Policy DRA continues to support a single pool of PCRFs at each PCA site over which policy Diameter signaling is distributed using the subscriber's IMSI. This allows the incorporation of new services or new PCRF infrastructure without disturbing existing services. For example, one set of PCRF servers handle policy control for all consumer data accesses to their network and a second set of PCRF servers handle all enterprise data accesses for their network. The policy rules and/or PCRF implementations might be different enough to necessitate that these two services are segregated at the PCRF level.
This means that a given IMSI might concurrently have a binding to one PCRF for APN A and a binding to a different PCRF for APN B. Each APN is mapped to a set of PCRFs; this is called a PCRF Pool. In addition, if a binding to a PCRF Pool already and a new session is created that maps to that same PCRF Pool, the request must be routed to the same PCRF. When new bindings are created for different IMSIs and a given APN, the binding-capable session initiation requests are distributed across the PCRFs in the PCRF Pool assigned to that APN.
PCRF Pooling expands this capability for the creation of multiple pools of PCRFs, which are selected using the combination of IMSI and Access Point Name (APN). This allows you to route policy Diameter signaling initiating from a given APN to a designated subset of the PCRFs that can provide specialized policy treatment using knowledge of the APN.
PCRF Pooling modifies the logic in the Policy DRA to inspect the contents of binding generating Gx CCR-I messages to select the type of PCRF to which the CCR-I messages are to be routed. In the initial P-DRA, it was assumed that all PCRFs could handle all Gx session bindings. PCRF Pooling provides service-specific sets of PCRFs. In this release, the APN used by the UE to connect to the network is used to determine the PCRF pool. The Origin-Host of the PCEF sending the CCR-I can then be used to select a PCRF sub-pool.
Multiple PCRF pools requires differentiation among the binding records in the binding SBR. It is possible for the same UE, as indicated by the IMSI, to have multiple active IPcan sessions spread across the different pools.
When deploying multiple PCRF pools, each pool supports either different policy-based services or different versions of the same policy based services. Each PCRF pool has a set of DSR PCA peers that are a part of the pool.
- Create new PCRF Pools
- Edit existing PCRF Pools
- Delete PCRF Pools
- Identify PCRF Sub-Pools
- Add optional comments for Pools
- If a binding exists for the IMSI and APN or PCRF Pool, route the request to the bound PCRF.
- Otherwise, distribute the request to a PCRF in the configured PCRF Pool.
If the IMSI and APN are bound to a PCRF, use that binding.
- Else, if the IMSI and PCRF Pool are bound to a PCRF, create a binding for the APN to the same PCRF as already bound to the PCRF Pool.
- Else, no binding exists for the IMSI and APN or PCRF Pool, so a new binding can be created.
| Concept | Before PCRF Pooling | After PCRF Pooling |
|---|---|---|
| PCRF Pools | One PCRF Pool for all APNs. | Up to 7 PCRF Pools selected for new bindings using APN. More than one APN can be mapped to a given PCRF Pool, but a given APN can only be mapped to one PCRF Pool. |
| Subscriber Bindings | A binding is a simple mapping between an IMSI and a PCRF. Once a binding exists, all sessions for that IMSI are routed to the bound PCRF. | A binding is a mapping from an IMSI and APN to a PCRF, but with the caveat that before a new binding is created, the logic must check for existence of another binding to the same PCRF Pool for the IMSI. If such a binding exists, the new APN is bound to the same PCRF as an existing APN mapped to the same PCRF Pool. Once a binding exists, all sessions for that IMSI and APN are routed to the bound PCRF. Sessions for that IMSI and a different APN mapped to a different PCRF Pool can be routed to a different PCRF. |
| Number of Sessions per Binding | An IMSI may have up to 10 binding capable sessions. | An IMSI may have up to 10 binding capable sessions, which may be bound to different PCRFs based on APN. |
| Origin Based Routing | PRT table for new bindings specified in Site Options allows for selection of route list based on origin-host/realm. | After PCRF Pool selection, Sub-Pool rule matching is performed to select a PCRF Sub-Pool given the PCRF Pool and the origin-host of the PCEF. |
| PRT Table for New Bindings | Each site defines one PRT table to be used for all new bindings. | Each site can define a PRT table to be used for new bindings for each PCRF Pool. |
Additionally, Pooling provides the ability to route to subsets of PCRFs in a PCRF Pool on the basis of the Diameter hostname of the PCEF that originated the binding capable session initiation request. These subsets are called PCRF Sub-Pools. This capability allows a controlled amount of policy Diameter signaling to be routed to one or more PCRFs within the PCRF Pool.
