4 Extending the Functionality of the Connector
This chapter discusses the following optional procedures:
Note:
From Oracle Identity Manager Release 11.1.2 onward, lookup queries are not supported. See Managing Lookups in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager guide for information about managing lookups by using the Form Designer in Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
Adding New Standard SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes for Provisioning
-
Removing SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes from Process Form
-
Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation and Provisioning
-
Configuring Transformation of Data During User Reconciliation
-
About Configuring the Connector for Multiple Installations of the Target System
4.1 Determining the Names of Target System Attributes
You can determine the name of a target system attribute that you want to add for reconciliation or provisioning on the SAP system.
The target system attributes can be single-valued or multivalued. The names that you determine are used to build values for the Decode column of the lookup definitions that hold attribute mappings. These lookup definitions and their corresponding Decode column formats are listed in the following table:
| Lookup Definition | Format of Value in the Decode Column |
|---|---|
|
Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ReconAttrMap |
FIELD_NAME; STRUCTURE_NAME For example: ACCNT;LOGONDATA |
|
Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ProvAttrMap |
FIELD_NAME;STRUCTURE_NAME;FIELD_NAME;STRUCTURE_NAME_X For example: ACCNT;LOGONDATA;ACCNT;LOGONDATAX |
Note:
You need not perform this procedure for custom attributes that you add on the target system. For custom attributes, the names are the same as those given in the custom BAPI that you create.
To determine the name of the target system attribute on which the connector can perform reconciliation and provisioning operations:
4.2 Adding New Attributes for Reconciliation
You can map new attributes between Oracle Identity manager and the target system for reconciliation.
Note:
-
