2 Deploying the Connector
2.1 Preinstallation
Preinstallation involves performing procedures such as copying external code files on Oracle Identity Manager, configuring encryption security on the target system, and so on.
2.1.2 Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations
Oracle Identity Manager requires a target system user account to access the target system during reconciliation and provisioning operations. You provide the credentials of this user account while performing the procedure described in Configuring the IT Resource for the Target System.
The target system user account for connector operations must have the following permissions:
-
Contact Organization Admin
-
Administrator
-
Check Unrestricted Access under Login/Access Details
-
User must have fixed (write) license
To assign these minimum permissions:
2.1.3 Understanding and Configuring Encryption Security
Learn about the various encryption options for your target system and how to configure encryption.
Note:
If you are using BMC Remedy AR System 7.1 as the target system, then to configure encryption you must modify the ar.conf (UNIX) or ar.cfg (Microsoft Windows) configuration file. See the target system documentation for complete information about configuring encryption.
2.1.3.1 Understanding the Encryption Security Options on the Encryption Tab
You use the Encryption tab to understand and configure encryption security options such as the following:
See Also:
The target system documentation for detailed information about topics discussed in this section
-
Encryption Level Available
Note:
If the level of encryption is Standard, then you must just enable encryption on the BMC Remedy Server (server). There is no need not perform any more procedures on the client side. For all other levels of encryption, see the target system guide for information of procedures to be performed on client side.
This field displays the level of encryption currently installed on the BMC Remedy Server (server). The following are the levels of encryption available:
-
Standard: This is the default and standard level of encryption.
-
Performance: This is the BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security.
-
Premium: This is the BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security.
The default encryption level is
Standard. -
-
Active Encryption Settings
This section contains a set of read-only fields that display the current encryption settings on the target system.
-
New Encryption Settings
This section contains a set of fields that you use to modify the encryption settings on your target system. All values that you specify in this section are saved to the target system configuration files ar.conf (UNIX) or ar.cfg (Microsoft Windows). In addition, these values are displayed in the Active Encryption Settings section.
2.1.3.2 Understanding the Encryption Options in the New Encryption Settings Section
The following sections provide more information on the encryption options that you can set in the New Encryption Settings section:
2.1.3.2.1 Security Policy
The following are the values that you can select from the Security Policy list:
-
Optional
When you select this option, clients can communicate with the server irrespective of whether or not encryption is installed. If the client supports server encryption configuration, then network traffic is encrypted. Otherwise, plain text is used in the network traffic.
This is the default selection for BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security and BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security FIPS noncompliance.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Security-Policy: 0 -
Required
When you select this option, clients can communicate with the server only if encryption is installed.
This is the default selection for BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security and BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security FIPS compliance.
Note that the encryption algorithms used by the server must be compatible with the encryption level installed on the client.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Security-Policy: 1 -
Disabled
When you select this option, communication with the server is not encrypted irrespective of whether or not encryption is installed on the client. Plain text is exchanged in network traffic.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file
Encrypt-Security-Policy: 2
2.1.3.2.2 Data Key Details
After the connection between the sever and clients is established, the data exchanged is processed by the data key. In this region, you specify values for the following UI elements to configure the cryptographic algorithm and size of the data key:
-
Algorithm Options
Select one of the following options to specify the data encryption algorithm:
Note:
Depending on the level of encryption installed on the server and whether FIPS is enabled, you can see one or more algorithms discussed in this section.
-
DES: This is the 56-bit Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm using Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 1 -
RC4-128: This is the 128-bit RC4 key algorithm. This algorithm is available for BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security that does not comply with FIPS.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 2 -
RC4-2048: This is the 2048-bit RC4 key algorithm. This algorithm is available for BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security that does not comply with FIPS.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 3 -
AES-128: This is the 128-bit AES CBC key algorithm. This algorithm is mandatory for BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security that complies with FIPS. However, servers that do not comply with FIPS can also use this algorithm.
The following is the setting in the configuration file of a server that does not comply with FIPS:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 6The following is the setting in the configuration file of a server that complies with FIPS:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 8 -
AES-256: This is the 256-bit AES CBC key algorithm. This algorithm is mandatory for BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security that complies with FIPS. However, servers that do not comply with FIPS can also use this algorithm.
The following is the setting in the configuration file of a server that does not comply with FIPS:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 7The following is the setting in the configuration file of a server that complies with FIPS:
Encrypt-Data-Encryption-Algorithm: 9
-
-
Key Expire Interval
Enter an integer value in this field. This value represent the life span of the key in seconds. The key expires after the specified time (in seconds) is reached, and then exchange of a new key happens.
Note that this is an optional field and its default value is
2700seconds. The following is the setting in the server configuration file:Encrypt-Symmetric-Data-Key-Expire: 2700
2.1.3.2.3 Public Key Details
When the data encryption key expires and the API session is about to begin, an private keys establishment (exchange of private keys) occurs. In order to establish or exchange private keys, BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security and BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security use the RSA algorithm for public key cryptography. In this region, you specify values for the following UI elements to configure the cryptographic algorithm and size of the public key:
-
Algorithm Options
Select one of the following options to specify the data encryption algorithm:
Note:
Depending on the level of encryption installed on the server and whether FIPS is enabled, you can see one or more algorithms discussed in this section.
-
RSA 512: This is the 512-bit RSA key algorithm and is the default value for standard security.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Public-Key-Algorithm: 4 -
RSA 1024: This is the 1024-bit RSA key algorithm and is the default value for BMC Remedy Encryption Performance Security.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Public-Key-Algorithm: 5 -
RSA 2048: This is the 2048-bit RSA key algorithm and is the default value for BMC Remedy Encryption Premium Security.
