1 Overview
Describes the product’s purpose.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center is a data center management solution for managing both hardware and software from one console. This document presents good practices for managing the security of Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center deployments.
Overview of the Architecture
Describes the components on the product’s solution.
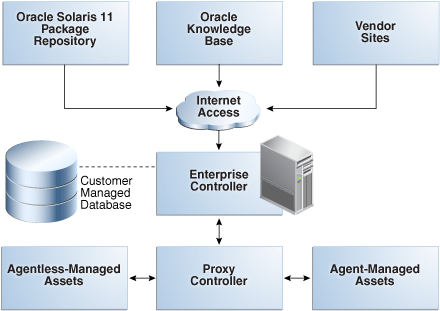
The Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center software has a distributed architecture with a single master controller (Enterprise Controller) and multiple controllers (Proxy Controllers). Each Proxy Controller connects either to multiple Agent Controllers hosted on an Operating System instance or to managed systems or to both. Figure 1-1 shows a deployment with one Proxy Controller, which can be located on the same system as the Enterprise Controller.
About the Knowledge Base (KB) and Package Repository
Describes the components of the product architecture that store images for operating systems.
The Knowledge Base is the repository for metadata about Oracle Solaris 10-8 and Linux OS components, which resides on Oracle's website. Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center can connect to the Knowledge Base through the Internet to obtain OS updates and updates to the product software itself. In a similar way, the Enterprise Controller can get access to the Oracle Solaris 11 Package Repository for updates to components of Oracle Solaris 11.
About the Enterprise Controller
Describes the role of the Enterprise Controller in the product architecture.
The Enterprise Controller is the central server for Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center and there is only one Enterprise Controller in each installation. The Enterprise Controller stores firmware and OS images, plans, profiles, and policies. The Enterprise Controller also stores the asset data and site customizations in a database and hosts the web container for the user interface components. The Enterprise Controller handles all user authentication and authorization. All operations are initiated from the Enterprise Controller.
Although the Enterprise Controller stores firmware and OS images, these images are not included in a backup of the Enterprise Controller. As a good practice, create the software library for OS images on networked storage (NAS). Then include the network storage device in your site's backup plan.
About the Proxy Controller
Describes the role of the Proxy Controller in the product architecture.
A Proxy Controller links the managed assets to the Enterprise Controller and acts for the Enterprise Controller in operations that must be located close to managed assets, such as OS provisioning. The Proxy Controller provides fan-out capabilities to minimize network load and to support complex network topologies. The Proxy Controller also contains the logic for agent-less monitoring and management of hardware.
About the Agent Controllers
Description of the role of the Agent.
An Agent is lightweight Java software that represents and manages an OS asset or OS instance and responds to requests from a Proxy Controller. Hardware management does not require an agent. The Agent receives the command from the Proxy Controller, performs the required action, and reports results to the Proxy Controller. An agent never communicates directly with the Enterprise Controller and does not initiate operations.
To manage operating systems using agents, an Oracle SE Java Runtime Environment is required. Non-Oracle versions work initially but might exhibit performance and memory issues.
You can choose to manage operating systems without an agent by providing credentials but some product features are not available. See Using Agent Management for Operating Systems in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Operate Reference for more information about Agent Controllers.
About the Database
Describes the types of databases used in the product.
The Enterprise Controller uses an Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition or Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition database to store Enterprise Manager Ops Center data. The database can be local or remote:
-
The local database is embedded in the Enterprise Controller, created during product installation.
-
A remote database is a new or existing customer-managed database.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center provides utilities to help you manage the local database, migrate your data from a local database to a customer-managed database, back up and recover the database schema, and change database credentials.
Security of the Architecture
Description of the locations in the architecture that need to be secured.
For a secure deployment, each communication direction must be protected. Use the procedures in Table 1-1 to secure each connection.
