1 Overview of the Oracle Database Firewall Installation
This chapter covers the following topics:
Downloading the Latest Version of This Manual
You can download the latest version of this manual from the Oracle Database Firewall Web site, which is in the Database section of Oracle Technology Network. The URL is as follows:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/indexes/documentation/index.html
About Installing Oracle Database Firewall
Oracle Database Firewall is a system for securing and monitoring data in SQL databases. It blocks and produces warnings of attempted attacks, logs activity, and provides intelligent tools to assess vulnerabilities.
The components that you will install are as follows:
-
One or more Database Firewalls. Each Database Firewall performs the following tasks:
-
Handles real-time recording and analysis of SQL transaction requests and responses from one or more Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Sybase Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE), Sybase SQL Anywhere, and IBM DB2 LUW databases.
-
Categorizes SQL transactions
-
Enforces data policies with the ability to block certain SQL statements if specified in the policy
-
Enables real-time alerting and event propagation
-
Sends SQL traffic log data to the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server and then deletes it locally
You will install each Database Firewall onto any Intel or AMD hardware that supports Oracle Enterprise Linux (OEL) 5.5, which will use Oracle Linux. This Linux server will be used exclusively for Database Firewall. Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide describes how to manage the standalone Database Firewall.
-
-
One or more Oracle Database Firewall Management Servers. The Management Server performs the following tasks:
-
Aggregates SQL data from one or more Database Firewalls
-
Serves as a reporting platform for business reports that describe this SQL data
-
Centralizes the distribution of data control policies, but still enables the use of different policies for specific databases
-
Stores and manages log files, including archiving and restoring the log files
-
Remotely manages all Database Firewalls that are connected to it
-
Integrates with third-party applications, such as HP ArcSight SIEM
You will install each Management Server onto an x86 server, which will use Oracle Linux. This Linux server will be used exclusively for Management Server. Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide describes how to manage the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server.
-
-
One or more Oracle Database Firewall Analyzers. The Analyzer reads the logs created by the Database Firewalls to create or update the policy used to block, alert, log, or permit SQL statements for the database. Oracle Database Firewall Security Guide describes how to use the Analyzer. You will install the Analyzer on a Microsoft Windows client computer.
After you install these components, you must add the databases that you want to monitor, and configure remote or local monitoring for each database. Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide describes how to configure Oracle Database Firewall to connect to your databases. For a list of supported database platforms for these databases, see "Supported Database Versions".
Figure 1-1 illustrates the architecture of your system after you have installed and configured Oracle Database Firewall. This diagram shows a high availability configuration for two of the Database Firewalls. "Deployment Scenarios" describes other possible deployments, including high availability configurations. The diagram also shows remote and local monitor configurations, which enable you to send SQL traffic directly from the protected database. The database using the remote or local monitor connects directly to a Database Firewall. Using the local monitor, the Database Firewall connects to the database to retrieve data. The remote monitor sends data from the database host to the Database Firewall.
Figure 1-1 Architecture of Oracle Database Firewall After Installation
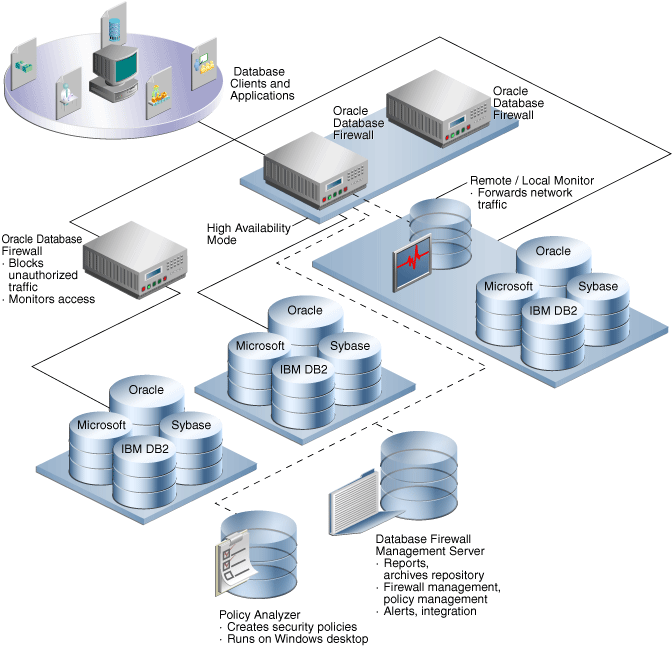
Description of "Figure 1-1 Architecture of Oracle Database Firewall After Installation"
General Oracle Database Firewall Installation Procedure
You will follow these general steps to install Oracle Database Firewall:
-
Plan the network scenario that best suits the needs of your site.
See "Planning the Oracle Database Firewall Installation" and "Deployment Scenarios".
-
Ensure that your system meets the requirements described in this guide.
