60.3 Enabling Impersonation With a Header Variable
Enabling impersonation with a header variable involves completing the procedures in the following sections.
-
Reviewing all Requirements for Impersonation with a Header Variable
60.3.1 Requirements for Impersonation with a Header Variable
Prepare the environment and confirm that it is operating properly before implementing Windows impersonation with the OAM Server.
Table 60-1 identifies the Access Manager platform requirements when you enable impersonation using a header variable.
Table 60-1 Requirements for Impersonation with a Header Variable
| Item | Platform |
|---|---|
|
11g WebGate (and Impersonation dll) |
Microsoft IIS 7.x and Windows Server 2008 and 2013 |
|
Impersonation dll |
Webgate_install_dir\webgate\iis\lib\IISImpersonationModule.dll
|
|
Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) and Active Directory |
Windows Server 2008 and 2013 |
|
Client and Server machines |
|
|
Security context |
Must have Act as operating system privileges. Note: IWAM_Machine is not recommended |
|
Mutual authentication is required |
Mutual authentication is supported remotely. |
60.3.2 Creating an Impersonator as a Trusted User
Whether you enable impersonation using a HeaderVar or user profile attribute, the return value must be a trusted user in Active Directory. This special user should not be used for anything other than impersonation.
The example in the following procedure uses SPPSImpersonator as the New Object - User. With OWAImpersonator as SPPSImpersonator denotes SharePoint impersonation specifically. Your environment will be different.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you choose a very complex password, because your trusted user is being given very powerful permissions. Also, be sure to check the box marked Password Never Expires. Since the impersonation module should be the only entity that ever sees the trusted user account, it would be very difficult for an outside agency to discover that the password has expired.
Figure 60-1 Setting up a Trusted User Account for Windows Impersonation
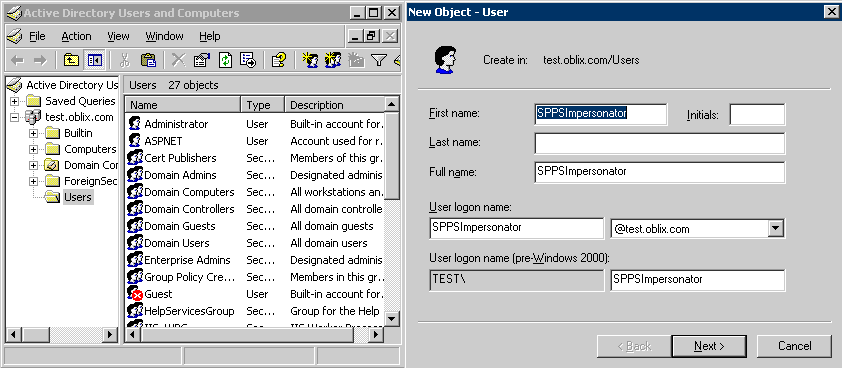
Description of "Figure 60-1 Setting up a Trusted User Account for Windows Impersonation"
60.3.3 Assigning Rights to the Trusted User
You can give the trusted user the right to act as part of the operating system.
To assign rights to the trusted user:
Figure 60-2 Configuring Rights for the Trusted User in Windows Impersonation
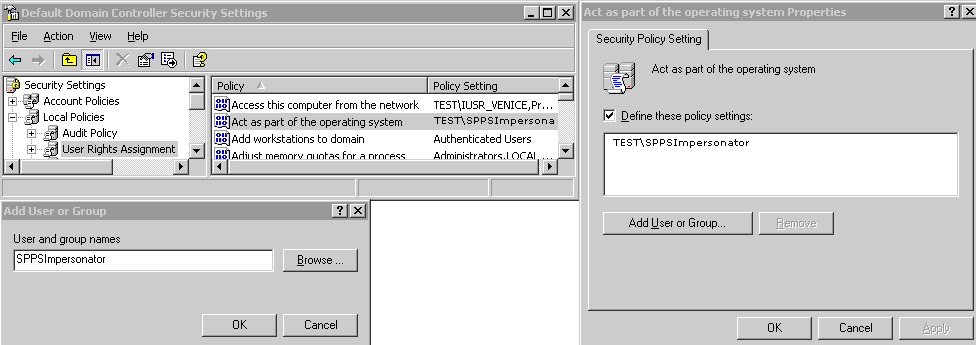
Description of "Figure 60-2 Configuring Rights for the Trusted User in Windows Impersonation"
60.3.4 Binding the Trusted User to Your WebGate
You need to bind the trusted user to the WebGate by supplying the authentication credentials for the trusted user.
The procedure presumes that you have registered an 11g WebGate with Access Manager. The values in the procedure are provided as an example only. Your environment will be different.
See Also:
60.3.5 Adding an Impersonation Response to An Application Domain
You must create or configure an application domain to protect your OWA resources.
For this you must add Responses in Authorization Policies (Header type Responses), as described in this procedure.
See Also:
Managing Policies to Protect Resources and Enable SSO in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Access Management.
The procedure presumes that you have an application domain created for the 11g WebGate you registered. The application domain in this example is MyImpersonationDomain. Your environment will be different.
This Response is used for the second WebGate request (for authorization).
60.3.6 Adding an Impersonation DLL to IIS
You are ready to configure IIS by adding the IISImpersonationModule.dll to your IIS configuration.
To add an Impersonation DLL to IIS:
60.3.7 Testing Impersonation
You can test Impersonation using an Event Viewer or a web page.
Following are the two ways of testing Impersonation:
60.3.7.1 Creating an IIS Virtual Site
To test the impersonation feature outside the Microsoft OWA 2010 context or to test single sign-on, you will need a target Web page on an IIS virtual Web site.
You create such a virtual Web site by performing the following task.
- Click Start > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
- Click the plus icon (+) to the left of the local computer icon on the tree in the left pane.
- Right-click Web Sites on the tree in the left pane, then select New, then select Web Site on the menu.
- Respond to the prompts by the Web site creation wizard.
- After you create the virtual site, you must protect it with an application domain, as described elsewhere in this guide.
60.3.7.2 Testing Impersonation Using the Event Viewer
When you perform impersonation testing using the Windows 2008 Event Viewer, you must configure the event viewer before conducting the actual test.
To test impersonation: