4 Review Bills of Material and Routings
This chapter contains these topics:
-
Section 4.2, "Reviewing Bills of Material and Routings for Product Costing,"
-
Section 4.3, "Reviewing Product Costing in Bills of Material,"
4.1 Review Bills of Material and Routings
The bill of material and routing for an item contain important information that affects costing.
4.2 Reviewing Bills of Material and Routings for Product Costing
To ensure that bill and routing information is set up correctly:
-
Review product costing in bills of material
-
Review routings for product costing
4.3 Reviewing Product Costing in Bills of Material
From Product Data Management (G30), choose Daily PDM Discrete
From Daily PDM Discrete (G3011), choose Enter/Change Bill
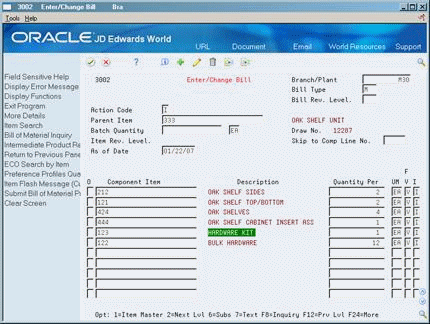
Review your bills of material to understand the bills' input to your material product costs. Only items with a bill type of M are costed.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Bill Type | Simulated Rollup will only cost an "M" type BOM. Alternate bills (BOMs) can be used but "M" is recognized as the standard. |
| Batch Quantity | Batch quantities are used when there are physical constraints on a manufacturing process or items must be produced in certain quantities. The batch BOM that matches the ACQ is recognized as the standard batch size and is used by the Simulated Rollup program.
Note: If the Batch quantity does not match the ACQ, the Simulated Rollup program will look for a 0 (zero) quantity BOM. Material costs (A1) will not roll if the batch quantity does not match the ACQ and if there is not a 0 (zero) batch quantity BOM. |
| Feature Cost and Feature Planned % | These fields are in the bill specifically for Kit and Planning Bills, but they affect all types of bills. Costing will be adjusted by the feature cost % if it is anything other than 100%. |
| Fixed/Variable | If a fixed quantity is used on the BOM, Simulated Rollup will divide the fixed amount by the ACQ to calculate the per unit cost. Fixed quantity components are not extended by the work order quantity. |
| Component Branch/Plant | The system defaults the Branch Plant entered on the Bill of Material header into this field. You can also change this field manually. |
| Percent of Scrap | This percent is a whole number entered directly onto the BOM. The amount of material required is increased by the scrap percent and therefore increases cost if there is a value. This additional material will generate an Scrap (A2) cost in the Simulated Rollup. Scrap costs require component scrap to be recorded via Component Scrap P31116. |
| Operation Scrap % | Operational scrap % is populated by the yield % in the routing. The material required is increased by this percentage. Operation scrap % does not generate A2 cost. |
| Additional Information about the BOM | Dates for all components should be "in effect" to be included in the cost rollup. |
To review bill of material information
On Enter/Change Bill
-
-
Component Item
-
Quantity Per
-
Unit Of Measure
-
Fixed or Variable
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 4-2 Enter/Change Bill (Detail) screen
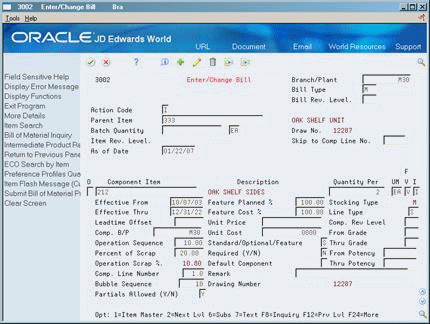
Description of "Figure 4-2 Enter/Change Bill (Detail) screen"
-
Review the following fields:
-
Feature Cost Percent
-
Percent of Scrap
-
Operation Scrap Percent
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Parent Item | A number that the system assigns to an item. It can be in short, long, or 3rd item number format.
Form-specific information The Parent Item field contains the item number of the item to be manufactured. |
| Component Item | This field contains the item number of the item(s) that are required to make the parent item. |
| Batch Quantity | A frequently manufactured quantity of the parent item in the production unit of measure. |
| Quantity Per | The number of units to which the system applies the transaction.
Form-specific information A number that indicates how many components you use to manufacture the parent item. A quantity of zero is valid. The default value is 1. |
| UM (Unit of Measure) | The default value coming from the component unit of measure in the Item Master table. |
| F V | Indicates if the quantity per assembly for an item on the bill of material varies according to the quantity of the parent item produced or is fixed regardless of the parent quantity. This value also determines if the component quantity is a percent of the parent quantity. Valid values are:
F – Fixed Quantity V – Variable Quantity (Default) % – Quantities are expressed as a percentage and must total 100% For fixed quantity components, the Work Order and MRP systems do not extend the component's quantity per assembly value by the order quantity. ACQ is used as a divisor by the cost rollup for fixed components. For Process Manufacturing, the system stores percent components. Therefore, the system treats zero batch sizes like variable quantity components, and treats batch sizes greater than zero like fixed quantity components. |
| Feature Cost % | A percentage used by the Simulate Cost Rollup program to calculate the cost of a feature or option item as a percentage of the total cost of the parent.
Enter the percentage as a whole number: 5% as 5.0. |
| Percent of Scrap | Scrap is the percentage of unusable component material created during the manufacture of a particular parent item. During DRP/MPS/MRP generation, the system increases gross requirements for the component item to compensate for the loss.
