The following minimum system requirements must be met on the computer on which you want to install Oracle VM Manager.
Before you install Oracle VM Manager, make sure that your computer meets the minimum hardware requirements listed in Table 4.1:
Table 4.1 Hardware Requirements for Oracle VM Manager
Items | Minimum Value |
|---|---|
Memory | 6.0 GB (8.0 GB if using local MySQL) |
Processor Type | 64 bit |
Processor Speed | 1.83 GHz*1 |
Swap Space | 2.1 GB |
Hard Disk Space | 5.5 GB in /u01 2 GB in /tmp 500 MB in /var 500 MB in /usr |
Before you install Oracle VM Manager, make sure that your computer meets the following minimum software and configuration requirements.
Oracle VM Manager is supported on the following operating systems:
Oracle Linux 5 Update 5 64-bit or later
Oracle Linux 6 64-bit or later
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Update 5 64-bit or later
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 64-bit or later
You can download Oracle Linux from:
https://edelivery.oracle.com/linux
For more information about Oracle Linux, see:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/linux/whatsnew/index.html
The host computer on which you install Oracle VM Manager must have the host name correctly configured (pingable). Make sure the computer's host name matches the host name in the /etc/hosts file. Use the following command to check the host name:
# hostname
Use a text editor to check the host name in the /etc/hosts file. For example, to use VI enter
# vi /etc/hosts
For example, if the computer's host name is hostname1.example.com, and the IP address is 10.1.1.1, the corresponding item in the /etc/hosts file should be:
10.1.1.1 hostname1.example.com hostname1
The Oracle VM Manager user interface is supported in the following Web browsers:
Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0 and above
Mozilla Firefox 3.5 and above
Apple Safari 5.0 and above
Google Chrome 1.0 and above
The createOracle.sh is a script that automatically:
Creates the required operating system users and groups (oracle/dba) in order for the components to run correctly.
Creates the /u01 directory if it does not already exist, and corrects permissions on required installation folders.
Sets the required parameters in the /etc/security/limits.conf file
Opens the required ports in the /etc/sysconfig/iptables file
To run the createOracle.sh script, you must first mount the
Oracle VM Manager installer ISO file or CD. See
Section 4.4.1, “Mounting the Oracle VM Manager Installation Media” for information on
mounting the installation media. Change directory to the mount
point that you created for the CD or ISO, for example,
/OVMCD. Then run the
createOracle.sh script as the
root user:
# cd /OVMCD # ./createOracle.sh
This section contains the prerequisite operating system packages that may be required prior to installing Oracle VM Manager.
A default Oracle Linux install has the firewall enabled (iptables on). In order to use Oracle VM Manager on a system with iptables enabled you can either open all the ports used by Oracle VM Manager, or open all ports by disabling iptables.
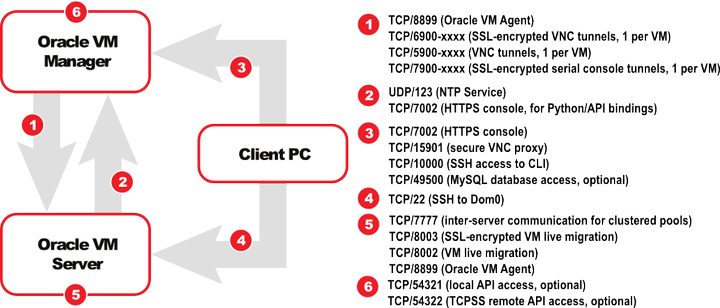
The ports required for the web browser connection to Oracle VM Manager are: 7002 and 15901. TCP 7002 is used by the Oracle VM Servers to connect to Oracle VM Manager. Oracle VM Manager, in turn, connects to the Oracle VM Servers through port 8899 for Oracle VM Agent communication, and port 6900 and up for secure VNC tunneling to virtual machines (one port per VM). Ports 7900 and up are used to allow Oracle VM Manager to open secure serial console tunnels to virtual machines (one port per VM) on the Oracle VM Servers. The Oracle VM Command Line Interface connects to Oracle VM Manager on port 10000. TCP ports 54321 and 54322 can be optionally enabled for remote API access to the Oracle VM Manager core. This must be done if using an external client, such as the Oracle VM Utilities, or UI instance to manage the deployment [1] . In a Simple installation, a MySQL database is configured on port 49500. Since the MySQL database is hosted on the same system as Oracle VM Manager it is not necessary to enable access to this port through the firewall, however in a Custom installation where the database may be hosted on a separate system, the appropriate port must be accessible to Oracle VM Manager through any firewall configuration. Be sure to open the necessary ports on the different firewalls that may be installed between different parts of your network. Follow the guidelines of in the diagram below:
To disable iptables and open all ports, enter the following commands as the root user:
# service iptables stop # chkconfig iptables off
To configure the firewall to open the required ports automatically, use the environment configuration script provided with the Oracle VM Manager installer. See Section 4.3.2.4, “Environment Configuration Script” for information on using this script.