The following is the setting in the server configuration file:
Encrypt-Public-Key-Algorithm: 6
-
-
Key Expire Interval
Enter an integer value in this field. This value represent the life span of the key in seconds. The key expires after the specified time (in seconds) is reached, and then the server generates a new key.
Note that this is an optional field and its default value is
86400seconds. The following is the setting in the server configuration file:Encrypt-Symmetric-Data-Key-Expire: 86400
2.2 Installation
Depending on where you want to run the connector code (bundle), the connector provides these installation options.
-
To run the connector code locally in Oracle Identity Manager, perform the procedure described in Installing the Connector in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
To run the connector code remotely in a Connector Server, perform the procedures described in Installing the Connector in Oracle Identity Manager and Deploying the Connector in a Connector Server.
2.2.1 Installing the Connector in Oracle Identity Manager
Installation on Oracle Identity Manager consists of the following procedures:
2.2.1.1 Running the Connector Installer
Note:
In this guide, the term Connector Installer has been used to refer to the Connector Installer feature of the Administrative and User Console.
To run the Connector Installer:
-
Copy the contents of the connector installation media directory into the following directory:
OIM_HOME/server/ConnectorDefaultDirectory
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x, then:
-
Log in to the Administrative and User Console.
-
On the Welcome to Identity Manager Advanced Administration page, in the System Management region, click Manage Connector.
-
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, then:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
In the left pane, under System Management, click Manage Connector.
-
-
In the Manage Connector page, click Install.
-
From the Connector List list, select BMC Remedy User Management Connector RELEASE_NUMBER. This list displays the names and release numbers of connectors whose installation files you copy into the default connector installation directory in Step 1.
If you have copied the installation files into a different directory, then:
-
In the Alternative Directory field, enter the full path and name of that directory.
-
To repopulate the list of connectors in the Connector List list, click Refresh.
-
From the Connector List list, select BMC Remedy User Management Connector RELEASE_NUMBER.
-
-
Click Load.
-
To start the installation process, click Continue.
The following tasks are performed, in sequence:
-
Configuration of connector libraries
-
Import of the connector XML files (by using the Deployment Manager)
-
Compilation of adapters
On successful completion of a task, a check mark is displayed for the task. If a task fails, then an X mark and a message stating the reason for failure is displayed. Depending on the reason for the failure, make the required correction and then perform one of the following steps:
-
Retry the installation by clicking Retry.
-
Cancel the installation and begin again from Step 1.
-
-
If all three tasks of the connector installation process are successful, then a message indicating successful installation is displayed. In addition, a list of steps that you must perform after the installation is displayed. These steps are as follows:
-
Ensuring that the prerequisites for using the connector are addressed
Note:
At this stage, run the Oracle Identity Manager PurgeCache utility to load the server cache with content from the connector resource bundle in order to view the list of prerequisites. See Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache for information about running the PurgeCache utility.
There are no prerequisites for some predefined connectors.
-
Configuring the IT resource for the connector
The procedure to configure the IT resource is described later in this guide.
-
Configuring the scheduled jobs
The procedure to configure these scheduled jobs is described later in this guide.
-
When you run the Connector Installer, it copies the connector files and external code files to destination directories on the Oracle Identity Manager host computer. These files are listed in Table A-1.
2.2.1.2 Configuring the IT Resource for the Target System
Note:
If you have configured your target system as a trusted source, then create an IT resource of type BMCRemedy. For example, BMCRemedy Trusted. The parameters of this IT resource are the same as the parameters of the IT resources described in Table 2-1 of this section. See Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about creating an IT resource.
The IT resource for the target system is created during connector installation. This IT resource contains connection information about the target system. Oracle Identity Manager uses this information during reconciliation and provisioning.
You must specify values for the parameters of the BMCRemedy Server IT resource as follows:
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x, then:
-
Log in to the Administrative and User Console
-
On the Welcome page, click Advanced in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
On the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Advanced Administration page, in the Configuration region, click Manage IT Resource.
-
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, then:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration
-
In the left pane, under Configuration, click IT Resource.
-
-
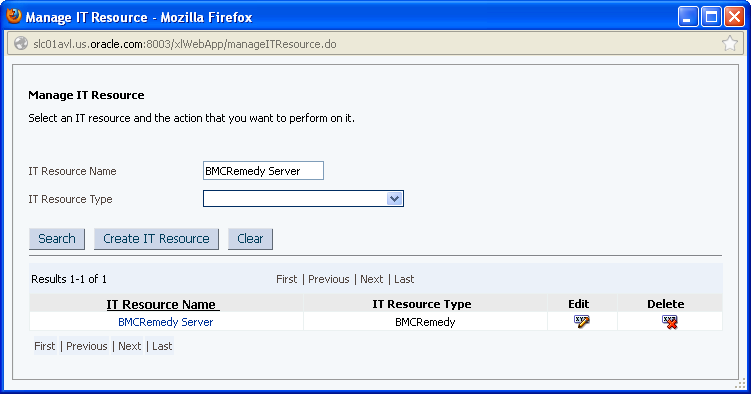
In the IT Resource Name field on the Manage IT Resource page, enter
BMCRemedy Serverand then click Search. Figure 2-1 shows the Manage IT Resource page. -
Click the edit icon corresponding to the BMCRemedy Server IT resource.
-
From the list at the top of the page, select Details and Parameters.
-
Specify values for the parameters of the BMCRemedy Server IT resource. Figure 2-2 shows the Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters page.
