 Understanding EPM Multiple Currency Processing Concepts
Understanding EPM Multiple Currency Processing ConceptsPeopleSoft enables you to manage financial information in multiple currencies. PeopleSoft provides specific input, processing, and reporting features that support the European Common Currency (euro), currency conversions, remeasurement, revaluation, translation, and a complete audit trail of all multi-currency processing.
You can define and maintain tables that describe currency codes, exchange rates, market rates, and currency rate types. All PeopleSoft products use the same market rate and currency pages and tables, which enables you to administer centralized currency controls throughout the integrated product lines.
This chapter provides an overview of multiple currency processing concepts and discusses how to:
Set up EPM currency tables
Set up market rates
Define currency quotations
Establish market rates
Calculate currency rates
Configure currency precision
Note. The multi-currency processing setup tasks documented
in this chapter are common to both the EPM Warehouses and the Analytical Applications.
However, additional multi-currency processing setup tasks are required for
the EPM Warehouses and the Analytical Applications:
EPM Warehouses: see the chapter entitled 'Implementing
Currency Conversion' in your specific EPM warehouse PeopleBook (for example,
the PeopleSoft Campus Solutions Warehouse PeopleBook).
Analytical Applications: see the chapter entitled
'Setting Up and Running Currency Conversion for the OWE' in this PeopleBook.
 Understanding EPM Multiple Currency Processing Concepts
Understanding EPM Multiple Currency Processing ConceptsBefore you begin to process multiple currencies, you should understand the concepts behind multi-currency processing in EPM.

 Currency and Calculation Types
Currency and Calculation Types
PeopleSoft software uses terminology associated with currency that is consistent with generally accepted accounting principles and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) accounting standards.
Currency refers to the denomination of a monetary transaction. PeopleSoft applications use a currency code (CURRENCY_CD) to identify and track individual currencies. Although the system does not require it, you should use International Standards Organization (ISO) currency codes. PeopleSoft applications have no limit on the number of currencies that you can use.
Important currency terms are:
Important currency calculation types are:

 Currency Precision
Currency Precision
Currency dictates the precision of monetary amounts. For example, United States dollar amounts have two digits to the right of the decimal and Japanese yen have none. The system addresses currency precision as follows:
PeopleSoft software provides currency-sensitive amount fields with a standard length of 23.3, or 23 digits to the left of the decimal point and 3 digits to the right of the decimal point.
By default, the system rounds all currency-sensitive amount fields to the currency precision of the associated currency. This action is a PeopleSoft PeopleTools option that you can deactivate.
All numbers on SQR reports are currency-sensitive. For reporting with Crystal and PS/nVision, the display is equal to the field precision, but you can increase the number of decimal places.

 Revaluation
Revaluation
When you adjust the base currency value of balance sheet accounts that are maintained in a foreign currency, this is called revaluation. You generally perform revaluations at the end of each accounting period to reflect the actual base currency value of assets and liabilities as exchange rates fluctuate between the base and foreign currencies. You make adjusting entries to the accounts that are being revalued with an offsetting entry to a revaluation gain or loss account. The gain or loss account is sometimes referred to as an unrealized exchanged gain or loss.
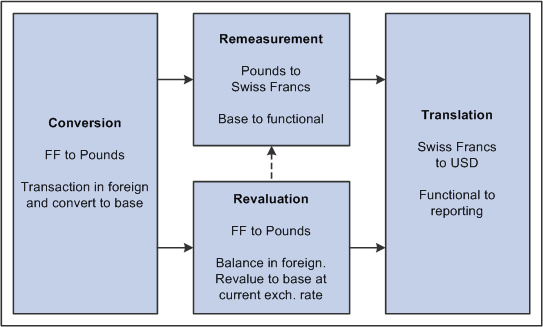
Revaluation
In this example, a London-based subsidiary of a Swiss company records a purchase made in Mexican pesos. The Swiss company is owned by a United States corporation. The following table correlates the terminology and the currencies:
|
Foreign currency |
MXN (Mexican Peso) |
|
Base currency |
GBP (British pounds) |
|
Functional currency |
CHF (Swiss francs) |
|
Reporting currency |
USD (United States dollars) |

 Currency as a ChartField
Currency as a ChartField
You get the best results when you record multi-currency transactions with a currency ChartField. This approach enables you to record multiple currencies in the same ledger and reinforces the concept of a ledger's role as a record for an entire category of information (such as actuals, budgets, forecasts, or commitments).

