54 Set Up Ledger Depreciation Rules
This chapter contains the topic:
A ledger depreciation rule is a definition of how a group of assets is depreciated. Ledger depreciation rules allow you to gather your assets into groups that require different depreciation methodologies.
54.1 Setting Up Ledger Depreciation Rules
From Fixed Assets (G12), enter 29
From Fixed Asset System Setup (G1241), choose Ledger Depreciation Rules
By using the various keys that determine groupings, you can group assets that have very little in common, other than their depreciation requirements. Depending on your requirements, you can create groups using any combination of the following parameters:
-
Company
-
Accounting category
-
Depreciation category
-
Asset cost account
-
Subledger and subledger type
-
Effective dates
Because you can use any combination of these parameters, you do not have to set up your rules by company. This allows you to group your assets across companies if that is more efficient. For example, you can group your assets by depreciation category alone and know that all those assets, regardless of which company they reside in, are treated exactly the same way when you calculate depreciation.
Caution:
You must cover your entire asset base with the ledger depreciation rules you set up. Each ledger depreciation rule must have at least the AA ledger defined.To set up ledger depreciation rules
On Company Ledger Depreciation Rules
Figure 54-1 Ledger Depreciation Rules screen
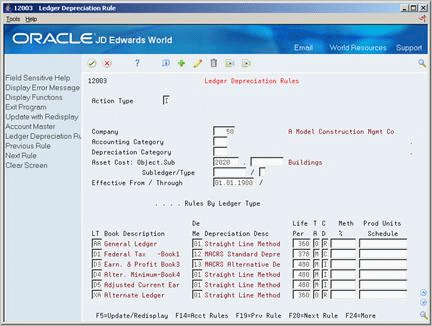
Description of "Figure 54-1 Ledger Depreciation Rules screen"
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Company
-
Accounting Category
-
Depreciation Category
-
Asset Cost Object
-
Asset Cost Subsidiary (if applicable)
-
Asset Cost Subledger (if applicable)
-
Subledger Type (if applicable)
-
Effective From Date
-
Effective Through Date
-
-
For each ledger that you want to associate with the depreciation accounting rule, complete the following fields:
-
Ledger Type
-
Depreciation Method
-
Life Periods
-
TA (Initial Term Apportionment Code)
-
Compute Direction
-
-
For fixed percentage depreciation methods, complete the following field:
-
Method Percent
-
-
If the depreciation method is Units of Production, complete the following field:
-
Production Units Schedule
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Company | A code that identifies the company that owns or is assigned to an asset or group of assets. You set up companies in the system to represent a reporting level that has a complete balance sheet and any intercompany transactions with other companies. You can define a specific organization, entity, partnership, and so on, as a company. You use Company Numbers and Names to define the companies in your system.
Note: Use Company 00000 only for default values, such as dates and Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAIs). You cannot use Company 00000 when entering transactions. |
| Accounting Category | A user defined code (12/C1) that determines the accounting class category code. You use this accounting category code to classify assets into groups or families, for example, 100 for land, 200 for vehicles, and 300 for general office equipment.
It is recommended that you set up major class codes that correspond to the major general ledger object accounts in order to facilitate the reconciliation to the general ledger. Note: If you do not want to use the major accounting class code, you must set up a value for blank in the user defined code table. |
| Depreciation Category | A user defined code (12/C2) that is used to classify assets into groups or families. You use the equipment category code as a subclass to further define the accounting class, for example, 310 for copy equipment, 320 for projectors, and 330 for typewriters within the accounting class for general office equipment.