Table 1-1 Secure Connections
| Connection | To Make Secure |
|---|---|
|
From Internet to the Enterprise Controller |
|
|
Between Enterprise Controller and database |
|
|
Between Enterprise Controller and LDAP server |
|
|
Between Enterprise Controller and the NFS server |
Verify that a firewall does not separate the Enterprise Controller and the NFS server. Verify that the NFS server uses the NFSv4 protocol. |
|
Between Enterprise Controller and remote Proxy Controllers |
Configure a reverse SSH tunnel when you install the product software. This option is described in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Installation for Oracle Solaris Operating System and the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Installation for Linux Operating Systems |
|
Between Proxy Controller and assets |
Authentication is configured when the asset is discovered and managed as described in About Authentication Between the Proxy Controller and Agents |
About Authentication Between the Proxy Controller and Agents
Description of the relationship between Proxy Controllers and Agent Controllers.
In the normal operation of the product, various Proxy Controllers make requests for asset data or status and receive the response from each asset. For each transaction, the Proxy Controller must authenticate the asset and each asset must authenticate the Proxy Controller, as described in this section.
For an agentless-managed asset, authentication requires an SSH password as described in About Credentials for Assets. An alternative procedure for an OS asset that does not require a password is to install a token manually, also described in that section.
About Authentication of Agent-Managed Asset
Describes the result of installing an Agent Controller on an asset.
For an agent-managed asset, authentication is configured when the asset is discovered and managed. The Enterprise Controller installs an agent controller on the asset. This triggers two actions:
-
Authentication of the Agent
-
Authentication of the Proxy Controller
Overview of the Authentication of the Agent
Describes the process of how a Proxy Controller authenticates an Agent Controller.
-
Agent creates a public/private key pair
-
Agent saves the key pair in
/var/opt/sun/xvm/persistence/scn-agent/connection.propertiesOnly the root user can read the agent properties file.
-
Agent sends the public key to the Enterprise Controller (through its Proxy Controller)
-
Enterprise Controller creates a unique client registration ID for this agent.
-
Enterprise Controller saves the public key and the client registration ID together in the database
-
Enterprise Controller sends the client registration ID to the agent,
-
Agent saves the client registration ID in t
/var/opt/sun/xvm/persistence/scn-agent/connection.propertiesfile.
Overview of the Authentication of the Proxy Controller
Describes the process of how an Agent Controller authenticates a Proxy Controller.
-
Proxy Controller's server-side certificate was prompted to the agent as part of the handshake.
-
Agent accepts the certificate.
-
Agent saves the certificate locally in
/var/opt/sun/xvm/security/jsse/scn-agent/truststore
About Authenticated Transactions
Description of the authentication process
When an agent gets an inquiry:
-
Proxy Controller's web server sends its certificate to the agent.
-
Agent confirms this certificate with the already-accepted certificate saved in
/var/opt/sun/xvm/security/jsse/scn-agent/truststore. This is the handshake.
If the agent does not confirm the Proxy Controller's certificate, the handshake fails. No data is sent. This protects against an interloper.
When an agent responds to an inquiry:
-
Agent creates a string from the client reg ID and the private key. The string is its signature
-
Agent sends an HTTPS POST of the signature and the requested data to the Proxy Controller.
-
Proxy Controller retrieves the public key for the agent's client reg ID from the database.
-
Proxy Controller verifies that the message's signature was created from the private key that matches the public key.
If the Proxy Controller detects that the message's private key does not match the public key, the Proxy Controller does not allow the connection. This protects against an entity misrepresenting itself as the agent.
General Principles of Security
Lists good security practices
This section describes the principles fundamental to using the software securely:
About Keeping Software Up To Date
Description of a good practice for security.
Good security is maintained when all software versions and patches are current. This document discusses Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center version 12c Release 3 (12.3.2.0.0). As new versions or updates of Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center become available, install the new software as soon as possible.
About Restricting Network Access
Describes how a firewall adds security to the product architecture.
