6 Viewing The POTS/DSL Flow-through Package
This chapter describes the POTS/DSL flow-through package. The description gives a high-level description of the data flow between the workflows in the package. As you read the sections in this chapter, open the workflows in Workshop and view the contents.
What's In the Package
The package contains workflows that can be used for both POTS and DSL activation.
For the POTS portion of the package, activation set up for the following activities:
-
Residential line: Add, Change, Disconnect
-
Line feature (call waiting): Add, Change, Delete
The switch used for POTS is the Lucent 5ESS. This switch determines the ASAP cartridge and CSDL commands used.
For DSL, activation is set up for adding DSL service for a user. Voice is not included in the DSL example. The DSLAM used for DSL is the Lucent Stinger. This equipment determines the ASAP cartridge and CSDL commands used.
-
Event management workflows
Table 6-1 lists the workflows that manage messages between Oracle Communications MetaSolv Solution, the integration layer, and Oracle Communications ASAP.
Table 6-1 Event Management Workflows
| Workflow | Description |
|---|---|
|
ActivationOrderCreateEventHandler ActivationOrderCompleteEventHandler AcitvationOrderFailEventHandle |
These workflows subscribe to ASAP outbound events and update MSS with the status and external keys. |
|
MSSOutboundEventHandler |
This workflow subscribes to the MetaSolv Solution JMS queue and processes the activation. |
-
Order management workflows
The following workflows manage the activation order by requesting data from MetaSolv Solution, decomposing the activation data it receives in response, and constructing an activation order for ASAP based on CSDL commands:
ActivationOrderManager
ConnectionAllocationsHandler
ConnectionAssignmentHandler
IndividualConnectionHandler
LineFeatureHandler
LineServiceActivationHandler
NetworkElementHandler
ServiceActivationHandler
SwitchActivationHandler
The order management workflows are structured in the hierarchy shown in Figure 6-1.
Figure 6-1 Order Management Workflow Hierarchy
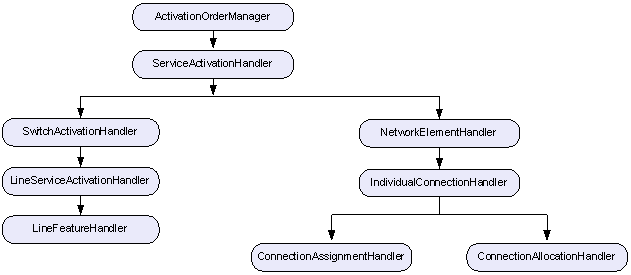
Description of "Figure 6-1 Order Management Workflow Hierarchy"
-
XQuery Transformation Files
The following transformation files use XQuery mappings to transform MetaSolv Solution and ASAP data into the proper XML formats as the data moves between the applications and the integration layer during the activation process.
-
ActivationRequestConverter (common XQuery workflows for requests)
makeASAPOrderFromServiceActivation
makeCreateOrderByValueRequestFromASAPOrder
makeGetActivationRequestFromMSSEvent
makeServiceActivationFromGetActivationResponse
-
ActivationResponseConverter (common XQuery workflows for responses)
makeEventStatusChangeFromCreateOrderException
makeEventStatusChangeFromOrderCompleteEvent
makeEventStatusChangeFromOrderCreateEvent
makeEventStatusChangeFromOrderFailEvent
-
LuStingerActivationRequestConverter (DSL workflows specific to the Lucent Stinger DSLAM)
makeAddDSLPortFromConnectionAssignment
makeAddVCFromConnectionAllocation
makeWanConnAllocArrayFromIndividualConnection
-
LU5ESSActivationRequestConverter (POTS workflows specific to the Lucent 5ESS switch)
makeAddPotsCallWaitingFromActivationData
makeAddPotsResLineFromActivationData
makeChangePotsCallWaitingFromActivationData
makeDeletePotsCallWaitingFromActivationData
makeDeletePotsLineFromActivationData
-
Naming Conventions
The flow-through package uses the same names for the workflows that appear in the schema as container names with a few exceptions.
