The EStore.International module extends the repository definitions for existing item types that have properties that require translation (category, product, SKU, etc.). It also adds several new helper item types that are used to store translated content for the existing item types. These two mechanisms work together to replace properties that require translation with derived properties that obtain their values based on the customer’s current locale. The following section describes this process in detail.
Extending the Repository Definitions
The International module makes the following modifications to each item type that has properties that require translation:
New properties are created that correspond to the item type’s translatable properties. For example, if an item type has three translatable properties, three new properties are created. The new properties are named using the convention
<translatableProperty>Default. They are tied to the original properties’ database columns and represent the default translations for the properties (thereby allowing us to redefine the original properties as derived properties). For example, theSKUitem descriptor has four properties that require translation:displayName,description,size, andcolor. TheInternationalmodule adds four new properties —displayNameDefault,descriptionDefault,sizeDefault, andcolorDefault— to theSKUitem descriptor. These four properties are tied to thedisplay_name,description,sku_size, andcolorcolumns, respectively, where the default translations for the content (English for Commerce Reference Store) are stored.A
translationsproperty is added to the item type. Thetranslationsproperty is a map whose key is alocaleand whose value is an item of type<baseType>Translation, described below. Note that thelocalekey does not have to be a fully qualified locale. In fact, Commerce Reference Store only uses the language code portion of the locale. We’ll coverlocalein more detail below as well.
The International module defines a set of helper item types that use the naming convention <baseType>Translation, where <baseType> refers to an existing item type. A corresponding <baseType>Translation item type is defined for all existing item types that have translatable properties (for example, a skuTranslation item type is created to correspond with the sku item type, a productTranslation item type is created to correspond with the product item type, and so on). <baseType>Translation items function as containers for locale-specific content. As such, each <baseType>Translation item type has properties that correspond to the translatable properties of its base item type. For example, the sku item type has four properties that require translation — displayName, description, size, and color — therefore, the skuTranslation item also has four properties for displayname, description, size, and color.
Each <baseType>Translation item type has its own table in the database, where each row represents a single <basetype>Translation item with a unique ID. For example, the crs_sku_xlate table contains all the skuTranslation items, the crs_prd_xlate table contains all the productTranslation items, and so on.
Note: For a detailed list of <baseType>Translation item types created by the International module, see Translation Items Created by the International Module.
Every base item (in other words, every SKU, every product, every category, and so on) is tied, through its translations property, to one or more <baseType>Translation items. For each base item, a separate <baseType>Translation item exists for each locale (with the exception of the default locale, which we will get to momentarily). The following illustration shows three sku items and six corresponding skuTranslation items which contain translated content for two locales, Spanish and German:
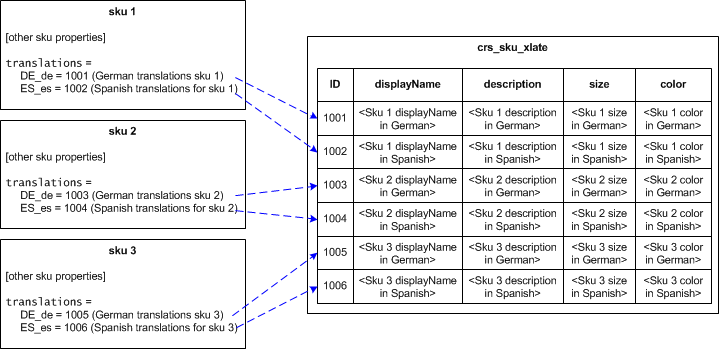
To create the relationships that connect a base item to its <baseType>Translation items, the International module changes the definitions of the translatable properties in the existing item types. The new definitions specify that each translatable property is a derived property whose value is determined as follows:
Use the current locale to look up a corresponding
<baseType>Translationitem in thetranslationsproperty map. The property derivation attempts to find a best match. First, it searches thelocalekeys for a match on the entire locale with a variant, then it searches for a match on the locale without a variant, and finally it searches on just the language code.If a
<baseType>Translationitem exists for the current locale, use its value for the property.If a
<baseType>Translationitem doesn’t exist for the current locale, or its value for the property is null, use the<translatableProperty>Defaultvalue instead.