Firewalls restrict access to systems to a specific network route that can be monitored and controlled. When firewalls are used in combination, they create a DMZ, a term for a subnetwork that controls access from an untrusted network to the trusted network. Using firewalls to create a DMZ provide two essential functions:
-
Blocks traffic types that are known to be illegal.
-
Contains any intrusion that attempts to take over processes or processors.
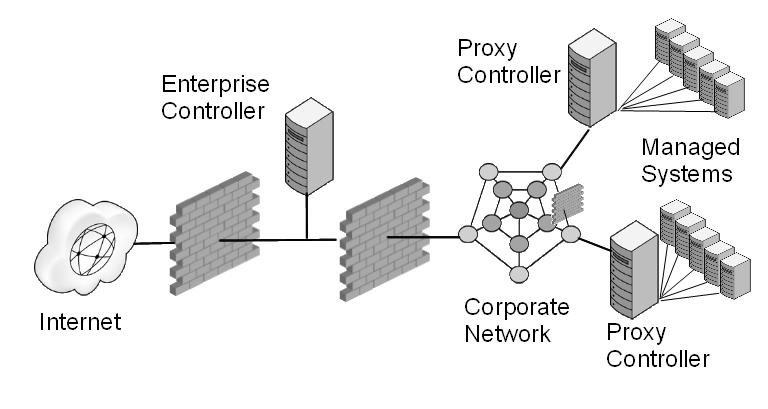
In your deployment, design an environment that locates the Enterprise Controller's system in a DMZ, that is, with a firewall between the system and the Internet and a firewall between the system and the corporate intranet, as in Figure 1-2. This type of environment allows the Enterprise Controller to get access to the Internet to perform operations while in Connected mode, and restricts access to assets to only those operations that manage the assets. When the Enterprise Controller is in Disconnected mode, it operates without access to the Internet.
Figure 1-2 Firewalls Restrict Access to Enterprise Controller
Description of "Figure 1-2 Firewalls Restrict Access to Enterprise Controller"
If your data center includes remote Proxy Controllers, use firewalls between the Enterprise Controller's system and the Proxy Controllers' systems.
To use Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center in Connected mode, use a firewall between the Enterprise Controller and the Internet.
To configure the firewalls, see Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Ports and Protocols for information about required URLs, ports, and protocol information.
About the Principle of Least Privilege
Describes the method of securing user access.
The principle of least privilege states that users are given the lowest level of permissions to perform their tasks. Granting roles or privileges in excess of a user's responsibilities leaves a system open for non-compliance. Review privileges periodically to determine whether they remain appropriate for each user's current job responsibilities.
You give each user a set of roles, which determine the tasks the user can and cannot perform, and a set of privileges which specify the assets, networks, or other objects to which the user's roles apply. This gives you fine-grained control of the actions that users can take.
Role Requirement for Tasks
Lists the role needed to perform each task.
Table 1-2 shows the permission needed to perform each action. Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center groups permissions into roles and assigns one or more roles to a user account. Table 1-3 shows the permissions granted by each role.