You must ensure that new fields you add for reconciliation contain only string-format data. Binary fields must not be brought into Oracle Identity Manager natively.
-
The procedure described in this section applies to both standard target system attributes and custom attributes that you create on the target system.
By default, the attributes listed in Table 1-10 are mapped for reconciliation between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. If required, you can add new attributes for reconciliation.
To add a new attribute for reconciliation, perform the procedures listed in the following sections:
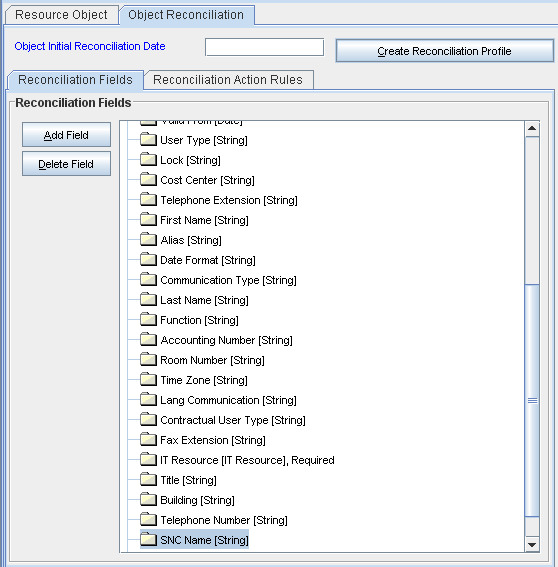
4.2.2 Adding the New Attribute to the Resource Object
To add the new attribute to the list of reconciliation fields in the resource object:
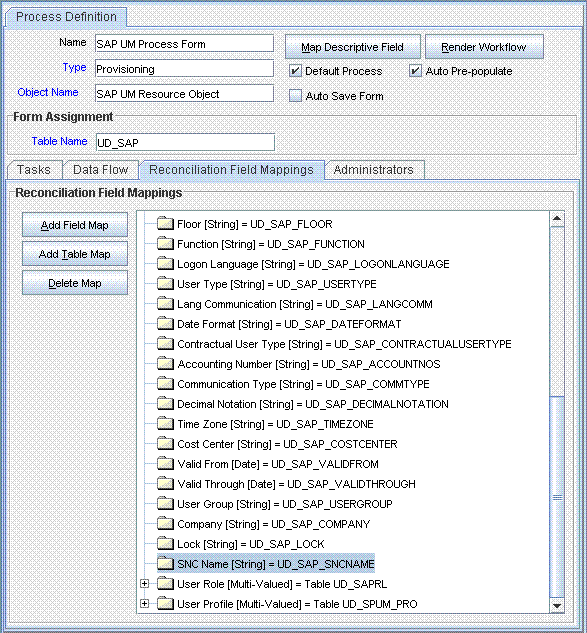
4.2.3 Creating a Reconciliation Field Mapping for the New Attribute in the Process Definition
To create a reconciliation field mapping for the new attribute in the process definition:
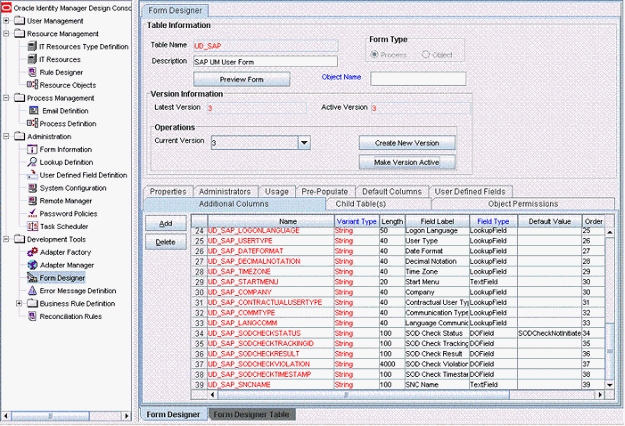
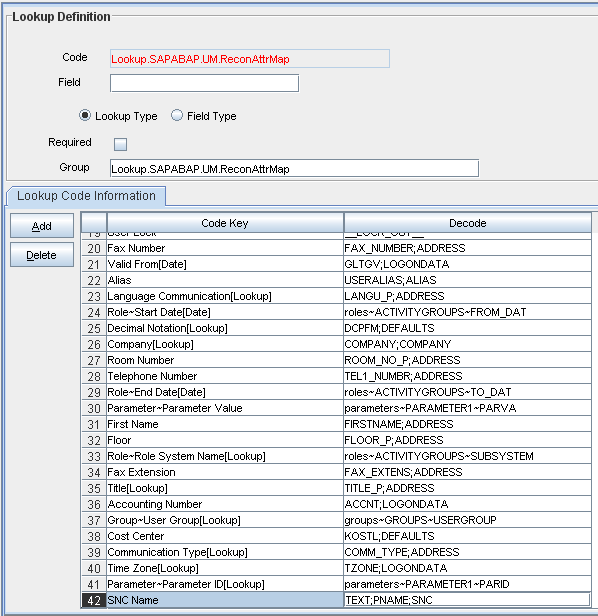
4.2.4 Creating an Entry for the Field in the Lookup Definition for Reconciliation
Note:
Skip this step if you are adding a custom attribute.
To create an entry for the field in the lookup definition for reconciliation:
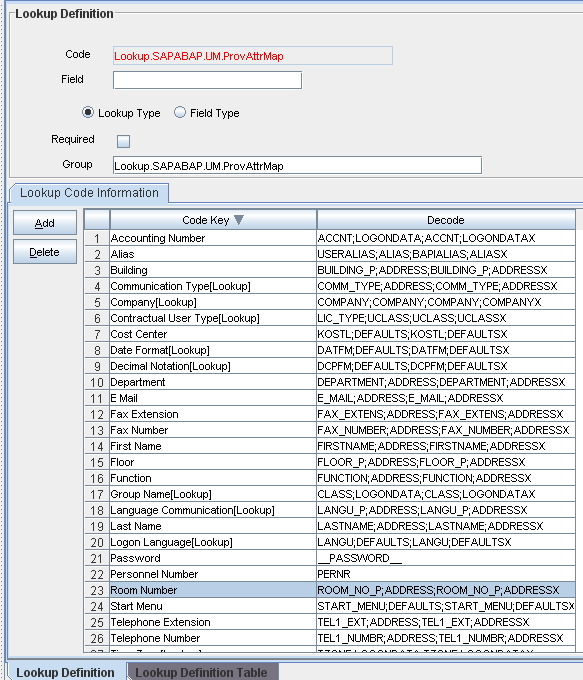
4.2.5 Creating an Entry for the Attribute in the Lookup Definition
The target system allows you to create custom structures and tables that hold custom fields. If you are mapping a custom attribute for reconciliation, then create an entry for the attribute in the Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition as follows:
Note:
Skip this step if you are adding a standard attribute.
Only single-valued custom attributes can be mapped for reconciliation.
For a change in a custom attribute to be detected during incremental reconciliation, at least one standard attribute in the same record must be modified.
-
In the Code Key column of the Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition, enter the name of the resource object field that you created for the custom attribute.
