Remote Boot Method
Oracle has implemented a ROM BIOS extension for its HCA cards. This extension, called XgBoot, enables you to use Oracle virtual I/O resources as boot devices for the server. You configure the system BIOS to include XgBoot in the boot order and configure the Oracle Fabric Interconnect to make sure virtual resources are bootable.
Whatever remote booting process you select, you use the following high-level steps:
-
Set up the boot volume.
You need the boot image to be available on the network.
-
Configure bootable I/O resources on the Oracle Fabric Interconnect.
For SAN booting, this is a VHBA configured as bootable. For PXE boot, you use a bootable VNIC. Either resource must be assigned to a server profile that is bound to the server that boots remotely.
-
Configure the server.
HCAs on the server must have compatible firmware, and their option ROM must be enabled.
-
Connect the server profile on the Oracle Fabric Interconnect to the server.
-
Set the server profile to SAN boot (sanboot=).
Related Information
PXE Boot Method
During the ESXi host BIOS boot sequence, the PXE agent in the HCA option ROM scans the network for a PXE server through a VNIC. The PXE server delivers the kernel boot image and the initrd containing the host drivers to the ESXi host for booting. The PXE server initially uses DHCP and then TFTP.
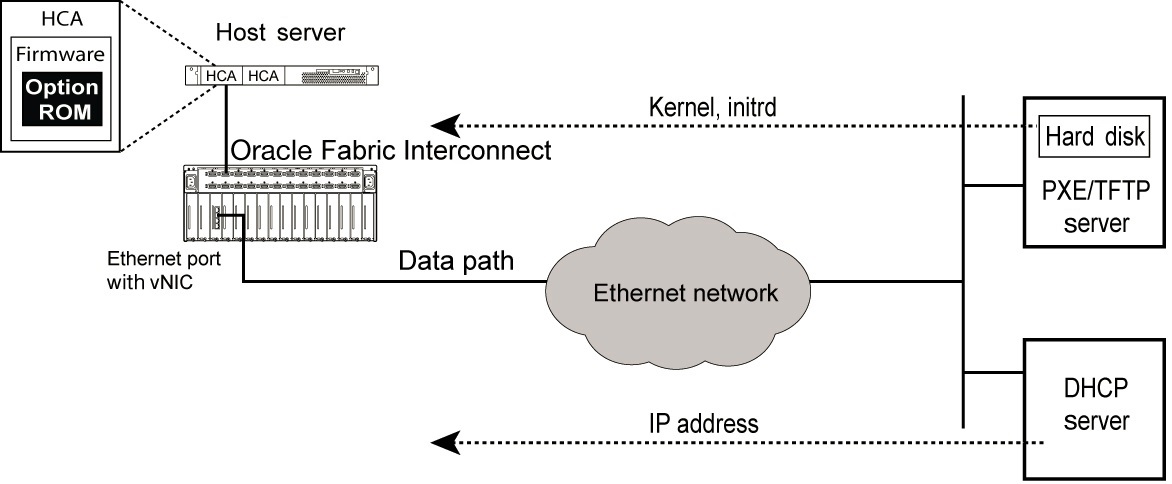
The process of PXE boot configuration is as follows:
-
Move the host drivers and OS image to the PXE server.
-
Load the host drivers into the initrd file.
-
Create a server profile.
-
Configure a bootable VNIC.
-
Modify the PXE configuration file.
-
Set the HCA to first in the boot order.
-
Load the initrd file and the OS image into the ESXi host.
iSCSI Boot Method
iSCSI boot enables you to boot an ESXi host from a LUN on an iSCSI array accessed through a VNIC. The remote disk to boot from is identified by a target IQN and LUN on a storage disk array device.
