3 Set Up Product Costing
This chapter contains these topics:
-
Section 3.7, "Setting Up Manufacturing Constants for Product Costing,"
-
Section 3.8, "Setting Up Simulated Rates for a Work Center,"
-
Section 3.9, "Setting Up Actual Rates for a Work Center and Overhead."
3.1 Setting Up Product Costing
You can customize the Product Costing system to meet your specific manufacturing environment needs. The system uses the values you define to determine your product costs.
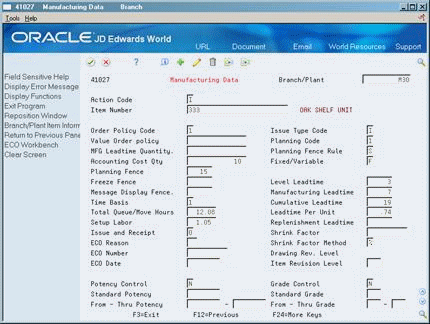
3.2 Setting Up Accounting Cost Quantities
From Inventory Management (G41), choose Item Revisions
From Item Revisions (G4112), choose Manufacturing Data under the Item Branch/Plant Information heading
The system uses accounting cost quantities to determine the allocation of fixed setup costs for an item. Accounting cost quantities represent the most commonly manufactured quantity of a work order for this item. During cost rollup, the system divides the fixed setup costs by the accounting cost quantity you specify to determine a unit setup and fixed cost.
To set up an accounting cost quantity (ACQ)
On Manufacturing Data
Complete or review the following field:
-
Accounting Cost Quantity
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Accounting Cost Qty (ACQ) | An amount that the system uses in the cost rollup program to determine the allocation of setup costs. The system totals the setup costs and divides the sum by this quantity to determine a unit setup cost. The default is 1. The system also uses ACQ as a divisor for fixed material costs in order to derive a per unit value. Since ACQ is a divisor, do NOT set ACQ to zero (0). |
3.3 Setting Up Item Cost Levels
From Inventory Management (G41), choose Inventory Master/Transactions
From Inventory Master/Transactions (G4111), choose Item Master Information
The cost level you assign to an item indicates the level at which the system maintains costs. You determine whether the system maintains one overall cost for an item (cost level 1) or a different cost for the item in each branch/plant (cost level 2). The system can also maintain a different cost for each location and lot within a branch/plant (cost level 3). However, in the Product Costing system, costs at cost level 3 are informational only. All items used in a manufacturing environment should have cost levels of 1 or 2, except configured items, which must be cost level 3. Cost level 3 is recommended for actual cost items (cost method 02).
Figure 3-2 Item Master Information screen
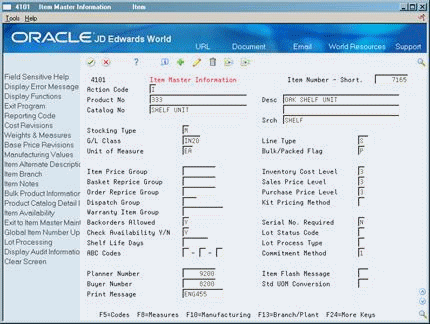
Description of "Figure 3-2 Item Master Information screen"
-
Complete or review the following fields:
-
Stocking Type
-
G/L Class Code
-
Line Type
-
Unit of Measure
-
Inventory Cost Level
-
-
Choose Manufacturing Values (F10) to display the Plant Manufacturing Data screen.
-
Figure 3-3 Plant Manufacturing Data screen
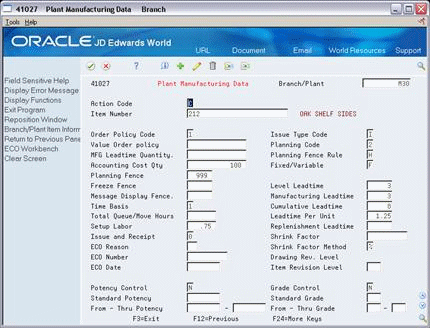
Description of "Figure 3-3 Plant Manufacturing Data screen"
-
Complete or review the following field:
-
Accounting Cost Qty
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Stocking Type | Stocking types are found in UDC Table 41/I. Product costing looks at the corresponding second description for "M" or "P" in this table. If the second description is "P", the cost in F4105 will be used. If the second description is "M", there must be a Bill of Material (BOM) and or Routing from which costs can be calculated. |
| G/L Class Code | G/L posting codes are setup in the UDC Table 41/9. G/L Class code is one of the keys to the product costing and manufacturing accounting AAI tables. It is the only key that is item specific and can be used to point journal entries associated with the item to specific object accounts in the general ledger.