Figure 2-2 Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters Page for the BMCRemedy Server IT Resource
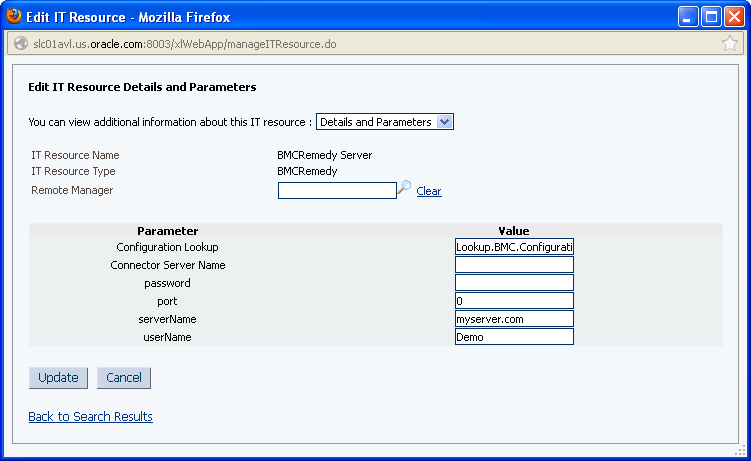
Description of "Figure 2-2 Edit IT Resource Details and Parameters Page for the BMCRemedy Server IT Resource"Table 2-1 describes each parameter of the BMCRemedy Server IT resource.
Table 2-1 Parameters of the BMCRemedy Server IT Resource for the Target System
Parameter Description Configuration Lookup
This parameter holds the name of the lookup definition that stores configuration information used during reconciliation and provisioning.
If you have configured your target system as a target resource, then enter
Lookup.BMC.Configuration.If you have configured your target system as a trusted source, then enter
Lookup.BMC.Configuration.Trusted.Default value:
Lookup.BMC.ConfigurationConnector Server Name
Name of the IT resource of the type "Connector Server." You create an IT resource for the Connector Server in Creating the IT Resource for the Connector Server.
Note: Enter a value for this parameter only if you have deployed the BMC User Management connector in the Connector Server.
Sample value:
BMC Connector ServerPassword
Enter the password of the user account that you create by performing the procedure described in Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations.
Port
Enter the TCP/IP port at which the BMC Remedy server is listening.
Default value:
0Note: You must specify a value for this parameter only if the BMC Remedy server is not registered with the port mapper. You need not specify a value for this parameter if the BMC Remedy server is registered with the port mapper.
serverName
Enter the IP address or computer name of the BMC Remedy User Management server.
userName
Enter the User ID of the user account that you created by performing the procedure described in Creating a Target System User Account for Connector Operations.
Default value:
Demo -
To save the values, click Update.
2.2.2 Deploying the Connector in a Connector Server
You can deploy the BMC User Management connector either locally in Oracle Identity Manager or remotely in the Connector Server. A connector server is an application that enables remote execution of an Identity Connector, such as the BMC User Management connector.
Note:
-
To deploy the connector bundle remotely in a Connector Server, you must first deploy the connector in Oracle Identity Manager, as described in Installing the Connector in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
See Creating the IT Resource for the Connector Server for related information.
This procedure can be divided into the following stages:
2.2.2.1 Installing and Configuring the Connector Server
Connector servers are available in two implementations:
-
As a .Net implementation that is used by Identity Connectors implemented in .Net
-
As a Java Connector Server implementation that is used by Java-based Identity Connectors
The BMC User Management connector is implemented in Java, so you can deploy this connector to a Java Connector Server.
Use the following steps to install and configure the Java Connector Server:
Note:
Before you deploy the Java Connector Server, ensure that you install the JDK or JRE on the same computer where you are installing the Java Connector Server and that your JAVA_HOME or JRE_HOME environment variable points to this installation.
Note:
Oracle Identity Manager has no built-in support for connector servers, so you cannot test your configuration.
2.2.2.2 Running the Connector Server
To run the Java Connector Server, use the ConnectorServer.bat script for Windows and use the ConnectorServer.sh script for UNIX as follows:
2.2.2.3 Installing the Connector on the Connector Server
See Also:
Using an Identity Connector Server in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for information about installing and configuring connector server and running the connector server
If you need to deploy the BMC User Management connector into the Java Connector Server, then follow these steps:
2.3 Postinstallation
Postinstallation involves performing certain procedures such as configuring Oracle Identity Manager, creating the IT resource for the Connector Server, enabling logging, localizing field labels, and so on.
2.3.1 Configuring Oracle Identity Manager 11.1.2 or Later
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2 or later, you must create additional metadata such as a UI form and an application instance. In addition, you must run entitlement and catalog synchronization jobs.
These procedures are described in the following sections:
2.3.1.4 Publishing a Sandbox
To publish the sandbox that you created in Creating and Activating a Sandbox:
2.3.1.5 Harvesting Entitlements and Sync Catalog
To harvest entitlements and sync catalog:
- Run the scheduled jobs for lookup field synchronization listed in Scheduled Job for Lookup Field Synchronization.
- Run the Entitlement List scheduled job to populate Entitlement Assignment schema from child process form table. See Predefined Scheduled Tasks in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about this scheduled job.
- Run the Catalog Synchronization Job scheduled job. See Predefined Scheduled Tasks in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information about this scheduled job.
2.3.2 Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache
When you deploy the connector, the resource bundles are copied from the resources directory on the installation media into the Oracle Identity Manager database. Whenever you add a new resource bundle to the connectorResources directory or make a change in an existing resource bundle, you must clear content related to connector resource bundles from the server cache.
To clear content related to connector resource bundles from the server cache:
2.3.3 Managing Logging
Oracle Identity Manager uses the Oracle Diagnostic Logging (ODL) logging service for recording all types of events pertaining to the connector.
The following topics provide detailed information about logging:
2.3.3.1 Understanding Log Levels
Oracle Identity Manager uses Oracle Java Diagnostic Logging (OJDL) for logging. OJDL is based on java.util.logger. To specify the type of event for which you want logging to take place, you can set the log level to one of the following:
-
SEVERE.intValue()+100
This level enables logging of information about fatal errors.