 Differentiating Between the Currency Conversion Process of the EPM
Warehouses and the Analytical Applications
Differentiating Between the Currency Conversion Process of the EPM
Warehouses and the Analytical Applications
Separate currency conversion processes are required in EPM, one for the EPM Warehouses and one for the Analytical Applications. After performing the basic multi-currency processing setup tasks in this chapter, you must perform additional multi-currency processing setup tasks that are specific either to the EPM Warehouses or the Analytical Applications. It is important to understand the difference between the two currency conversion processes, as they are quite different.
The following table describes the differences between the EPM Warehouse and Analytical Application currency conversion processes:
|
Subject |
Analytical Application Currency Conversion |
EPM Warehouse Currency Conversion |
|
Technology Platform |
Based on Application Engine (AE) technology for seamless integration with application processing that is also based on AE technology. |
Based on ETL technology. |
|
Set Processing |
Business unit is required in set processing. |
Business unit is optional in set processing. This allows for a single conversion process to convert all transaction amounts for global reporting. |
|
Business/Conversion Rules |
Currency conversion involves complex rules for compliance reporting and simulation. The complex rules are stored in various EPM metadata. |
Currency conversion is used to convert monetary amounts to a common currency for trend analysis. Trend analysis requires a simple currency conversion rule based on an exchange date and rate type that does not require extensive rule setup. |
The remaining currency conversion setup tasks required for the EPM Warehouses can be found in your specific EPM warehouse PeopleBook (for example, PeopleSoft Campus Solutions Warehouse PeopleBook).
The remaining currency conversion setup tasks required for the Analytical Applications can be found in this PeopleBook.
See Setting Up and Running Currency Conversion.
 Setting Up EPM Currency Tables
Setting Up EPM Currency Tables
Currency code pages define each currency that you use. To meet your multicurrency requirements, PeopleSoft supports the euro and delivers the Currency Code table with many common ISO standard currencies. The table also supports the ISO standard of zero, two, and three decimal positions.
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move currency code data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the currency code PIA pages to redefine or modify your existing currency code data.
This section discusses how to:
Maintain currency codes.
Update the status of a euro currency code.

 Pages Used to Maintain Currency Tables
Pages Used to Maintain Currency Tables|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Currency Code |
CURRENCY_CD_TABLE |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Codes |
Maintain currency codes and the currency precision by currency. |
|
Currency Codes (Euro) |
CURRENCY_EURO |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Code (Euro) |
Update the status of a euro currency code. |

 Maintaining Currency Codes
Maintaining Currency Codes
Access the Currency Code page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Codes).
|
Currency Symbol |
PeopleSoft delivers many currencies with a currency symbol such as $ for Australian dollar (AUD) or ? for British pound (GBP). You can enter new symbols for delivered currencies or for currencies that you might add. |
|
Country |
Displays the code for the country from which the currency originates. |
|
Decimal Positions |
Enter the number of decimal positions that should appear in the notation for the currency. For example, use two decimal positions for Australian dollars (5.00 AUD), but no decimal positions for Japanese yen (500 JPY). |
|
Scale Positions |
Enter the scale positions that you want to round for this currency. Scale positions control how many numbers appear to the left of the decimal when displayed. The data is stored with full precision in the database. For example, if you want all dollar amounts in the millions displayed as the number of millions without the zeros, enter 6 as your scale position. In this case, 24,000,000 is displayed as 24, but is stored in the database as 24,000,000. |
Note. The data on this page is stored in the Currency Code table. The values on this table are effective-dated. The software is shipped with the Currency Code table in compliance with ISO standards for decimal positions. You can increase the number of decimals to a maximum of three.
Note. PeopleSoft updates the Currency Code table and the fully populated country, state, and province code tables as national boundaries and designations change.

