| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
International Language Environment Guide Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
International Language Environment Guide Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library |
2. Unicode and UTF-8 Locale Support
3. Working with Languages and Locales
4. Desktop Keyboard Preferences and Input Methods
About Keyboard Layout and Input Method Settings
Keyboard Layout Selection in GNOME Desktop Manager
How to Select the Keyboard Layout in GNOME Desktop Manager
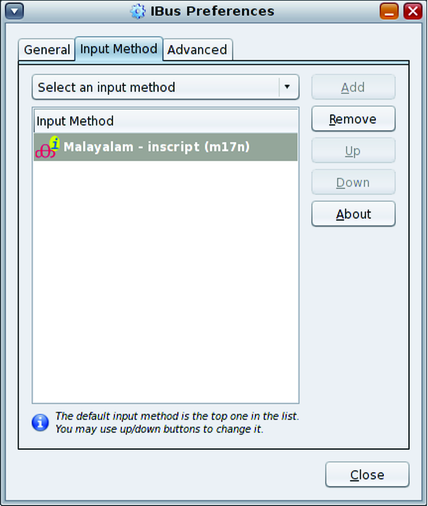
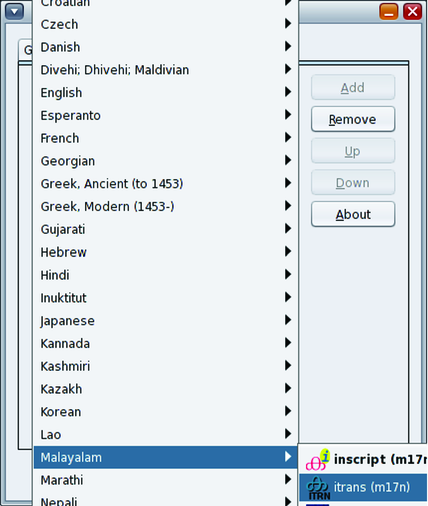
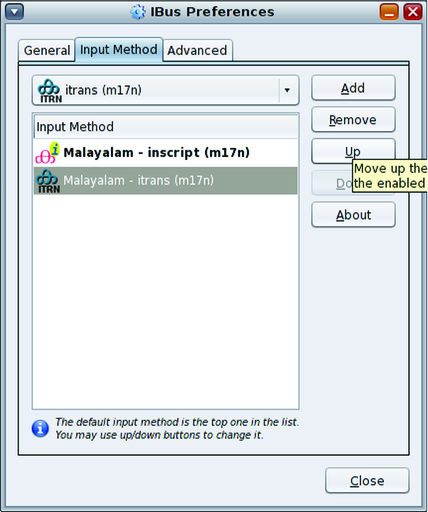
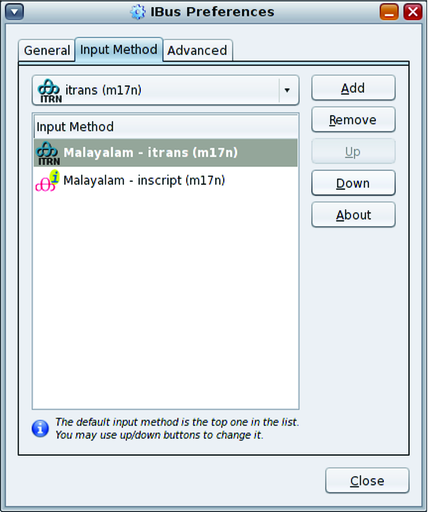
How to Activate and Deactivate Input Methods
Language Engines Available on the IBus Input Method Framework
Input Method for Indic Languages
IBus Virtual Keyboard (ibus-keyboard)
Internet Intranet Input Method Framework
How to Use the ATOK and Wnn Language Engines With IIIMF
How to Set Keyboard Preferences and Customization
Keyboard Layout Options and Default Behavior
GNOME Keyboard Layout Indicator (Keyboard Selector)
Keyboard Layout Settings Using the X Keyboard Extension (setxkbmap)
Input Method (IM) is a mechanism to input specific characters which are not provided on input devices like a keyboard to the various desktop applications. IM is required for some languages such as Chinese, Indic, Japanese, Korean, and Thai because these languages contain a much larger set of characters than what is available on the input devices. IM converts combinations of keystrokes from input devices to language-specific characters, and sends the information back to the focused application.