-
SEVERE
This level enables logging of information about errors that might allow Oracle Identity Manager to continue running.
-
WARNING
This level enables logging of information about potentially harmful situations.
-
INFO
This level enables logging of messages that highlight the progress of the application.
-
CONFIG
This level enables logging of information about fine-grained events that are useful for debugging.
-
FINE, FINER, FINEST
These levels enable logging of information about fine-grained events, where FINEST logs information about all events.
These log levels are mapped to ODL message type and level combinations as shown in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2 Log Levels and ODL Message Type:Level Combinations
| Log Level | ODL Message Type:Level |
|---|---|
|
SEVERE.intValue()+100 |
INCIDENT_ERROR:1 |
|
SEVERE |
ERROR:1 |
|
WARNING |
WARNING:1 |
|
INFO |
NOTIFICATION:1 |
|
CONFIG |
NOTIFICATION:16 |
|
FINE |
TRACE:1 |
|
FINER |
TRACE:16 |
|
FINEST |
TRACE:32 |
The configuration file for OJDL is logging.xml, which is located at the following path:
DOMAIN_HOME/config/fmwconfig/servers/OIM_SERVER/logging.xml
Here, DOMAIN_HOME and OIM_SERVER are the domain name and server name specified during the installation of Oracle Identity Manager.
2.3.3.2 Enabling Logging
To enable logging in Oracle WebLogic Server:
-
Edit the logging.xml file as follows:
-
Add the following blocks in the file:
<log_handler name='bmcremedy-handler' level='[LOG_LEVEL]' class='oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory'> <property name='logreader:' value='off'/> <property name='path' value='[FILE_NAME]'/> <property name='format' value='ODL-Text'/> <property name='useThreadName' value='true'/> <property name='locale' value='en'/> <property name='maxFileSize' value='5242880'/> <property name='maxLogSize' value='52428800'/> <property name='encoding' value='UTF-8'/> </log_handler>
<logger name="org.identityconnectors.bmc" level="[LOG_LEVEL]" useParentHandlers="false"> <handler name="bmcremedy-handler"/> <handler name="console-handler"/> </logger> -
Replace both occurrences of
[LOG_LEVEL]with the ODL message type and level combination that you require. Table 2-2 lists the supported message type and level combinations.Similarly, replace
[FILE_NAME]with the full path and name of the log file in which you want log messages to be recorded.The following blocks show sample values for
[LOG_LEVEL]and[FILE_NAME]:<log_handler name='bmcremedy-handler' level='NOTIFICATION:1' class='oracle.core.ojdl.logging.ODLHandlerFactory'> <property name='logreader:' value='off'/> <property name='path' value='F:\MyMachine\middleware\user_projects\domains\base_domain1\servers\oim_server1\logs\oim_server1-diagnostic-1.log'/> <property name='format' value='ODL-Text'/> <property name='useThreadName' value='true'/> <property name='locale' value='en'/> <property name='maxFileSize' value='5242880'/> <property name='maxLogSize' value='52428800'/> <property name='encoding' value='UTF-8'/> </log_handler> <logger name="org.identityconnectors.bmc" level="NOTIFICATION:1" useParentHandlers="false"> <handler name="bmcremedy-handler"/> <handler name="console-handler"/> </logger>
With these sample values, when you use Oracle Identity Manager, all messages generated for this connector that are of a log level equal to or higher than the
NOTIFICATION:1level are recorded in the specified file. -
-
Save and close the file.
-
Set the following environment variable to redirect the server logs to a file:
For Microsoft Windows:
set WLS_REDIRECT_LOG=FILENAMEFor UNIX:
export WLS_REDIRECT_LOG=FILENAMEReplace FILENAME with the location and name of the file to which you want to redirect the output.
-
Restart the application server.
2.3.4 Setting up the Lookup Definition for Connection Pooling
By default, this connector uses the ICF connection pooling. Table 2-3 lists the connection pooling properties, their description, and default values set in ICF:
Table 2-3 Connection Pooling Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
Pool Max Idle |
Maximum number of idle objects in a pool. Default value: |
|
Pool Max Size |
Maximum number of connections that the pool can create. Default value: |
|
Pool Max Wait |
Maximum time, in milliseconds, the pool must wait for a free object to make itself available to be consumed for an operation. Default value: |
|
Pool Min Evict Idle Time |
Minimum time, in milliseconds, the connector must wait before evicting an idle object. Default value: |
|
Pool Min Idle |
Minimum number of idle objects in a pool. Default value: |
If you want to modify the connection pooling properties to use values that suit requirements in your environment, then:
2.3.5 Configuring Oracle Identity Manager for Request-Based Provisioning
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x.
In request-based provisioning, an end user creates a request for a resource by using the Administrative and User Console. Administrators or other users can also create requests for a particular user. Requests for a particular resource on the resource can be viewed and approved by approvers designated in Oracle Identity Manager.
The following are features of request-based provisioning:
-
A user can be provisioned only one resource (account) on the target system.
Note:
Direct provisioning allows the provisioning of multiple BMC Remedy accounts on the target system.
-
Direct provisioning cannot be used if you enable request-based provisioning.
To configure request-based provisioning, perform the following procedures:
2.3.5.1 Importing Request Datasets
A request dataset is an XML file that specifies the information to be submitted by the requester during a provisioning operation. These request datasets specify information about the default set of attributes for which the requester must submit information during a request-based provisioning operation.
There are two ways of importing request datasets:
Note:
Request datasets imported either into MDS or by using Deployment Manager are same.