Figure 6-2 shows the switchActivation portion of the schema for the getActivationDataByKeyResponse. The figure also shows the schema displayed graphically in XMLSpy. The switchActivation name in the schema is SwitchActivationHandler in the workflows, and the lineServices name from the schema is LineServiceActivationHandler in the workflows.
Figure 6-2 Schema Showing Switch Activation Container
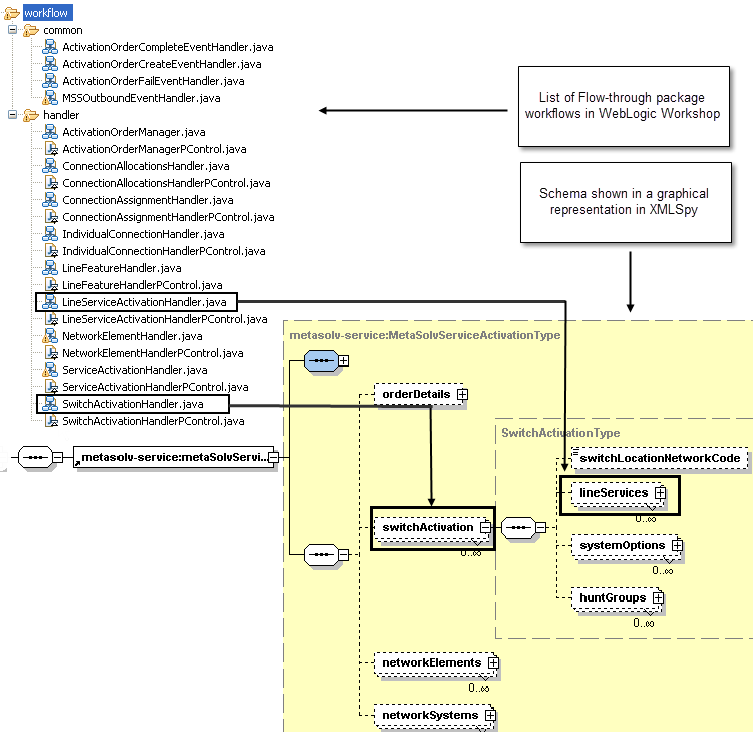
Description of "Figure 6-2 Schema Showing Switch Activation Container"
How the Workflows for POTS and DSL Handle Data
The following section describes how the workflows handle data and events for activation. The entire activation process is triggered when the Activate task in MetaSolv Solution is completed and an event is sent to the MSSOutboundEvent processor in the integration layer.
Figure 6-3 shows how the data flow in the integration layer is controlled by processors.
Figure 6-3 Data Flow in the Integration Layer is Controlled by Processors
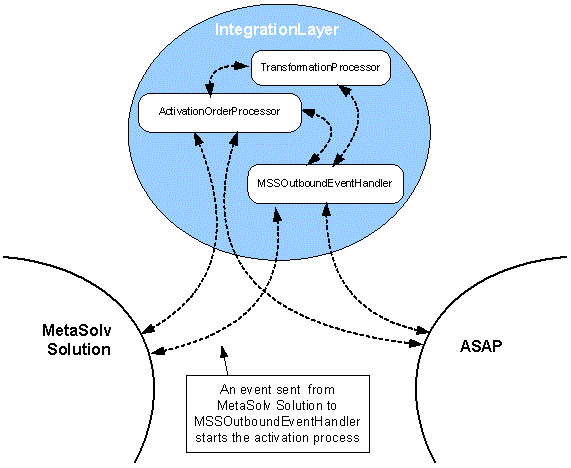
Description of "Figure 6-3 Data Flow in the Integration Layer is Controlled by Processors"
Figure 6-4 shows the MSSOutboundEventHandler workflow. This workflow is initially called when an event is detected. The remaining workflows for order management and transformation management are called from this workflow.
