- 4.2.1. Administrative Name and Password
- 4.2.2. Admin GUI Tab Descriptions
- 4.2.3. How to Log In to the Administration Tool (Admin GUI)
- 4.2.4. How to Change the Admin GUI Locale
- 4.2.5. How to Change the Admin GUI to English Locale
- 4.2.6. How to Change the Admin GUI Timeout
- 4.2.7. How to Enable or Disable Multiple Administration Accounts (Oracle Linux)
- 4.2.8. How to Enable or Disable Multiple Administration Accounts (Oracle Solaris 11)
- 4.2.9. How to Enable or Disable Multiple Administration Accounts (Oracle Solaris 10)
- 4.2.10. How to Audit Admin GUI Sessions
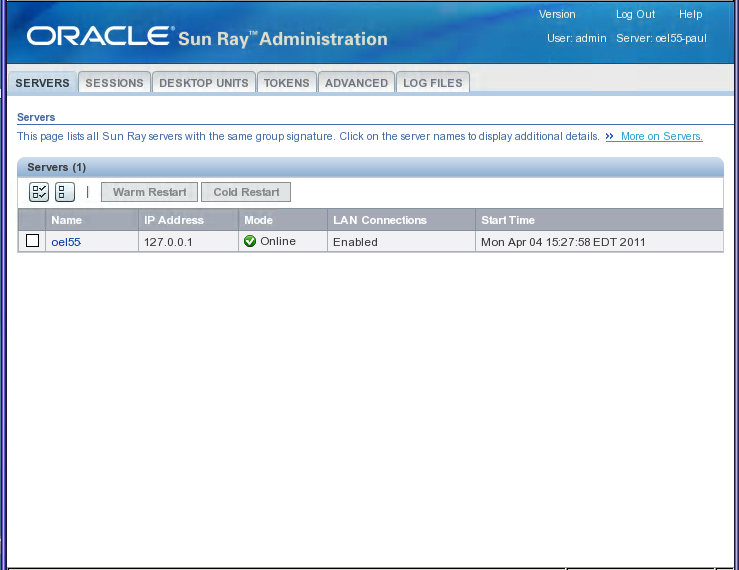
The Sun Ray Administration Tool (Admin GUI) is organized around primary Sun Ray objects such as servers, sessions, desktop units, and tokens. Each type of object has a dedicated tab that provides related functionality. Figure 4.1, “Admin GUI Home Screen” shows the home screen.
The default user name for the administration account is
admin.
The password is set during the Sun Ray server configuration. If you can't remember the administration password, you can use the utconfig -w command to reconfigure the administration software, including the password. To change the administration password, use the Advanced tab in the Admin GUI or the utpw command.
To allow another user account to perform administrative functions, see How to Enable or Disable Multiple Administration Accounts (Oracle Linux) or How to Enable or Disable Multiple Administration Accounts (Oracle Solaris).
Table 4.2, “Admin GUI Tab Descriptions” describes tabs provided with the Admin GUI. See Appendix B, Admin GUI Help for detailed reference information.
Table 4.2. Admin GUI Tab Descriptions
Tab | Functions |
|---|---|
Servers | From the Servers tab, you can do the following tasks:
|
Sessions | From the Sessions tab, you can do the following tasks:
|
Desktop Units | From the Desktop Units tab, which includes the Sun Ray Clients and Oracle Virtual Desktop Clients, you can do the following tasks:
|
Tokens | From the Tokens tab, you can do the following tasks:
|
Advanced | The Advanced tab includes the following subtabs: |
Security Subtab From the Security subtab, you can disable and re-enable security settings, such as encryption of communication between client and server, server authentication, security mode, and device access. | |
System Policy Subtab From the System Policy subtab, you can regulate authentication manager policy settings, such as:
| |
Kiosk Mode Subtab From the Kiosk Mode subtab, you can configure Kiosk Mode for your system. | |
Card Probe Order Subtab From the Card Probe Order subtab, you can rearrange the order that smart cards are probed. You can move the cards that are used most frequently to the top of the list. | |
Data Store Password Subtab From the Data Store Password subtab, you can change the password for the administrator account. | |
Log Files | From the Log Files tab, you can do the following tasks:
|
All actions performed within the Admin GUI that modify system settings are logged in an audit trail.
