27 Set Up a Tank
This chapter contains these topics:
27.1 Setting Up a Tank
To set up a tank, you specify the structural information about the tank, such as capacity, height, and tank specifications. The system uses this information to calculate volume and optimize tank usage.
Complete the following tasks:
-
Setting Up Basic Tank Information
-
Setting Up a Blending Tank (Optional)
-
Setting Up Additional Tank Information
-
Setting Up Tank Strapping Information
Figure 27-1 Tank Master Maintenance screen
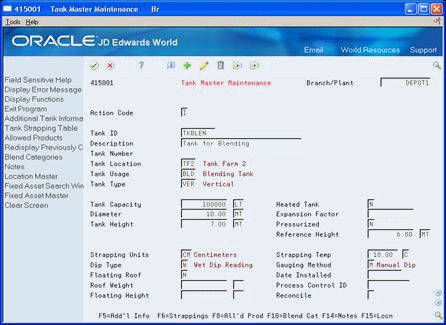
Description of "Figure 27-1 Tank Master Maintenance screen"
27.2 Setting Up Basic Tank Information
From Bulk Stock Management (G4150), enter 29
From Bulk Stock Management Setup (G415041), choose Tank Master Maintenance
You must define the basic structural information about a tank. The system retrieves this information when processing transactions to calculate volume. This information is stored in the Tank Master table (F41500). If your tanks are set up as fixed assets, you can record the asset number while setting up basic tank information. You can also record whether a tank is heated and requires an expansion correction factor to calculate volume, such as for tanks containing asphalt or bitumen products. If you set up a heated tank, you must also record an expansion correction factor and a strapping temperature.
27.2.1
To set up basic tank information
On Tank Master Maintenance
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Tank ID
-
Tank Number
-
Tank Location
-
Tank Usage
-
Tank Type
-
Tank Capacity
-
Unit of Measure
-
Tank Height
-
Unit of Measure
-
Reference Height
-
Unit of Measure
-
Strapping Units
-
Dip Type
-
Gauging Method
-
-
Complete any or all of the following optional fields:
-
Heated Tank
-
Diameter
-
Expansion Factor
-
Pressurized
-
Strapping Temperature
-
Floating Roof
-
Date Installed
-
Roof Weight
-
Process Control ID
-
Floating Height
-
Reconcile
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Tank ID | An 8-character field identifying the tank as defined on the Branch/Plant Constants form.
Form-specific information Note: Do not enter a tank and owner ID. The information on this form applies only to the entire physical tank. |
| Tank Number | Identifies a tank in the Bulk Stock Management System. This unique number is assigned by the system. |
| Tank Location | A user defined code (system 39/type TL) that indicates the tank's location, for example, Tank Farm 1, Tank Farm 2, and so forth. |
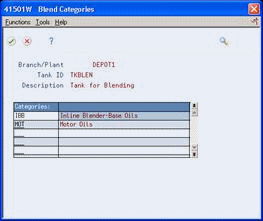
| Tank Usage | A user defined code (system 39/type TU) that identifies how the tank is used. A blending tank should be identified with a code that begins with the letter ''B." If the tank is a blending tank, the Blend Categories Window appears when you press Enter at tank setup time.
Note: Blending tanks allow more than one product to be put in the tank. All other tanks can contain only one product, which is considered the current product. |
| Tank Type | A user defined code (system 39/type TY) that indicates the physical shape of the tank and whether the tank is on scale. |
| Tank Capacity | The total volumetric storage capacity of a tank. Tank Capacity consists of two fields. The first is the total storage capacity of the tank. The second is the unit of measure (UM) associated with the capacity measurement. The capacity is checked while receiving products and recording general stock movements. If you enter a value that is greater than the tank's capacity, the system displays an error message and will not allow you to record the transaction.
