JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server Data Service Configurations
Use the data service configurations in this section to plan the installation and configuration of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server.
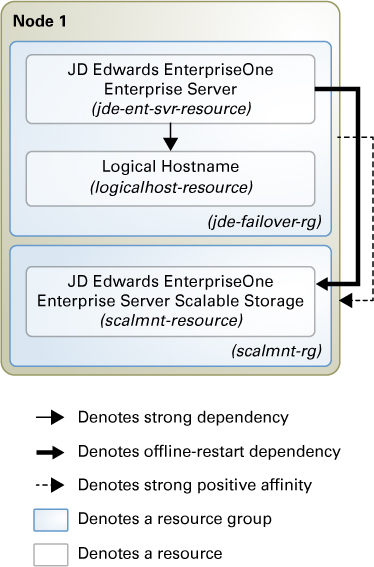
Failover Configuration
When the JD Edwards software is installed in a traditional file system, a failover deployment requires a configuration where one failover resource group contains the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resource, the logical hostname resource, and the failover storage resource. This type of configuration is shown in Figure 2–1.
Figure 2-1 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server Configured for Failover with Traditional File Storage

When the JD Edwards software is installed on NAS, a failover resource group is configured with the logical hostname resource and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resource. A scalable resource group is configured with the NAS storage resource. This type of configuration is shown in Figure 2–2.
Figure 2-2 JD Edwards Enterprise One Server Configured for Failover with NAS
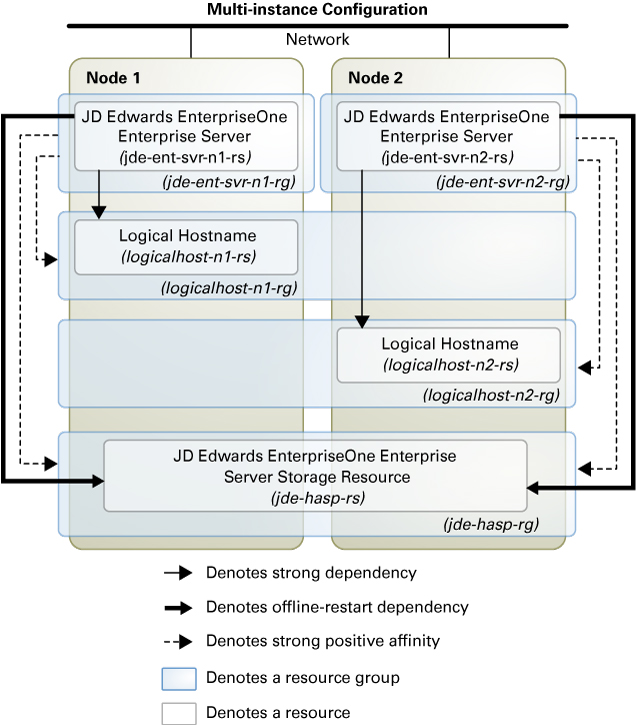
Multi-Instance Configuration
Multi-instance configuration is an application deployment topology where multiple instances of the same application provide an aggregation of services. This topology can be achieved independently from using a data service because you can manually start and stop the instances on the cluster nodes. When you require high availability of such instances, you can enable a data service for the instances by creating multiple single-node resource groups or a few multi-master resource groups.
Figure 2–3 illustrates a multi-instance configuration using single-node resource groups. A single-node resource group is created for each of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resources. Each resource group has a strong positive affinity on a storage resource group whose primary node is the node containing the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resource group.
Figure 2-3 JD Edwards Enterprise One Server Configured as a Multi-Instance Application With Single-Node Resource Groups
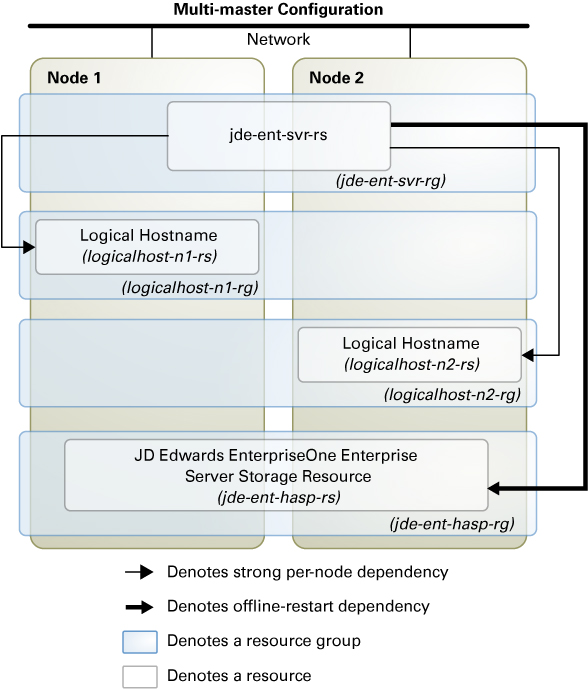
Multi-Master Configuration
The multiple-master configuration is similar to a multi-instance configuration, except that all the instances of JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server are managed by a single resource. In a multi-master data service configuration, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resource is created in a scalable resource group. The server resource is online on multiple nodes at the same time.
Figure 2–4 illustrates a multi-master configuration using a scalable resource group. A scalable resource group is created for managing multiple instances of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server in a single resource. The resource group has a strong positive affinity on a storage resource group whose primary node is the node containing the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server resource group.
Figure 2-4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server in a Multi-Master Configuration Using a Scalable Resource Group