This procedure describes how to log in to the Sun Ray Administration tool.
If a session is inactive for 30 minutes, you must log in again. To change the timeout value, see How to Change the Admin GUI Timeout.
Log in to your Sun Ray server's console or to any client attached to it.
Open a browser window and type the following URL:
http://
localhost:1660NoteIf you specified a different port number when you configured the Sun Ray Software, use that port number in the URL. If you enabled secure communication, the browser might be redirected to a secure port. The default secure port is 1661.
In the User Name window, type the administrator user name and click OK.
In the password challenge screen, type the administration password and click OK.
The Sun Ray Administration tool is displayed.
If you get a message denying access, check the following items:
You are running a browser on a Sun Ray server or one of its clients.
The browser is not using a different machine as an HTTP proxy server.
If you get a blank browser page:
To access the Admin GUI from a system instead of the Sun Ray server, you must have remote access enabled (it is disabled by default). To enable remote access to the Admin GUI, unconfigure the Admin GUI using the utconfig -w -u command and then run utconfig -w to reconfigure. Choose Yes to enable remote access.
To display the locale correctly in the Admin GUI, change your browser's language preferences to the desired locale.
This procedure describes how to change the Admin GUI to display English if it is displaying an undesired language.
Become superuser on the Sun Ray server.
Export the English locale.
export LC_ALL=C
Stop the web admin services.
/etc/init.d/utwadmin stop
Start the web admin services.
/etc/init.d/utwadmin start
For a more permanent solution, you can remove the non-English Sun Ray Software packages from the server. The following example removes the French packages and restarts the web admin services.
# /etc/init.d/utwadmin stop # pkgrm SUNWfuta SUNWfutwa SUNWfutwh SUNWfutwl # /etc/init.d/utwadmin start
This procedure describes how to change the timeout for the Admin GUI. By default, the Admin GUI timeout value is 30 minutes.
Become superuser on the Sun Ray server.
Edit the
/etc/opt/SUNWut/webadmin/webadmin.confconfiguration file.Change the following timeout value:
... # The session timeout (specified in minutes) session.timeout=30 ...
Restart the webadmin program.
# /opt/SUNWut/lib/utwebadmin restart
This tool automatically updates the
web.xmlfile used by the web server hosting the Admin GUI.
The Sun Ray server administrator can allow any valid UNIX user ID, which has been added to the utadmin authorized user list, to administer Sun Ray services using the Admin GUI. An audit trail of activity on these accounts is provided. The utadminuser command enables you to add existing UNIX users to the utadmin authorized user list.
Authentication for accounts with administrative privileges is based on the PAM authentication framework.
Use the following procedure to configure the Sun Ray Admin GUI
to allow access by the UNIX users in the
utadmin authorized user list instead of the
default admin account. Once you enable Admin
GUI privileges for authorized users, you can add or remove users
to the utadmin authorized list to manage
access to the Admin GUI.
For each UNIX user that needs authorization to the Admin GUI, add the user to the authorized user list.
# utadminuser -a
usernameYou can run the utadminuser command without any options to list the current authorized users or with the
-doption to delete a user.Add the following auth entries to the
/etc/pam.d/utadminguifile:#%PAM-1.0 # BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui auth include system-auth # END: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui
Make sure to include the comment lines, which are needed for the cleanup to work properly.
This is the default Admin GUI privilege configuration when the Sun Ray Software is installed.
To limit Admin GUI privileges to the default
admin user, replace the PAM entries in the
/etc/pam.d/utadmingui file with the
pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 module.
# BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui auth sufficient /opt/SUNWut/lib/pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 # END: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui
Make sure to include the comment lines, which are needed for the cleanup to work properly.
The Sun Ray server administrator can allow any valid UNIX user ID, which has been added to the utadmin authorized user list, to administer Sun Ray services using the Admin GUI. An audit trail of activity on these accounts is provided. The utadminuser command enables you to add existing UNIX users to the utadmin authorized user list.
Authentication for accounts with administrative privileges is based on the PAM authentication framework.
