If a failed energy storage module (ESM) is not replaced, you run the risk of losing the data that is temporarily stored in the flash memory. If the external power to the Controller is lost as well, the potential for data loss rises dramatically. In case of an ESM failure, the Controller should go into write-through (conservative) mode so there is no data loss. Nevertheless, a failed ESM must be replaced as soon as possible to avoid the risk of data loss and to restore system performance.
- Prerequisites:
Before handling a component, touch a grounded surface to discharge any static electricity.
Attach an electrostatic discharge (ESD) wrist strap to your wrist, and stand on an ESD mat while replacing components.
Ensure that a replacement ESM or a filler panel available to replace the ESM that you will be removing.
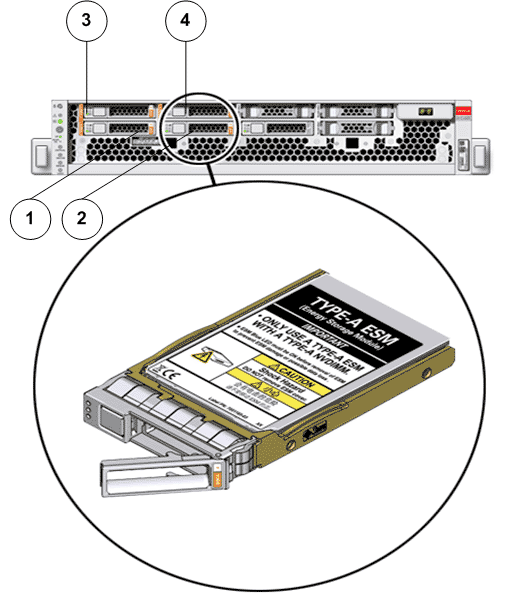
- Legend
1 ESM 0 2 ESM1 3 ESM 2 4 ESM 3