The system uses the unit of measure as the basic unit of measure for the tank. All other volume units of measure associated with the tank must match this unit of measure. If the dip type is slip tube or normal dip, then the Tank Capacity is an informational field only. If the dip type is roto percent (for LPG bullets/spheres only), then Liquid Volume equals Roto % multiplied by Gross Capacity. Vapour Space equals Gross Capacity minus Liquid Volume. |
| Tank Height | Identifies the distance from the bottom to the top of a tank and the unit of measure. These fields are display only fields. |
| Reference Height | Identifies the maximum dip height of the product within the tank, or the point from which ullages are to be converted to height of liquid. The reference height must be below tank height. |
| Strapping Units | A user defined code that identifies strapping table increments (for example, centimeters, millimeters, half inches, or quarter inches). If the depot is in U.S. increments, you must enter FF in this field. |
| Dip Type | A user defined code (system 39/type DP) that identifies the method of measurement that the system uses to calculate the volume from tank dips. Valid values are:
W = Wet Dip Reading U = Ullage Dip Reading R = Roto Gauge Percent Reading S = Slip Tube Reading E = Electronic Gauge Reading |
| Gauging Method | A user defined code that identifies the measuring method that the system uses to determine the quantity of liquid in the tank. |
| Expansion Factor | Factor used to calculate the volume of a product in relation to a heated tank. |
| Floating Roof | Indicates whether the tank has a floating roof, and if so, whether a floating roof calculation is required. Valid values are:
Y or 1 = Floating roof - requires calculation. N or 0 = No floating roof. S or 2 = Floating roof - strappings already account for floating roof calculation (no calculations required). If you enter Y or 1, the program requires roof weight and floating height entries. |
| Roof Weight | Identifies the unit of measure for the roof weight. If you use a unit of measure that is not equal to kilograms, you must set up a conversion between your unit of measure and kilograms in the Standard Unit of Measure Conversion program. The Roof Weight field is required if the Floating Roof field is set to Y or 1. This value is used to calculate the roof displacement correction. |
| Process Control ID | Identifies the process control system. You can identify one or more process control systems associated by depot, tank, or mode of transport. The system uses this field for downloads of automated gantry information. |
| Reconcile | This code indicates whether the Item or Tank should be included in the reconciliation process as follows:
T or 1 = Include this item in the Throughput Reconciliation process only O or 2 = Include this item or tank in the Operational Reconciliation process only B or 3 = Include this item in both the Throughput and Operational Reconciliation processes N or 0 = Do not include this item or tank in either of the Reconciliation processes |
27.2.2 What You Should Know About
27.3 Setting Up a Blending Tank (Optional)
From Bulk Stock Management (G4150), enter 29
From Bulk Stock Management Setup (G415041), choose Tank Master Maintenance
A blending tank can hold more than one product. You set up a blending tank to define the blending categories that will be allowed in that tank.
On Tank Master Maintenance
27.4 Setting Up Additional Tank Information
From Bulk Stock Management (G4150), enter 29
From Bulk Stock Management Setup (G415041), choose Tank Master Maintenance
You must define additional information about a tank that the system needs to calculate volume and manage depot transactions. This information includes discharge and filling rates, tank status, and commingled stock.
If you set up a tank as carrying commingled stock, all transactions, such as general stock movements, load confirm, and disposition, require you to enter the owner of the product. All tanks for the product must be defined as commingled, since any could be the current tank at any time.
27.4.1 Before You Begin
-
Set up the tank in the Tank Master table (F41500). See Section 27.2, "Setting Up Basic Tank Information".
To set up additional tank information
On Tank Master Maintenance
-
Access Additional Tank Information.
Figure 27-3 Additional Tank Information screen
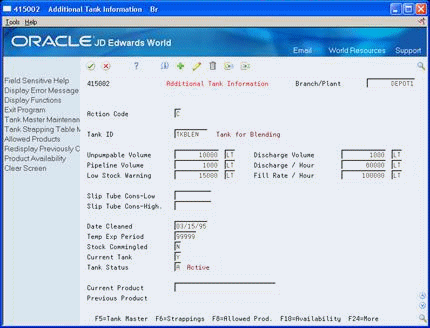
Description of "Figure 27-3 Additional Tank Information screen"
-
On Additional Tank Information, locate the tank.
-
Enter a C in the following field:
-
Action Code
-
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Tank Status
-
Current Product
-
-
Complete one or more of the following optional fields:
-
Unpumpable Volume
-
Discharge Volume
-
Pipeline Volume
-
Discharge/Hours
-
Low Stock Warning
-
Fill Rate/Hour
-
Date Cleaned
-
Temperature Expiration Period
-
-
Complete the following fields or leave blank to accept the default values:
-
Temperature Expiration Period
-
Current Tank
-
-
If the tank contains commingled stock, complete the following field:
-
Stock Commingled
-
-
Indicate a change.
-
Accept the entries.
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Tank Status | Identifies whether the tank is active or inactive. A tank must have a status of active to assign product to it. A tank that has a status of inactive indicates that the tank is empty and not being used. Multiple tanks can be active for a product, but only one tank can be defined as the current, or default, tank. Valid values are:
A – Active I – Inactive |
| Unpumpable Volume | This field displays the volume in the tank that is below the level of the discharge pipeline and, therefore, cannot be removed by the normal discharge pump. The system edits this volume during load confirmation, but it is not used when calculating tank dip volumes. The Unpumpable Volume quantity is used for information purposes only. |
| Current Product | A number that the system assigns to an item. It can be in short, long, or 3rd item number format.