Note: Shrink is the expected loss of parent items (and hence, components) due to the manufacturing process. Shrink and scrap are compounded to figure the total loss in the manufacture of a particular item. Accurate shrink and scrap factors can help to produce more accurate planning calculations. Enter percents as whole numbers: 5% as 5.0. Form-specific information The Shop Floor Control and Material Requirements Planning systems inflate component requirements by this percentage. This scrap percent is unique to the relationship of one parent and one component. |
| Operation Scrap % | The system uses this value to increase or decrease the amount of materials to account for loss within the operation. The system updates this value on Enter/Change Bill of Material when you run the Planned Yield Update program. The system calculates this value by compounding the yield percentages from the last operation to the first operation. Use a processing option in Enter/Change Routing to enable the system to calculate the component scrap percent. |
4.4 Reviewing Routings for Product Costing
From Product Data Management (G30), choose Daily PDM Discrete
From Daily PDM Discrete (G3011), choose Enter/Change Routing
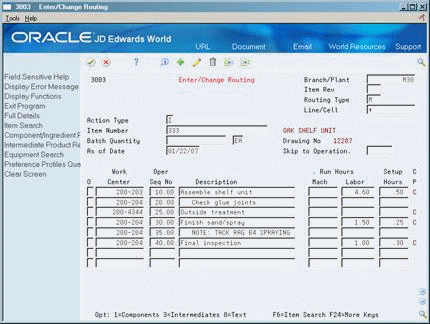
Review your routings to understand their input to your labor and overhead costs.
On Enter/Change Routing
-
-
Work Center
-
Machine Run Hours
-
Labor Run Hours
-
Setup Hours
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 4-4 Enter/Change Routing (Detail) screen
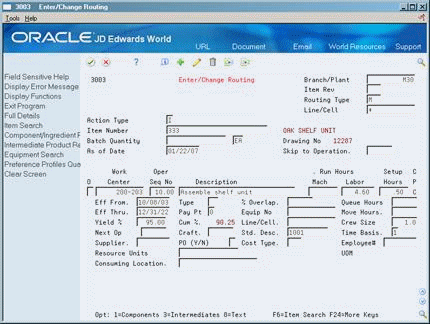
Description of "Figure 4-4 Enter/Change Routing (Detail) screen"
-
Review the following fields:
-
Time Basis
-
Crew Size
-
Cost Type
-
Type
-
Yield Percent
-
Cumulative Percent
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Work Center | A number that identifies a branch, plant, work center, or business unit.
Form-specific information For Equipment users, this is the craft/resource responsible for completing the maintenance activity. |
| Routing Type | Simulated Rollup will only cost an "M" type routing. |
| Mach | This is the standard machine hours expected to be incurred in the normal production of this item. |
| Labor | This is the standard hours of labor expected in the normal production of this item.
The run labor hours in the Routing Master table (F3003) are the total hours it takes the specified crew size to complete the operation. The hours are multiplied by the crew size during shop floor release and product costing. Form-specific information For Equipment/Plant: This is the estimated number of hours needed to complete a maintenance activity. |
| Setup Hours | The standard setup hours you expect to incur in the normal completion of this item. |
| Time Basis | A user-defined code (system 30, type TB) that identifies the time basis or run rate per hour for machine or labor hours entered for any routing step. You can set rates per unit, per 10, per 1000, and so on.
The system uses the values in the Description-2 field on the User Defined Codes screen for costing and scheduling calculations. The description is what the code represents, but is not used in calculations. Simulated Rollup uses the Time Basis Code as a divisor to calculate per unit cost: {10 routing hours / 100 (TB Description 2) = .1 (hours per unit)} The Time Basis code will default from the Item Branch Plant into each operation sequence of the routing. |
| Crew Size | The number of people who work in the specified work center or routing operation.
The system automatically populates this field with the information from the Work Center. The system multiplies the Run Labor value in the Routing Master table (F3003) by crew size during cost simulation to generate total labor dollars used in the cost simulation. Form-specific information For Shop Floor Control: If the Prime Load Code is L or B, the system uses the total labor hours for backscheduling. If the Prime Load Code is C or M, the system uses the total machine hours for backscheduling without modification by crew size. The Crew Size field on the Routing Revisions screen displays the value set on the Enter/Change Work Centers screen (P3006). You can override the value by changing this field on the Routing Revisions form. However, the Enter/Change Work Centers form will not reflect this change. |
| Cost Type | This code designates each element of cost for an item. An example of the coding structure is:
A1 – Purchased raw material B1 – Direct labor routing sheet rollup B2 – Setup labor routing sheet rollup C1 – Variable burden routing sheet rollup C2 – Fixed burden routing sheet rollup Dx – Usually used for outside processing routing sheet rollup Xx – Usually used for extra add-ons, such as electricity, water, and so forth The optional add-on computations usually operate with the type "X" extra add-ons. This cost structure allows you to use an unlimited number of cost components to calculate alternative cost rollups. The system then associates these cost components with one of six user-defined summary cost buckets. |
| Type | A user-defined code (system 30, type OT) that indicates the type of operation. For example:
A – Alternate routing TT – Travel time IT – Idle time T – Text (Enter text at Description) Form-specific information For Product Costing: Only operations with a "blank" type operation code are costed. |
| Yield % | Represents the planned output yield percent for a step. The Planned Yield Update program uses this value to update the Cumulative Percent in the bill of material and the Operation Scrap Percent in the routing. Materials Requirements Planning uses the step scrap percent and the existing component scrap percent to plan component demand. |
| Cum % | Represents the cumulative planned output yield percent for a step. The system uses this value to adjust the operation step scrap percent for the components at that operation step. This enables the MRP system to use the operation step scrap percent along with the existing component scrap percent to plan component demand. |