| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Sun Blade X4-2B Installation Guide for Oracle Solaris Operating System |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Sun Blade X4-2B Installation Guide for Oracle Solaris Operating System |
About Oracle Solaris OS Installation
Installing the Oracle Solaris OS
Installing the Oracle Solaris OS
Install the Solaris OS (Oracle System Assistant)
Install the Oracle Solaris OS (Manually)
When you are configuring an operating system for a networked server, you might need to provide the logical name (assigned by the OS) and the physical name (MAC address) of each network interface. This topic shows you how to get this information.
Use this procedure to display information about MAC addresses and network interfaces, including their logical and physical names (MAC addresses).
If a message appears about mounting an OS instance, select q. You should not mount any OS instance.
The message "Starting Shell" appears. See the following figure.
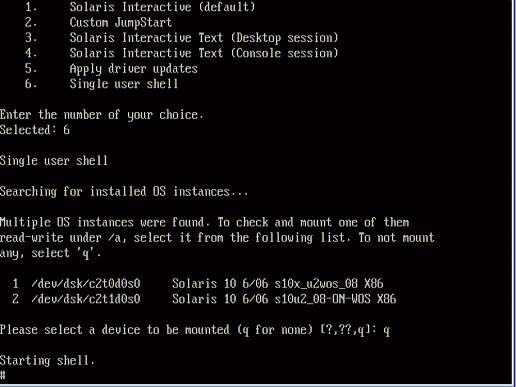
# ifconfig -a plumb
# ifconfig -a
The output of Solaris named interfaces and MAC addresses appears. For example:
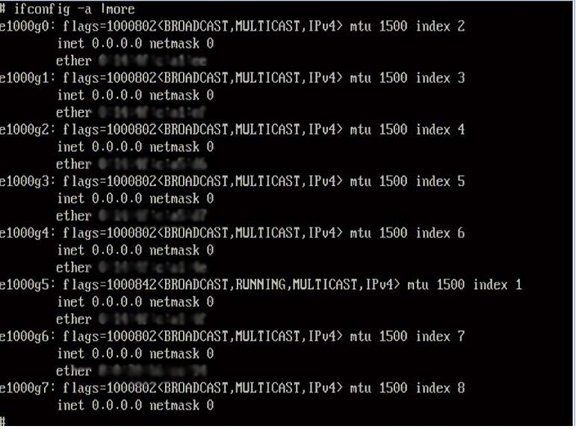
In the sample output above:
The el000g# entry in the first column is the Solaris logical named interface. This first column in the output identifies the logical names assigned by Solaris to the network interfaces.
The ether #:#:#:#:#:# entry in second column (third row) is the physical MAC address name of the network port.
For example:
The physical MAC address for the Solaris named network interface is e1000g0 is 0:14:4f:c:a1:ee.
This command restores the system configuration to the factory defaults.
Caution - The sys-unconfig(1M) command halts the system and restores the factory settings. Do not run this command unless you are ready to reconfigure your system. |
For example:
# sys-unconfig WARNING This program will unconfigure your system. It will cause it to revert to a "blank" system - it will not have a name or know about other systems or networks. This program will also halt the system. Do you want to continue (y/n) ?
The system reboots and the configuration script starts.