The following illustration is a graphic representation of the repository changes made by the International module. It shows a sku base item with two supporting skuTranslation items, one for German and the other for Spanish. The sku base item has been modified to add four <translatableProperty>Default properties: displayNameDefault, descriptionDefault, sizeDefault, and colorDefault. The sku base item has also been modified to add the translations property, which contains the map connecting the base sku item to its German and Spanish translation items. Finally, the displayName, description, size, and color property definitions have been changed to derived properties.
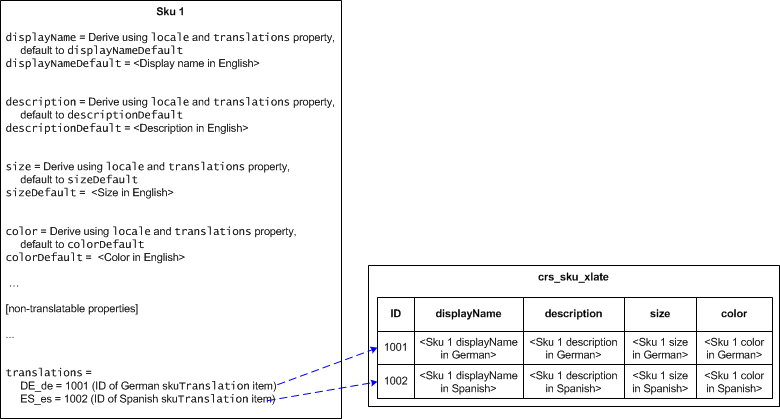
Repository Item Translation Examples
The following illustration shows how the sku.displayName property is derived for a store that has English (default), German, and Spanish translations:
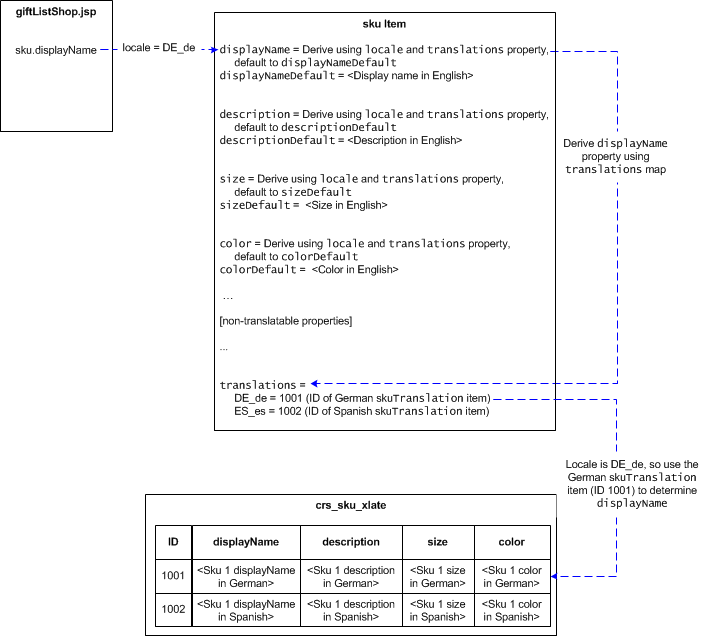
In this illustration, the following happens:
giftListShop.jsprequests thesku.displayNameproperty for a SKU. The locale for the request is determined according to the rules described in Determining a Customer’s Locale and, in this example, isDE_de.The catalog repository finds the corresponding
skuTranslationitem using thesku.translationsproperty map. The repository determines that, for aDE_delocale, the GermanskuTranslationitem should be referenced.The catalog repository returns the
displayNameproperty from the GermanskuTranslationitem.