 Updating the Status of a Euro Currency Code
Updating the Status of a Euro Currency Code
Access the Currency Code (Euro) page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Code (Euro)).
|
Status |
Displays whether a currency is an active participant in the euro. |
Note. Do not attempt to modify the currency quotation methods for currencies that are linked to the euro.
 Setting Up Market Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
Setting Up Market Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
The PeopleSoft approach to market rates and currency conversion is driven by the need to accommodate business practices related to the European Common Currency (euro). In addition to currency exchange rates, PeopleSoft supports the many different types of global market rates, such as interest rates, stock exchange indexes, and economic indicators.
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move market rate data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the market rate PIA pages to redefine or modify your existing market rate data.
This section discusses how to:
Define market rate indexes.
Define market rate types.
Define market rate tolerances.

 Pages Used to Manage Market Rates
Pages Used to Manage Market Rates|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Market Rate Index |
RT_INDEX_TBL |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Index |
Describe the indices for which you track rates. Typical market rate indexes include LIBOR, Bloomberg foreign exchange, and Reuters foreign exchange. An index categorizes the various market rates that you track. |
|
Market Rate Type |
RT_TYPE_TBL |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Type |
Define market rate types. Rate types include commercial, floating, average, and historical. |
|
Market Rate Definition |
RT_RATE_DEF_TBL |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Definition, |
Define tolerance limits for rates and determine what action should occur if a new rate occurs outside of the tolerance limit. The fields on this page differ according to the rate category of the market rate index. |

 Defining Market Rate Indexes
Defining Market Rate Indexes
Access the Market Rate Index page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Index).
|
Rate Category |
Select a Rate Category from the list: Options include: Commodity Price, Economic Indicator, Exchange Rate, Futures Price, Interest Rate, Other, Stock Exchange, Index, or Stock Price. |
|
Default Exchange Rate Index |
If you are entering exchange rate indexes, select this check box to indicate which index should be used to retrieve currency exchange rates. You can specify only one index code as the default. |

 Defining Market Rate Types
Defining Market Rate Types
Access the Market Rate Type page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Type).
Enter a description and short description for each market rate type that you use.

 Defining Market Rate Tolerances
Defining Market Rate Tolerances
Access the Market Rate Definition page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rate Definition).
The information that appears on this page depends on the type of index that you select. For example, if you select an index with interest rates, interest rates appear on this page.
Market rate definitions specify the valid term, currency, and other appropriate field combinations for market rates. For example, if you have a market rate definition for an exchange rate with a term of 30, a from currency of EUR, and a to currency of USD, you can enter a rate using this combination in the market rate table. If you do not have a market rate definition, the system creates one for you using the default values.
|
From Currency Code |
Enter the from currency code. |
|
Refresh |
Click the Refresh button to limit the display to the specified from currency code. |
|
Term |
Enter the desired term (expressed in days). A zero term indicates a spot rate. |
|
From Currency |
Enter the appropriate from currency. This value is used with the to currency value as part of an exchange rate pair. When you use triangulation, include a definition for each of the currency pairs involved in the triangulation. |
|
To Currency |
Enter the appropriate to currency. This value is used with the from currency value as part of an exchange rate pair. |
|
Maximum Variance |
Indicate the percentage of variance that is allowed when the user maintains the market rate. The system generates an error message if the change exceeds the tolerance. The default value is 2.50 (2.5 percent). |
|
Error Type |
Enter the type of error processing that should occur if the maximum variance is exceeded. Values are: None: No error processing occurs, and the new rate is used even though it exceeds the limit. Stop: Processing halts, and the system prevents you from saving the new rate. Warning: Default value. A warning appears; you can ignore it and save the new rate. |
 Defining Currency Quotations for EPM Currency Conversion
Defining Currency Quotations for EPM Currency ConversionThis section provides an overview of currency quotations and discusses how to maintain currency quotation methods.

