3 Using the Connector
This chapter is divided into the following sections:
Note:
These sections provide both conceptual and procedural information about configuring the connector. It is recommended that you read the conceptual information before you perform the procedures.
3.1 Scheduled Jobs for Lookup Field Synchronization
Lookup field synchronization involves copying additions or changes made to the target system lookup fields into the lookup definitions in Oracle Identity Manager.
The following scheduled jobs are used for lookup field synchronization:
-
SAP UM CommType Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Company Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM ContractUserType Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM DateFormat Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM DecimalNot Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM LangComm Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Parameter Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Profile Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Role Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Systems Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM TimeZone Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM Title Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM UserGroup Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP UM UserType Lookup Reconciliation
Note:
Before running a scheduled job for lookup field synchronization, you must copy all the third-party libraries to the following directory:
OIM_HOME/xellerate/ConnectorDefaultDirectory/targetsystems-lib/sap-11.1.1.5.0
You can specify values for the attributes of these scheduled jobs. Table 3-1 describes the attributes of these scheduled jobs. Configuring Scheduled Jobs describes the procedure to configure scheduled jobs.
Table 3-1 Attributes of the Scheduled Jobs for Lookup Field Synchronization
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Code Key Attribute |
Name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Code Key column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
Note: You must not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Decode Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Decode column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Filter |
Enter a filter to filter out records to be stored in the lookup definition. For more information about the Filter attribute, see Limited Reconciliation. |
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile records. Default value: |
|
Lookup Name |
Enter the name of the lookup definition in Oracle Identity Manager that must be populated with values fetched from the target system. Note: If the lookup name that you specify as the value of this attribute is not present in Oracle Identity Manager, then this lookup definition is created while the scheduled job is run. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Class |
Enter the name of the class of the object you want to reconcile. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Type |
Enter the name of the type of object you want to reconcile. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
3.2 Scheduled Jobs for SAP BusinessObjects AC Lookup Field Synchronization
Lookup field synchronization involves copying additions or changes made to the target system lookup fields into the lookup definitions in Oracle Identity Manager.
The following scheduled jobs are used for SAP BusinessObjects AC lookup field synchronization:
-
SAP AC UM BusinessProcess Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM CommType Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Company Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM ContractUserType Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM DateFormat Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM DecimalNot Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC FunctionalArea Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM ItemProvAction Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM LangComm Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Parameter Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Priority Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Profile Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM ReqInitSystem Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM RequestType Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Role Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Systems Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM TimeZone Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM Title Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM User Delete Recon
-
SAP AC UM UserGroup Lookup Reconciliation
-
SAP AC UM User Recon
-
SAP AC UM UserType Lookup Reconciliation
You can specify values for the attributes of these scheduled jobs. Table 3-2 describes the attributes of these scheduled jobs. Configuring Scheduled Jobs describes the procedure to configure scheduled jobs.
Table 3-2 Attributes of the Scheduled Jobs for SAP BusinessObjects AC Lookup Field Synchronization
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Code Key Attribute |
Name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Code Key column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
Note: You must not change the value of this attribute. |
|
Decode Attribute |
Enter the name of the connector or target system attribute that is used to populate the Decode column of the lookup definition (specified as the value of the Lookup Name attribute). Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource for the target system installation from which you want to reconcile records. Default value: |
|
Lookup Name |
Enter the name of the lookup definition in Oracle Identity Manager that must be populated with values fetched from the target system. Note: If the lookup name that you specify as the value of this attribute is not present in Oracle Identity Manager, then this lookup definition is created while the scheduled job is run. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Class |
Enter the name of the class of the object you want to reconcile. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
|
Object Type |
Enter the name of the type of object you want to reconcile. Depending on the scheduled job you are using, the default values are as follows:
|
3.3 Guidelines on Performing Reconciliation
These are the guidelines that you must apply while performing reconciliation operations.
Apply the following guidelines while configuring reconciliation:
-
On SAP CUA, an account that is directly created on the target system must be assigned a master system before changes to that account can be detected and brought to Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation.