Use the following procedure to configure the Sun Ray Admin GUI
to allow access by the UNIX users in the
utadmin authorized user list instead of the
default admin account. Once you enable Admin
GUI privileges for authorized users, you can add or remove users
to the utadmin authorized list to manage
access to the Admin GUI.
For each UNIX user that needs authorization to the Admin GUI, add the user to the authorized user list.
# utadminuser -a
usernameYou can run the utadminuser command without any options to list the current authorized users or with the
-doption to delete a user.Add the following auth entries to the
/etc/pam.d/utadminguifile:#%PAM-1.0 # BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui auth requisite pam_authtok_get.so.1 auth required pam_dhkeys.so.1 auth required pam_unix_cred.so.1 auth required pam_unix_auth.so.1
Make sure to include the comment lines, which are needed for the cleanup to work properly.
This is the default Admin GUI privilege configuration when the Sun Ray Software is installed.
To limit Admin GUI privileges to the default
admin user, replace the PAM entries in the
/etc/pam.d/utadmingui file with the
pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 module.
#%PAM-1.0 # BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui
auth sufficient /opt/SUNWut/lib/pam_sunray_admingui.so.1
Make sure to include the comment lines, which are needed for the cleanup to work properly.
The Sun Ray server administrator can allow any valid UNIX user ID which has been added to the utadmin authorized user list to administer Sun Ray services using the Admin GUI. An audit trail of activity on these accounts is provided. The utadminuser command enables you to add existing UNIX users to the utadmin authorized user list.
Authentication for accounts with administrative privileges is based on the PAM authentication framework.
Use the following procedure to configure the Sun Ray Admin GUI
to allow access by the UNIX users in the
utadmin authorized user list instead of the
default admin account. Once you enable Admin
GUI privileges for authorized users, you can add or remove users
to the utadmin authorized list to manage
access to the Admin GUI.
For each UNIX user that needs authorization to the Admin GUI, add the user to the authorized user list.
# utadminuser -a
usernameYou can run the utadminuser command without any options to list the current authorized users or with the
-doption to delete a user.Modify the
/etc/pam.conffile to use the other authentication PAM stack auth entries to create the PAM stack for utadmingui# BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui utadmingui auth requisite pam_authtok_get.so.1 utadmingui auth required pam_dhkeys.so.1 utadmingui auth required pam_unix_cred.so.1 utadmingui auth required pam_unix_auth.so.1
Make sure to include the comment line, which is needed for the cleanup to work properly.
This is the default Admin GUI privilege configuration when the Sun Ray Software is installed.
To limit Admin GUI privileges to the default
admin user, modify the
/etc/pam.conf file and replace the PAM
stack for utadmingui with the
pam_sunray_admingui.so.1 module.
# BEGIN: added to utadmingui by SunRay Server Software -- utadmingui utadmingui auth sufficient /opt/SUNWut/lib/pam_sunray_admingui.so.1
Make sure to include the comment line, which is needed for the cleanup to work properly.
The administration framework provides an audit trail of the Admin
GUI. The audit trail is an audit log of the activities performed
by multiple administration accounts. All events that modify system
settings are logged in the audit trail. Sun Ray Software uses the
syslog implementation.
The events are logged in the following log file:
/var/opt/SUNWut/log/messages
All audit events are prefixed with the keyword
utadt:: so you can filter events from the
messages file.
For example, session termination from the Admin GUI generates the following audit event:
Jun 6 18:49:51 sunrayserver usersession[17421]: [ID 521130 user.info] utadt:: username= /
{demo} hostname={sunrayserver} service={Sessions}
cmd={/opt/SUNWut/lib/utrcmd sunrayserver /opt/SUNWut/sbin/utsession -x -d 4 -t /
Cyberflex_Access_FullCrypto.1047750b1e0e -k 2>&P1}
message={terminated User "Cyberflex_Access_FullCrypto.1047750b1e0e" with display number="4" on /
"sunrayserver"}
status={0} return_val={0}where:
username= User's UNIX IDhostname= Host on which the command is executedservice= Name of the service being executedcmd= Name of the command being executedmessage= Details about the action being performed