 Understanding Currency Quotations
Understanding Currency Quotations
PeopleSoft supports direct and indirect rate quotation, quote units, and triangulation. These are flexible and accurate tools that enable you to convert and manage multicurrency operations.
The currency quotation method controls how a stored rate is displayed and how an entered rate is interpreted and stored in the database. You maintain a currency quotation method for each from currency and to currency pair.
You do not typically maintain rates online for currency pairs that triangulate. Instead, the Cross rate/Triangulation Generation SQR determines the cross rate by using the rates between the from currency and the reference currency, and between the reference currency and the to currency. Currency quotation methods must be set up correctly to yield the desired triangulation results.
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move currency quotation data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the Currency Quotation Method PIA page to redefine or modify your existing currency quotation data.
Note. Define currency quotation options before you enter and calculate the rates.

 Page Used to Define and Maintain Currency Quotations
Page Used to Define and Maintain Currency Quotations|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Currency Quotation Method |
CURR_QUOTE_PNL |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Quotation Method |
Maintain a currency quotation method for each from currency and to currency pair. |

 Maintaining Currency Quotation Methods
Maintaining Currency Quotation Methods
Access the Currency Quotation Method page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Quotation Method).
Rate Quotation Basis
|
Direct |
Determine whether you want the rates for a currency pair quoted directly. For example, in converting United States dollars (USD) to euro (EUR), a direct quote would indicate that USD 1 = EUR x.xxxx. In this case, euros are quoted directly against the United States dollar. |
|
Indirect |
Determine whether you want the rates for a currency pair quoted indirectly. For example, in converting United States dollars (USD) to euros (EUR), an indirect quote would indicate that USD x.xxxx = EUR 1. |
|
Quote Units |
Sometimes called "scaling factors," these preserve decimal position. You can enter any value in this field, although quote units generally are on a scale of 10 (such as 10, 100, 1000). The default value for this field is 1. |
|
Auto Reciprocate |
Select this check box to create or update the rate for the reciprocal currency pair automatically whenever an exchange rate is added or updated. For example, when you enter a new USD to GBP rate, the GBP to USD rate will be updated automatically. You can only apply this feature to currency pairs for which quotation methods have been established. |
Note. Currency pairs that triangulate must be classified as either direct or indirect to use in displaying the calculated cross rate. Two fields store the rate conversion factor: RATE_DIV and RATE_MULT. The currency conversion formula is always: (From currency ÷ RATE_DIV) ? (RATE_MULT) = To currency
Select the Triangulate check box to have the system convert two currencies through a third currency (the reference currency). Triangulation is used in hyperinflationary environments in which all conversions to the local currency are done through a more stable currency such as USD.
Note. Triangulation was initially used for European countries
participating in the euro. However, since 1999 all countries participating
in the euro are quoted directly against the foreign currency.
Any countries newly participating in the euro might be initially subject
to triangulation, however. The triangulation example below and any other examples
in this chapter that show triangulation, use a fictional country, with a currency
code of NEW, that has just joined the euro. This country is subject to triangulation.
The following are examples of indirect quotation, direct quotation with quote units, and triangulation:
USD 100 to GBP (indirect) = (USD 100 x 1.6) x 1 = GBP 62.50.
CHF 1000 to German marks (DEM) (direct with units) = (CHF 1000 / 100) x 119.335 = DEM 1193.35.
USD 100 to NEW (triangulate) = (USD 100 / 1.25) x 6.8 = NEW 544.
For example, to convert from USD to NEW with triangulation, you perform two conversions:
Convert the USD amount to the reference currency using the appropriate triangulated rate.
The triangulated rate uses the USD to EUR component of the USD to NEW triangulated rate that is stored in RATE_DIV.
Convert the reference currency to NEW using the fixed exchange rate.
The exchange rate uses the EUR to NEW component of the USD to NEW triangulated rate that is stored in RATE_MULT.
Typically, you do not maintain triangulation rates directly. Instead, you process these and all rates through the Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calculator.
Select a reference currency through which the from currency will be converted.
You must consider three exchange rates for triangulated currency pairs:
The rate between the from currency code and reference currencies.
The rate between the reference and the to currency code currencies.
The cross rate between the from currency code and to currency code currencies.
Select one of the three conversion rates as the primary rate that appears on primary pages and reports.
Select the Allow Override check box to enable users to override the cross rate for a triangulated currency pair. If this option is deselected, you can change the components of only the triangulated rate.
Recalculate
If you select the Allow Override check box, you must maintain triangulation accuracy by specifying which currency pair the system should use to recalculate if the cross rate is overridden.
Automatic Reciprocation of Quote Methods
The Currency Quotation Method page automatically provides reciprocal methods. For example, if you define the conversion of USD to NEW as indirect, this record is automatically created to indicate a quote method of direct. If you change the quote method on the NEW to USD record, the USD to NEW record is updated automatically.
Note. This example uses a hypothetical currency NEW that has just begun participating in the euro and is still subject to triangulation for an initial period.
Using the conversion of USD to NEW as an example, this table shows each possible field value and its corresponding reciprocal value.
|
Field |
Value (for USD to NEW) |
Reciprocal Value (for NEW to USD) |
|
Quotation Basis |
Direct Indirect |
Indirect Direct |
|
Quote Units |
Any valid value |
Same value |
|
Rate Decimal Positions |
4 (default value) |
Same value |
|
Auto Reciprocate |
Yes No |
Yes No |
|
Triangulate |
Yes No |
Yes No |
|
Reference Currency |
Any valid value |
Same value |
|
Primary Visual Rate |
From - To (USD - NEW) From - Ref (USD - EUR) Ref - To (EUR - NEW) |
From - To (NEW - USD) Ref - To (EUR - USD) From - Ref (NEW - EUR) |
|
Cross rate Allow Override |
Yes No |
Yes No |
|
Cross rate Recalculate |
From - Ref (USD - EUR) Ref - To (EUR - NEW) |
Ref - To (EUR - USD) From - Ref (NEW - EUR) |
 Establishing Market Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
Establishing Market Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move market rate data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the market rate PIA pages to redefine or modify your existing market rate data.
This section discusses how to:
Define market rates.
Establish rate definitions.
Maintain exchange rates.
Load market rates.