Table 1-2 Tasks and Permissions
| Tasks | Permission |
|---|---|
|
Read Access |
Read Access |
|
Add Assets Find Assets |
Discover Assets |
|
Manage Assets Delete Assets |
Manage Assets |
|
Create Group Edit Group Add Assets to Group Delete Group |
Asset Group Management |
|
New Update OS Job Deploy or Update Software Compare System Catalog Create Catalog Snapshot View and Modify Catalog |
Update |
|
New Simulated OS Update Job |
Update Simulation |
|
Configure and Deploy Server Install Server Configure RAID |
Server Deployment |
|
Add or delete storage Assign or detach network Start Guest Shut Down Guest Migrate Guest Clone Guest Lifecycle actions |
Virtualization Guest Management |
|
Assign Incidents Add Annotation to incidents Acknowledge incidents Take Actions on Incidents Mark Incidents as Repaired Close Incidents Delete Notifications Take Actions on Notification |
Fault Management |
|
Update Management Credentials Any Actions related to changing credentials |
Credential Management |
|
Edit Network Domain Edit Network Attributes Edit Network Services |
Network Management |
|
Fabric Management |
Fabric Management |
|
Import ISO Upload image Edit Attributes |
Storage Management |
|
Create reports Delete reports |
Report Management |
|
Create, delete, and modify profiles and plans |
Plan/Profile Management |
|
Create/Update/Delete Instance Attach/Detach Volume to Instance Create/Delete/Update Security Group Create/Update/Delete Volume Upload/Register/Delete templates Create/RollbackTo/Delete Snapshot Shutdown All servers Link/Launch OVAB |
Cloud Usage |
|
Create/Delete/Update Cloud Create/Delete/Update Cloud Domain Create Public Security Group Share Public Security Group Create VM Instance Type |
Cloud Management |
|
Manage Enterprise Controller |
Enterprise Controller Management |
|
Unconfigure/Uninstall Proxy Controller Configure Agent Controller Unconfigure Agent Controller DHCP configuration Subnets External DHCP Servers |
Proxy Controller Management |
|
Configure/Connect Disconnect/Unconfigure Cloud Control Console |
Cloud Control Management |
|
Unconfigure SCCM Configuration |
Windows Update Management |
|
Add Users Remove Users |
User Management |
|
Assign Roles |
Role Management |
|
Asset Management |
Asset Management |
|
Write Access |
Write Access |
|
Open Service Request |
Service Request |
|
Power On Power Off Power on with Net Boot Set Power Policy |
Power Management |
|
Chassis Management |
Chassis Management |
|
Storage Server Management |
Storage Server Management |
|
Launch Switch UI |
Switch Management |
|
Reset Servers Reset Service Processors Refresh Locator Light On/Off Snapshot Bios Configuration Update Bios Configuration |
Server Management |
|
Reboot Upgrade Agent Controller |
Operating System Management |
|
Cluster Management |
Cluster Management |
|
Aggregate Links |
Link Aggregation |
|
IPMP Groups |
IPMP Groups |
|
Update Firmware |
Update Firmware |
|
Upgrade Proxy Controller |
Proxy Controller Upgrade |
|
Execute Operation |
Operation Execution |
|
Unconfigure Enterprise Controller |
Unconfigure EC |
|
Add Product Alias |
Add Product Alias |
|
Upgrade Enterprise Controller |
EC Upgrade |
|
Set Enterprise Controller Storage Library |
EC Storage Library Management |
|
Configure Local Agent Unconfigure Local Agent |
EC Local Agent Management |
|
Proxy Deployment Wizard |
EC Proxy Management |
|
Set up Connection Mode |
EC Connection Mode Management |
|
Register Enterprise Controller |
EC Registration |
|
Change HTTP Proxy |
EC HTTP Proxy Management |
|
Edit Energy Cost |
EC Energy Cost Management |
|
Ops Center Downloads |
Ops Center Downloads |
|
Activate Boot Env and Reboot Create New Boot Env. Synchronize Boot Env. |
Boot Environment Management |
|
Create Server Pool |
Server Pool Creation |
|
Delete Server Pool |
Server Pool Deletion |
|
Rebalance Resource Edit Server Pool Attribute Attach Network to Server Pool Associate Library to Server Pool Add/Remove Virtual Host |
Server Pool Management |
|
Create OVM virtual Servers Create zone servers Create Logical Domains |
Server Pool Usage |
|
Create Virtualization Host |
Virtualization Host Creation |
|
Delete Virtualization Host |
Virtualization Host Deletion |
|
Add/Remove Virtual Host to/from Server Pool Edit Tags Edit Attributes Reboot Change Routing Configuration Change NFS4 Domain Change Naming Service Change Remote Logging Configuration |
Virtualization Host Management |
|
Create Logical Domains Create zones Create OVM virtual servers |
Virtualization Host Usage |
|
Create Logical Domains Create zones Create OVM virtual servers |