-
If you want a custom BAPI to fetch values from this attribute, then enter the following value in the Decode column of the lookup definition:
CUSTOM_BAPI_NAME;FIELD_TYPE;TABLE_NAME;FIELD_NAME;KEY_USER_ID_FIELD -
If you want a custom RFC table to fetch values from this attribute, then enter the following value in the Decode column of the lookup definition:
RFC_READ_TABLE;FIELD_TYPE;TABLE_NAME;FIELD_NAME;KEY_USER_ID_FIELD
-
In the Code Key column of the Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition, enter the name of the resource object field that you created for the custom attribute.
-
If you want a custom BAPI to fetch values from this attribute, then enter the following value in the Decode column of the lookup definition:
CUSTOM_BAPI_NAME;FIELD_TYPE;TABLE_NAME;FIELD_NAME;KEY_USER_ID_FIELD -
If you want a custom RFC table to fetch values from this attribute, then enter the following value in the Decode column of the lookup definition:
RFC_READ_TABLE;FIELD_TYPE;TABLE_NAME;FIELD_NAME;KEY_USER_ID_FIELD
In these formats:
-
CUSTOM_BAPI_NAMEis the name of the custom BAPI that you created for fetching values from the custom attribute. -
FIELD_TYPEis the type of data that is stored in the custom attribute. It can beTEXT,DATE, orCHECKBOX. -
TABLE_NAMEis the name of the custom table that contains the attribute. -
FIELD_NAMEis the name of the attribute in the custom table. -
KEY_USER_ID_FIELDis the attribute in the custom table that holds user ID values.
The following is a sample value for the Decode column:
ZBAPI_CUSTFIELDS;TEXT;ZCUSTFIELDS;FIELD1;USERNAME
4.2.6 Creating a New UI Form to Make the New Attribute Visible
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, create a new UI form and attach it to the application instance to make this new attribute visible. See Creating a New UI Form and Updating an Existing Application Instance with a New Form for detailed procedures.
4.3 Adding New Standard Attributes for Provisioning
You can map addition attributes for provisioning between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system.
By default, the attributes listed in Table 1-14 are mapped for provisioning between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. If required, you can map additional attributes for provisioning.
Perform the following procedures described in this section only if you want to map standard target system attributes for provisioning:
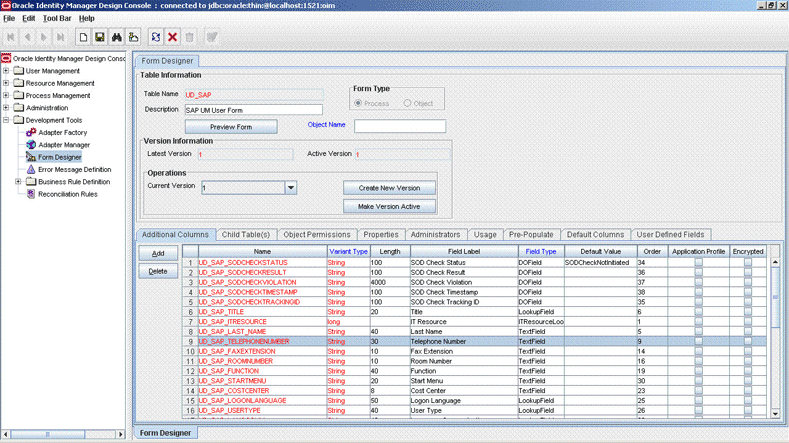
4.3.1 Creating a New Version of the Process Form
Create a new version on the process form as follows:
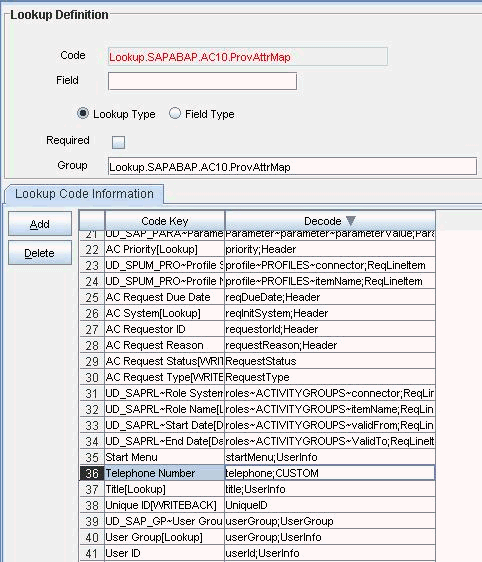
4.3.2 Creating an Entry for the Attribute in the Lookup Definition for Provisioning
Create an entry for the attribute in the lookup definition for provisioning as follows:
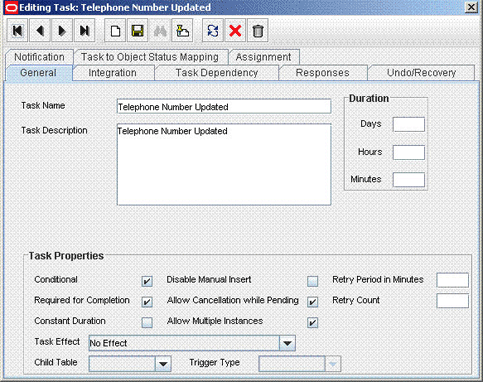
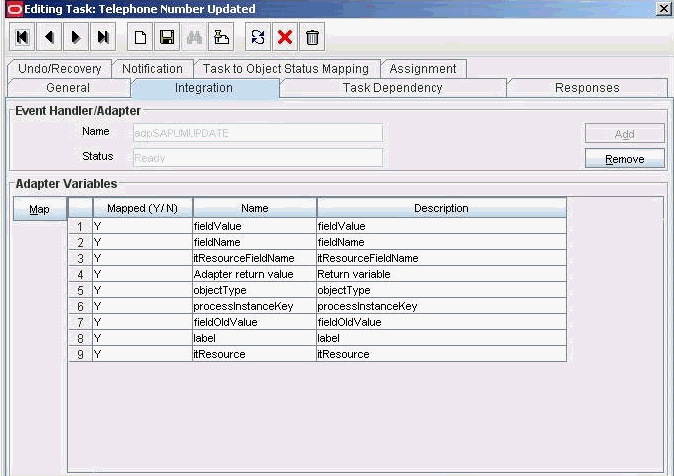
4.3.3 Creating a Task to Update the Attribute During Provisioning Operations
If you do not perform this procedure, then you will not be able to modify the value of the attribute after you set a value for it during the Create User provisioning operation.
To enable the update of the attribute during provisioning operations, add a process task for updating the attribute:
See Also:
Configuring Requests in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about these steps