-
On a Microsoft Windows platform, if you encounter the org.quartz.SchedulerException exception during a reconciliation run, then download and install the Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package from the Microsoft Web site.
3.4 Configuring Reconciliation
You can configure the connector to specify the type of reconciliation and its schedule.
As mentioned earlier in this guide, reconciliation involves duplicating in Oracle Identity Manager the creation of and modifications to user accounts on the target system.
This section discusses the following topics related to configuring reconciliation:
3.4.1 Full Reconciliation and Incremental Reconciliation
Full reconciliation involves reconciling all existing user records from the target system into Oracle Identity Manager. After you deploy the connector, you must first perform full reconciliation. In addition, you can switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation whenever you want to ensure that all target system records are reconciled in Oracle Identity Manager.
To perform a full reconciliation run, ensure that no value is specified for the Filter attribute. However, to reconcile user records, set the value for the Latest token attribute as 0 (Zero) in the scheduled job:
At the end of the reconciliation run, the Latest Token attribute of the scheduled job for user record reconciliation is automatically set to the time stamp at which the run ended. From the next run onward, only records created or modified after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. This is incremental reconciliation.
3.4.2 Batched Reconciliation
This section discusses the batchSize attribute of the Lookup.SAPABAP.Configuration lookup definition.
By default, all target system records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are reconciled during the current reconciliation run. Depending on the number of records to be reconciled, this process may require a large amount of time. In addition, if the connection breaks during reconciliation, then the process would take longer to complete.
You can configure batched reconciliation to avoid such problems.
To configure batched reconciliation, specify a value for the following attribute while performing the procedure described in Setting Up the Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager:
batchSize: Use this attribute to specify the number of records that must be included in each batch.
After you configure batched reconciliation, if reconciliation fails during a batched reconciliation run, then you only need to rerun the scheduled task without changing the values of the task attributes.
3.4.3 Limited Reconciliation
By default, all target system records that are added or modified after the last reconciliation run are reconciled during the current reconciliation run. You can customize this process by specifying the subset of added or modified target system records that must be reconciled. You do this by creating filters for the reconciliation module.
The connector provides a Filter attribute that allows you to use any of the resource attributes to filter the target system records.
The syntax for this parameter is as follows:
Note:
You can use a shortcut for the <and> and <or> operators. For example: <filter1> & <filter2> instead of and (<filter1>, <filter2>), analogically replace or with |.
syntax = expression ( operator expression )*
operator = 'and' | 'or'
expression = ( 'not' )? filter
filter = ('equalTo' | 'contains' | 'containsAllValues' | 'startsWith'
| 'endsWith' | 'greaterThan' | 'greaterThanOrEqualTo' | 'lessThan'
| 'lessThanOrEqualTo' ) '(' 'attributeName' ',' attributeValue ')'
attributeValue = singleValue | multipleValues
singleValue = 'value'
multipleValues = '[' 'value_1' (',' 'value_n')* ']'
For example, to limit the number of reconciled accounts to only matching account names, you could use the following expression:
equalTo('FirstName;ADDRESS','AP10A1')
While deploying the connector, follow the instructions in Configuring Scheduled Jobs to specify attribute values.
3.4.4 Reconciliation Scheduled Jobs for the SAP UM Connector
You can use reconciliation scheduled job to reconcile user account data from the target system.
You must specify values for the attributes of the following scheduled tasks:
3.4.4.1 SAP UM User Recon
You use the SAP UM User Recon scheduled job to reconcile user data from the target system. Table 3-3 describes the attributes of this scheduled job.
