21 Set Up Work Order Supplemental Data
This chapter contains the topic:
21.1 Setting Up Work Order Supplemental Data
From Work Order/Service Billing Processing (G48), enter 29
From Work Order/Service Billing Setup (G4841), choose Define Your Own Data Types
Use supplemental data to further define the work orders in your system. You can use supplemental data to report and track work order details that are important to your company, but are not included in the record types. You can define as many types of supplemental data as you need.
You define and maintain supplemental data by work order database. Work order databases are user defined (system 00, type WD). For example, you might set up supplemental data for an engineering change order database. The data types might include detail types, pending orders, and so on.
21.1.1 Before You Begin
Set up the user defined codes table for the valid work order databases with which you want to associate supplemental data. See Section 16.1, "Setting Up User-Defined Codes" for more information.
Verify that you have installed the Time Accounting and Human Resources Management Base, or the Payroll system.
To set up work order supplemental data
Figure 21-1 Define Your Own Data Types screen
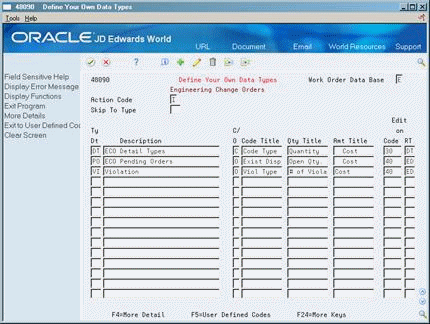
Description of "Figure 21-1 Define Your Own Data Types screen"
-
To specify a work order database, complete the following field:
-
Work Order Data Base
-
-
To define a data type, complete the following fields:
-
Type Data
-
Description
-
Display Format - Code or Order (CO)
-
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Code Title
-
Quantity Title
-
Amount Title
-
System Code (Cod)
-
User Defined Code (RT)
-
-
Choose More Detail (F4).
Figure 21-2 Define Your Own Data Types (Detail) screen
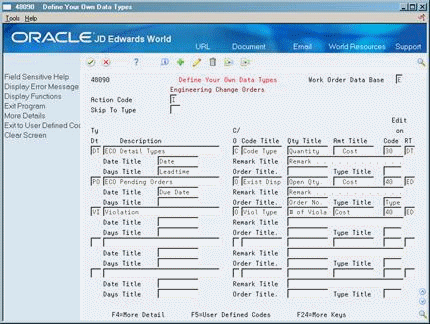
Description of "Figure 21-2 Define Your Own Data Types (Detail) screen"
-
Complete the following optional fields:
-
Date Title
-
Remark Title
-
Days Title
-
Order Title
-
Type Title
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Work Order Data Base | The code representing what Work Order Data Base is to be used. |
| Ty Dt | User defined code system 00, type WT, which indicates the type of data being entered within the supplemental database. The code is often an abbreviation for the data it represents, for example, EC might represent Engineering Change. |
| C/O O | A code that determines the display mode for Supplemental Data. Valid codes are:
C – Automatically takes you to the Data Entry program where you can enter code-specific information. The code values you enter can be edited against values in the User Defined Codes file (F0005). O – Automatically takes you to the Related Order Entry program, bypassing code-specific information. If you use an O, narrative text will not be tied to specific codes. |
| Code Title | The heading for a column on Supplemental Data Entry that relates to user defined codes. Enter the user defined codes for the supplemental data type in this column. For example, if the supplemental data type relates to the educational degrees of employees (BA, MBA, PHD, and so on), the heading could be Degree. |
| Code | A user defined code (98/SY) that identifies a JD Edwards World system. |
| RT | Identifies the table that contains user defined codes. The table is also referred to as a code type. |
21.1.2 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Defining user defined codes as valid values for a data type | You can set up your system to edit the values that you enter on supplemental data forms against the values that you set up in user defined code tables. Use the following guidelines to define user defined codes as valid values for a data type:
See the JD Edwards World Technical Foundation Guide for more information about user defined codes. |