 Pages Used to Establish Market Rates
Pages Used to Establish Market Rates|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Market Rate |
RT_RATE_PNL |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rates, Market Rate |
Define market rates. |
|
Rate Definition |
RT_RATE_DEF_SEC |
Click the Rate Definition link on the Market Rates page. |
Establish rate definitions. |
|
Exchange Rate Detail |
EXCH_RT_DTL |
Click the Exchange Rate Detail button on the Market Rates page. This page can also be accessed from other pages in the system. |
Maintain exchange rates. |

 Defining Market Rates
Defining Market Rates
Access the Market Rates page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Market Rates, Market Rate).
You can edit the rate for non triangulated rates and for triangulated rates if a quotation method has been defined for the currency pair and the Cross rate Allow Overridecheck box is selected on the Currency Quotation Method page. If an override is not allowed, you can update the exchange rate values to and from the reference currency on the Exchange Rate Detail page.
Changing a Triangulated Cross Rate
If you change a triangulated cross rate, the system recalculates one of the component rates. This can result in the cross rate being recalculated in a manner that is slightly different from the one that you entered. For example, you start with a triangulated rate of RM=6.80000000 and RD=1.25000000 for a cross rate of 5.44000000. If you change the cross rate to 5.43550000:
The system first recalculates RD to 1.25103486.
The system then recalculates the cross rate to 5.43550001 based on the first recalculation.
In rate maintenance, you must accept the recalculation. However, in a situation such as journal entry, a warning message enables you to override triangulation and to use the exact rate that you entered, which results in the rate being stored as RM equal to 5.43550000 and RD equal to 1.
You can edit the Rate field except when all of these conditions are true:
The rate is triangulated.
The primary visual rate is the cross rate.
The Allow Override check box on the Currency Quotation Method page is deselected for the exchange rate's quotation method.
Note. Typically, you do not maintain triangulated exchange rates online. Instead, maintain the rates of the from currency to the reference currency and the reference currency to the to currency, and then run the Cross rate Reciprocal SQR (EO9030.SQR) to define the triangulated exchange rates.
If a quotation method has been defined for the currency pair and if the Auto Reciprocate check box is selected, creating or maintaining a rate for a currency pair automatically creates or updates the rate of the reciprocal currency pair. For example, if you change the USD to GBP rate, the GBP to USD rate automatically is automatically updated. You can only automatically reciprocate currency pairs for which quotation methods have been defined.
If a rate definition does not already exist for the currency pair, one will be automatically created with the default values of 2.5 percent maximum variance and warning message processing.