Table 3-3 Attributes of the SAP UM User Recon Scheduled Job
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Filter |
Expression for filtering records. Use the following syntax: syntax = expression ( operator expression )*
operator = 'and' | 'or'
expression = ( 'not' )? filter
filter = ('equalTo' | 'contains' | 'containsAllValues'
| 'startsWith' | 'endsWith' | 'greaterThan' | 'greaterThanOrEqualTo'
| 'lessThan' | 'lessThanOrEqualTo' ) '(' 'attributeName' ',' attributeValue')'
attributeValue = singleValue | multipleValues
singleValue = 'value'
multipleValues = '[' 'value_1' (',' 'value_n')* ']'
Default value: None See Limited Reconciliation for more information. |
|
Incremental Recon Attribute |
Time stamp at which the last reconciliation run started Default value: Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value for this attribute. |
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource instance that the connector must use to reconcile data Sample value: |
|
Latest Token |
This attribute holds the time stamp (in the YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format) at which the last reconciliation run ended. For the next reconciliation run, only target system records that have been added or modified after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. For consecutive reconciliation runs, the connector automatically enters a value for this attribute. However, you can use this attribute to switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation. See Full Reconciliation and Incremental Reconciliation for more information. Note: The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value in this attribute. Sample value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object against which reconciliation runs must be performed Default value: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Default value: |
3.4.4.2 SAP UM User Delete Recon
You use the SAP UM User Delete Recon scheduled job to reconcile data about deleted users from the target system. Table 3-4 describes the attributes of this scheduled job.
Table 3-4 Attributes of the SAP UM User Delete Recon Scheduled Job
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Disable User |
Enter Default value: |
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource instance that the connector must use to reconcile data Sample value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object against which reconciliation runs must be performed Default value: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Default value: |
|
Sync Token |
Time stamp at which the last reconciliation run ended in YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format (for example, 20120417123006). For the next reconciliation run, only target system records that have been deleted after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. If you set this attribute to an empty value, then incremental reconciliation operations fetch all the records (perform full reconciliation). Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value in this attribute. |
3.4.4.3 SAP AC UM User Recon
You use the SAP AC UM User Recon scheduled job to reconcile users from SAP BusinessObjects AC target system. Table 3-5 describes the attributes of this scheduled job.
Table 3-5 Attributes of the SAP AC UM User Recon Scheduled Job
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Filter |
Expression for filtering records. Use the following syntax: syntax = expression ( operator expression )*
operator = 'and' | 'or'
expression = ( 'not' )? filter
filter = ('equalTo' | 'contains' | 'containsAllValues'
| 'startsWith' | 'endsWith' | 'greaterThan' | 'greaterThanOrEqualTo'
| 'lessThan' | 'lessThanOrEqualTo' ) '(' 'attributeName' ',' attributeValue')'
attributeValue = singleValue | multipleValues
singleValue = 'value'
multipleValues = '[' 'value_1' (',' 'value_n')* ']'
Default value: None See Limited Reconciliation for more information. |
|
Incremental Recon Attribute |
Time stamp at which the last reconciliation run started Default value: Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value for this attribute. |
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource instance that the connector must use to reconcile data Sample value: |
|
Latest Token |
This attribute holds the time stamp (in the YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format) at which the last reconciliation run ended. For the next reconciliation run, only target system records that have been added or modified after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. For consecutive reconciliation runs, the connector automatically enters a value for this attribute. However, you can use this attribute to switch from incremental reconciliation to full reconciliation. See Full Reconciliation and Incremental Reconciliation for more information. Note: The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value in this attribute. Sample value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object against which reconciliation runs must be performed Default value: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Default value: |
3.4.4.4 SAP AC UM User Delete Recon
You use the SAP AC UM User Delete Recon scheduled job to reconcile deleted users from SAP BusinessObjects AC target system. Table 3-6 describes the attributes of this scheduled job.
Table 3-6 Attributes of the SAP AC UM User Delete Recon Scheduled Job
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource instance that the connector must use to reconcile data Default value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object against which reconciliation runs must be performed Default value: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Default value: |
|
Sync Token |
Time stamp at which the last reconciliation run ended in YYYYMMDDHHMMSS format (for example, 20120417123006). For the next reconciliation run, only targets ystem records that have been deleted after this time stamp are considered for reconciliation. If you set this attribute to an empty value, then incremental reconciliation operations fetch all the records (perform full reconciliation). Note: Do not enter a value for this attribute. The reconciliation engine automatically enters a value in this attribute. Default value: |
|
Disable User |
Enter Default value: |
3.4.4.5 SAP AC UM Request Status
You use the SAP AC UM Request Status scheduled job to reconcile request status from SAP BusinessObjects AC target system. Table 3-7 describes the attributes of this scheduled job.