Figure 6-4 MSSOutboundEventHandler Workflow
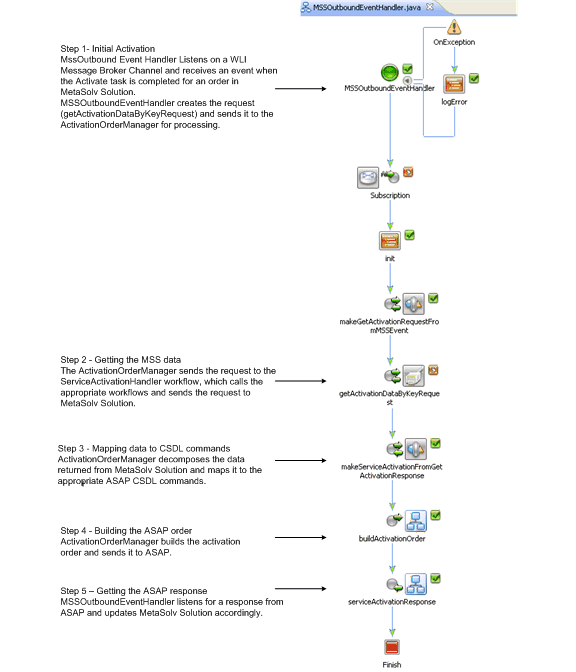
Description of "Figure 6-4 MSSOutboundEventHandler Workflow"
Step 1: Initial Activation Event
Figure 6-5 shows how event messages were set up in WebLogic for the flow-through package:
-
WebLogic Integration setup of the JMS queue for outbound MetaSolv Solution activation events
-
Identification of the channel name that MSSOutboundEventHandler subscribes to in the workflow in WebLogic Workshop
Figure 6-5 Event Setup in the WebLogic Integration Console and in Workshop
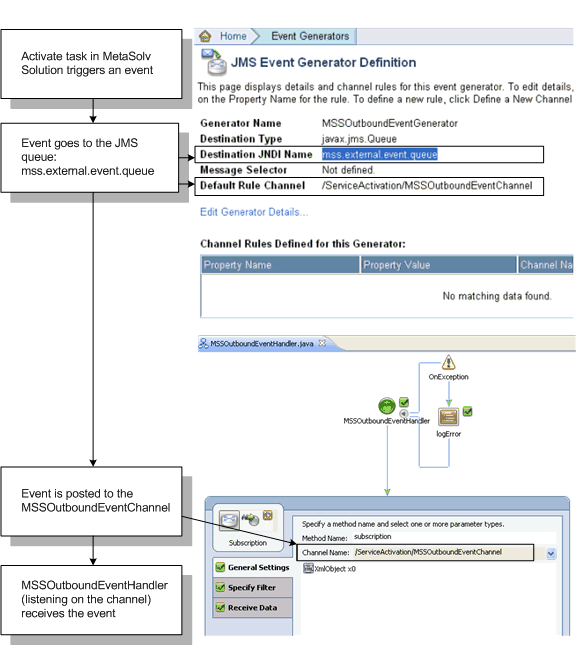
Description of "Figure 6-5 Event Setup in the WebLogic Integration Console and in Workshop"
Step 2: Getting MetaSolv Solution Data
MSSOutboundEventHandler sends the request to ActivationOrderManager which handles getting activation data from MetaSolv Solution, decomposing the data, mapping the data to CSDL commands and building the ASAP order.
Figure 6-6 shows the ActivationOrderManager workflow.
Figure 6-6 ActivationOrderManager Workflow
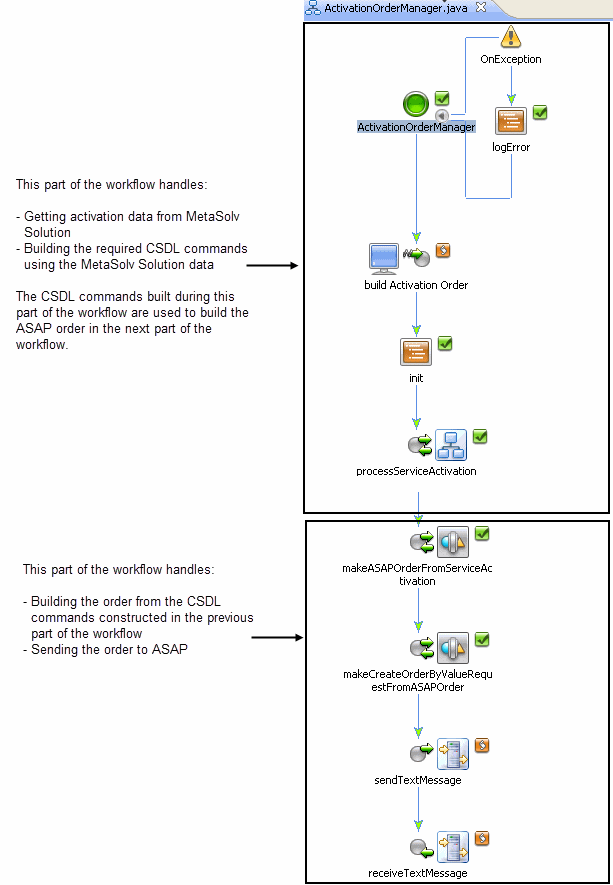
Description of "Figure 6-6 ActivationOrderManager Workflow"
ServiceActivationHandler (a workflow called by ActivationOrderManager) determines the workflows required by a request and makes the call for data to MetaSolv Solution.