The G/L Class code will default to the Item Branch/Plant (BP) record, and from the Item BP record to the primary location in the item location record. This primary location in the item location record is where manufacturing costing and accounting will look to find the G/L Class code for the item. |
| Line Type | Line Types control how lines in a transaction are processed and the systems with which the transaction interfaces - G/L, AP, AR, Inventory Management, etc. |
| Unit of Measure | The primary unit of measure MUST be the smallest unit of measure.
Units of Measure to consider for manufacturing are:
Set up all units of measure to convert to the primary unit of measure (UOM) in the Unit of Measure Conversion table. The Simulated Rollup will write item costs to the F30026 in the primary unit of measure. The F4105 costs are also maintained in the primary UOM. |
| Inventory Cost Level | A code that indicates whether the system maintains one overall inventory cost for the item, a different cost for each branch/plant, or a different cost for each location and lot within a branch/plant. The system maintains inventory costs in the Cost Ledger table (F4105).
Valid codes are: 1 – Item level (The item will have only one F4105 record. Every Branch/Plant and every location will use the same F4105 record.) 2 – Item/Branch level (For every item Branch/Plant, there is a unique or separate item cost. If there are two branch/plants, then the F4105 will have two F4105 records.) 3 – Item/Branch/Location level (Not recognized by the Manufacturing system, except for configured and actual cost items.) |
| Accounting Cost Qty | Product costing uses this quantity as the standard quantity produced. Since the ACQ is considered the standard quantity, the Simulated Rollup will look for a batch BOM and a batch routing that match the ACQ to use for the cost simulation.
If there is no matching BOM, or routing, the 0 (zero) quantity BOM and routing will be used to calculate standard cost. A zero or blank on the BOM or routing represents the amount of components needed to make one item. Setup costs (B2) are divided by the ACQ to determine a per unit setup cost. This value cannot be zero or blank. |
3.4 Converting Item Cost Levels
From Inventory Management (G41), enter 27
From Inventory Advanced & Technical Ops (G4131), choose Item Cost Level Conversion
After you have entered cost information, you might need to change an item's cost level. You must use the Item Cost Level Conversion program to change an item's cost level after cost information has been entered.
If you run this program, it deletes all existing cost records for the item in the Cost Ledger table (F4105) and creates new cost records that correspond to the level. The system uses the sales/inventory cost method for the item to create the new cost records.
The program does not change the cost valuation of items and does not create journal entries. For example, if you change an item's cost level from branch/plant and location to branch/plant, all existing cost records for the branch/plant and location must contain the same sales/inventory cost method and cost.
You can run Item Cost Level Conversion in proof mode or final mode. When you run the program in proof mode, the system generates the Item Cost Level Conversion report, showing errors that need correction. You should always run the program in proof mode first and correct any discrepancies.
When you run the program in final mode, the system updates the following tables:
-
Inventory Cost Level field in the Item Master (F4101)
-
Cost Ledger (F4105)
|
Caution: Changing your item cost levels changes data throughout the system. You should restrict access to this program. |
3.4.1 Before You Begin
-
Back up your data tables completely before you begin the data conversion process. If the results of the conversion are unsatisfactory, you can use the backup tables to restore data tables to their original format.
-
Verify that no users are accessing the Item Master or Cost Ledger tables when this program is running in final mode.