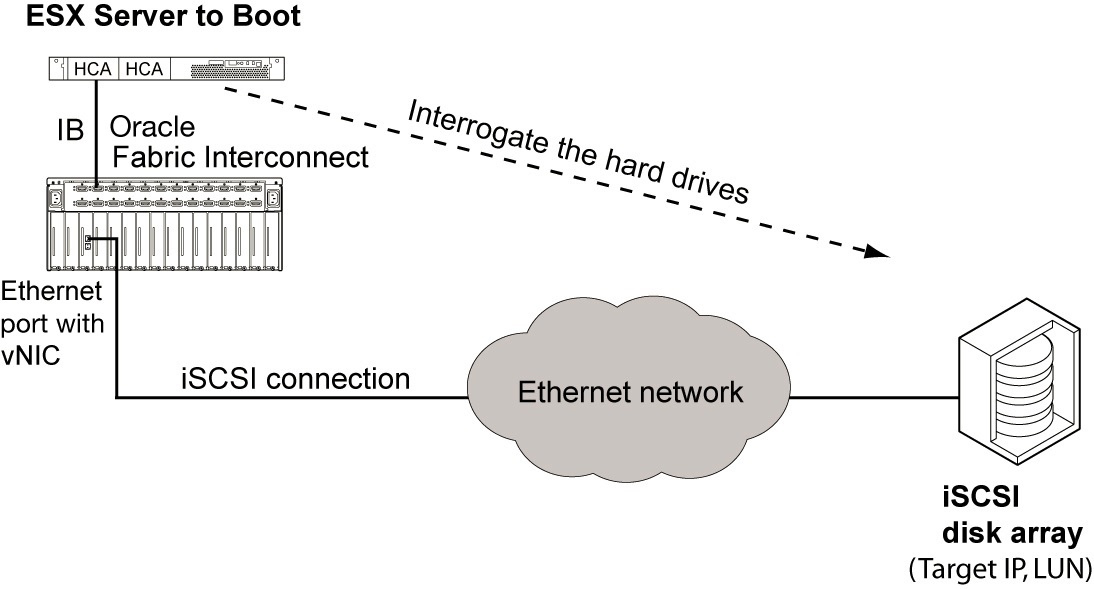
The process for iSCSI boot configuration is as follows:
-
Load the host drivers on to the OS image.
-
Move the OS image to a remote LUN.
-
Create a server profile.
-
Configure a bootable VNIC.
-
Set the HCA to first in the boot order.
-
Load the image into the ESXi host.
-
Reboot the host.
During the iSCSI boot process, the ESXi host logs in to the iSCSI array and gets the IQN information it needs. Because the VNIC has an OS available to boot from (on the iSCSI LUN connected to the VNIC), that OS is used, and the ESXi host boots over the VNIC. This procedure occurs each time the ESXi host is booted using the iSCSI boot method.
Note - The login message displayed while the VNIC is logging in to the iSCSI array appears so rapidly that you might not recognize that the ESXi host is booting from a VNIC. Additionally, no IQN or other recognizable iSCSI information is displayed on the screen.
SAN Boot Method
SAN boot enables you to boot an ESXi host from a SAN volume accessed through a VHBA. The remote disk to boot from is identified by a target WWPN and LUN on a storage disk array device.
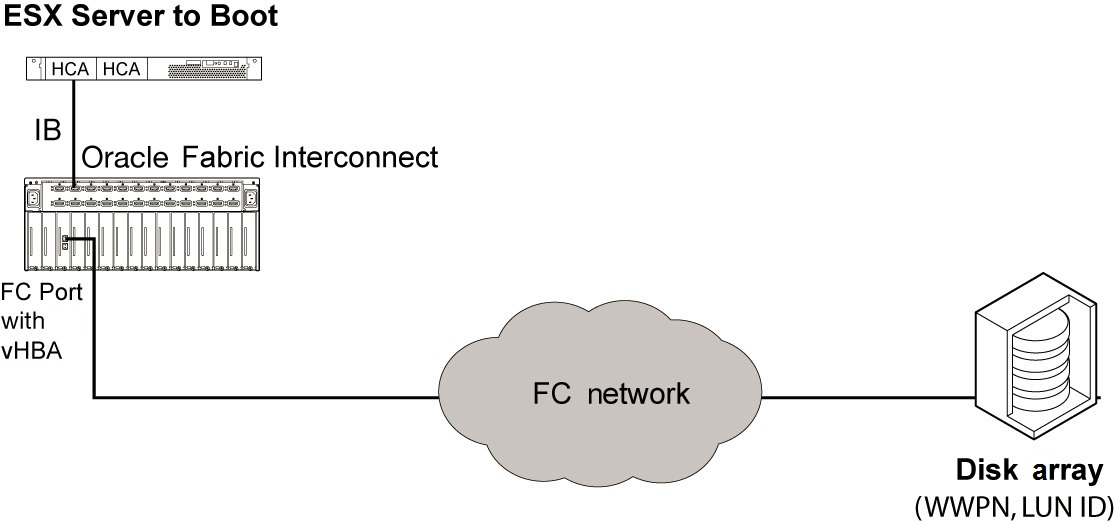
The process of configuring for PXE boot is as follows:
-
Load the host drivers into the OS image.
-
Move the OS image to a remote LUN.
-
Create a server profile.
-
Configure a bootable VHBA.
-
Set the HCA to first in the boot order.
-
Load the image into the ESXi host.
-
Reboot the host.
Note - During SAN boot, the text VHBA installing indicates the name of the VHBA configured for SAN boot.