| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Monitoring Java EE Components in Oracle Java CAPS Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Monitoring Java EE Components in Oracle Java CAPS Java CAPS Documentation |
Starting the Enterprise Manager Server
To Start the Enterprise Manager Server
Logging In to Enterprise Manager
To Log In to Enterprise Manager
Adding an Application Server Domain to Enterprise Manager
To Add an Application Server Domain to Enterprise Manager
Adding an Application Server Instance to Enterprise Manager
To Perform Prerequisite Steps on the Application Server
To Add an Application Server Instance to Enterprise Manager
Using the Connectivity Map Controls
To Adjust the Position of the Connectivity Map
To Zoom In on the Connectivity Map
To Zoom Out from the Connectivity Map
To Specify an Exact Zoom Percentage
Monitoring Application Servers
Viewing Basic Information About an Application Server
To View Basic Information About an Application Server
Viewing Summary Information For an Application Server
To View Summary Information for an Application Server
Stopping Application Server Domains
To Stop an Application Server Domain
Hiding, Showing, and Removing Application Servers
To Make All of the Hidden Application Servers Reappear
To Remove an Application Server
Viewing Basic Information About a Collaboration
To View Basic Information About a Collaboration
Viewing Consumption Information For a Collaboration
To View Consumption Information For a Collaboration
Viewing Summary Information For a Collaboration
To View Summary Information For a Collaboration
Stopping and Restarting Collaborations
Displaying Information About an Adapter
To Display Information About an Adapter
Stopping and Starting Inbound Adapters
Viewing the Application Server Log File
To View the Application Server Log File
Viewing the Message Server Log File
To View the Message Server Log File
To Change the Status of an Alert
To Delete More Than One Alert at a Time
To Delete All Alerts For the Selected Component
To Configure the Alert Table Name (Databases Other Than Derby)
To Set Up Database Access (Databases Other Than Derby)
To Run the Database Scripts (Databases Other Than Derby)
To Log In to the Configuration Agent
To Modify the Alert Notification Fields
About Enterprise Manager Topic and Queue Management
Monitoring Topics and Queues for JMS IQ Manager
Sending and Publishing Messages for JMS IQ Manager
Viewing Message Properties for JMS IQ Manager
Viewing and Editing Message Payload for JMS IQ Manager
Monitoring Java System Message Queue
Monitoring Topics and Queues for Java System Message Queue
Sending and Publishing Messages for Java System Message Queue
Viewing Message Properties for Java System Message Queue
Viewing and Editing Message Payload for Java System Message Queue
Monitoring Oracle Advanced Queueing
Monitoring Topics and Queues for Oracle Advanced Queueing
Sending and Publishing Messages for Advanced Queueing
Viewing Message Payload for Advanced Queueing
To View the Payload of Text and Byte Messages
Monitoring WebLogic Server JMS
Monitoring Topics and Queues for WebLogic Server JMS
Sending and Publishing Messages for WebLogic Server JMS
Viewing Message Properties for WebLogic Server JMS
Viewing Message Payload for WebLogic Server
To View the Payload of Text and Byte Messages
Monitoring Java Message Service Grid
Monitoring Application Servers, Collaborations, and Alerts (Command Line)
Enterprise Manager Command-Line Client Syntax
Monitoring Application Servers and Collaborations (Command Line)
Listing the Available Methods For the Runtime Service
Displaying the List of Components
Starting and Stopping Collaborations
Monitoring Alerts (Command Line)
Enterprise Manager is a web-based interface with which you can manage running Java CAPS applications for both the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE platform) and the Schema Runtime Environment (SRE). For information about supported browsers for accessing Enterprise Manager, see Java CAPS 6.3 System Requirements in Planning for Oracle Java CAPS 6.3 Installation .
Enterprise Manager contains an Explorer panel on the left and a Details panel on the right. Java EE platform applications and SRE applications appear in different branches of the Explorer panel.
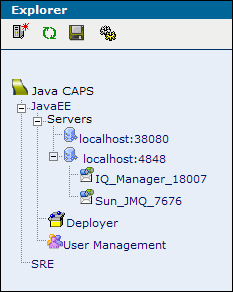
Enterprise Manager also includes a command-line client.
Before users can log in to Enterprise Manager, you must start the server component.
INFO: Server startup in 130006 ms
On UNIX platforms, this message appears in the catalina.out file in the JavaCAPS-install-dir/emanager/server/logs directory. On Windows platforms, this message appears in the command-line window.