Figure 3-4 Item Cost Level Conversion report
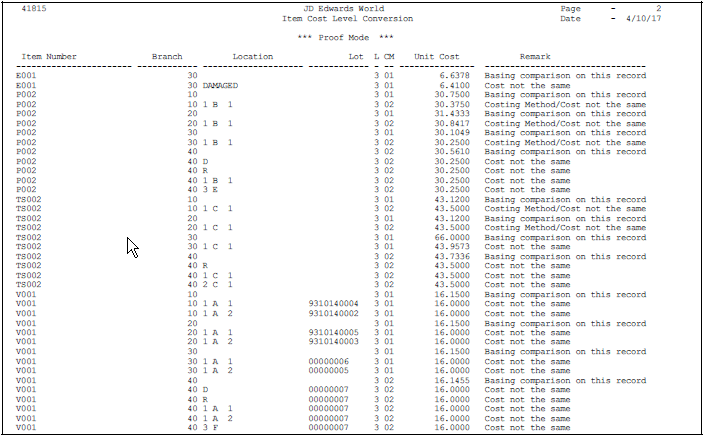
Description of "Figure 3-4 Item Cost Level Conversion report"
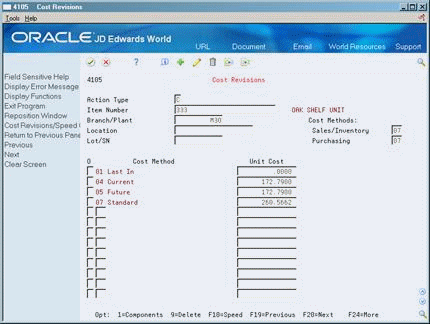
3.5 Setting Up Item Costs
You must provide cost information for each of your items for the system to track inventory costs. You specify the cost method that the system uses to determine an item's cost for:
-
Sales/inventory transactions
-
Purchase orders
For example, in a distribution environment, you can have the system use the weighted average cost method to determine the inventory cost for an item and use the last-in cost method to determine the item's unit cost for purchase orders. In a manufacturing environment, you must choose between Standard (07) and Weighted Average (02) cost methods to determine the inventory cost.
For each cost method you assign to an item, you must also specify a cost. For example, to use the last-in cost method for an item, you must enter an initial cost for that cost method. The system updates the last-in cost based on the cost of the item as of the last receipt date.
For purchased items and outside operations, the main inputs to product costing are entered on Cost Revisions or Cost Components.
To set up item costs, complete the following tasks:
-
Set up new cost methods
-
Assign cost methods
You can set up user-defined codes (40/CM) to define your own cost methods. For example, you might want to establish a cost method to maintain a history of last year's costs. Codes 01 through 08 are hard-coded and cannot be altered. Codes 09 through 19 are reserved for JD Edwards World use.
On General User Defined Codes
Figure 3-5 General User Defined Codes screen
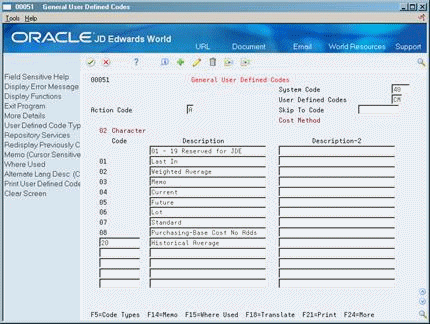
Description of "Figure 3-5 General User Defined Codes screen"
Complete the following fields:
-
Code
-
Description
-
Description-2
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Code | This column contains a list of valid codes for a specific user-defined code list. The number of characters that a code can contain appears in the column title. |
| Description | A user-defined name or remark. |
| Description-2 | Additional text that further describes or clarifies a field in JD Edwards World systems. |
3.5.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Code | This code defines cost methods that are used in the cost rollup and assigned to items. This is a two-character, alphanumeric field. |
| Description 1 | Identifies the cost method. |
| Description 2 | Identifies additional information about the cost method. |
From Product Data Management (G30), choose Daily Product Costing
From Daily Product Costing (G3014), choose Enter/Change Item Costs
Each time you add an item on this form, the program displays all cost methods set up in the user defined code table 40/CM. This includes eight predefined methods that the program provides and any additional methods you create. You specify which methods to apply to an item by assigning a unit cost for each method.
On Cost Revisions
-
1. Complete the following field for each applicable cost method:
-
Unit Cost
-
-
2. Enter the appropriate cost methods in the following fields:
-
Sales/Inventory
-
Purchasing
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Unit Cost | Depending on the cost method, this data can come from various sources, for example, purchasing or the cost update.
Form-specific information The cost for one unit of this item, based on the corresponding cost method in the primary unit of measure. |
| Sales/Inventory | A code (table 40/CM) that indicates the cost method that the system uses to calculate the cost of goods sold value for the item. Cost methods 01-08 are hard-coded.
Form-specific information If you maintain costs at the item level, the system retrieves the default value for this field from the data dictionary. If you maintain costs at the item and branch/plant level, the system retrieves the default value from Branch/Plant Constants. |
| Purchasing | A code (table 40/CM) that indicates the cost method that the system uses to determine the cost of the item for purchase orders. Cost methods 01-08 are hard-coded.