2.3.5.1.1 Importing Request Datasets into MDS
To import a request dataset definition into the metadata store (MDS):
2.3.5.1.2 Importing Request Datasets Using Deployment Manager
The request datasets (predefined or generated) can also be imported by using the Deployment Manager (DM). The predefined request datasets are stored in the xml directory on the installation media.
To import a request dataset definition by using the Deployment Manager:
The request datasets are imported into MDS.
2.3.5.2 Enabling the Auto Save Form Feature
To enable the Auto Save Form feature:
- Log in to the Design Console.
- Expand Process Management, and then double-click Process Definition.
- Search for and open the BMCPROCESS process definition.
- Select the Auto Save Form check box.
- Click the Save icon.
2.3.5.3 Running the PurgeCache Utility
Run the PurgeCache utility to clear content belonging to the Metadata category from the server cache. See Clearing Content Related to Connector Resource Bundles from the Server Cache for instructions.
The procedure to configure request-based provisioning ends with this step.
2.3.6 Localizing Field Labels in UI Forms
You can localize UI form field labels by using the resource bundle corresponding to the language you want to use. The resource bundles are available in the connector installation media.
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later and you want to localize UI form field labels.
To localize field label that you add to in UI forms:
-
Log in to Oracle Enterprise Manager.
-
In the left pane, expand Application Deployments and then select oracle.iam.console.identity.sysadmin.ear.
-
In the right pane, from the Application Deployment list, select MDS Configuration.
-
On the MDS Configuration page, click Export and save the archive to the local computer.
-
Extract the contents of the archive, and open the following file in a text editor:
-
For Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 PS2 (11.1.2.2.0):
SAVED_LOCATION\xliffBundles\oracle\iam\ui\runtime\BizEditorBundle_en.xlf
-
For releases prior to Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 2 PS2 (11.1.2.2.0):
SAVED_LOCATION\xliffBundles\oracle\iam\ui\runtime\BizEditorBundle.xlf
-
-
Edit the BizEditorBundle.xlf file in the following manner:
-
Search for the following text:
<file source-language="en" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">
-
Replace with the following text:
<file source-language="en" target-language="LANG_CODE" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">In this text, replace LANG_CODE with the code of the language that you want to localize the form field labels. The following is a sample value for localizing the form field labels in Japanese:
<file source-language="en" target-language="ja" original="/xliffBundles/oracle/iam/ui/runtime/BizEditorBundle.xlf" datatype="x-oracle-adf">
-
Search for the application instance code. This procedure shows a sample edit for BMCFORM application instance. The original code is:
<trans-unit id="${adfBundle['oracle.adf.businesseditor.model.util.BaseRuntimeResourceBundle']['persdef.sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.user.entity.userEO.UD_BMC_LOGINNAME__c_description']}"> <source>LoginName</source> <target/> </trans-unit> <trans-unit id="sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.BMCFORM.entity.BMCFORMEO.UD_BMC_LOGINNAME__c_LABEL"> <source>LoginName</source> <target/> </trans-unit> -
Open the resource file from the connector package, for example BMCRemedy-UM_ja.properties, and get the value of the attribute from the file, for example, global.udf.UD_BMC_LOGINNAME=\u30ED\u30B0\u30A4\u30F3\u540D.
-
Replace the original code shown in Step 6.c with the following:
<trans-unit id="${adfBundle['oracle.adf.businesseditor.model.util.BaseRuntimeResourceBundle']['persdef.sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.user.entity.userEO.UD_BMC_LOGINNAME__c_description']}"> <source>LoginName</source> <target>\u30ED\u30B0\u30A4\u30F3\u540D<target/> </trans-unit> <trans-unit id="sessiondef.oracle.iam.ui.runtime.form.model.BMCFORM.entity.BMCFORMEO.UD_BMC_LOGINNAME__c_LABEL"> <source>LoginName</source> <target>\u30ED\u30B0\u30A4\u30F3\u540D<target/> </trans-unit> -
Repeat Steps 6.c through 6.e for all attributes of the process form.
-
Save the file as BizEditorBundle_LANG_CODE.xlf. In this file name, replace LANG_CODE with the code of the language to which you are localizing.
Sample file name: BizEditorBundle_ja.xlf.
-
-
Repackage the ZIP file and import it into MDS.
See Also:
Deploying and Undeploying Customizations in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager, for more information about exporting and importing metadata files
-
Log out of and log in to Oracle Identity Manager.
2.3.7 Creating the IT Resource for the Connector Server
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this section only if you have deployed the connector bundle remotely in a Connector Server.
To create the IT resource for the Connector Server:
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.1.x, then:
-
Log in to the Administrative and User Console
-
On the Welcome page, click Advanced in the upper-right corner of the page.
-
On the Welcome to Oracle Identity Manager Advanced Administration page, in the Configuration region, click Create IT Resource.
-
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, then:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration
-
In the left pane, under Configuration, click IT Resource.
-
In the Manage IT Resource page, click Create IT Resource.
-
-
On the Step 1: Provide IT Resource Information page, perform the following steps:
-
IT Resource Name: Enter a name for the IT resource.
-
IT Resource Type: Select Connector Server from the IT Resource Type list.
-
Remote Manager: Do not enter a value in this field.
-
-
Click Continue. Figure 2-3 shows the IT resource values added on the Create IT Resource page.