4.3.4 Updating the Request Dataset
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, update the request dataset.
When you add an attribute on the process form, you also update the XML file containing the request dataset definitions. To update a request dataset:
4.3.5 Running the PurgeCache Utility
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, run the PurgeCache utility to clear content related to request datasets from the server cache.
See Purging Cache in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about the PurgeCache utility.
4.3.6 Importing the Request Dataset Definitions
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, import into MDS, the request dataset definitions in XML format.
See Importing Request Datasets Using Deployment Manager for detailed information about the procedure.
4.3.7 Creating a New UI Form to make the New Attribute Visible
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, create a new UI form and attach it to the application instance to make this new attribute visible. See Creating a New UI Form and Updating an Existing Application Instance with a New Form for detailed procedures.
4.4 Adding New Standard SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes for Provisioning
You can map additional single-valued attributes between Oracle Identity Manager and SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management.
By default, the attributes listed in Table 1-8 are mapped for sending requests from Oracle Identity Manager to SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management. If required, you can map additional single-valued attributes.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you want to map additional standard Access Request Management attributes for requests sent from Oracle Identity Manager to Access Request Management.
To add a new SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management attribute for provisioning, perform the following procedures:
4.4.1 Creating a New Version of the Process Form
If the attribute does not already exist on the process form, then add it on the process form as follows:
4.4.2 Creating an Entry for the Attribute in the Lookup Definition
Create an entry for the attribute in the Lookup.SAPAC10ABAP.UM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition according to the configured GRC system as follows:
4.4.3 Creating a Task to Update the Attribute During Provisioning Operations
Create a process task to enable update of the attribute during provisioning operations if the following conditions are true:
-
The task does not already exist.
-
This attribute exists on both SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management and the target system.
Note:
If you do not perform this procedure, then you will not be able to modify the value of the attribute after you set a value for it during the Create User provisioning operation.
To enable the update of the attribute during provisioning operations, add a process task for updating the attribute:
See Also:
Creating Provisioning Metadata in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about creating a process form
4.4.4 Updating the Request Dataset
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, update the request dataset.
