| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Oracle Solaris Administration: IP Services Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |

|
Oracle Solaris Administration: IP Services Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library |
1. Planning the Network Deployment
2. Considerations When Using IPv6 Addresses
3. Configuring an IPv4 Network
4. Enabling IPv6 on the Network
5. Administering a TCP/IP Network
7. Troubleshooting Network Problems
11. Administering the ISC DHCP Service
12. Configuring and Administering the DHCP Client
13. DHCP Commands and Files (Reference)
14. IP Security Architecture (Overview)
Encapsulating Security Payload
Security Considerations When Using AH and ESP
Authentication and Encryption Algorithms in IPsec
Authentication Algorithms in IPsec
Encryption Algorithms in IPsec
Transport and Tunnel Modes in IPsec
IPsec and Oracle Solaris Zones
16. IP Security Architecture (Reference)
17. Internet Key Exchange (Overview)
19. Internet Key Exchange (Reference)
20. IP Filter in Oracle Solaris (Overview)
Part IV Networking Performance
22. Integrated Load Balancer Overview
23. Configuration of Integrated Load Balancer (Tasks)
24. Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (Overview)
25. VRRP Configuration (Tasks)
26. Implementing Congestion Control
Part V IP Quality of Service (IPQoS)
27. Introducing IPQoS (Overview)
28. Planning for an IPQoS-Enabled Network (Tasks)
29. Creating the IPQoS Configuration File (Tasks)
30. Starting and Maintaining IPQoS (Tasks)
31. Using Flow Accounting and Statistics Gathering (Tasks)
A configured tunnel is a point-to-point interface. The tunnel enables one IP packet to be encapsulated within another IP packet. A correctly configured tunnel requires both a tunnel source and a tunnel destination. For more information, see How to Create and Configure an IP Tunnel.
A tunnel creates an apparent physical interface to IP. The physical link's integrity depends on the underlying security protocols. If you set up the security associations (SAs) securely, then you can trust the tunnel. Packets that exit the tunnel must have originated from the peer that was specified in the tunnel destination. If this trust exists, you can use per-interface IP forwarding to create a virtual private network (VPN).
You can add IPsec protections to a VPN. IPsec secures the connection. For example, an organization that uses VPN technology to connect offices with separate networks can add IPsec to secure the traffic between the two offices.
The following figure illustrates how two offices form a VPN with IPsec deployed on their network systems.
Figure 14-7 Virtual Private Network
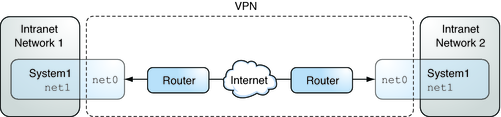
For a detailed example of the setup procedure, see How to Protect a VPN With IPsec in Tunnel Mode.