Table 3-7 Attributes of the SAP AC UM Request Status Scheduled Job
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
IT Resource Name |
Name of the IT resource instance that the connector must use to reconcile data Default value: |
|
Object Type |
Type of object you want to reconcile Default value: |
|
Resource Object Name |
Name of the resource object against which reconciliation runs must be performed Default value: |
|
Scheduled Task Name |
Name of the scheduled task Default value: |
3.5 Configuring Scheduled Jobs
This section describes the procedure to configure scheduled jobs. You can apply this procedure to configure the scheduled jobs for lookup field synchronization and reconciliation.
See Scheduled Jobs for Lookup Field Synchronization, Scheduled Jobs for SAP BusinessObjects AC Lookup Field Synchronization, and Reconciliation Scheduled Jobs for the SAP UM Connector for information about scheduled jobs and their attributes.
To configure a scheduled job:
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x, then you must perform the following steps:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
On the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Self Service page, click Advanced in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x, then you must perform the following steps:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
In the left pane, under System Management, click Scheduler.
-
-
Search for and open the scheduled job as follows:
-
On the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Advanced Administration page, in the System Management region, click Search Scheduled Jobs.
-
On the left pane, in the Search field, enter the name of the scheduled job as the search criterion. Alternatively, you can click Advanced Search and specify the search criterion.
-
In the search results table on the left pane, click the scheduled job in the Job Name column.
-
-
On the Job Details tab, you can modify the parameters of the scheduled job:
-
Retries: Enter an integer value in this field. This number represents the number of times the scheduler tries to start the job before assigning the Stopped status to the job.
-
Schedule Type: Depending on the frequency at which you want the job to run, select the appropriate schedule type.
Note:
See Creating Jobs in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about schedule types.
In addition to modifying the job details, you can enable or disable a job.
-
-
On the Job Details tab, in the Parameters region, specify values for the attributes of the scheduled task.
-
Click Apply to save the changes.
Note:
You can use the Scheduler Status page in Identity System Administration to either start, stop, or reinitialize the scheduler.
3.6 Guidelines on Performing Provisioning
3.6.1 Guidelines on Performing Provisioning in Supported Deployment Configuration
These are the guidelines that you must apply while performing provisioning operations in any of the supported deployment configurations.
-
Through provisioning, if you want to create and disable an account at the same time, then you can set the value of the Valid Through attribute to a date in the past. For example, while creating an account on 31-Jul, you can set the Valid Through date to 30-Jul. With this value, the resource provisioned to the OIM User is in the Disabled state immediately after the account is created.
However, on the target system, if you set the Valid Through attribute to a date in the past while creating an account, then the target system automatically sets Valid Through to the current date. The outcome of this Create User provisioning operation is as follows:
-
The value of the Valid Through attribute on Oracle Identity Governance and the target system do not match.
-
On the target system, the user can log in all through the current day. The user cannot log in from the next day onward.
You can lock the user on the target system so that the user is not able to log in the day the account is created.
-
-
Remember that if password or system assignment fails during a Create User provisioning operation, then the user is not created.
-
When you try to provision a multivalued attribute, such as a role or profile, if the attribute has already been set for the user on the target system, then the status of the process task is set to Completed in Oracle Identity Governance. If required, you can configure the task so that it shows the status Rejected in this situation. See Modifying Process Tasks in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Governance for information about configuring process tasks.
-
When you perform the Lock User or Unlock User provisioning operation, remember that the connector makes the required change on the target system without checking whether the account is currently in the Locked or Unlocked state. This is because the target system does not provide a method to check the current state of the account.
-
The target system does not accept non-English letters in the E-mail Address field. Therefore, during provisioning operations, you must enter only English language letters in the E-mail Address field on the process form.
