About the Oracle Solaris Network Protocol Stack
The following figure shows the layers of the Oracle Solaris network protocol stack. This information can help you determine which networking strategies to adopt at your site. By being familiar with the layers, you can also better detect networking connectivity problems, track and diagnose sources of performance issues, and troubleshoot configuration issues.
Note the figure shows only those layers of the stack that pertain to the various networking features described in this document.
Figure 1 Physical and Virtual Network Administration Within the Network Protocol Stack
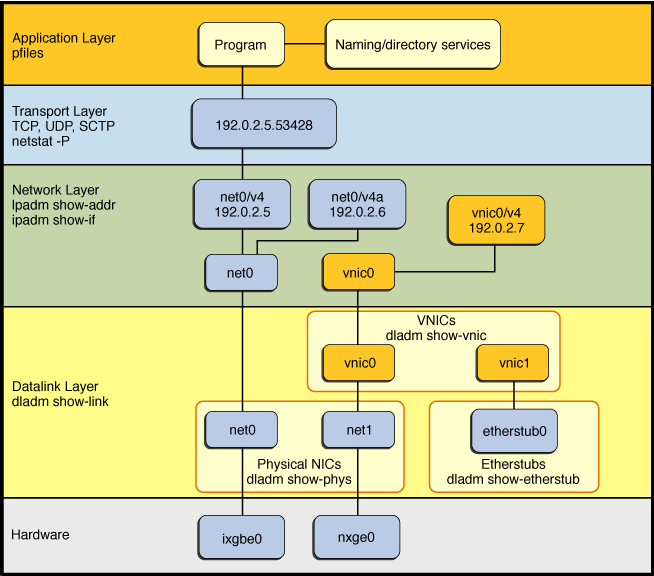
The following table further describes which layer of the stack each feature is administered. Some features are administered at more than one layer of the stack.
|