This next illustration shows what happens when a locale is specified that doesn’t exist in the sku.translations property map.
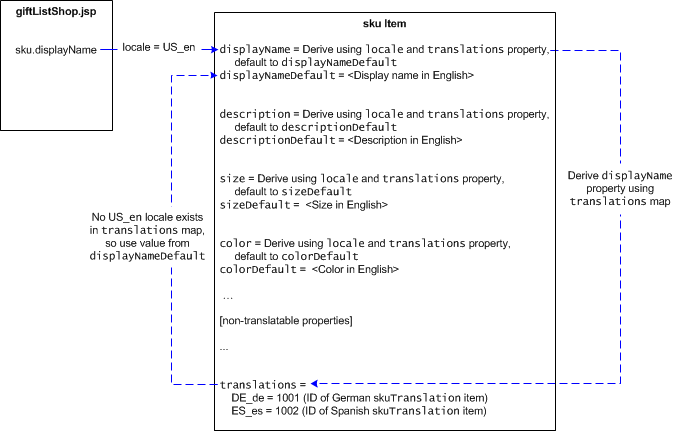
In this illustration, the following happens:
giftListShop.jsprequests thesku.displayNameproperty for a SKU. The locale for the request is determined according to the rules described in Determining a Customer’s Locale and, in this example, isUS_en.The catalog repository derives the display name for the SKU using the
sku.translationsproperty map. The repository determines that noskuTranslationitem exists for theUS_enlocale, so it returns the value from thesku.displayNameDefaultproperty, which for Commerce Reference Store is the English translation.
Repository Item Translation Benefits
The approach Commerce Reference Store takes to handling the translation of repository items offers several significant benefits over other internationalization approaches:
An application may switch between international and non-international modes without requiring any JSP page changes. The same property names are used in the JSP page code and each repository derives the appropriate language as necessary.
Adding another language is accomplished by adding more
<baseType>Translationitems, referred to by their base items through the appropriatelocalekey. No database schema changes are required to add additional languages.
Translation Items Created by the International Module
Several repository definition files in the International module’s config.jar file (<ATG10dir>/CommerceReferenceStore/Store/EStore/International/config/config.jar) define the <baseType>Translation items for Commerce Reference Store.
The /atg/commerce/catalog/custom/customCatalog.xml file defines the following <baseType>Translation items for the catalog repository:
categoryTranslation(stored in thecrs_cat_xlatetable)productTranslation(stored in thecrs_prd_xlatetable)skuTranslation(stored in thecrs_sku_xlatetable)featureTranslation(stored in thecrs_fea_xlatetable)asSeenInTranslation(stored in thecrs_asi_xlatetable)promotionalContentTranslation(stored in thecrs_prmcnt_xlatetable)
The /atg/commerce/pricing/pricingModels.xml file defines the following <baseType>Translation items for the promotions repository:
promotionTranslation(stored in thecrs_prm_xlatetable)closenessQualifierTranslation(storedcrs_cq_xlatetable)
The /atg/seo/SEORepository.xml file defines the following <baseType>Translation items for the SEO repository:
SEOTranslation(stored in thecrs_seo_xlatetable)
The /atg/store/stores/storeText.xml file defines the following <baseType>Translation items for the store text items held in the StoreRepository:
storeTextTranslation(stored in thecrs_txt_xlatetable)storeLongTextTranslation(stored in thecrs_txt_long_xlatetable)
A Note About the StoreRepository
The /atg/store/stores/StoreRepository holds store items as well as storeText and storeLongText items. store items define properties for store locations such as address, phone, and fax numbers. storeText and storeLongText items hold text-based content that appears on the static information pages such as About Us, Corporate Site, Careers, and so on (storeText holds content that is 256 characters or less; storeLongText holds content that is greater than 256 characters).
To view storeText and storeLongText items:
Start the Business Control Center.
Expand Merchandising, and then click Browse.
Click the arrow next to Store Text.

