6 Work with Profile Data
This chapter contains these topics:
6.1 Working with Profile Data
Profile data is any type of additional information that you want to track, such as the person to contact for an employee in an emergency situation, or certifications and job skills for applicants and employees.
You can use the profile data feature to track detailed information about any of the following:
-
Employees
-
Applicants
-
Jobs
-
Dependents
-
Beneficiaries
-
Requisitions
-
Safety and health cases
When you set up your Human Resources system, you specify the types of profile information you want to track for each of the items listed above. You can track different types of profile information for each item. For example, you might choose to track job skills for applicants but not for employees.
With the exception of Applicant Status, in the applicant database, profile information is not required by the system.
6.1.1 Before You Begin
-
Define your types of profile data and associated user defined codes. See Chapter 62, "Set Up Profile Data."
6.2 Entering Employee Profile Data
Profile data is any type of additional information that you want to track. Profile information is not required by the system.
For employees, typical types of profile data might include:
-
Emergency contacts
-
Job skills
-
Foreign language competencies
-
Work history
When you set up your Human Resources system, you specify the types of profile data (data types) that you want to track. For each data type, you specify the format in which you want to track information. Valid formats include:
-
Narrative
-
Code
For narrative format data types, you enter free-form text. For code format data types, you enter information in predefined columns. When you enter information in code format, you also can associate narrative information with it.
Entering profile data includes:
-
Entering profile data in narrative format
-
Entering profile data in code format
6.2.1 What You Should Know About
6.2.2 Entering Profile Data in Narrative Format
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile Data Entry
When you enter profile data in narrative format, you enter free-form text. You typically use narrative format for general information that is unique for each employee. For example, you might use narrative format for performance appraisal information.
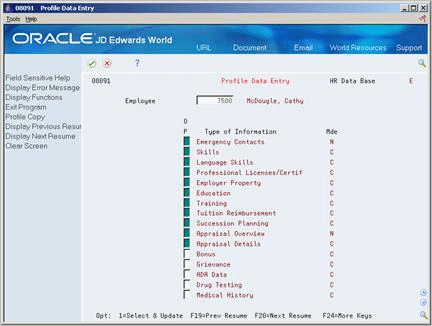
To enter profile data in narrative format
-
Locate the employee for whom you want to enter profile data.
-
To determine which types of profile data are in narrative format, review the information in the following field:
-
Mode
-
-
Choose the Select and Update option for one or more types of narrative format information.
The system displays the form for the first type of data.
-
Enter the appropriate information and press Enter.
-
Choose the Field Exit function to advance to the next type of data you chose.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Mde | The format of a data type. This code determines the display mode for supplemental data. Valid codes are:
C – Code format, which displays the form for entering code-specific information. These codes are associated with User Defined Codes table (F0005). N – Narrative format, which displays the form for entering narrative text. P – Program exit, which allows you to exit to the program you specified in the Pgm ID field. M – Message format, which displays the form for entering code-specific information. However, the system can edit the code values you enter against values in the Generic Rates and Messages table (F00191). This code is not used by the Human Resources or Financials systems. |
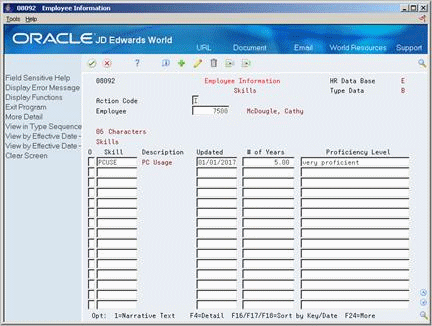
6.2.4 Entering Profile Data in Code Format
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile Data Entry
When you enter profile data in code format, you enter information in predefined columns. For example, the form for entering job skills information might have columns for skill code, number of years of experience, and proficiency level.
To ensure consistency of data entry, code fields are typically associated with user defined code tables. Any value that you enter in one of these fields must be included in the associated user defined code table. For fields that are associated with a user defined code table, the length of the field and the user defined code description display above the column.
When you enter information in code format, you also can associate narrative information with it.
To enter profile data in code format
On Profile Data Entry
-
Locate the employee for whom you want to enter profile data.
-
To determine which types of profile data are in code format, review the information in the following field:
-
Mode
-
-
Choose the Select and Update option for one or more types of code format information.
The system displays the form for the first type of data you choose.
-
Enter the appropriate information.
-
To add additional information in narrative format, use the Change action and choose the Narrative Text option.
-
Enter the additional information and press Enter twice.
-
Choose the Field Exit function to advance to the next type of data you chose.
6.2.5 What You Should Know About
6.3 Copying Profile Data
When you need to enter the same profile data for two or more employees, you can save time and reduce keying errors by copying information from one employee's record to another employee's record. You also can copy all of one employee's profile data to another employee's record.