Figure 2-3 Step 1: Provide IT Resource Information
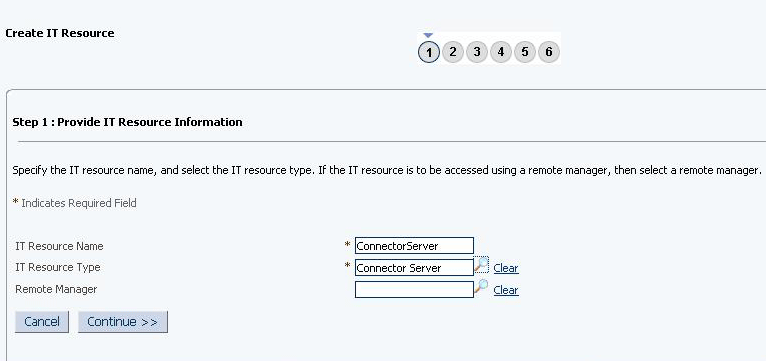
Description of "Figure 2-3 Step 1: Provide IT Resource Information" -
On the Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values page, specify values for the parameters of the IT resource and then click Continue. Figure 2-2 shows the Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values page.
Figure 2-4 Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values
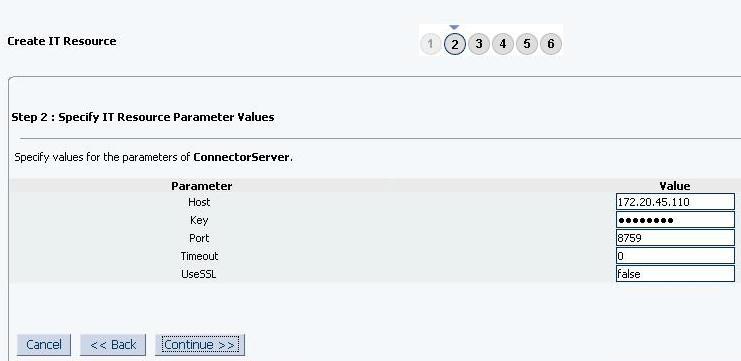
Description of "Figure 2-4 Step 2: Specify IT Resource Parameter Values"Figure 2-5 provides information about the parameters of the IT resource.
Table 2-4 Parameters of the IT Resource for the Connector Server
Parameter Description Host
Enter the host name or IP address of the computer hosting the connector server.
Sample value:
RManagerKey
Enter the key for the Java connector server.
Port
Enter the number of the port at which the connector server is listening.
Default value:
8759Timeout
Enter an integer value which specifies the number of milliseconds after which the connection between the connector server and Oracle Identity Manager times out.
Sample value:
300UseSSL
Enter
trueto specify that you will configure SSL between Oracle Identity Manager and the Connector Server. Otherwise, enterfalse.Default value:
falseNote: It is recommended that you configure SSL to secure communication with the connector server. To configure SSL, run the connector server by using the /setKey [
key] option. The value of this key must be specified as the value of the Key IT resource parameter of the connector server.To use SSL, you must set the value of connectorserver.usessl property to
true,and then set the value of connectorserver.certifacatestorename to the certificate store name. -
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, the
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORSgroup is displayed by default in the list of groups that have Read, Write, and Delete permissions on the IT resource that you are creating.Note:
This step is optional.
If you want to assign groups to the IT resource and set access permissions for the groups, then:
-
Click Assign Group.
-
For the groups that you want to assign to the IT resource, select Assign and the access permissions that you want to set. For example, if you want to assign the
ALL USERSgroup and set the Read and Write permissions to this group, then you must select the respective check boxes in the row, as well as the Assign check box, for this group. -
Click Assign.
-
-
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, if you want to modify the access permissions of groups assigned to the IT resource, then:
Note:
-
This step is optional.
-
You cannot modify the access permissions of the
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORSgroup. You can modify the access permissions of only other groups that you assign to the IT resource.
-
Click Update Permissions.
-
Depending on whether you want to set or remove specific access permissions for groups displayed on this page, select or deselect the corresponding check boxes.
-
Click Update.
-
-
On the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page, if you want to unassign a group from the IT resource, then:
Note:
-
This step is optional.
-
You cannot unassign the
SYSTEM ADMINISTRATORSgroup. You can unassign only other groups that you assign to the IT resource.
-
Select the Unassign check box for the group that you want to unassign.
-
Click Unassign.
-
-
Click Continue. Figure 2-5 shows the Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource page.
Figure 2-5 Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource
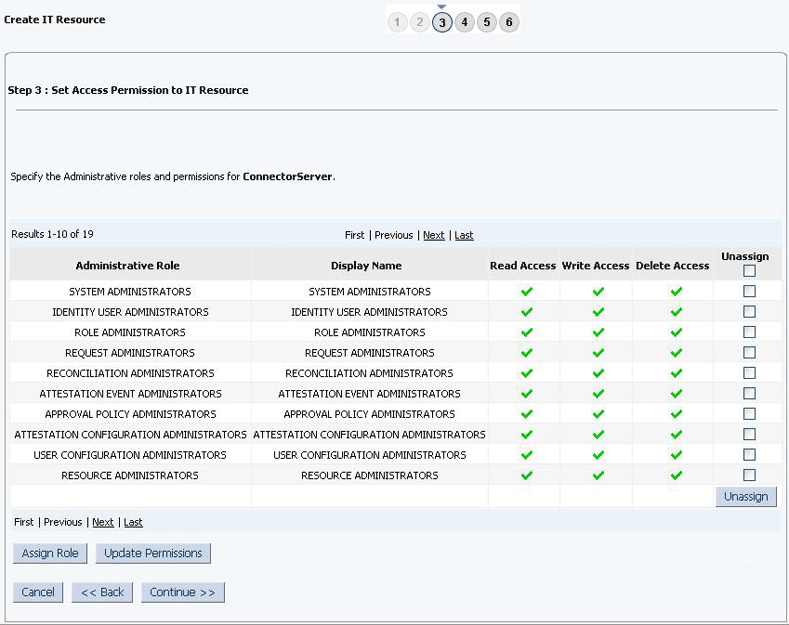
Description of "Figure 2-5 Step 3: Set Access Permission to IT Resource" -
On the Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details page, review the information that you provided on the first, second, and third pages. If you want to make changes in the data entered on any page, click Back to revisit the page and then make the required changes.