Alternatively, to open the required ports manually by using the iptables command as the root user:
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 7002 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 15901 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT # iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m udp -p tcp --dport 10000 -j ACCEPT
To remotely connect to the Oracle VM Manager core API using an alternate UI instance or an alternate client, also enter the following command:
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 54321 -j ACCEPT
To enable the Oracle VM Command Line Interface, enter the following command:
# iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 10000 -j ACCEPT
When all the ports have been opened, save the iptables configuration:
# service iptables save
This does not require iptables to be restarted as the commands open the ports while iptables is running and the save ensures they are opened on reboot/restart in future.
During the Oracle VM Manager installation, you may be required to set or enter the following ports, passwords and database connection information:
The database system hostname. This is the IP address or hostname of the host on which the database to use as the Oracle VM Manager database repository is located. The default is
localhost. This is only required during a Custom installation.The Oracle Database System ID (SID). This is the database SID to use to connect to the Oracle VM Manager database repository. This is only required during a Custom installation.
For installations using MySQL as the database backend, this can be set to the name of the database to use for the installation. By default, this is
ovs.The Oracle Database HTTP port. The default port number is
8080. This is only required during a Custom installation.The database listener port. The default port number for installations using an Oracle Database is
1521. This is only required during a Custom installation.The port number that is set for MySQL during a Simple installation is set to
49500by default.A system-wide password is required when performing a Simple installation. This password is used for all components used by Oracle VM Manager including MySQL, Oracle WebLogic and the Oracle VM Manager application itself. Note that the password should at least adhere to the requirements for an Oracle WebLogic password as set out below.
The password for the Oracle Database SYS and SYSTEM accounts. You cannot use special characters for this password. Use only alpha numeric characters. This is only required during a Custom installation.
The password for the Oracle VM Manager OVS database schema. This is only required during a Custom installation.
The password for the Oracle WebLogic admin account. This is only required during a Custom installation.
The password you use for the Oracle WebLogic admin account must conform to the following rules:
Be between 8 and 16 characters in length.
Contain at least 1 lower case and 1 upper case letter.
Contain at least 1 numeric value or special character.
You must have an oracle user that is a member of a group named dba and which has the correct security limits set.
To configure the oracle user automatically, use the environment configuration script provided with the Oracle VM Manager installer. See Section 4.3.2.4, “Environment Configuration Script” for information on using this script.
Alternatively, you can setup the oracle user by following the commands below:
If the oracle user does not exist on the Oracle VM Manager host, enter the following commands as the root user to create the user, create the group, add the user to the group, and set the user's password:
# groupadd dba # useradd -g dba oracle
If the oracle user already exists, add it to the dba group using the following command:
# usermod -g dba oracle
The oracle user must also have a
hard nofilesandsoft nofilesminimum of at least 8192, as well as some other security limits set. To set these, edit the /etc/security/limits.conf file to include the following:oracle hard nofile 8192 oracle soft nofile 8192 oracle soft nproc 4096 oracle hard nproc 4096 oracle soft core unlimited oracle hard core unlimited
Oracle VM Manager and supporting products are installed into the /u01/app/oracle directory. Before you begin the Oracle VM Manager installation, make sure a /u01 directory exists, and it has at least 2.4 GB of space available.
To create the /u01 directory automatically, use the environment configuration script provided with the Oracle VM Manager installer. See Section 4.3.2.4, “Environment Configuration Script” for information on using this script.