When you add an attribute on the process form, you also update the XML file containing the request dataset definitions. To update a request dataset:
4.4.5 Running the PurgeCache Utility
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, run the PurgeCache utility to clear content related to request datasets from the server cache.
See Purging Cache in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about the PurgeCache utility.
4.4.6 Importing the Request Datasets into MDS
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release prior to 11.1.2, import into MDS, the request dataset definitions in XML format.
See Importing Request Datasets Using Deployment Manager for detailed information about the procedure.
4.4.7 Creating a New UI Form to make the New Attribute Visible
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, create a new UI form and attach it to the application instance to make this new attribute visible. See Creating a New UI Form and Updating an Existing Application Instance with a New Form for detailed procedures.
4.5 Removing SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes from Process Form
You can remove SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management attributes if the connector is not configured for SAP BusinessObjects AC.
The form attributes used for Access Request Management are prefixed with AC. These attributes are available in the process form. If the connector is not configured for SAP BusinessObjects AC, then the AC-specific attributes can be removed manually.
See SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes for a consolidated list of SAP BusinessObjects AC attributes.
To remove the AC attributes from the process form:
-
From Oracle Identity Manager Design Console, expand Development Tools.
-
Double-click Form Designer.
-
Search for and open the UD_SAP_UMAC process form.
-
Click Create New Version.
-
In the Label field, enter the version name. For example,
version#1. -
Click the Save icon.
-
Select the current version created in Step 5 from the Current Version list.
-
Select the AC field to be removed.
-
Click Delete to remove the selected attribute row from the form.
-
Similarly, repeat Steps 8 and 9 until you remove all the AC attributes.
-
Click the Save icon.
-
Click Make Version Active.
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1, after you remove an attribute on the process form, you must update the XML file containing the request dataset definitions. To update a request dataset:
-
Locate and open the SAPUM-Datasets.xml file, which is located in the xml directory of the installation media.
-
Search for and find the AC field tags. You can either comment or delete the entire set of AC field tags in the XML file.
-
Save and close the XML file.
-
Run the PurgeCache utility to clear content related to request datasets from the server cache.
See Purging Cache in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about the PurgeCache utility.
-
Import into MDS the request dataset definitions in XML format.
See Importing Request Datasets Using Deployment Manager for detailed information about the procedure.
-
4.5.1 SAP BusinessObjects AC Access Request Management Attributes
The form attributes used for Access Request Management are prefixed with AC. These attributes are available in the process form.
The following is the list of AC attributes:
-
AC Manager
-
AC Manager email
-
AC Priority
-
AC System
-
AC Requestor ID
-
AC Requestor email
-
AC Request Reason
-
AC Manager First Name
-
AC Manager Last Name
-
AC Manager Telephone
-
AC Request Due Date
-
AC Functional Area
-
AC Business Process
-
AC Requestor First Name
-
AC Requestor Last Name
-
AC Requestor Telephone
-
AC Request Reason
-
AC Request Status
-
AC Request Type
-
AC Company
4.6 Configuring Validation of Data During Reconciliation and Provisioning
You can configure validation of reconciled and provisioned single-valued data according to your requirements. For example, you can validate data fetched from the First Name attribute to ensure that it does not contain the number sign (#). In addition, you can validate data entered in the First Name field on the process form so that the number sign (#) is not sent to the target system during provisioning operations.
To configure validation of data:
4.7 Configuring Transformation of Data During User Reconciliation
You can configure transformation of reconciled single-valued user data according to your requirements. For example, you can use First Name and Last Name values to create a value for the Full Name field in Oracle Identity Manager.
To configure transformation of single-valued user data fetched during reconciliation:
4.8 Configuring Resource Exclusion Lists
You can specify a list of accounts that must be excluded from reconciliation and provisioning operations. Accounts whose user IDs you specify in the exclusion list are not affected by reconciliation and provisioning operations.
In one of the lookup definitions for exclusion lists, enter the user IDs of target system accounts for which you do not want to perform provisioning and reconciliation operations. See Lookup Definitions for Exclusion Lists for information about the lookup definitions and the format of the entries in these lookups.
To add entries in the lookup for exclusions during provisioning or reconciliation operations:
4.9 Modifying Field Lengths on the Process Form
You might want to modify the lengths of fields (attributes) on the process form. For example, if you use the Japanese locale, then you might want to increase the lengths of process form fields to accommodate multibyte data from the target system.