-
On a Microsoft Windows platform, if you encounter the java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError exception during a provisioning operation, then download and install the Microsoft Visual C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package from the Microsoft Web site.
3.6.2 Guidelines on Performing Provisioning After Configuring Access Request Management
These are the guidelines that you must apply while performing provisioning operations after configuring the Access Request Management feature of the connector.
-
During a Create User operation performed when the Access Request Management is configured, first submit process form data. Submit child form data after the user is created on the target system. This is because when Access Request Management is enabled, the connector supports modification of either process form fields or child form fields in a single Modify User operation.
-
The following fields on the process form are mandatory parameters on SAP GRC Access Request Management:
Note:
When the Access Request Management feature is configured, you must enter values for these fields even though some of them are not marked as mandatory fields on Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
AC Manager
-
AC Manager email
-
AC Priority
-
AC System
-
AC Requestor ID
-
AC Requestor email
-
AC Request Reason
The following fields may be mandatory or optional based on the configuration in SAP GRC system:
-
AC Manager First Name
-
AC Manager Last Name
-
AC Manager Telephone
-
AC Request Due Date
-
AC Functional Area
-
AC Business Process
-
AC Requestor First Name
-
AC Requestor Last Name
-
AC Requestor Telephone
-
AC Company
-
-
As mentioned earlier in this guide, SAP GRC Access Request Management does not process passwords. Therefore, any value entered in the Password field is ignored during Create User provisioning operations. After a Create User operation is performed, the user for whom the account is created on the target system must apply one of the following approaches to set the password:
-
To use the Oracle Identity Governance password as the target system password, change the password through Oracle Identity Governance.
-
Directly log in to the target system, and change the password.
-
-
You perform an Enable User operation by setting the Valid From field to a future date. Similarly, you perform a Disable User operation by setting the Valid Through field to the current date. Both operations are treated as Modify User operations.
-
When you delete a user (account) on Oracle Identity System Administration (process form), a Delete User request is created.
-
When you select the Lock User check box on the process from, a Lock User request is created.
-
When you deselect the Lock User check box on the process from, an Unlock User request is created.
-
The Enable User and Disable User operations are implemented through the Valid From and Valid Through fields on the process form.
-
In a Modify User operation, you can specify values for parameters that are mapped with SAP GRC Access Request Management and parameters that are directly updated on the target system. A request is created SAP GRC Access Request Management only for parameters whose mappings are present in these lookup definitions. If you specify values for parameters that are not present in these lookup definitions, then the connector sends them to directly the target system.
-
You cannot perform an assign or revoke groups operation in SAP UM AC account on GRC server. Groups must be managed in the SAP ECC system (backend ABAP system).
3.7 Performing Provisioning Operations in Oracle Identity Manager Release 11.1.2
You create a new user in Oracle Identity Self Service by using the Create User page. You provision or request for accounts on the Accounts tab of the User Details page.
To configure provisioning operations in Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x:
Note:
The time required to complete a provisioning operation that you perform the first time by using this connector takes longer than usual.
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
Create and activate a sandbox. For detailed instructions on creating and activating a sandbox, see Managing Sandboxes in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Create an application instance and specify values for the following fields in the Create Application Instance page. See Creating Application Instances in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Name: The name of the application instance.
-
Display Name: The display name of the application instance.
-
Description: A description of the application instance.
-
Resource Object: The resource object name. Click the search icon next to this field to search for and select SAP UM Resource Object.
-
IT Resource Instance: The IT resource instance name. Click the search icon next to this field to search for and select SAP UM IT Resource.
-
Form: Select the form name, for example, SAPUM. To do so, click Create. against the Form list, specify the form name, and then create it. On the Create Application Instance page, click the Refresh icon next to the Form field. From this list, select the form name that you created.
-
-
Publish the sandbox.
-
Run lookup field synchronization.
-
Search for and run the Entitlement List scheduled job to populate the ENT_LIST table.
-
Publish the application instance (created in Step 3) to an organization. To do so:
-
On the Organizations tab of the Application Instance page, click Assign.
