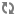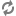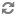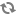To enable the Performance Monitor to monitor a section of your Java code:
Import the
atg.service.perfmonitor.*package.Declare an
opNameparameter to label the section of the code. This parameter is displayed in the Performance Monitor page under the Operation heading.(Optional) Declare a parameter name if you want to gather data on individual executions of an operation.
Call the
startOperationmethod at the beginning of the operation whose performance you want to be able to measure.Call the
endOperationmethod at the end of the operation whose performance you want to be able to measure.Optionally, call the
cancelOperationmethod if an exception occurs. This causes the results of the current execution to be ignored.
For details about the Performance Monitor’s startOperation, endOperation, and cancelOperation methods, see Methods for Storing Performance Data.
For example:
String opName = "render jsp";
String parameter = "foo.jsp";
boolean exception = false;
PerformanceMonitor.startOperation(opName, parameter);
try {
... code to actually render foo.jsp
} catch (Exception e) {
PerformanceMonitor.cancelOperation(opName, parameter);
exception = true;
} finally {
if (! exception)
PerformanceMonitor.endOperation(opName, parameter);
}These methods can be nested with different or the same opNames. For example:
private final String RENDER_JSP = "Render JSP page"; private final String EXECUTE_SQL = "Execute SQL Query"; private String mPageName = "page.jsp"; private String mSQLQuery = "select * from table"; PerformanceMonitor.startOperation(RENDER_JSP, mPageName); ... source code to start render PerformanceMonitor.startOperation(EXECUTE_SQL, mSQLQuery); ... source code to read from table 1 in database PerformanceMonitor.startOperation(EXECUTE_SQL); ... source code to read from database PerformanceMonitor.endOperation(EXECUTE_SQL); ... more source code to read from table 1 in database PerformanceMonitor.endOperation(EXECUTE_SQL, mSQLQuery); ... more source code to finish render PerformanceMonitor.endOperation(RENDER_JSP, mPageName);
Note that the calls to startOperation are nested within other calls to startOperation. You must place the endOperation and cancelOperation calls in the code in opposite order that the startOperation calls were placed. If this requirement is not followed, then the endOperation or cancelOperation call throws a PerfStackMismatchException. This exception tells you that the calls to endOperation are not being matched up. Either they were not called in the correct order or the arguments were not exactly the same as those that were passed into the methods.
To ensure that endOperation is always called, wrap the Performance Monitor methods in a try ... finally block, as in this example:
boolean exception = false;
try {
PerformanceMonitor.startOperation(OP_NAME);
performOperation (pParameter);
} catch (Exception e) {
PerformanceMonitor.cancelOperation(OP_NAME);
exception = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!exception)
PerformanceMonitor.endOperation(OP_NAME);
} catch (PerfStackMismatchException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}