You can also choose specific types of narrative information, including information that is associated with code format information, to copy from one employee's record to another employee's record. For example, if two employees share the same emergency contact information, but do not have any other profile data in common, you can copy only emergency contact information.
After you copy profile data, you can revise it, if necessary.
Copying profile data includes:
-
Copying narrative text
-
Copying all profile data for an employee
6.3.1 Copying Narrative Text
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile Data Entry
When you need to enter the same profile data for two or more employees, you can save time and reduce keying errors by copying information from one employee's record to another employee's record.
You can copy narrative information by data type. For example, if two employees have the same emergency contact, you can enter this information for one of the employees and then copy it into the other employee's record.
You also can copy any narrative information that is associated with a code format data type. For example, assume that:
-
A group of employees attended the same training class
-
You track training information in code format
-
You need to enter a description of the class as narrative text
In this case, you do not need to enter the class description for each employee. Instead, you can enter the class description for one employee and then copy it into the training records for all the other employees who attended the class.
On Profile Data Entry
-
Locate the employee for whom you want to copy information.
-
Choose the Select and Update option to access the data type into which you want to copy narrative format information.
-
Using the Change action, choose the Copy Text option.
-
On Copy Text, complete the following field with the employee number of the employee from whom you want to copy information:
-
Employee
The system lists the types of profile data that contain narrative information for that employee.
-
-
Choose the Select option to specify the data type from which you want to copy information.
The system displays the narrative information for that employee and data type.
-
On the data type form, choose the Select option to specify the lines of text you want to copy.
The system copies the text.
6.3.2 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Using the roll keys | You can scroll through the lines of information to locate the lines you want to copy. However, you cannot select text in one form, scroll up, and then select text from another form. You can select to copy text from only one form at a time. |
6.3.3 Copying All Profile Data for an Employee
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile Data Entry
In some cases, you might want to copy all of the profile data for one employee into the record for another employee. You might do this when you need to enter very similar information for two employees. After you copy profile data, you can revise it as necessary.
To copy all profile data for an employee
On Profile Data Entry
-
Locate the employee whose profile data you want to copy.
-
Choose the Profile Copy function.
-
On Profile Copy, complete the following field to specify the employee to whom you are copying profile data:
-
To Employee
-
-
Choose the Update function to copy all of the profile data.
6.4 Reviewing Profile Data
After you enter profile data, you can review that information to determine whether one or more people meet certain criteria. For example, you might be looking for someone who speaks French, or you might need a list of the employees that have completed CPR training.
You can review complete profile information for a particular employee, or you can review all employees who have information in one or more data types.
Reviewing profile data includes:
-
Reviewing profile data for a specific employee
-
Reviewing profile data by data type
-
Working with multi-skill search
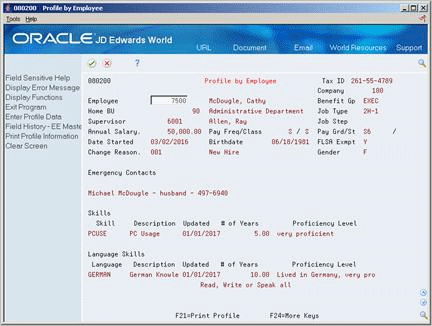
6.4.1 Reviewing Profile Data for a Specific Employee
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile by Employee
Use Profile by Employee to review complete information for a specific employee. This program compiles all of an employee's profile information into an easy-to-read, resume-style format.
You can also print employee resumes for internal use.
To review profile data for a specific employee
Complete the following field:
-
Employee
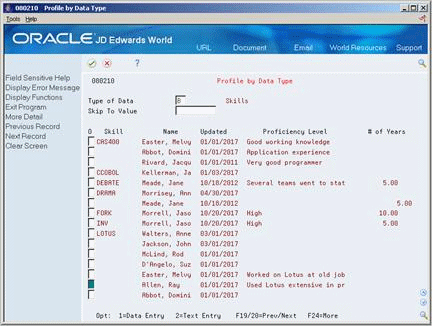
6.4.3 Reviewing Profile Data by Data Type
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile by Data Type
You can review all employees who have information for a specific data type. For example, you can review training profile information to identify employees who have had management training. Or, you can review professional licenses information to identify which employees need to renew their licenses within the next month.
To review profile data by data type
-
Complete the following field:
-
Type of Data
-
-
To locate a specific value within a list of data types, complete the following field:
-
Skip To Value
-
-
Choose More Detail to review additional information.
6.4.5 Working with Multi-Skill Search
From Human Resources (G08), choose Employee Information
From Employee Information (G08E1), choose Profile Multiskill Search
You can search your database for employees and applicants who meet multiple criteria. You typically use this type of search when you are looking for a person to fill a vacancy within your organization.
