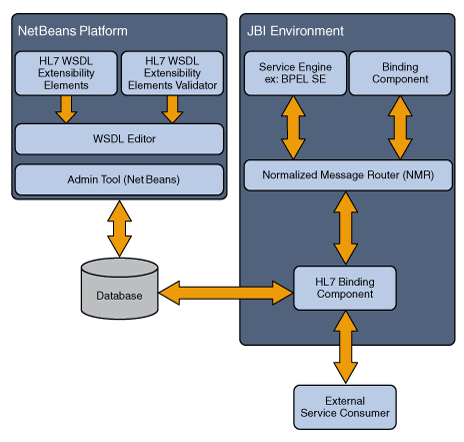
The HL7 Binding Component enables Java CAPS to establish and maintain connection with HL7 messaging systems, manage message enveloping and routing, perform message validations, and implement optional HL7 protocol sequence numbering. The following topics provide overview information for the HL7 messaging standard and the HL7 BC:
The HL7 Messaging Standard has been around for over 20 years, providing administrative, financial, and clinical messaging standards for the health care industry. This sharing of electronic health care information using the HL7 protocol allows hospitals to streamline all areas of patient care, communicating this information between numerous computer systems and applications from different departments and agencies. The problem is that these various systems and applications are not designed to communicate with each other. The HL7 Binding Component provides a solution by configuring and connecting the HL7 servers and clients within a JBI environment.
The HL7 Binding Component supports HL7 Version 2 Messaging Standard (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.3.1, 2.4, 2.5, 2.5.1, and 2.6). HL7 Version 3 can be implemented using other JBI components, such as the HTTP Binding Component using the SOAP protocol.
The HL7 Binding Component enables communication between HL7 servers and clients within a JBI environment. The binding component converts HL7 messages to XML messages within the JBI environment, and converts them back to HL7 messages. It provides both design-time and runtime functionality. The design-time portion uses a set of well-defined WSDL extensibility elements to configure HL7 service endpoints and message mapping. The runtime portion provides connectivity between the JBI framework and external HL7 clients and servers.
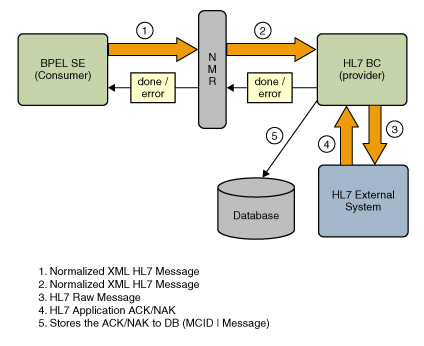
Inbound, in the role of consumer, the HL7 Binding Component (BC) acts as follows:
The HL7 BC receives the HL7 message from an external HL7 system.
The HL7 BC parses the received message. If parsing fails, the HL7 BC sends a NAK to the external HL7 sender.
If validate MSH is enabled, the HL7 BC validates the MSH segment fields for message acceptance. If validation fails, the HL7 BC sends a NAK to the external HL7 sender.
If sequence number is enabled, the HL7 BC validates the MSH-13–Sequence Number field in the received message against the persisted sequence in the database for the inbound endpoint. If the sequence number does not match, the HL7 BC sends a NAK to the external HL7 message sender.
If the HL7 message proves acceptable, the HL7 BC sends the normalized message to the BPEL Service Engine. An ACK or NAK is sent to the external HL7 message sender, based on the message exchange status received from the Normalized Message Router, as follows:
An ACK is sent when the message exchange status is Done.
A NAK is sent when the message exchange status is Error.
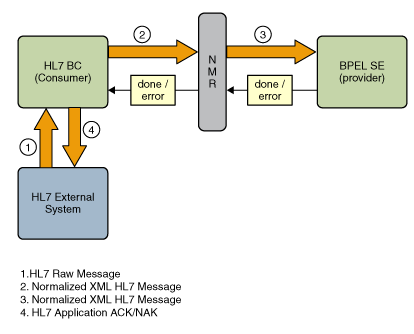
Outbound, in the role of provider, the HL7 Binding Component acts as follows:
The HL7 BC receives the HL7 message from the BPEL Service Engine.
If validate MSH is enabled, the HL7 BC validates the MSH segment fields, MSH-11–Processing ID and MSH-12–Version ID, against the configured Processing ID and Version ID. If validation fails, the HL7 BC sets the message exchange status to Error and sends the message back to the Normalized Message Router.
If sequence number is enabled, the HL7 BC inserts the sequence number in the message.
The HL7 BC converts the normalized message to the HL7 encoded form and sends it to the external HL7 system.
The HL7 BC receives the acknowledgement from the HL7 external system, and determines whether the acknowledgement is an ACK or NAK, and responds as follows:
An ACK is sent when the message exchange status is Done.
A NAK is sent when the message exchange status is Error.
If the HL7 message proves acceptable, the HL7 BC sends the normalized message to the BPEL Service Engine. An ACK or NAK is sent to the external HL7 message sender, based on the message exchange status received from the Normalized Message Router, as follows:
For an ACK, the HL7 BC sets the message exchange status to Done and sends it to the BPEL Service Engine. The ACK is also stored in a database.
For a NAK, the HL7 BC sets the message exchange status to Error and sends it to the BPEL Service Engine. The NAK is also stored in a database.
The HL7 protocol specifies that the system that receives an HL7 message will acknowledge the message by sending an acknowledgement to the message sender. HL7 protocol supports two types of message acknowledgement, Original Mode and Enhanced Mode.
Original Acknowledgement Mode: Original mode acknowledges message delivery to a receiving system by requiring an Application Acknowledgement. This is an acknowledgement from the system's application layer, sent after the application has successfully processed the message.
Application Acknowledgement: The receiving system sends an acknowledgement to the message sender, acknowledging that the application has successfully processed the message.
Enhanced Acknowledgement Mode:In case of Enhanced mode, the HL7 external system processes two acknowledgments, the Accept Acknowledgment and the Application Acknowledgment described above.
Accept Acknowledgement: The receiving system sends an acknowledgement to the message sender, acknowledging that the message has been committed to safe storage and that there is no need to resend the message. The binding component can also be set to check the payload (MSH.15) of incoming HL7 messages to see if an acknowledgment needs to be generated.
Valid Acknowledgment condition values for MSH-15 and MSH-16 files in an HL7 messages are:
ALWAYS_CONDITION (AL) – Always sends the ACK whether it is a success or not.
NEVER_CONDITION (NE) – The sender does not require an ACK, so the receiver should not send any ACKs back to the sender.
ERROR_CONDITION (ER) – If any errors occur during processing, the receiver sends an ACK; otherwise, the ACK is not sent.
SUCCESS_CONDITION – The receiver sends an ACK only for a success.
The HL7 protocol uses the sequence number protocol to avoid duplication of messages between sending and receiving systems. The HL7 Binding Component can either play the role of the service consumer (that is, the inbound service endpoint) or the service provider (that is, the outbound service endpoint). In both roles, it supports the sequence numbering protocol for HL7 message transactions.
The negotiation and incrementing of the sequence number is automatically performed by the binding component. The HL7 Binding Component receives the message with the sequence number from the external system, validates the message based on the excepted sequence number stored in the database, and sends a positive or negative acknowledgment with the expected sequence number back to the external system. Sequence numbering is enabled or disabled as an attribute of the HL7 protocolproperties WSDL element.