Form-specific information If you maintain costs at the item level, the system retrieves the default value for this field from the data dictionary. If you maintain costs at the item and branch/plant level, the system retrieves the default value from Branch/Plant Constants. |
3.5.2 What You Should Know About
3.6 Setting Up Cost Components
Use cost components to identify and track each element or type of cost for an item. Cost components that begin with A, B, and C are hard-coded by JD Edwards World and cannot be changed. You can define an unlimited number of additional cost components to account for extra costs for an item, such as electricity or research and development. These user defined cost components can begin with any letter except A, B, or C. JD Edwards World recommends, but does not require, that you use cost component D for outside operations. You can assign separate cost components by categories that are applicable to your business.
|
Note: Although it might appear that you can set up extra cost components that begin with A, B, or C, the Simulate Cost Rollup program actually deletes these cost components. JD Edwards World recommends that you define extra costs with an "X" for easy identification. |
On General User Defined Codes
Figure 3-7 General User Defined Codes (Cost Component) screen
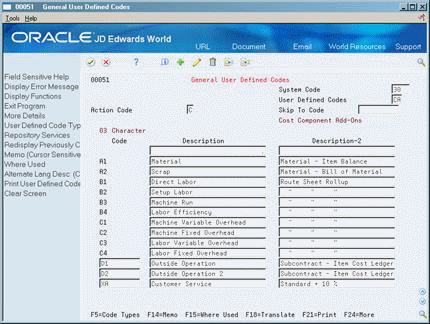
Description of "Figure 3-7 General User Defined Codes (Cost Component) screen"
Complete the following fields:
-
Code
-
Description
-
Description-2
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Code | This column contains a list of valid codes for a specific user defined code list. The number of characters that a code can contain appears in the column title.
Use this code to identify all of the possible cost components that can be used in the cost rollup for an item. |
| Description | A user defined name or remark that identifies what each cost component represents. |
| Description-2 | Additional text that further describes or clarifies a field in JD Edwards World systems. |
3.7 Setting Up Manufacturing Constants for Product Costing
From Product Data Management (G30), enter 29
From Product Data Management Setup (G3041), choose Manufacturing Constants
You must establish information that is unique to your branch/plant. Use manufacturing constants to set options that determine:
-
Overhead types to be included in the cost rollup and how to calculate overhead costs
-
Whether to consider work center efficiency when calculating direct labor and overhead
-
Whether overheads are calculated as percents or rates
-
Costing separately for each work center
|
Note: If you select to modify cost by Work Center Efficiency, the system creates B4 in the Simulation Rollup. Also, overheads calculated as percents or rates determine how the Overhead cost components (C1 - C4) are expressed in the Work Center Rate Revisions. |
To set up manufacturing constants for Product Costing
On Manufacturing Constants
Figure 3-8 Manufacturing Constants screen
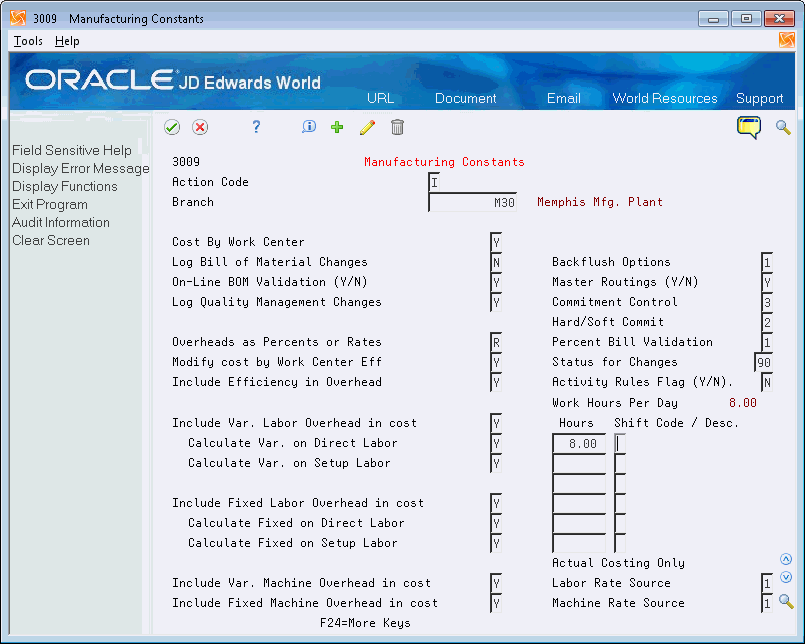
Description of "Figure 3-8 Manufacturing Constants screen"
Complete the following fields:
-
Cost by Work Center
-
Overheads as Percents or Rates
-
Modify cost by Work Center Efficiency
-
Include Work Center Efficiency in Overhead
-
Include Variable Labor Overhead in Cost
-
Calculate Variable on Direct Labor
-
Calculate Variable on Setup Labor
-
Include Fixed Labor Overhead in Cost
-
Calculate Fixed on Direct Labor
-
Calculate Fixed on Setup Labor
-
Include Variable Machine Overhead in Cost
-
Include Fixed Machine Overhead in Cost
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cost by Work Center | A code, maintained in the Manufacturing Constants program (P3009), that indicates whether the system tracks cost variances for discrete and process items on a summarized level in the Item Cost Component Add-Ons file (F30026) on a detailed level in the Item Cost Component Detail file (F300261).