Note: If you do not want to use the major equipment class, you must set up a value for blank in the user defined code table. |
| Asset Cost Object Default | The general ledger account (object number) used to record a fixed asset's acquisition cost. Within each company, you define default coding instructions for asset cost accounts. Then, based on these default codes, when you set up a new asset, the system automatically assigns the following:
|
| Asset Account Subsidiary Default | The subsidiary account used in conjunction with the asset cost account. |
| Subledger - G/L | A code that identifies a detailed auxiliary account within a general ledger account. A subledger can be an equipment item number, an address book number, and so forth. If you enter a subledger, you must also specify the subledger type. |
| Subledger Type | A user defined code (00/ST) that is used with the Subledger field to identify the subledger type and subledger editing. On the User Defined Codes screen, the second line of the description controls how the system performs editing. This is either hard-coded or user defined. For example:
A – Alphanumeric field, do not edit N – Numeric field, right justify and zero fill C – Alphanumeric field, right justify and blank fill |
| Effective From / Through | The date on which an address, item, transaction, or table becomes active or the date from which you want transactions to display. The system uses this field depending on the program. For example, the date you enter in this field might indicate when a change of address becomes effective, or it could be a lease effective date, a price or cost effective date, a currency effective date, a tax rate effective date, and so on. |
| Ledger Type | The user defined ledger type code (list 09, type LT) that identifies the account ledger, or book, for the asset. You can maintain as many sets of depreciation books (ledger types) for an asset as you need so you can depreciate an asset in different ways for different purposes. For example, an asset might have a three-year life for tax purposes, but a five-year life for financial statement purposes. Each set of books can have different depreciation methods and depreciation values. |
| Depreciation Method | The user defined code (system 12, type DM) that indicates the method of depreciation for the specified book. In addition to any user defined depreciation methods you set up for your company, the following standard depreciation methods are available in the Fixed Assets system:
00 – No depreciation method used 01 – Straight Line Depreciation 02 – Sum of the Year's Digits 03 – 125% Declining Balance to Cross-Over 04 – 150% Declining Balance to Cross-Over 05 – Double Declining Balance to Cross-Over 06 – Fixed % on Declining Balance 07 – ACRS Standard Depreciation 08 – ACRS Optional Depreciation 09 – Units of Production Depreciation 10 – MACRS Luxury Cars - Domestic 11 – Fixed % Luxury Cars - Foreign 12 – MACRS Standard Depreciation 13 ACRS Alternative Depreciation 14 – ACRS Alternate Real Property 15 – Fixed % of Cost 16 – Fixed % on Declining Balance to Cross-Over 17 – AMT Luxury Auto 18 – ACE Luxury Auto Note: Any additional depreciation methods you create for your organization must have an alpha code and are considered User Defined Depreciation. |
| Life Per | The life of an asset in months or periods. The system uses months or periods only to express the life of an asset. For example, if your company uses a 12-month calendar, then a five-year ACRS asset has a 60-month life. If your company uses a 13-month calendar, then a five-year ACRS asset has a 65-month life, and so on. You must specify a life month value for all user defined depreciation methods, and for all standard depreciation methods, except the standard methods 00, 06, 09, 11, and 15. |
| Depreciation Information | A code for additional depreciation information. This code is used for Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and averaging conventions. The system validates the code you enter in this field against user defined code table 12/AC. Valid codes are:
0 – No ITC Taken 1 – Three Year Method (3 1/3%) 2 – Five Year Method (6 2/3%) 3 – Seven Year Method (10%) 4 – ACRS Method with Basis Reduction (10% ITC) 5 – ACRS Method without Basis Reduction (2% ITC or No ITC) A – Actual Date of Depreciation Start Period M – Mid-Month Convention Q – Mid-Quarter Convention Y – Mid-Year Convention P – Middle of Period F – First-half/Second-half W – Whole Year N – First Day of Next Period R – First Day of Next Year S – Actual Start Date for Primary Rule/First Day of Period for Secondary Rule Note: Numeric codes apply to standard depreciation methods only. To determine the date for F (First-half/Second-half), use the following guidelines:
|
| Computation Method - ITD or Rem | A code that indicates the method of computation that the system uses to calculate depreciation based on the depreciation method you specify.
Valid codes are: C – Current year to date. Calculates only the current year's depreciation. I – Inception to date. Recalculates the entire depreciation amount from the start date through the current year. Prior-year depreciation is then subtracted to determine current year depreciation. This method results in a one-time current period correction for any errors in prior period depreciation. F – Inception to date. Calculates inception to date for the first rule (if there are two rules) and uses a C for the second rule. P – Current period. Calculates depreciation for the current period and then extrapolates the annual amount based on the cumulative percent from the period pattern and year-to-date posting. Any depreciation calculated for the current period is subtracted. R – Remaining months. Depreciates the net book value as of the beginning of the current tax year over the remaining life of the asset. This results in the amortization of prior period calculation errors over the remaining life of the asset. |
| Method % | Enter the percentage you want the system to use when calculating depreciation. Use whole numbers. For example, enter 10 for 10%. The system uses a percentage when computing the following methods of depreciation:
06 – Fixed % on Declining Balance. (This method of depreciation is commonly used by Canadian and utility companies.) 11 – Fixed % Luxury Car - Foreign. 15 – Fixed % of Cost. 16 – Fixed % on Declining Balance to Cross-Over. The system also uses this field to compute any user defined depreciation method in which you specify a percentage. |
| Prod Units Schedule | The alphanumeric code you assign to a units of production schedule. You must set up the schedules you want to use for method 09 (Units of Production Depreciation) in advance on the Units of Production Schedule screen. |