 Establishing Rate Definitions
Establishing Rate Definitions
Access the Market Rate - Rate Definition page (Click the Rate Definition link on the Market Rates page).
|
Maximum Variance |
You can modify the maximum variance—that is, the percentage of variance allowed when you maintain the market rate. If the change exceeds the tolerance, an error results. The default value is 2.50 (2.5 percent). |
|
Error Type |
You can modify the type of error that results when the tolerance defined in the Maximum Variance field is exceeded during data entry. Error type values are: None: No error processing occurs. The new rate is used even though it exceeds the limit. Stop : Processing halts. The system prevents you from saving the new rate. Warning: A warning appears. You can ignore it and save the new rate. |
Note. The results of changing the rate definition do not take effect until you save the Market Rates page.
Click OK to return to the Market Rates page.

 Maintaining Exchange Rates
Maintaining Exchange Rates
Access the Market Rate - Exchange Rate Detail page (Click the Exchange Rate Detail button on the Market Rates page. This page can also be accessed from other pages in the system.).
The read-only fields include:
|
Rate Quotation Basis |
Displays the quotation basis for the exchange rate as it is defined on the Currency Quotation Method page. If no quotation method is defined, the quotation basis is Direct. |
|
Quote Units |
Displays the quote units for the exchange rate as defined on the Currency Quotation Method page. If no quotation method is defined, the quote unit is 1. |
|
Triangulate |
Displays the triangulated setting for the exchange rate as it is defined on the Currency Quotation Method page. If no quotation method is defined, the triangulated setting is N. |
|
Reference Currency |
Displays triangulated exchange rates only, and shows the reference currency used in the triangulated exchange. |
|
Current Quote |
Displays the current exchange rate used to convert the from currency to the to currency. A direct, non-triangulated rate shows quote units (or 1) on the left side of the equal sign and the visual rate on the right. For example: 1 USD = 1.40000000 CAD. A triangulated rate displays two component rates of the triangle: the rate for converting the from currency to the reference currency, and the rate for converting the reference currency to the to currency. |
|
Historic Quote |
Displays a quote to indicate the quotation method originally used by a historic exchange rate if the system determines that the original quotation method of the historic rate differs from the current quotation method. This field displays the following information:
|
|
Exchange Rate |
Displays a single visual rate for non-triangulated exchange rates or displays all three component visual rates for triangulated exchange rates. The cross rate for triangulated exchange rates is editable only if the Allow Override check box is selected in the exchange rate's quotation method definition. |

 Loading Market Rates
Loading Market Rates
Market rates can be loaded to the RT_RATE_TBL from any external source using the DataStage ETL tool.
Note. Use the Market Rates page to verify that the market rates were loaded correctly.
 Calculating Currency Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
Calculating Currency Rates for EPM Currency Conversion
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move currency rate data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the currency rate PIA pages to redefine or modify your existing currency rate data.
This section provide an overview of currency calculations and discusses how to:
Calculate cross rates and reciprocal rates.
Run the Currency Exchange Calculator tool.

 Understanding Currency Calculations
Understanding Currency Calculations
PeopleSoft calculates currency rates for cross rates, triangulated rates, and reciprocal rates.
EPM utilizes two tools for currency calculations:
The Currency Exchange Calculator tool quickly performs ad hoc currency conversion using the exchange rates that are stored on the market rates table.
The Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calculator calculates exchange rates and updates the market rates table.
It performs three functions by generating the rates shown in this table:
|
Cross rates for nontriangulated currency pairs |
For example, an organization subscribes to a rate service that provides all rates respective to the USD. Starting with a USD to Canadian dollar rate and a USD to Mexican peso rate, the system can calculate a new Canadian dollar to Mexican peso cross rate. |
|
Triangulated rates for triangulated currency pairs |
For example, the euro to NEW (a fictitious country that has just joined the euro and is subject to triangulation) fixed rate has been established on the market rate table and a new euro to USD rate has just been entered. Using this information, the process can create a new USD to NEW triangulated rate. The difference between triangulated rates and cross rates affects how the data is stored in the database. When calculating a cross rate, you actually create a new rate. When calculating a triangulated rate, the individual components of the source rates are stored on the target. |
|
Reciprocal rates for those currency pairs that are not automatically reciprocated |
For example, using a USD to CAD rate as the source, the process calculates the CAD to USD reciprocal. If quote methods are in place, the visual rate remains the same and a difference exists in how the data is stored in the database (RATE_MULT and RATE_DIV are inverse). If quote methods are not used, the process calculates an inverse rate, meaning that the visual rates differ. |