Valid values are: Y - Yes, Maintain costs on a detailed level by cost component and work center Blank or N - No, Maintain costs on a summarized level by cost component only |
| Overheads as Percents or Rates | Determines how values for overhead fields (cost components C1 through C4) in the Work Center Rate Revisions table (F30061) are expressed. Valid codes are:
R – Express overhead values as rates (currency values). For example, enter five dollars as 5.00. P – Express overhead values as percents. Enter percents as whole numbers. For example, enter five percent as 5.00. |
| Modify cost by Work Center Eff | Controls whether the cost rollup creates cost component B4 (for labor efficiency) based on the direct labor value (cost component B1) and the Work Center Efficiency percent from the Work Center Revisions table (F3006). Valid values are:
Y – Yes. Create cost component B4. N – No. Do not create cost component B4. |
| Include Efficiency in Overhead | If you specified that you want to modify costs by work center efficiency, this field determines whether the cost rollup includes work center efficiency when calculating overhead values. Valid values are:
Y – Include work center efficiency. N – Exclude work center efficiency. |
| Include Var. Labor Overhead in cost | Controls whether the cost rollup creates cost component C3 (for variable labor overhead) in the Cost Components table (F30026). Valid values are:
Y – Yes. Create cost component C3. N – No. Do not create cost component C3. |
| Calculate Var. on Direct Labor | Determines whether the cost rollup includes direct labor expenses (cost component B1) in the total used to calculate variable labor overhead (cost component C3). Valid values are:
Y – Include direct labor expenses. N – Exclude direct labor expenses. |
| Calculate Var. on Setup Labor | Determines whether the cost rollup includes setup labor expenses (cost component B2) in the total used to calculate variable setup overhead (cost component C3). Valid values are:
Y – Include setup labor expenses. N – Exclude setup labor expenses. |
| Include Fixed Labor Overhead in cost | Controls whether the cost rollup creates cost component C4 (for fixed labor overhead) in the Cost Components table (F30026). Valid values are:
Y – Yes. Create cost component C4. N – No. Do not create cost component C4. |
| Calculate Fixed on Direct Labor | Determines whether the cost rollup includes direct labor expenses (cost component B1) in the total used to calculate fixed labor overhead (cost component C4). Valid values are:
Y – Include direct labor expenses. N – Exclude direct labor expenses. |
| Calculate Fixed on Setup Labor | Determines whether the cost rollup includes setup labor expenses (cost component B2) in the total used to calculate fixed setup overhead (cost component C4). Valid values are:
Y – Include setup labor expenses. N – Exclude setup labor expenses. |
| Include Var. Machine Overhead in cost | Controls whether the cost rollup creates cost component C1 (for variable machine overhead) in the Cost Components table (F30026). Valid values are:
Y – Yes. Create cost component C1. N – No. Do not create cost component C1. |
| Include Fixed Machine Overhead in cost | Controls whether the cost rollup creates cost component C2 (for fixed machine overhead) in the Cost Components table (F30026). Valid values are:
Y – Yes. Create cost component C2. N – No. Do not create cost component C2. |
3.7.1 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Overhead Rates | Overhead rates are established in the Manufacturing Constants by selecting the type costs that will be included. |
| Labor Rates | Actual cost allows two choices for the source of labor rates in the Manufacturing Constants. Standard cost will not read this option, but will continue to use frozen 07 work center rates as the source for labor rates.
|
| Machine Rates | The source for machine rates for an actual cost item can come from one of two choices in Manufacturing Constants. Standard cost will not read this option, but will continue to use frozen 07 work center rates as the source for labor rates.
