Architecture
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center is designed to provide increased scalability, high availability and optimized performance in large, distributed data centers. The architecture is scaled as your organization grows. The Enterprise Controller, Proxy Controllers, Agent Controllers, and user interface are the major architectural components. They are supported by the Knowledge Base, which is hosted by Oracle and accessed through the Internet. This architecture lets you customize your deployment for the size and network topology of your organization by varying the placement of the Proxy Controllers and use of Agent Controllers.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center, downloads information from the Knowledge Base and Package Repository to the Enterprise Controller, which stores the information along with basic management tools, such as the profiles and plans. At least one Proxy Controller distributes the Enterprise Controller's work. Secure network connections between all components transfer control commands and data. For operating systems, Agent Controllers provide update capabilities, management and monitoring, and control of virtualization environments. Agent Controllers are required for Oracle Solaris 9 and 10 and Linux catalogs. Oracle Solaris 9 and Oracle Solaris 10 boot environment management also requires an agent-managed operating system.
Figure 1-1 shows the relationship between the browser console, Enterprise Controller, Proxy Controller, and multiple Agent Controllers. See the Related Resources for Product Architecture section for details on the communication direction, protocol and port, and the purpose for each level of communication.
Figure 1-1 Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Architecture
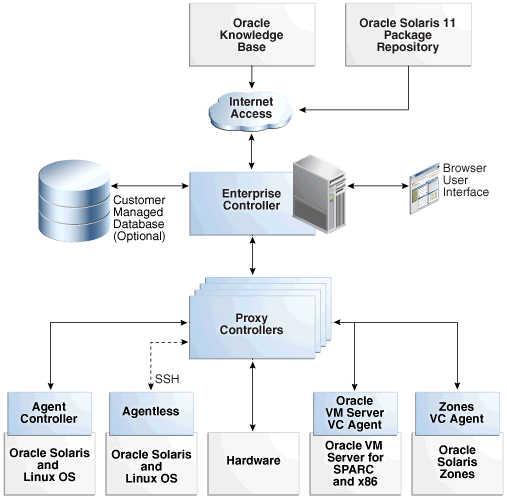
Description of "Figure 1-1 Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Architecture"
Knowledge Base and Package Repository
The Knowledge Base and Oracle Solaris 11 Package Repository store metadata about Oracle Solaris and Oracle Linux operating system components. The metadata includes patch dependencies, standard patch compatibilities, withdrawn patches, and rules for download and deployment.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center is configured to connect to Oracle Corporation sites for updated metadata for operating systems. However, you can configure the product software without a direct connection to these sites.
Enterprise Controller
The Enterprise Controller is the central server for Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center. All operations, or jobs, are initiated from the Enterprise Controller.
The Enterprise Controller manages firmware and operating system images, plans, profiles, and policies. The Enterprise Controller relies on a database of asset data and site customizations. The database is a local embedded database or a remote customer-managed Oracle Enterprise Edition database that is accessible on the network to the Enterprise Controller. Include the Enterprise Controller in an active-standby High Availability configuration to increase the availability of the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center software.
The Enterprise Controller connects to the Internet to get access to contract information, to create service requests, and to download updates, Oracle Solaris images, and updates to the product software itself. When an update is requested, the Enterprise Controller retrieves the software from the Knowledge Base, package repository, or vendor. This default mode of operation is called Connected mode.
If your site policy does not permit an Internet connection, you can operate the software in Disconnected mode. In this mode, you must load and maintain the Knowledge Base and package repository data and updates in the Enterprise Controller. For Oracle Solaris and Oracle Linux operating systems, Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center provides a script that you run on a system that is connected to the Internet to retrieve the contents of Oracle's Knowledge Base or Oracle Solaris 11 Package Repository and then you upload the baselines and updates to the Enterprise Controller.
Proxy Controller
Proxy Controllers distribute the operation load and provide fan-out capabilities to minimize network load. The Proxy Controller can also be used to provide a network presence behind a firewall or to provide access to a private network.
A Proxy Controller links the managed assets to the Enterprise Controller and performs operations that must be located close to the managed assets, such as operating system provisioning. Proxy Controller performs management operations on assets and reports the results to the Enterprise Controller. The actions required to manage, provision, and update assets are handled as a queue of jobs.
You must have at least one Proxy Controller. When you install the Enterprise Controller, a Proxy Controller is automatically installed on the same system. To enhance performance and scalability, the preferred method is to install the Proxy Controllers on separate machines.
Most sites benefit from using multiple Proxy Controllers. The following are some reasons for using multiple Proxy Controllers:
-
Some assets are in remote locations and you want to maintain performance.
-
You anticipate creating multiple jobs to run concurrently.
-
Some assets are behind a firewall and need their own Proxy Controller.
-
To provision Oracle Solaris 10 or Linux with ISO boot, you will need a local Proxy Controller. To provision Oracle Solaris 11 SPARC or Oracle Solaris 10 SPARC with Solaris Flash archive, you can use WAN boot to provision the operating system on a wide area network.
-
You can designate a Proxy Controller for the Management Network and another Proxy Controller for the Data Network.
Agent Controllers
Physical and virtual Oracle Solaris and Oracle Linux operating systems require agent software to perform many functions, such as creating update reports, creating and using system catalogs, and managing Oracle Solaris 9, 10 and 11 boot environments. Some monitoring and Analytics data also require an agent-managed operating system. However, you can use many of the monitoring and management features without installing an Agent Controller on the operating system.
The Agent Controller is a lightweight Java software that identifies the asset and responds to Proxy Controller. When an operating system is agent-managed, the agent receives the command from its Proxy Controller, performs the required action, and notifies the Proxy Controller of the results. When an operating system is agentlessly managed, the Proxy Controller uses SSH (Secure Shell protocol) to perform tasks and to monitor the operating system. You can change the method of managing an operating system asset.
Hardware management does not require the Agent Controller. Instead, a Proxy Controller runs commands on the hardware system and reports the results to the Enterprise Controller.