Figure 6-7 shows how POTS and DSL activation data requests are managed by ServiceActivationHandler.
Figure 6-7 ServiceActivationHandler Managing POTS and DSL Activation
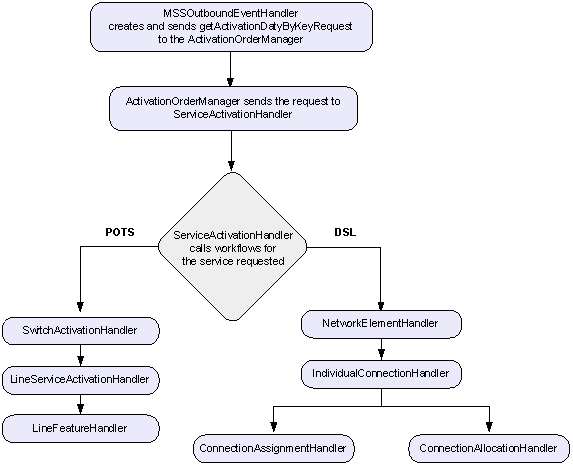
Description of "Figure 6-7 ServiceActivationHandler Managing POTS and DSL Activation "
For DSL, ServiceActivationHandler calls NetworkElementHandler. SwitchActivationHandler is not involved in the request for DSL data because there is no switch involved directly in DSL activation. The physical line for a DSL activation is connected to a DSLAM. All lines from the DSLAM to the Internet are virtual lines. The properties required for activation in the case of DSL can be captured through network elements in the network system over which service is provisioned.
Step 3: Mapping the Data to CSDL Commands
When the request data is returned from MetaSolv Solution (through the method getActivationDataByKeyResponse), ActivationOrderManager maps the data to the appropriate ASAP CSDL command. For POTS, the XQuery workflows that map CSDL commands for the Lucent 5ESS switch for the flow-through package are shown in the following figures. The POTS portion of the flow-though package was designed to add or delete a residential line.
Figure 6-8 shows the XQuery workflows that map CSDL commands for adding and deleting a line.
Figure 6-8 Mapping CSDL Commands for Adding or Deleting a POTS Residential Line
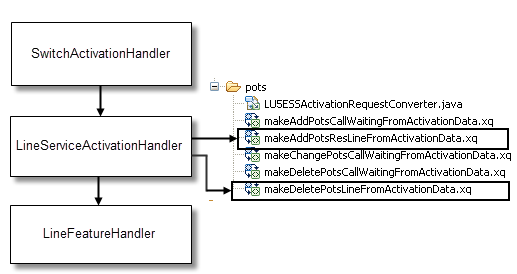
Description of "Figure 6-8 Mapping CSDL Commands for Adding or Deleting a POTS Residential Line"
Figure 6-9 shows the XQuery workflows that map CSDL commands for adding, changing, or deleting call waiting, which is a line feature (or line option).