 Pages Used to Calculate Currency Rates
Pages Used to Calculate Currency Rates|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calc (calculator) |
RUN_FIN9030 |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calc, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calculator, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Parameters |
Calculate cross rates and reciprocal rates by defining parameters to run the FIN9030 SQR report. |
|
Currency Exchange Calculator |
CURRENCY_EXCHNG_PN |
EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Exchange Calculator |
Run the Currency Exchange Calculator to calculate the currency exchange between currencies. |

 Calculating Cross Rates and Reciprocal Rates
Calculating Cross Rates and Reciprocal Rates
Access the Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calculator page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calc, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Calculator, Cross/Reciprocal Rate Parameters page).
|
Language Code |
Select the language for translation. |
|
Market Rate Index |
Select a market rate index. |
|
Term |
The system displays this value by default from the value entered on the Market Rate Definition page. |
|
From Common Currency |
Select a currency code from which to calculate a reciprocal rate. |
|
Exchange Rate Type |
Select the type of exchange rate to use for this calculation. |
|
As of Date |
Determines the effective date of newly created exchange rates (the output of the process) and rates that are used as the basis for calculations (the input to the process). The report uses the most current currency quotation method for the currency pair as input for the process. If the as of date is the current effective rate as of the specified date, it can affect triangulation. |
|
Generate Report |
Select to specify that the system generate a report that displays exchange rates and reciprocal and cross rate calculations. |
|
Override Existing Rates |
Select to direct the calculated rate to override rates for the exchange rate type, regardless of the as of date. |
Generating Reciprocal Rates
You can select the Generate Reciprocal Rate check box by itself or in combination with the Rate Triangulate and Generate Cross Rate check boxes. When this option is selected, the system automatically calculates reciprocal rates for currency pairs for which the autoreciprocate option on the currency method is disabled.
The system does not directly manipulate the exchange rates. The system uses numerator and denominator values such that:
(From currency / RATE_DIV) x RATE_MULT = To currency
Generating Cross Rates
When you select the Generate Cross Rates check box, the system automatically generate cross rates. For example, to generate cross-currency rates for USD, (CAD), and (MXP), you enter USD to CAD = 1.473 and USD to MXP = 9.8793. The system automatically generates CAD to MXP = 9.8793 / 1.473 = 6.7069246.
If you generate cross rates, you must select a from currency and a to currency. You can enter a wild card of % in either field or both fields to indicatefrom all orto all currencies.
Generating Triangulation Rates
When you select the Rate Triangulate check box, the system converts two currencies through a third currency. If you select rate triangulation, you must select a from currency and a to currency. You can enter a wild card of % in either field or both fields to indicate from all or to all currencies.

 Running the Currency Exchange Calculator Tool
Running the Currency Exchange Calculator Tool
Access the Currency Exchange Calculator page (EPM Foundation, EPM Setup, Common Definitions, Currencies and Rates, Currency Exchange Calculator).
This tool enables you to enter a rate or an amount in a currency other than the base currency, or to compute an exchange using an alternative rate type.
|
From Amount |
Enter a from amount. The currency exchange is based on the from amount that you enter and the current exchange rate set up on the Market Rates page. |
|
From Currency Code |
Select the currency code from which to calculate the exchange amount. |
|
To Currency Code |
Select the currency code to which to calculate the exchange amount. |
|
Exchange Rate Type |
Select the type of exchange rate to use for this calculation. |
|
Converted Amount |
Displays the converted amount. The system automatically calculates this amount when you save the page. |
Note. Do not decrease the number of decimals after you have created transactions for that currency; the system will not properly round the previous rounded amount fields with the new precision.
 Configuring Currency Precision for Currency Conversion
Configuring Currency Precision for Currency Conversion
This section provides an overview of currency precision and discusses how to:
Activate currency precision.
Maintain currency precision by currency.
Report with currency precision.