-
To proceed with the creation of the IT resource, click Continue. Figure 2-6 shows Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details page.
Figure 2-6 Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details
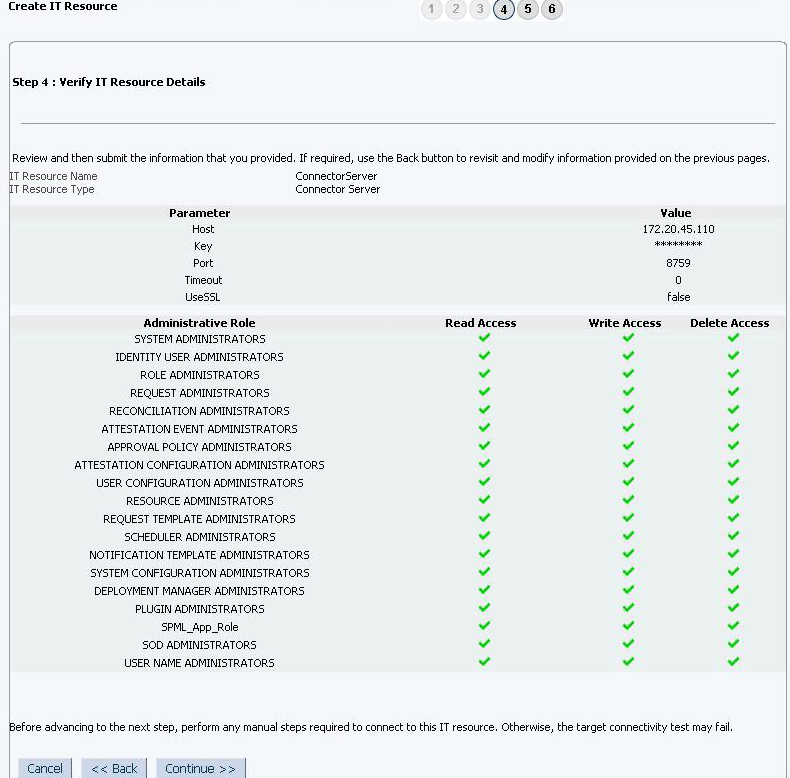
Description of "Figure 2-6 Step 4: Verify IT Resource Details" -
The Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result page displays the results of a connectivity test that is run using the IT resource information. If the test is successful, then click Continue. If the test fails, then you can perform one of the following steps:
-
Click Back to revisit the previous pages and then make corrections in the IT resource creation information.
-
Click Cancel to stop the procedure, and then begin from the first step onward.
Figure 2-7 shows the Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result page.
Figure 2-7 Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result
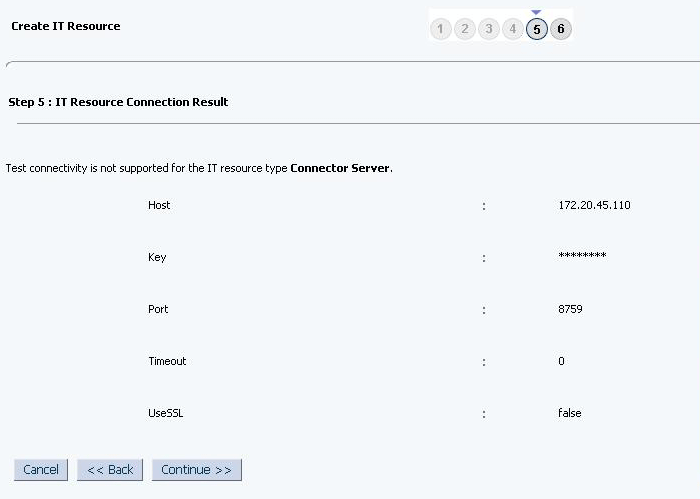
Description of "Figure 2-7 Step 5: IT Resource Connection Result"
-
-
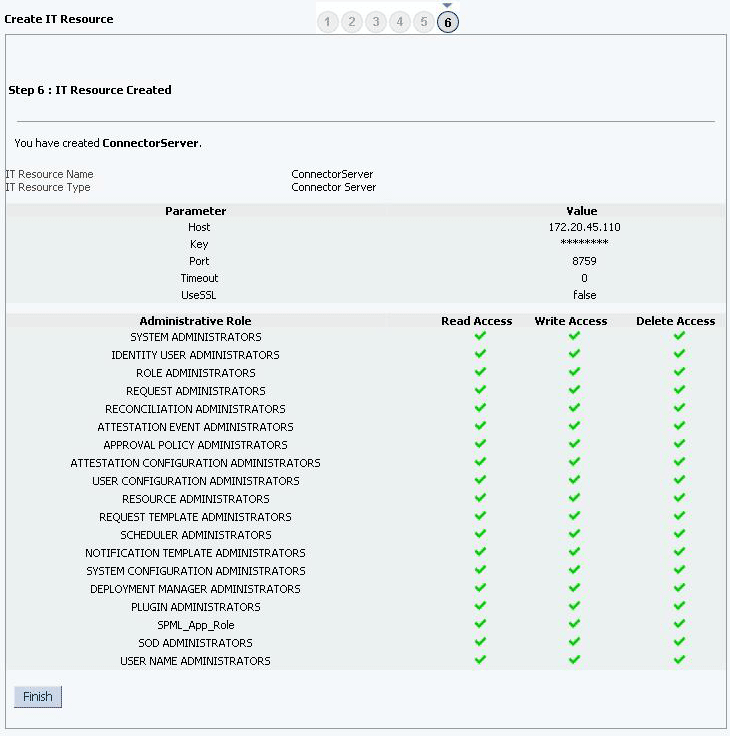
Click Finish. Figure 2-8 shows the IT Resource Created page.