Figure 6-9 Mapping CSDL Commands for a POTS Line Feature (Call Waiting)
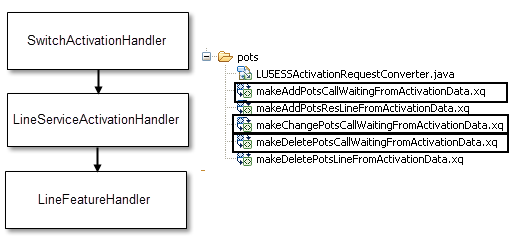
Description of "Figure 6-9 Mapping CSDL Commands for a POTS Line Feature (Call Waiting)"
Figure 6-10 shows the XQuery workflows that map CSDL commands for adding DSL service.
Figure 6-10 Mapping CSDL Commands for Creating the Physical and Virtual Connections for DSL
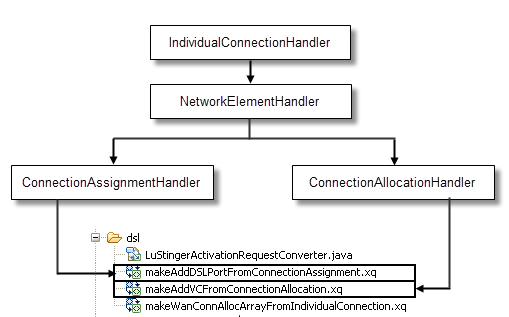
Description of "Figure 6-10 Mapping CSDL Commands for Creating the Physical and Virtual Connections for DSL"
Figure 6-11 shows the XQuery workflows that map CSDL commands for creating an array of connections that represent the DSL service.
Figure 6-11 Mapping CSDL commands for creating an array of connections that represent the DSL service
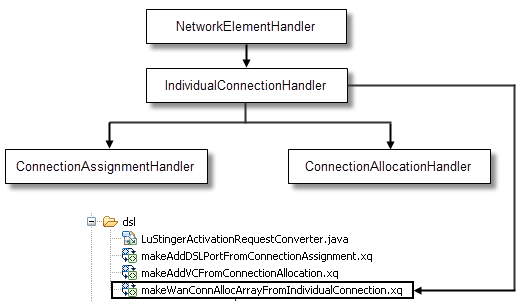
Description of "Figure 6-11 Mapping CSDL commands for creating an array of connections that represent the DSL service"
Step 4: Building and Sending the ASAP Order
ActivationOrderManager builds the ASAP order from the CSDL commands mapped to MetaSolv Solution data and sends the order to ASAP as shown in Figure 6-12.
Figure 6-12 ActivationOrderManager Group that Creates and Sends the ASAP Order
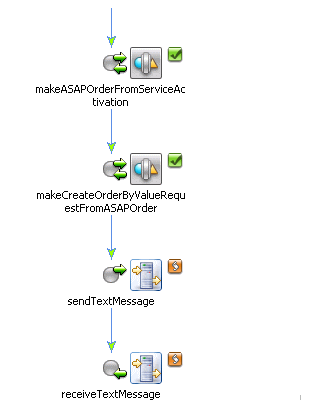
Description of "Figure 6-12 ActivationOrderManager Group that Creates and Sends the ASAP Order"
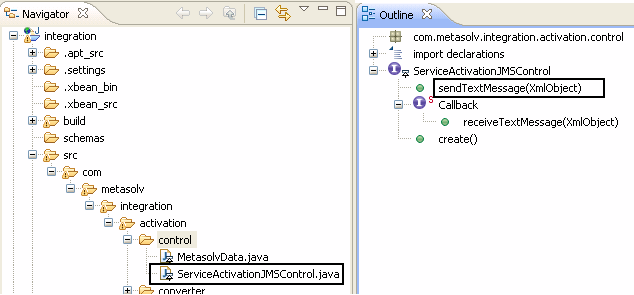
ActivateOrderManager sends the text message that contains the request by calling the sendTextMessage method in the ServiceActivationJMSControl shown in Figure 6-13. The result is a message posted on ASAP.MessageQueue.
ServiceActivationJMSControl is a basic WebLogic Integration control that you can configure. The properties defined for the ServiceActivationJMSControl are the same as the foreign JMS server as shown in Figure 6-14.