Users log in to Enterprise Manager from a browser. For detailed information about Enterprise Manager user names and passwords, see Managing Java CAPS Users.
This procedure assumes that the Enterprise Manager server has been started.
http://hostname:portnumber/
Set the hostname to the TCP/IP host name or IP address of the server where Enterprise Manager is installed. Set the port number to the port number that was specified during the installation of Enterprise Manager. For example:
http://myserver.company.com:15000/
The Enterprise Manager Security Gateway screen appears.
In order to manage a GlassFish Application Server domain in Enterprise Manager, you must first add the domain.
The Manage Servers tab appears.
|
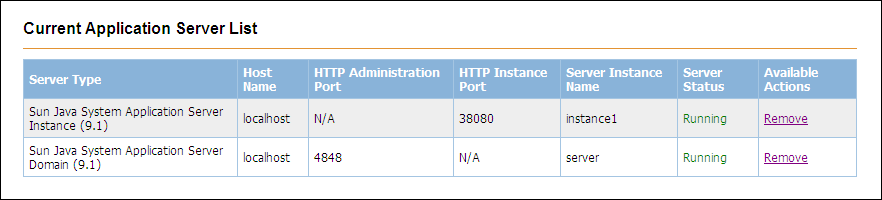
The application server domain is added to the Current Application Server List table.
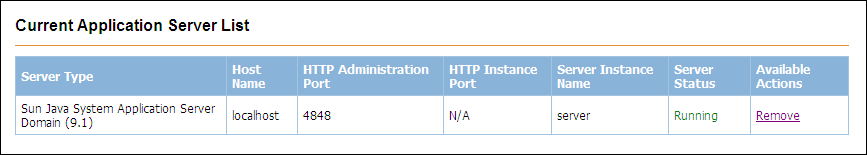
In order to manage a GlassFish Application Server instance in Enterprise Manager, you must first add the instance. Managing instances is more limited than managing domains.
You cannot deploy, undeploy, enable, or disable projects for an instance.
The message server nodes (for example, IQ_Manager_18007 and Sun_JMQ_7676) do not appear in the Explorer panel of Enterprise Manager.
The instance can receive alerts only if the corresponding domain has been added to Enterprise Manager.
When you add the instance to Enterprise Manager, authentication is not performed.
Before You Begin
In this procedure, you manage targets for the SeeBeyondSunOneDeployer web application and the logging connector module. These components are part of the Java CAPS runtime. The default application server domain includes the runtime. Any additional domains that you create do not include the runtime. Follow the steps inInstalling Oracle Java CAPS Domains and Runtime Components to manually install the runtime on any additional domains.
The URL is http://hostname:port. The default port number is 4848.
The Manage Servers tab appears.
|
The application server instance is added to the Current Application Server List table.
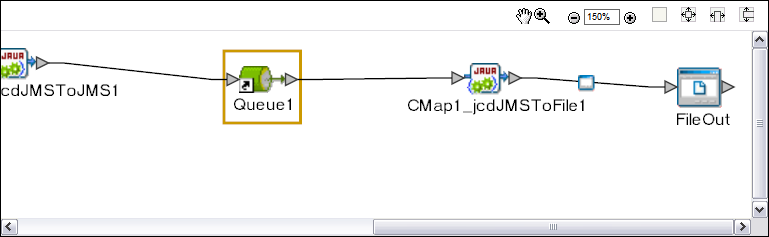
When you select a Connectivity Map node in the Explorer panel of Enterprise Manager, the actual Connectivity Map appears in the Details panel.
You can adjust the position of the Connectivity Map, and you can zoom in and out. In order to perform these tasks, you must enable the Zoom and Pan icon. The Zoom and Pan appears on the left of the toolbar. By default, the icon is disabled. To enable the icon, click the icon.
If you are using Internet Explorer, then you must install the SVG Viewer in order for the zoom functionality to work correctly. Follow the steps in the Java CAPS installation documentation to upload the Enterprise_Manager_SVGPlugin-win32.sar file to the Repository. Then download the executable file to the computer where the browser is located. Run the executable file to install the SVG Viewer.
The 100%, Fit All, Fit Width, and Fit Height icons provide the following functionality:
The Fit All icon sets the width and height of the Connectivity Map to the width and height of the upper Details panel.
The Fit Width icon sets the width of the Connectivity Map to the width of the upper Details panel.
The Fit Height icon sets the height of the Connectivity Map to the height of the upper Details panel.
Your cursor becomes a hand symbol.
You use a script to stop the server component of Enterprise Manager.