-
In the Select Organizations dialog box, select the organization to which you want to publish the application instance.
-
Select the Apply to entitlements checkbox.
-
Click OK.
-
-
Search for and run the Catalog Synchronization Job scheduled job.
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
Create a user. See Managing Users in Oracle Fusion Middleware Performing Self Service Tasks with Oracle Identity Manager for more information about creating a user.
-
On the Account tab, click Request Accounts.
-
In the Catalog page, search for and add to cart the application instance created in Step 3, and then click Checkout.
-
Specify value for fields in the application form and then click Ready to Submit.
-
Click Submit.
-
If you want to provision entitlements, then:
-
On the Entitlements tab, click Request Entitlements.
-
In the Catalog page, search for and add to cart the entitlement, and then click Checkout.
-
Click Submit.
-
3.8 Performing Provisioning Operations in an SoD-Enabled Environment
Provisioning a resource for an OIM User involves using Oracle Identity Manager to create a target system account for the user.
The following are types of provisioning operations:
-
Direct provisioning
-
Request-based provisioning of accounts
-
Request-based provisioning of entitlements
-
Provisioning triggered by policy changes
This section discusses the following topics:
3.8.1 Overview of the Provisioning Process in an SoD-Enabled Environment
The following is the sequence of steps that take places during a provisioning operation performed in an SoD-enabled environment:
-
The provisioning operation triggers the appropriate adapter.
-
SAP BusinessObjects SoD Invocation Library (SIL) Provider passes the entitlement data to the Web service of SAP BusinessObjects AC.
-
After SAP BusinessObjects AC runs the SoD validation process on the entitlement data, the response from the process is returned to Oracle Identity Manager.
-
The status of the process task that received the response depends on the response itself. If the entitlement data clears the SoD validation process, then the adapter carries provisioning data to the corresponding BAPI on the target system and the status of the process task changes to Completed. This translates into the entitlement being granted to the user. If the SoD validation process returns the failure response, then status of the process task changes to Canceled.
3.8.2 Guidelines on Performing Provisioning Operations in an SoD-Enabled Environment
These are the guidelines that you must apply while performing provisioning operations in an SoD-enabled environment.
-
When you assign a role to a user through provisioning, you set values for the following attributes:
-
Role System Name
-
Role Name
-
Start Date
-
End Date
However, when you update a role assignment, you can specify values only for the Start Date and End Date attributes. You cannot set new values for the Role System Name and Role Name attributes. This also applies to new child forms that you add.
-
-
You can only assign profiles. You cannot update an assigned profile.
3.8.3 Direct Provisioning in an SoD-Enabled Environment
This section describes the prerequisites and the procedure to perform direct provisioning. It contains the following sections:
3.8.3.1 Enabling the Use of the Process Form During Direct Provisioning in an SoD-Enable Environment
Note:
Perform the procedure in this section only in the following situations:
-
The first time you perform direct provisioning.
-
If you switch from request-based provisioning to direct provisioning.
When you run the Connector Installer, the configuration for direct provisioning of SAP user accounts is installed. Although the process form is displayed during direct provisioning, the connector cannot complete direct provisioning operations unless you enable the use of the process form. If you want to enable the use of the process form during direct provisioning, then perform the procedure described later in this section.
To enable the use of the process form during direct provisioning:
Note:
Request-based provisioning is disabled after you perform this procedure.
-
Log in to the Design Console.
-
Disable the Auto Save Form feature as follows:
-
Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Process Form process definition.
-
Deselect the Auto Save Form check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
-
If the Self Request Allowed feature is enabled, then:
-
Expand Resource Management, and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Resource Object resource object.
-
Deselect the Self Request Allowed check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
3.8.3.2 Performing Direct Provisioning
To provision a resource by using the direct provisioning approach:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
If you want to first create an OIM User and then provision a target system account, then:
-
On the Welcome to Identity Administration page, in the Users region, click Create User.
-
On the Create User page, enter values for the OIM User fields, and then click Save.