Note:
On mySAP ERP 2005 (ECC 6.0 running on WAS 7.0), the default length of the password field is 40 characters. The default length of the password field on the process form is 8 characters. If you are using mySAP ERP 2005, then you must increase the length of the password field on the process form.
If you want to modify the length of a field on the process form, then:
- Log in to the Design Console.
- Expand Development Tools, and double-click Form Designer.
- Search for and open the UD_SAP process form. If you are using the SAP AC UM connector, open the UD_SAP_UMAC process form.
- Click Create New Version.
- Enter a label for the new version, click the Save icon, and then close the dialog box.
- From the Current Version list, select the version that you create.
- Modify the length of the required field.
- Click the Save icon.
- Click Make Version Active.
- If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, create a new UI form and attach it to the application instance to activate this modified field length. See Creating a New UI Form and Updating an Existing Application Instance with a New Form for detailed procedures.
4.10 About Configuring the Connector for Multiple Installations of the Target System
You might want to configure the connector for multiple installations of the target system.
The following example illustrates this requirement:
The London and New York offices of Example Multinational Inc. have their own installations of the target system. The company has recently installed Oracle Identity Manager, and they want to configure Oracle Identity Manager to link all the installations of the target system.
To meet the requirement posed by such a scenario, you can create copies of connector objects, such as the IT resource and resource object.
The decision to create a copy of a connector object might be based on a requirement. For example, an IT resource can hold connection information for one target system installation. Therefore, it is mandatory to create a copy of the IT resource for each target system installation.
With some other connector objects, you do not need to create copies at all. For example, a single attribute-mapping lookup definition can be used for all installations of the target system.
All connector objects are linked. For example, a scheduled task holds the name of the IT resource. Similarly, the IT resource holds the name of the configuration lookup definition, Lookup.SAPABAP.Configuration. If you create a copy of an object, then you must specify the name of the copy in associated connector objects. Table 4-1 lists associations between connector objects whose copies can be created and the other objects that reference these objects. When you create a copy of a connector object, use this information to change the associations of that object with other objects.
Note:
On a particular Oracle Identity Manager installation, if you create a copy of a connector object, then you must set a unique name for it.
Table 4-1 Connector Objects and Their Associations
| Connector Object | Name | Referenced By | Comments on Creating a Copy |
|---|---|---|---|
|
IT resource |
SAP UM ITResource |
Scheduled tasks |
Create a copy of the IT resource. See Configuring the IT Resource for more information. |
|
Resource object |
SAP UM Resource Object |
Scheduled tasks |
Create copies of the resource object only if there are differences in attributes between the various installations of the target system and if the same user ID exists in different target systems. See Scheduled Jobs for Lookup Field Synchronization and Reconciliation Scheduled Jobs for the SAP UM Connector for more information. |
|
Process definition |
SAP UM Process Form |
NA |
Create copies of this process definition only if there are differences in attributes between the various installations of the target system and if the same user ID exists in different target systems. |
|
Attribute Mapping Lookup Definition |
Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ProvAttrMap Lookup.SAPABAP.UM.ReconAttrMap |
NA |
Create copies of these lookup definition only if you want to map a different set of attributes for the various installations of the target system. See the following sections for more information: Connector Objects Used During Target Resource Reconciliation |
|
Process form |
UD_SAP |
NA |
Create a copy of a process form if there are differences in attributes between the various installations of the target system and if the same user ID exists in different target systems. |
|
Configuration lookup definition |
Lookup.SAPABAP.Configuration |
SAP UM ITResource (IT resource) |
Create copies of this lookup definition only if you want to use a different set of configuration values for the various installations of the target system. See Section 2.3.3, "Setting Up the Configuration Lookup Definition in Oracle Identity Manager" for more information. |
|
Lookup mappings lookup definitions |
See Lookup Definitions Synchronized with the Target System for the list of lookups. |
Scheduled tasks |
Create copies of these lookup definition only if you want to use a different set of lookup mappings for the various installations of the target system. |
When you configure reconciliation:
To reconcile data from a particular target system installation, specify the name of the IT resource for that target system installation as the value of the scheduled task attribute that holds the IT resource name. For example, you enter the name of the IT resource as the value of the IT resource attribute of the SAP UM User Recon scheduled task.
When you perform provisioning operations:
When you use Oracle Identity System Administration to perform provisioning, you can specify the IT resource corresponding to the target system installation to which you want to provision the user.