Virtualization Guest Creation |
|
Delete Logic Domain Delete Zones Delete OVM Virtual Servers. |
Virtualization Guest Deletion |
|
Start Guest Shutdown Guest Migrate Guest Clone Guest |
Virtualization Guest Usage |
|
Create Library |
Storage Creation |
|
Delete Library |
Storage Deletion |
|
Associate Library |
Storage Usage |
|
Create Network Domain Create Network |
Network Creation |
|
Delete Network Domain Delete Network |
Network Deletion |
|
Assign Network Connect Guests |
Network Usage |
|
Create Fabric |
Fabric Creation |
|
Delete Fabric |
Fabric Deletion |
|
Fabric Management |
Fabric Usage |
|
Chassis Usage |
Chassis Usage |
|
Storage Server Usage |
Storage Server Usage |
|
Switch Usage |
Switch Usage |
|
Launch LOM Controller Edit Tags |
Server Usage |
|
Edit Tags Edit Attributes |
Operating System Usage |
|
Create Rack |
Rack Creation |
|
Directory Server Management |
Directory Server Management |
|
Power Distribution Unit Usage |
Power Distribution Unit Usage |
|
Power Distribution Unit Management |
Power Distribution Unit Management |
|
Rack Creation |
Rack Creation |
|
Rack Deletion |
Rack Deletion |
|
Rack Management |
Rack Management |
|
Rack Usage |
Rack Usage |
|
OVM Manager Usage |
OVM Manager Usage |
|
OVM Manager Management |
OVM Manager Management |
|
Network Domain Creation |
Network Domain Creation |
|
Network Domain Deletion |
Network Domain Deletion |
|
Network Domain Management |
Network Domain Management |
|
Network Domain Usage |
Network Domain Usage |
|
Asset Network Management |
Asset Network Management |
|
Job Management |
Job Management |
Table 1-3 Roles and Permissions
| Role | Permissions |
|---|---|
|
Asset Admin |
Asset Management Asset Network Management Boot Environment Management Chassis Management Chassis Usage Cluster Management Discover Assets IPMP Groups Link Aggregation Manage Assets Network Management Operating System Management Operating System Usage Power Distribution Unit Management Power Distribution Unit Usage Power Management Rack Creation Rack Deletion Rack Management Rack Usage Read Access Server Management Server Usage Service Request Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Switch Management Switch Usage Write Access |
|
Cloud Admin |
Asset Management Asset Network Management Cloud Management Cloud Usage Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Management Fabric Usage IPMP Groups Link Aggregation Manage Assets Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Creation Network Domain Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Operating System Management Operating System Usage OVM Manager Management OVM Manager Usage Profile Plan Management Read Access Role Management Server Management Server Pool Management Server Pool Usage Server Usage Storage Management Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Switch Management Switch Usage Virtualization Guest Creation Virtualization Guest Deletion Virtualization Guest Management Virtualization Guest Usage Virtualization Host Management Virtualization Host Usage Write Access |
|
Cloud User |
Asset Management Asset Network Management Cloud Usage Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Usage Manage Assets Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Operating System Management Operating System Usage OVM Manager Usage Read Access Server Pool Usage Server Usage Storage Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Switch Usage Virtualization Guest Creation Virtualization Guest Deletion Virtualization Guest Management Virtualization Guest Usage Virtualization Host Management Virtualization Host Usage Write Access |
|
Exalogic Systems Admin |
Asset Management Credential Management Directory Server Management EC Energy Cost Management EC HTTP Proxy Management EC Registration Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Management Fabric Usage Job Management Link Aggregation Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Creation Network Domain Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Operating System Management Operating System Usage Operation Execution OVM Manager Management OVM Manager Usage Power Distribution Unit Management Power Distribution Unit Usage Profile Plan Management Proxy Controller Management Read Access Report Management Role Management Server Deployment Server Management Server Usage Service Request Storage Creation Storage Deletion Storage Management Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Switch Usage Update Firmware User Management Write Access |
|
Fault Admin |
Fault Management Read Access Write Access |
|
Network Admin |