-
-
If you want to provision a target system account to an existing OIM User, then:
-
On the Welcome to Identity Administration page, search for the OIM User by selecting Users from the drop-down list on the left pane.
-
From the list of users displayed in the search results, select the OIM User. The user details page is displayed on the right pane.
-
-
On the user details page, click the Resources tab.
-
From the Action menu, select Add Resource. Alternatively, you can click the add resource icon with the plus (+) sign. The Provision Resource to User page is displayed in a new window.
-
On the Step 1: Select a Resource page, select SAP UM Resource Object from the list and then click Continue.
-
On the Step 2: Verify Resource Selection page, click Continue.
-
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for process data, enter the details of the account that you want to create on the target system and then click Continue.
-
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for profile data, search for and select profiles for the user on the target system and then click Continue.
-
On the Step 5: Provide Process Data page for role data, search for and select roles for the user on the target system and then click Continue.
-
On the Step 6: Verify Process Data page, verify the data that you have provided and then click Continue.
-
The "Provisioning has been initiated" message is displayed. Close the window displaying this message.
-
On the Resource tab of the user details page, click Refresh to view the newly provisioned resource.
-
To view the Resource Provisioning Details page, which shows the details of the process tasks that were run:
On the Resources tab of the user details page, from the Action menu, select Resource History.
-
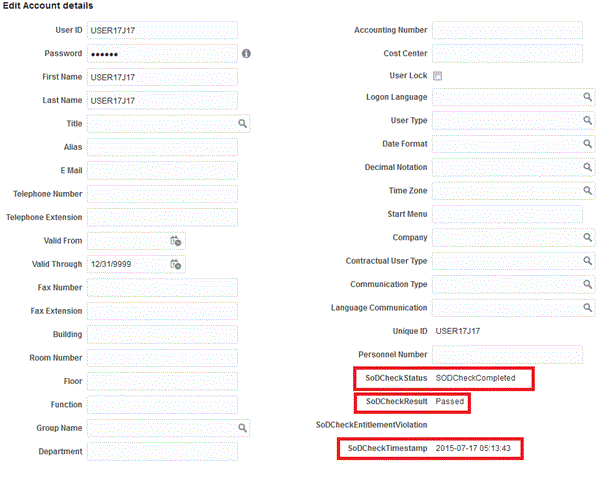
The SOD Check Status field is updated with SOD Check Completed status.
-
As the administrator assigning a resource to a user, you can either end the process when a violation is detected or modify the assignment data and then resend it. To modify the assignment data, on the Resource tab of the user details page, select the row containing the resource, and then click Open.
-
In the Edit Form window that is displayed, you can modify the role and profile data that you had selected earlier.
Note:
To modify a set of entitlements In the Edit Form window, you must first remove all entitlements and then add the ones that you want to use.
In the following screenshot, one of the roles selected earlier is marked for removal:
-
After invoking the risk analysis web service, the results of the SoD validation process are brought to Oracle Identity Manager. If you open the process form, the results will be displayed as shown in the screenshot in Step 17.
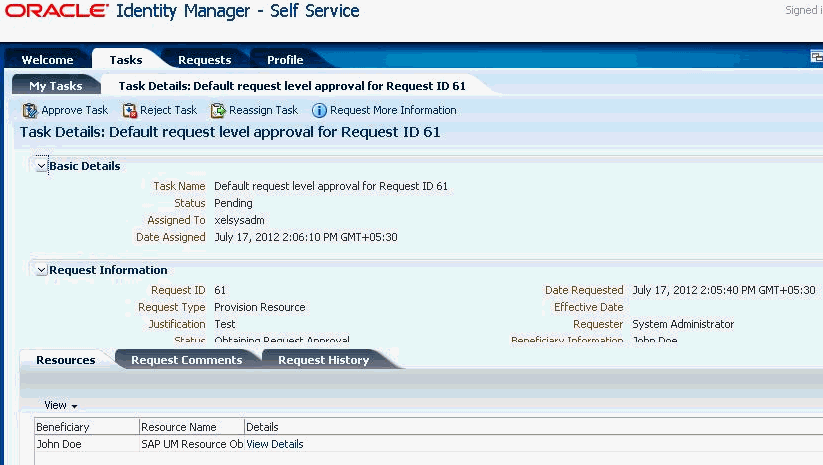
3.8.4 Request-Based Provisioning in an SoD-Enabled Environment
In request-based provisioning, an end user creates a request for a resource by using the Administrative and User Console. Administrators or other users can also create requests for a particular user. Requests for a particular resource on the resource can be viewed and approved by approvers designated in Oracle Identity Manager.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x.