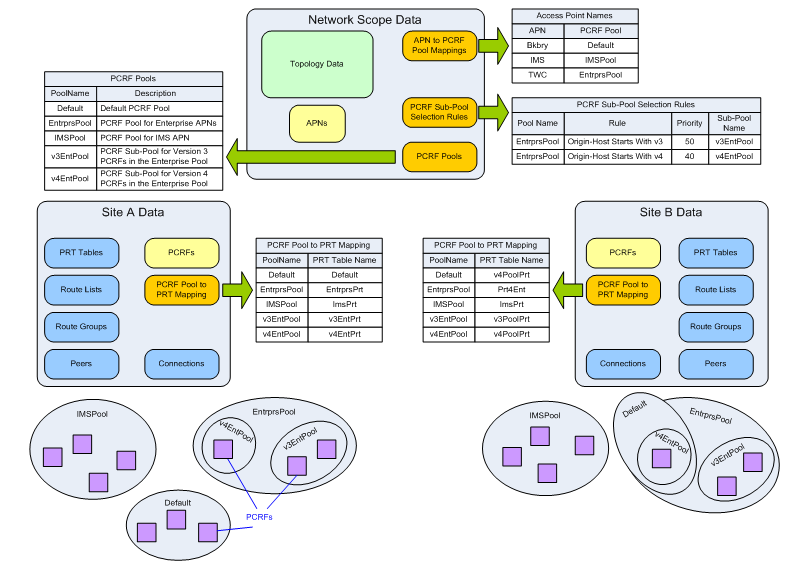
The following figure illustrates a sample PCA network configured for PCRF Pooling. The upper third of the figure shows data that is configured with the Policy and Charging GUI at the NOAM server. This data, including PCRF Pools, APN to PCRF Pool mapping, and PCRF Sub-Pool Selection Rules applies to all sites in the Policy DRA network.
The middle third of the figure shows data configured at the SOAM Policy and Charging GUI at each of two PCA sites. This data includes the PCRF Pool to PRT mappings, PCRFs, PRT tables, Route Lists, Route Groups, Peer Nodes, and Connections. This data can differ at each PCA site.
The bottom third of the figure shows the PCRFs logically grouped into PCRF Pools as defined by the network operator.
| Configuration Order | GUI Page | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PCRF Pools | Define the names of the PCRF Pools and Sub-Pools that are needed for grouping PCRFs to handle policy signaling for the various APNs. |
| 2 | PCRF Pool to PRT Mapping | At each site, select a PRT table that is used to route binding-capable session initiation requests for new bindings destined for each PCRF Pool. Each PCRF Pool should be configured with a PRT table, unless it is known that the PCRF Pool will never be selected at the site being configured. Note: Before this step can be performed, PRT tables must be defined in the Diameter folder.
|
| 3 | PCRF Sub-Pool Selection Rules | An optional table. If it is necessary to subdivide a PCRF Pool so that policy requests from a limited number of policy clients (based on Origin-Host) are routed differently, configure appropriate rules in the PCRF Sub-Pool Selection Rules table. During routing, this table is examined after the APN is mapped to a PCRF Pool. If a matching PCRF Sub-Pool Selection Rule exists, the request is routed to the PCRF Sub-Pool. Otherwise, the PCRF Pool selected by the APN mapping is used. |
| 4 | Access Point Names | After all Diameter configuration is completed (including PRT Rules, Route Lists, Route Groups, Peer Nodes, and Connections), each APN can be mapped to a PCRF Pool. After an APN is mapped to a PCRF Pool, binding-capable session initiation requests that result in creation of a new binding are routed using the PCRF Pool. |