The default for both labor and machine rates is the work center rate. |
3.8 Setting Up Simulated Rates for a Work Center
From Manufacturing Systems (G3), choose Product Costing
From Product Costing (G3014), choose Enter/Change Work Center Rate
You can effectively manage changes to a work center by tracking rates for labor and machine costs. You can update simulated rates for machine and labor hours by work center and cost method. The system uses these values in other manufacturing calculations, such as costed routings, labor rate variance reports, and direct labor efficiency reports.
Each operation sequence in the routing is associated with a work center. The number of people who work in a work center (crew size), although not directly used in product costing, will default into the routing.
Standard Costing uses frozen (07) work center rates. Standard work center rates are set up for each work center by keying in simulated costs for all categories, including labor, overhead and machine.
Work Center rates are then frozen when you run the Frozen Update (P30835) with the processing option for Update Work Center Rates turned on.
Work Centers can have rates for both the standard and actual cost methods by entering simulated costs in the Work Center rates, and selecting the cost method in the Frozen Update processing options.
Work Center rates can be frozen independent of an item by using the Freeze Work Center Rates program (P30860).
As an alternative to entering rates manually, you can use the Work Center Rate Revisions Z File program (P30061Z) to import an extensive amount of data into your system. See Appendix H, "Import Mass Data into Manufacturing Systems" for more information.
3.8.1 Before You Begin
-
You must set up your work centers on Enter/Change Work Centers before you can assign rates. See Entering Work Centers in the JD Edwards World Product Data Management - Discrete Guide for complete information on setting up work centers.
To set up simulated rates for a work center
On Enter/Change Work Center Rate
Figure 3-9 Enter/Change Work Center Rate screen
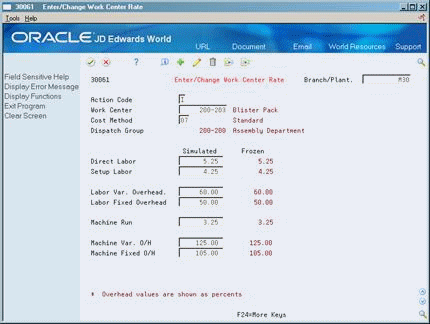
Description of "Figure 3-9 Enter/Change Work Center Rate screen"
Complete the following fields:
-
Work Center
-
Cost Method
-
Simulated Direct Labor
-
Simulated Setup Labor
-
Simulated Labor Variable Overhead
-
Simulated Labor Fixed Overhead
-
Simulated Machine Run
-
Simulated Machine Variable Overhead
-
Simulated Machine Fixed Overhead
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Work Center | A number that identifies a branch, plant, work center, or business unit. |
| Cost Method | A user defined code (system 40, type CM) that identifies a cost method. Cost methods 01 through 08 are hard-coded.
Form-specific information This code was entered on Branch/Plant Constants. |
| Direct Labor | This rate, in cost per hour, is the rate used to calculate the current labor cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Setup Labor | This rate, in cost per hour, is the rate used to calculate the current setup labor cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Labor Var. Overhead | This rate, in cost per hour or percent of labor, is the rate used to calculate the current variable labor overhead cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Labor Fixed Overhead | This rate, in cost per hour or percent of labor, is the rate used to calculate the current fixed labor overhead cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Machine Run | This rate, in cost per hour, is the rate used to calculate the current machine cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Machine Var. O/H | This rate, in cost per hour or percent of labor, is the rate used to calculate the current variable machine overhead cost as of the last simulation and update. |
| Machine Fixed O/H | This rate, in cost per hour or percent of labor, is the rate used to calculate the current fixed machine overhead cost as of the last simulation and update. |
3.9 Setting Up Actual Rates for a Work Center and Overhead
The frozen work center rates (F30008) are maintained for actual cost by entering 02 cost method rates for the work center in the F30008 and running the frozen update P30835 or the Freeze Work Center Rates program (P30860). Standard cost 07 and actual cost 02 rates can all be maintained for the same work center. The system uses the rates for the cost method of the parent item to calculate work order cost.
The actual cost Work Order Overhead Rates (F30006) are calculated using the rates or percentages found in the Work Center Rates Table (F30006) for the cost method of the parent item.