You can search for:
-
Applicants only
-
Employees only
-
Both employees and applicants
For example, you can search for all employees and applicants who:
-
Have an MBA degree
-
Speak French
-
Are certified public accountants
-
Know the RPG computer programming language
When you perform the search, the system lists all the people who meet the multiple criteria. You can enter up to 20 search criteria.
The criteria you specify can be based on either an "and" condition or an "or" condition. This means that you can search for people who meet either some criteria or some other criteria. For example, you can search for people who:
-
Have an MBA degree from any college or a BA in business from Harvard
-
Know the C programming language and have a degree in either computer science or mathematics
The system processes search criteria in the order in which you list them. When any of the criteria you specify are based on an "or" condition, the order in which you enter the search criteria is important. To ensure that the results of the search are what you would expect, you typically order the search criteria so that all of the "or" conditions come before any "and" conditions that you want to apply to all records.
6.4.5.1 Example: Specifying Search Criteria
When you specify search criteria, the order in which you list the criteria determines the outcome of the search. Suppose that you are searching for people who know the C programming language and have a degree in either mathematics or computer science. To locate that group of people, specify the following search criteria in the order listed:
Degree in computer science
or
Degree in mathematics
and
C programming language
To locate the people who meet this search criteria, the system completes the following steps:
-
Locates the people who know C programming (For demonstration purposes, call this group of people group A.)
-
Searches group A for people who have degrees in computer science. (Call these people group B).
-
Searches group A for people who have degrees in mathematics. (Call these people group C).
The result of the search is the total of the people in groups B and C.
To work with multi-skill search
Figure 6-5 Profile Multiskill Search screen
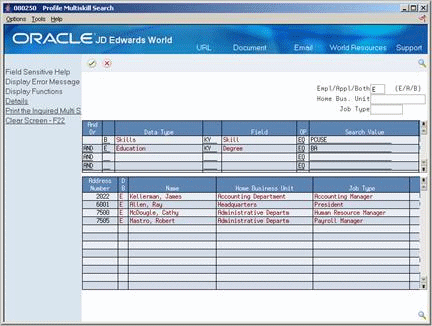
Description of ''Figure 6-5 Profile Multiskill Search screen''
-
To choose the database to search, complete the following field:
-
Employee/Applicant/Both
-
-
To limit the search, complete the following optional fields:
-
Home Business Unit
-
Job Type
-
-
To determine the search criteria, complete the following fields:
-
And/Or
-
Data Type
-
Field
-
OP (Operator)
-
Search Value
-
-
To review additional information, choose More Detail.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| And Or | A code that designates whether the test parameters or criteria are based on an AND condition or an OR condition.
Form-specific information For example, to identify employees who are either CPAs or who have MBAs, enter the code for professional licenses and certificates in the Data Type field and CPA in the Search Value field. On the second line, enter the code for education in the Data Type field and MBA in the Search Value field. Link the two lines by entering Or in the And/Or field of the second line. As another example, to identify employees who are both CPAs and who have MBAs, enter the code for professional licenses and certificates in the Data Type field and CPA in the Search Value field. On the second line, enter the code for education in the Data Type field and MBA in the Search Value field. Link the two lines by typing And in the And/Or field of the second line. To search for applicants who speak Spanish and German, enter Spanish as the first search value, German as the second search value, then enter And in this field. To search for applicants who speak Spanish or German, enter Spanish as the first search value, German as the second search value, then enter Or in this field. |
| Data Type | The type of data from the profile database that the system uses in a multiple information search. |
| Field | A code that indicates which data item within the data type is to be included in the multiskill search. |
| OP | A code the identifies the operands in Boolean logic. You can specify any of the following:
EQ – Equal to LT – Less than LE – Less than or equal to GT – Greater than GE – Greater than or equal to NE – Not equal to NL – Not less than NG – Not greater than |
| Search Value | You must enter a search value based on the data you entered in the profile for the selected field.
This field is case sensitive. For example, assume that you want to search for the word Active. If the data was originally entered into the database as Active, then you must enter the value into the search field as Active. Do not enter ACTIVE or active. You can also use the % wildcard character to search for data starting with, ending with, or containing one or more consecutive characters. For example:
|
6.5 Purging Profile Data
From Employee Information (G08E1), enter 27
From Employee Advanced/Technical Operations (G08E3), choose Purge Profile Data
To conserve computer disk space and eliminate obsolete information from your system, you probably need to purge profile data periodically. For example, your organization might have a policy of keeping applicant profile data for only one year. Also, if you are using profile data to track information about a specific project, you might want to delete the profile data after the project has been completed.
You can purge profile data for a single data type, or for multiple data types. You can delete all profile data or only narrative profile data.
This program deletes data from the Profile Database User Defined Code Entry table (F08092) and the Profile Database Narration table (F08093).
This program does not print a report.