Input Method has two main components, the IM Framework and the IM Language Engine. The IM Framework is a software component providing functions that enable cooperation between the IM Language Engine and user applications. The IM Language Engine is a software component which takes keystroke combinations from the IM Framework and converts them to specific language characters to send them back to the IM Framework.
IBus is the default IM Framework on the Oracle Solaris desktop system. IIIMF is available in the installation repository as a secondary IM Framework.
By default, Input Method is activated only when you log in into the following languages:
Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Traditional)
Japanese
Korean
Indic
Thai
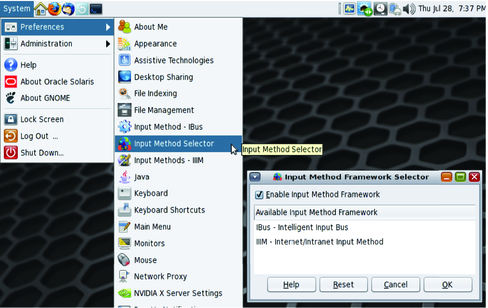
For other languages, if necessary, IM can be activated manually through the Input Method Framework Selector.
The Input Method Framework Selector (imf-selector) is a configuration tool used for selecting the preferred Input Method Framework and enabling or disabling them for the desktop session.
The Input Method Framework Selector window appears.
Intelligent Input Bus (IBus) for the Linux and Unix operating systems is a powerful multilingual Input Method Framework working with many open-source IM language engines. IBus uses bus-like architecture to process communication between the IBus IM Framework and the IM language engines. This process runs per user session. There is no shared process between different user desktop sessions.
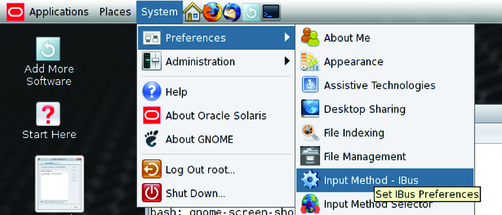
IBus is configured per user by the IBus Preference tool (ibus-setup). To access this tool, choose System-> Preferences-> Input Method - IBus. The following tasks describe some major configuration changes you can make.
There are three possible locations for language panel position.
Embedded in menu (default) - Language panel is embedded in notification area of GNOME panel
When active - Language panel is shown as independent window only when Input Method is activated
Always - Language panel is always shown as independent window.
The following Language Engines are available on the IBus Input Method Framework.
Installed by default during installation process for the desktop
Anthy - Japanese
Chewing - Traditional Chinese
Hangul - Korean
IBus-Sayura -- Sinhala
IBus-XKBC - Keyboard Emulation IM Engine framework
SunPinyin - Simplified Chinese
Various Language Engines based on m17n
Optional Language Engines
Pinyin - Simplified Chinese Language Engine
Various Language Engines based on IBus table framework
The following table summarizes the available input methods for Indic languages.
Table 4-1 Input Method for Indic Languages
|
IBus XKBC emulates keyboard layout usingthe XKeyboard Configuration Database. All keyboard layouts available in XkeyboardConfig, including keyboard layout variants, can be emulated on the IBus IM Framework. IBus XKBC is available in the Other language category in the IBus Preference tool. The IBus XKBC help provides detailed configuration information.
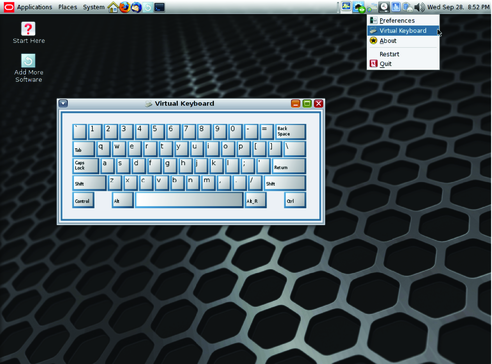
IBus Virtual Keyboard is a graphical keyboard emulator based on theIBus XKBC Language Engine. It displays a graphical keyboard in a window, and enables the user to input characters to the focused application by clicking key icons. As with IBus XKBC, the IBus Virtual Keyboard supports various keyboard layouts and variants for emulation. To launch the IBus Virtual Keyboard, choose Virtual Keyboard from the IBus menu in the GNOME panel, as shown in the following figure.
To display the configuration menu for the virtual keyboard, right-click on the Virtual Keyboard application window.