2.4 Upgrading the Connector
If you have already deployed an earlier release of this connector, then upgrade the connector to the current release 11.1.1.5.0.
The following sections discuss the procedure to upgrade the connector:
Note:
-
Upgrade of the connector from release 9.0.4.x to 11.1.1.x. is supported.
-
Before you perform the upgrade procedure, it is strongly recommended that you create a backup of the Oracle Identity Manager database. Refer to the database documentation for information about creating a backup.
-
As a best practice, first perform the upgrade procedure in a test environment.
2.4.1 Preupgrade Steps
Perform the following preupgrade steps:
Note:
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager 11g Release 1 PS1 BP07 (11.1.1.5.7), then you must apply patch 16819090.
To download a patch, sign in to My Oracle Support and search for the patch number on the Patches and Updates page at:
- Perform a reconciliation run to fetch all latest updates to Oracle Identity Manager.
- Define the source connector (an earlier release of the connector that must be upgraded) in Oracle Identity Manager. You define the source connector to update the Deployment Manager XML file with all customization changes made to the connector. See Managing Connector Lifecycle in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for more information.
- If required, create the connector XML file for a clone of the source connector.
- Disable all the scheduled jobs.
2.4.2 Upgrade Steps
Depending on the environment in which you are upgrading the connector, perform one of the following steps.
-
Staging Environment
Perform the upgrade procedure by using the wizard mode.
-
Production Environment
Perform the upgrade procedure by using the silent mode.
See Managing Connector Lifecycle in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about the wizard and silent modes.
2.4.3 Postupgrade Steps
Postupgrade steps involve running the SQL script, running the Form Version Contol (FVC) utility, packaging the arapiVERSION_NUM.jar and log4j-1.2.14.jar files with the connector bundle jar, and so on.
-
Perform the postupgrade procedure documented in Managing Connector Lifecycle in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager.
-
Run the PostUpgradeScript.sql script as follows:
-
Connect to the Oracle Identity Manager database by using the OIM User credentials.
-
Run the PostUpgradeScript. This script is located in the Upgrade directory on the installation media.
-
-
Run the FVC utility to manage data changes on a form after an upgrade operation. To do so:
-
In a text editor, open the fvc.properties file located in the OIM_DC_HOME directory and include the following entries:
ResourceObject;BMCRO FormName;UD_BMC FromVersion;9.0.4.1 ToVersion;SPECIFY_THE_VERSION_OF_FORM_THAT_IS_IN_THE_ACTIVE_STATUS_AFTER_THE_UPGRADE -
Run the FVC utility. This utility is copied into the following directory when you install the design console:
For Microsoft Windows:
OIM_DC_HOME/fvcutil.bat
For UNIX:
OIM_DC_HOME/fvcutil.sh
When you run this utility, you are prompted to enter the login credentials of the Oracle Identity Manager administrator, and the logger level and log file location.
See Also:
Using the Form Version Control Utility in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed information about the FVC utility
-
-
Package the arapiVERSION_NUM.jar and log4j-1.2.14.jar files with the connector bundle jar as follows:
-
Extract the contents of the org.identityconnectors.bmc-1.0.1115.jar file into a temporary directory.
-
Create a directory named lib.
-
Copy the arapiVERSION_NUM.jar and log4j-1.2.14.jar files to the lib directory.
-
Update the connector bundle (org.identityconnectors.bmc-1.0.1115.jar) by running the following command:
jar -cvfm org.identityconnectors.bmc-1.0.1115.jar META-INF/MANIFEST.MF *
Note:
While updating the connector bundle, ensure that META-INF\MANIFEST.MF file is unchanged.
-
-
Run the Oracle Identity Manager Upload JARs utility to post the new connector bundle (updated in Step 4) to the Oracle Identity Manager database. This utility is copied into the following location when you install Oracle Identity Manager:
Note:
Before you use this utility, verify that the
WL_HOMEenvironment variable is set to the directory in which Oracle WebLogic Server is installed.For Microsoft Windows:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.bat
For UNIX:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.sh
When you run the utility, you are prompted to enter the login credentials of the Oracle Identity Manager administrator, URL of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer, context factory value, type of JAR file being uploaded, and the location from which the JAR file is to be uploaded. Specify 4 as the value of the JAR type.
-
Configure the upgraded IT resource of the source connector. See Configuring the IT Resource for the Target System for information about configuring the IT resource.
-
Purge the cache to get the changes reflected in Oracle Identity Manager. See Purging Cache in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for information on purging cache.
-
If you are using Oracle Identity Manager release 11.1.2.x or later, then all changes made to the Form Designer of the Design Console must be done in a new UI form as follows:
-
Log in to Oracle Identity System Administration.
-
Create and activate a sandbox. See Creating and Activating a Sandbox.
-
Create a new UI form to view the upgraded fields. See Creating a New UI Form for more information about creating a UI form.
-
Associate the newly created UI form with the application instance of your target system. To do so, open the existing application instance for your resource, from the Form field, select the form (created in Step 8.8.c), and then save the application instance.
-
Publish the sandbox. See Publishing a Sandbox.
-
After upgrading the connector, you can perform either full reconciliation or incremental reconciliation. This ensures that records created or modified since the last reconciliation run (the one that you performed in Preupgrade Steps) are fetched into Oracle Identity Manager. From the next reconciliation run onward, the reconciliation engine automatically enters a value for the Latest Token attribute.
Before you perform lookup field synchronization, ensure to remove all preupgrade entries from the lookup definitions Oracle Identity Manager. After upgrade these values must be synchronized with the lookup fields in the target system.
See Configuring Reconciliation for more information about performing full or incremental reconciliation.