Figure 6-14 Properties for ServiceActivationJMSControl
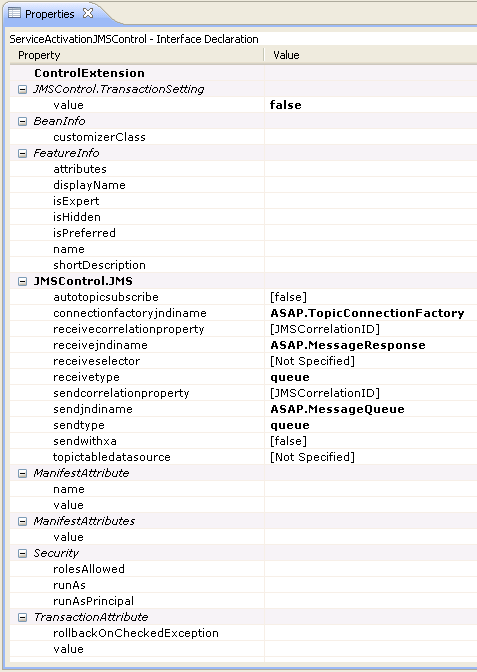
Description of "Figure 6-14 Properties for ServiceActivationJMSControl"
To see the properties defined for the foreign JMS server for the flow-through package, see "Step 2: Setting Up the Foreign JMS Server".
Step 5: Getting the Service Activation Response
When the request is sent to ASAP, the MSSOutboundEventHandler listens on the specified channel for an event from ASAP. The following ASAP events are possible:
-
createOrderResponse
This event indicates that the initial data was accepted and an order was created. The following event types can result from the order being created in ASAP.
-
orderCreateEvent: the order is successfully created.
-
orderCompleteEvent: the order is successfully completed and activation occurs.
-
orderFailEvent: the order is successfully created but fails on deployment.
-
-
createOrderFail
This event indicates the initial data was not accepted, and the order was failed without being created in ASAP.
Figure 6-15 shows the Event Handler workflows.
Figure 6-16 shows the ASAPOutboundEventChannel. All event workflows subscribe to this channel. See "Step 4: Creating the ASAP Event Generator" for information on how the channel was set up for the flow-through package.
When ASAP posts an event to a topic, the event generator moves the event to the appropriate channel. Workflows listen on the channel, waiting for an event that is specific to them.
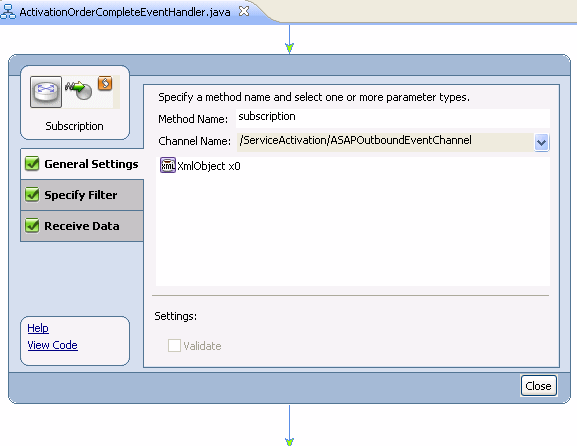
Figure 6-17 shows the properties for a method named Subscription.
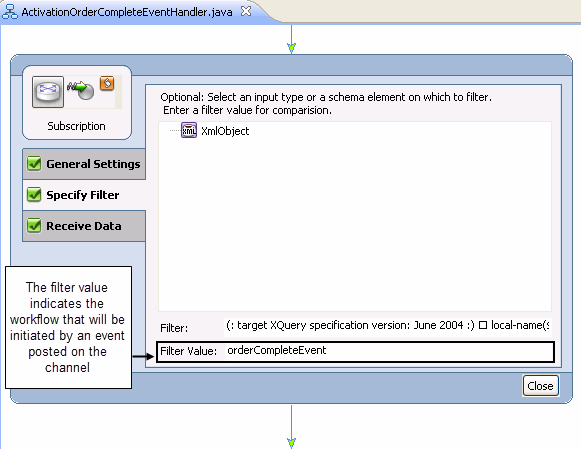
A filter determines when an event is intended for a workflow.
Figure 6-18 shows the filter set for the Subscription method shown in Figure 6-17.