Figure 4-1 Virtual Keyboard
The Internet Intranet Input Method Framework (IIIMF) is another IM Framework in Oracle Solaris 11, which has been supported since Solaris 9. IIIMF runs per user instead of as a shared system-wide process. The configuration tool for the IIIM is the Input Method Preference Editor (iiim-properties). To access the tool, choose System->Preferences-> Input Method - IIIM.
IIIMF has two very powerful Japanese language engines, ATOK and Wnn. The following procedure describes how to use the ATOK or Wnn language engines with IIIMF.
Note - For more information about this tool, see the ATOK for Oracle Solaris User Guide and Wnn8 User's Guide provide more information for these language engines. These documents are available in Japanese only.
IIIMF core package: system/input-method/iiim
ATOK package: system/input-method/iiim/atok
Wnn package: system/input-method/iiim/wnn
To list the IIIMF Language Engines available for installation, run the following command:
$ pkg list -a system/input-method/iiim/*
IIIMF will be used for your desktop session at the next login. (The desktop session needs to be restarted.)
# svcadm enable wnn8/server
The Oracle Solaris 11 Desktop has more than 400 keyboard layouts available for more than 100 languages. Multiple keyboard layout variants are available for almost every language. Regardless of the keyboard layout model and physical layout, you can always configure and use any keyboard layout available in the Oracle Solaris 11 Desktop. Use the GNOME Keyboard Preferences tool to set and customize keyboard preferences such as keyboard model, layout, variant, and so on.
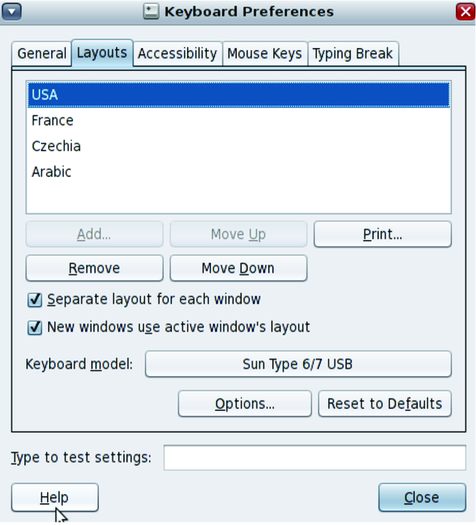
The Layouts tab provides all necessary tools to set and customize the keyboard layout. You can add up to 4 different keyboard layouts and easily switch between them by using the Keyboard Layout Indicator menu in the panel or by setting a keyboard shortcut to switch between them.
In the Layouts tab you can also customize different settings of your keyboard, such as keyboard model, specific keyboard layout variants or you can set special behavior for specific keys such as Shift, Alt, Meta, Super, Hyper, CapsLock, etc.
The layout at the top of the list in the Layouts tab is the default layout. You can move layouts up and down in the list by using the Move Up and Move Down buttons.
The following illustration shows the Layouts tab.
The following list shows the most common transactions performed in the Layouts tab in the Keyboard preferences window:
In case you use more than one keyboard layout, you can assign a shortcut to switch between them easily.
Keyboard Layout Indicator is automatically activated and visible on the panel when two or more keyboard layouts are selected as shown in the following figure. When only one keyboard is selected (default behavior), the Keyboard Layout Indicator is not visible on the panel.
Figure 4-2 Keyboard Layout Indicator

When the Keyboard Layout Indicator menu is activated and visible on the panel you can switch between selected keyboard layouts by using the mouse. Single click to immediately switch to the next keyboard layout. Right-click to open a menu with three options:
Groups – Contains a list of selected keyboard layouts.
Keyboard Preferences – Launches the Keyboard Layout Preferences window
Show Current Layout – Launches a window with an interactive application showing the current keyboard layout.
You can use the setxkbmap(1), a command to set and customize all keyboard layout settings in the X Server from the command line rather than using the GNOME Keyboard Layout Preference tool.
The setxkbmap command maps the keyboard to use the keyboard layout determined by the options specified on the command line. Configurable options of the setxkbmap command include geometry, keyboard model, layout symbols, layout variant, rules, and the like.
The following example shows how to set two keyboard layouts (US/English and French) from the command line:
$ /usr/bin/setxkbmap us,fr
For more information, see the setxkbmap(1) man page.