See Configuring SoD (Segregation of Duties) for related information.
The request-based provisioning operation involves both end users and approvers. Typically, these approvers are in the management chain of the requesters. The request-based provisioning process described in this section covers steps to be performed by both entities.
In the example used in this section, the end user creates a request for two roles on the target system. The request clears the SoD validation process and is approved by the approver.
The following sections provide more information about request-based provisioning:
3.8.4.1 Creation of Request-Based Provisioning by End-Users
The following are types of request-based provisioning:
-
Request-based provisioning of accounts: OIM Users are created but not provisioned target system resources when they are created. Instead, the users themselves raise requests for provisioning accounts.
-
Request-based provisioning of entitlements: OIM Users who have been provisioned target system resources (either through direct or request-based provisioning) raise requests for provisioning entitlements.
The following steps are performed by the end user in a request-based provisioning operation:
3.8.4.2 Approving Request-Based Provisioning
This section discusses the role of the approver in a request-based provisioning operation.
The approver to whom the request is assigned can use the Pending Approvals feature to view details of the request.
In addition, the approver can click the View link to view details of the SoD validation process.
The approver can decide whether to approve or deny the request, regardless of whether the SoD engine accepted or rejected the request. The approver can also modify entitlements in the request.
The following steps are performed by the approver in a request-based provisioning operation:
3.9 Switching Between SAP ERP and SAP CUA Target Systems
You can switch your target systems between SAP ERP and SAP CUA for reconciliation and provisioning.
The following sections provide information about the procedure to switch between the SAP ERP and SAP CUA target systems:
3.9.1 Switching Between the SAP R/3 and SAP CUA Target Systems for Reconciliation
To switch between SAP R/3 and SAP CUA target systems for reconciliation:
3.10 Switching From an SAP R/3 or SAP CUA Target Systems to an SAP BusinessObjects AC Target System and Vice Versa
You can switch from an SAP R/3 or SAP CUA target system to an SAP BusinessObjects AC target system and viceversa.
If you want to switch from an SAP R/3 or SAP CUA target system to a SAP BusinessObjects AC target system and vice versa, then perform the following steps:
3.11 Switching Between Request-Based Provisioning and Direct Provisioning
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1. It is assumed that you have performed the procedure described in Enabling Request-Based Provisioning.
The following sections discuss the steps to be performed to switch between request-based provsioning and direct provisioning:
3.11.1 Switching from Request-Based Provisioning to Direct Provisioning
To switch from request-based provisioning to direct provisioning, do the following:
-
Log in to the Design Console.
-
Disable the Auto Save Form feature as follows:
-
Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Process Form process definition.
-
Deselect the Auto Save Form check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
-
If the Self Request Allowed feature is enabled, then:
-
Expand Resource Management, and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Resource Object resource object.
-
Deselect the Self Request Allowed check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
3.11.2 Switching from Direct Provisioning to Request-Based Provisioning
To switch from direct provisioning to request-based provisioning, do the following:
-
Log in to the Design Console.
-
Enable the Auto Save Form feature as follows:
-
Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Process Form process definition.
-
Select the Auto Save Form check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
-
If you want to enable end users to raise requests for themselves, then:
-
Expand Resource Management, and then double-click Resource Objects.
-
Search for and open the SAP UM Resource Object resource object.
-
Select the Self Request Allowed check box.
-
Click the Save icon.
-