Form-specific information Identifies the current product that the tank contains. When you enter a product, the system checks the current product associated with a tank. If the new product differs from the current product, you cannot enter it into the tank unless the quantity of the current product is zero. Also, when you enter a product, the system checks the Allowed Products matrix to determine if the product group that this product is attached to is allowed to enter the tank, based upon the tank's previous contents. If the tank is set up as a blending tank, there is no current product. You can enter any product. |
| Discharge Volume | Identifies the volume of the product in a tank's discharge pipeline. The system adds this value to obtain the total ambient volume. |
| Pipeline Volume | Identifies the volume of product held in the pipeline that is connected to the subject tank. The tank's content capacity includes the volume capacity of the pipeline. To reflect the total product volume in the tank and pipeline, Pipeline Volume is added to the observed (ambient) volume calculated on the Tank Dip form. |
| Low Stock Warning | Identifies the volume of product below which a low stock warning is issued. A low stock warning indicates that the volume is close to the safety stock level.
Enter the quantity and unit of measure that the system uses to provide a low stock warning. This field information is used during the Load Confirm process. If the quantity being loaded will bring the tank to the low stock point, a "soft" error occurs. That is, the user can press Enter and continue with load confirm. |
| Temp Exp Period | The number of hours the tank temperature remains valid. This number is used to calculate the next expiration date/time on the Default Tank Information screen. It is also checked at load confirm time to ensure the default temperature reading is valid. Enter 99999, if there is no expiration (for example, stocks are stored at a third-party site). |
| Current Tank | Indicates whether this tank is the current tank used for product sales. Only one tank per product can be the current tank. Valid values are:
The default value is N. |
| Stock Commingled | A stock value that identifies the type of commingled stock. If any tank for a product contains commingled stock, you must set up all tanks for that product as containing commingled stock. You also use this field to divide product in the tank into two quantities. For example, enter a value if you want to separate duty-paid from unpaid product in the same tank. If the stocks are commingled, you must record all the product movements at the "owner" level. Valid values are:
Y or 1 - Stocks are commingled for custody N or 0 - Stocks are not commingled D or 2 - Stocks are commingled for duty B or 3 - Stocks are commingled for both custody and duty |
27.5 Setting Up Tank Strapping Information
From Bulk Stock Management (G4150), enter 29
From Bulk Stock Management Setup (G415041), choose Tank Master Maintenance
You must set up the strappings information for the storage, blending, and holding tanks in a depot. The system uses tank strappings (reading height) when you record tank dips to convert tank dip readings to gross volumes.
For example, if you enter before and after dip readings in the Dip Volume Calculator program, the program uses the tank strappings information to calculate the volume.
You can enter information in both metric and U.S. measurements. The delimiter for U.S. measurements is the one you defined in the U.S. Increments Delimiter field on Branch/Plant Constants - Page 3.
27.5.1 Before You Begin
-
Set up the tank in the Tank Master table (F41500). See Section 27.2, "Setting Up Basic Tank Information".
To set up tank strappings information
On Tank Master Maintenance
-
Access Additional Tank Information.
-
On Additional Tank Information, access Tank Strapping Table Maintenance.
Figure 27-4 Tank Strapping Table Maintenance screen
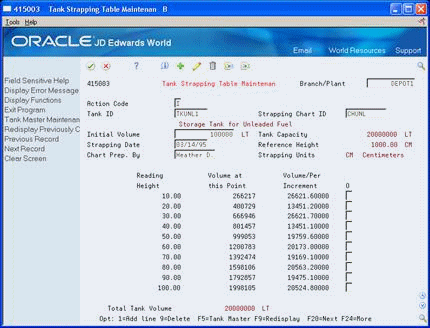
Description of "Figure 27-4 Tank Strapping Table Maintenance screen"
-
On Tank Strapping Table Maintenance, complete the following fields for each strapping point:
-
Reading Height
-
Volume at this Point
-
Volume/Per Increment
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Strapping Chart ID
-
Strapping Date
-
Chart Prepared By
-
Initial Volume
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reading Height | This value is a linear measurement that represents either the depth of oil or free space (ullage) available in a tank. |
| Volume at this Point | The volume contained in the tank at this reading height. You can enter an amount or have the system calculate it. If you want the system to calculate the volume, you must enter information in the Volume/Per Increment field. |
| Volume/Per Increment | This value is the gradient above a strapping point in terms of volume increase per strapping unit. If you enter a value in this field, the system calculates the volume at this point. |
| Strapping Chart ID | Identifies the person responsible for the strapping. This field is for reference only. |
| Initial Volume | The volume of liquid below the zero reference point. The initial volume is added to the total tank volume. When taking a dip reading, this volume is added to the Volume at this point to arrive at the ambient value. |