Asset Management Asset Network Management Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Management Fabric Usage IPMP Groups Link Aggregation Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Creation Network Domain Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Read Access Write Access |
|
Ops Center Admin |
Add Product Alias Discover Assets EC Connection Mode Management EC Energy Cost Management EC HTTP Proxy Management EC Local Agent Management EC Proxy Management EC Registration EC Storage Library Management EC Upgrade Enterprise Controller Management Cloud Control Management Job Management Manage Assets Ops Center Downloads OVM Manager Management OVM Manager Usage Proxy Controller Management Proxy Controller Upgrade Read Access Unconfigure EC Windows Update Management Write Access |
|
Plan/Profile Admin |
Plan/Profile Management Read Access Write Access |
|
Read |
Read Access |
|
Report Admin |
Read Access Report Management Update Simulation Write Access |
|
Role Management Admin |
Read Access Role Management Write Access |
|
Security Admin |
Credential Management Read Access Write Access |
|
Apply Deployment Plans |
Operation Execution Read Access Server Deployment Update Firmware Write Access |
|
Storage Admin |
Asset Management Read Access Storage Creation Storage Deletion Storage Management Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Write Access |
|
SuperCluster Systems Admin |
Asset Management Cluster Management Credential Management Directory Server Management EC Energy Cost Management EC HTTP Proxy Management EC Registration Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Management Fabric Usage Job Management Link Aggregation Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Creation Network Domain Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Operating System Management Operating System Usage Operation Execution Power Distribution Unit Management Power Distribution Unit Usage Profile Plan Management Proxy Controller Management Read Access Report Management Role Management Server Deployment Server Management Server Usage Service Request Storage Creation Storage Deletion Storage Management Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Switch Usage Update Firmware User Management Write Access |
|
Update Admin |
Boot Environment Management Read Access Update Update Simulation Windows Update Management Write Access |
|
Update Simulation Admin |
Read Access Update Simulation Write Access |
|
User Management Admin |
Directory Server Management Read Access User Management Write Access |
|
Virtualization Admin |
Asset Management Asset Network Management Fabric Creation Fabric Deletion Fabric Management Fabric Usage IPMP Groups Link Aggregation Manage Assets Network Creation Network Deletion Network Domain Creation Network Domain Deletion Network Domain Management Network Domain Usage Network Management Network Usage Operating System Management OVM Manager Management OVM Manager Usage Read Access Server Deployment Server Management Server Pool Creation Server Pool Deletion Server Pool Management Server Pool Usage Storage Creation Storage Deletion Storage Management Storage Server Management Storage Server Usage Storage Usage Virtualization Guest Creation Virtualization Guest Deletion Virtualization Guest Management Virtualization Guest Usage Virtualization Host Creation Virtualization Host Deletion Virtualization Host Management Virtualization Host Usage Write Access |
Assigning Roles and Privileges to a User
Procedure for changing a user’s role and privileges.
The user accounts are created from the local authentication subsystem of the Enterprise Controller's operating system or from a separate directory server, as described in About Configuring an LDAP Server.
You must have the Role Admin role to grant roles to user accounts and to change privileges.
-
Select Administration in the Navigation pane.
-
Click the Roles tab. The Roles page is displayed.
-
Select a user from the list of users.
-
Click the Manage User Roles icon.
-
Add or remove one or more roles from the roles list. By default, a user has all the permissions of the assigned role. To control the scope of a user's role, remove a specific permission:
-
Deselect the Use the default Role associations box. Click Next.
-
The privileges for each type of target are displayed on separate pages. Select the roles to apply to each target, then click Next.
-
-
The Summary page is displayed. Review the roles and privileges assigned to the user, then click Finish.
About Monitoring System Activity
Describes the logging features of the product.