See Chapter 2, "Oracle Database Firewall Preinstallation Requirements."
-
Install Oracle Database Firewall and Oracle Database Firewall Management Server.
As part of this process, you will change the administrator password.
See "Installing Database Firewall and Database Firewall Management Server"
-
Install the Analyzer.
After you complete the installation, the Database Firewall administrator is responsible for configuring Oracle Database Firewall to monitor SQL data coming from your protected databases. See Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide.
You may periodically need to update Oracle Database Firewall software. Chapter 4, "Updating the Oracle Database Firewall Software," provides instructions.
Planning the Oracle Database Firewall Installation
It is essential that Oracle Database Firewall monitors all network traffic to the protected database. In general, this means that each Database Firewall must connect to a point in the network that is close to the database. An additional advantage of this approach is that Oracle Database Firewall will process less non-database traffic.
An alternative approach is to place an Oracle Database Firewall behind a client application, or at strategic points in the network. However, in all cases, you must ensure that database network traffic does not bypass the Oracle Database Firewall system.
If statement blocking is not used, then you should use a spanning port to direct network traffic to an Oracle Database Firewall port. The spanning port enables statement scanning without affecting network performance. The Oracle Database Firewall components connect using standard gigabit Ethernet network adapters.
If statement blocking is required (DPE mode), then you must place the Oracle Database Firewall in between the monitored database and the database clients and applications. You must also ensure that the Database Firewall bridge IP address is on the same subnet as the database. In the unlikely event that an Oracle Database Firewall should fail, if you have the appropriate networking hardware, all network traffic passes through, ensuring service continuity.
Note:
To simplify deployment, Oracle Database Firewall requires no change to the IP address of the database server or other network devices.See Also:
Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide for detailed information about configuration, such as configuring local monitoring.Deployment Scenarios
You can use any of the following deployment scenarios:
-
Install Database Firewall and Database Firewall Management Server onto one server. In this scenario, the simplest, you install the Database Firewall onto one server, which uses an Oracle Linux environment. Then, you will install the Analyzer onto a client Microsoft Windows computer.
-
Install one or more Database Firewalls each onto a separate server and one Database Firewall Management Servers onto one server. In this scenario, you install Database Firewall onto separate servers. Each of these servers communicates with one central Database Firewall Management Server. In turn, each protected database connects to a Database Firewall. You can install as many Database Firewalls as your site needs.
-
Configure one or more Database Firewalls and Database Firewall Management Servers for high availability. In this scenario, you can build on the previous scenario by adding servers for high availability. For example, you can configure one additional Database Firewall Management Server for the first Management Server, and you can configure an additional Database Firewall for each existing Database Firewall. One is used as the primary device, and the other is designated as the secondary device. The primary server performs monitoring and all normal operations, while the secondary server only monitors network traffic. The secondary server alerts only if the primary server fails.
You can install a maximum of two Management Servers for your system for use as a resilient pair.
-
Configure a local monitor. If you want to monitor the SQL data from connections made directly to the database server that do not pass through the network, then you can install the local monitoring software onto the protected database. Then, configure this database to communicate directly with a Database Firewall, which will retrieve data from the database and send SQL data to a Management Server. Be aware that local monitoring does not block SQL statements. For detailed information about local monitoring, see Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide.
-
Configure a remote monitor. If you have many small databases in a distributed environment and you want Oracle Database Firewall to manage all of these small databases centrally, then you can install a remote monitor on a Linux server that can see all the database traffic that is sent to that Database Firewall. (Be aware that remote monitoring does not block SQL statements.) Typically, Database Firewall server is located close to the database and connected to a span port on a switch. The remote monitor runs from the database host's operating system and sends the database SQL traffic over the network to a Database Firewall that manages the remote monitor installations. For detailed information about remote monitoring, see Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide.
For all of these scenarios, follow these guidelines:
-
Install Oracle Database Firewall on a dedicated x86 server. The Database Firewall installation formats the hard drives and any existing data on them is lost.
-
Install Oracle Database Firewall in a physically secure, controlled environment.
-
Ensure that the database network is logically or physically separate from the network that runs the Database Firewall applications. Configure the network firewalls, switches, taps, and hubs specifically to exclude traffic to and from unnecessary IP addresses.
-
Ensure that the Database Firewalls are as close as possible, through the networking route, to the database server that you want to protect. The Management Server can be in any location, as long as it can access the other Database Firewall components.
-
Ensure that Database Firewall has at least three network ports. The Management Server only needs one network port.
-
Be aware that in DPE mode, the Database Firewall system blocks all IPv6 traffic, regardless of the policies set in place. In monitoring mode, the Database Firewall does not detect IPv6 traffic.
Security Guidelines
Consult the Oracle Database Firewall Security Guide for information on protecting your data and general recommendations about deploying Database Firewall in a network and in special configurations.