 Understanding Currency Precision
Understanding Currency Precision
According to the ISO standard, currency precision can range from zero decimals to three decimals. For example, USD amounts have two digits to the right of the decimal, and JPY have none. To support this dynamic currency precision, the system delivers all of its currency-sensitive amount fields with a standard length of 23.3, or 23 digits to the left of the decimal and three digits to the right. A control currency on the same record exists to control the display and processing of such amount fields.
PeopleSoft applications round all currency-sensitive amount fields to the currency precision of the controlled currency during all online or background processes. For example, in a database that contains amount fields with a length of 23.3, JPY are rounded to 123.000 and USD are rounded to 123.230. The system does not place a nonzero after the decimal for a JPY amount or after the second digit to the right of the decimal for a USD amount.
Although amount fields are stored in the database with decimal placeholders, the system displays amount fields with the precision that is appropriate for the currency. For example, it displays JPY as 123 and USD as 123.23. When you enter an amount, you cannot enter more than the defined precision. If you attempt to do so, the system treats the entry as an online error.
PeopleCode programs and background processes round all currency-sensitive amount fields to the currency precision of the controlled currency.
PeopleSoft-delivered ETL jobs move currency precision data from your source transaction system to EPM target warehouse tables. You need only use the currency precision PIA pages to redefine or modify your existing currency precision data.
See Also
Configuring Currency Precision for Currency Conversion

 Activating Currency Precision
Activating Currency Precision
Currency precision is a PeopleSoft PeopleTools option. When it is selected using the PeopleTools Options page, all features of currency precision are activated. When the option is deselected, all amount fields behave as if no controlled currency exists. The system displays amount fields as defined in the PeopleSoft Application Designer and rounds them to the number of decimals defined in the Application Designer.
Note. If you deselect the multicurrency check box, the system only supports the default amount field size of 15.3—it does not support the larger amount field size of 23.3. After you deselect this check box, selecting it again does not automatically round existing transaction amounts.

 Maintaining Currency Precision by Currency
Maintaining Currency Precision by CurrencyUse the Currency Code page to access the currency code table, in which you define the decimal position by currency. The values in this table are effective dated. The software is shipped with the currency code table in compliance with ISO standards for decimal positions. You can increase the number of decimals to a maximum of three.
Warning! Do not decrease the number of decimals after transactions are entered in that currency; the system does not properly round the previously rounded amount fields with the new precision.
See Also

 Reporting with Currency Precision
Reporting with Currency PrecisionMost PeopleSoft SQR reports display currency-controlled amounts with the number of decimal places that are defined by the associated currency. For example, a JPY amount appears as 123 on a report, and a United USD amount appears as 123.23.
Amounts on Crystal and PS/nVision (Microsoft Excel) reports appear as two-decimal-place numbers. If you want to show three decimal places on these reports, you must configure the reports to do so.
Third-party reporting tools used by PeopleSoft do not fully support numeric fields greater than 15 digits. Microsoft Excel uses an eight-byte float for numeric fields, which causes values to be truncated after the fifteenth digit.
Crystal displays up to 15 digits correctly. When a value exceeds 15 digits, Crystal inserts invalid numbers into the decimal positions. This is an issue for only very large currency amounts. For any of these reporting tools, the accuracy of the results is:
Hundreds of trillions of yen (precision = 0).
Trillions of dollars (precision = 2).
Hundreds of billions of dinar (precision = 3).
For example, if you populate a 23.3 numeric database amount field with the number 2, the following table illustrates the number that is displayed in each type of report.
|
Number of Digits |
Crystal |
Excel |
SQR |
|
16 |
2,222,222,222,222.222 |
2,222,222,222,222.220 |
2,222,222,222,222.222 |
|
17 |
22,222,222,222,222.219 |
22,222,222,222,222.200 |
22,222,222,222,222.220 |
|
18 |
222,222,222,222,222.188 |
222,222,222,222,222.000 |
222,222,222,222,222.200 |