Each Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center component has some auditing capability. Follow audit advice in this document and monitor audit records routinely.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center performs each action as a job. The details of a job show the order of operations in the job and the managed assets that were targets of the job. You can view the details of a job from either the browser or the command-line interface. Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center stores each job until the job is deleted explicitly.
In addition to the jobs record, log files can be a source of activity records. Events are recorded during operations and can provide additional detail about system activity. Log files are protected by file permissions and therefore require a privileged user to get access to them.
About Audit Logs for Performance and Security
Description of the role of audit logs
The information in this section is also in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center Operations Reference.
The audit log files record the following types of events:
-
Adding and deleting a user account
-
Changing the roles for a user account
-
Logging in and information about the connection
-
Starting and ending jobs
The files are located on the Enterprise Controller in the following location:
-
On Oracle Solaris:
/var/cacao/instances/oem-ec/logs/audit-logs.* -
On Linux:
/var/opt/sun/cacao2/instances/oem-ec/logs/audit-logs.*
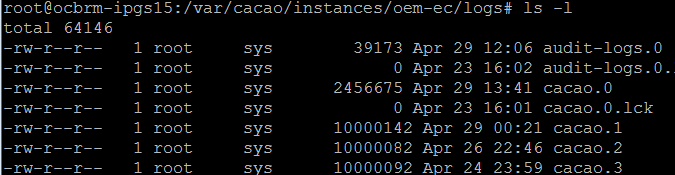
Each audit log file has a maximum size of 10 Mb. When this limit is reached, the file is closed and a new file is created with an incremented file extension. The maximum number of audit log files is 15, accumulating 150 Mb of logged activity. When audit-logs.14 is closed, the next audit file is audit-log.0, overwriting the original audit-log.0 file.
Figure 1-3 shows the series of log files.
Figure 1-3 Contents of Log Directory on Oracle Solaris 11
Description of "Figure 1-3 Contents of Log Directory on Oracle Solaris 11"
-
User root logs in at 3:06.
-
User root creates a new user, stanfield.
-
User root gives the OPS_CENTER_ADMIN privilege to user stanfield.
-
User root logs out.
-
User stanfield logs in at 3:12.
-
User stanfield starts a DHCP configuration job.
-
Job is completed.
-
User stanfield logs out.
Starting with Release 12.3.1, the audit log contains the sessionID to differentiate among multiple sessions of the same user. Also, starting in this release, you have the option to specify the format of the date and time in any of the formats supported by Javadoc’s SimpleDateFormat class. You specify the format using the audit.dateformat system property.
Syntax of an Audit Log Entry
Lists the components of an event in the audit log file.
The entries in the audit log file have the following syntax:
datetime action connect_info additional_info
- action
-
- LOGIN
- DISCONNECT If a connection expires, the disconnection is not logged.
- JOB_START
- JOB_END
- USER_ADD
- USER_DELETE
- ROLES_ASSIGN
- SCHEDULED_JOB_STARTED
- REMOTE_INFO Indicates a connection through the browser interface and includes the IP address and port of the
httpclient making the connection, as in the following example:
REMOTE_INFO rmi://127.0.0.1 yogi 52, Remote Info: User yogi Session ID:c2870004d5308069ffbf367fde6b connected from 192.168.134.249:57391 / JMX Session: com.sun.cacao.sessionrmi://127.0.0.1:9 com.sun.cacao.useryogi
- connect_info
-
Unique identifier for the connection, depending on the type of connection:
-
Connections through the browser interface or the command line interface:
rmi://ip_address username connection_id -
Connections through the API:
jmxmp://ip_address:port username connection_id
-
- additional_info
-
-
When the system property
audit.dateformatis set, a timestamp is included. -
For job actions, the additional information is the job ID, which consists of the Enterprise Controller's name and the job number as listed in the Job pane.
-
For user actions, the additional information is the username.
-
Changing the Date and Time Format of the Audit Log
Procedure for changing the system property that controls the timestamp in audit logs for Oracle Enterprise Manager Ops Center.
- Select Administration in the Asset pane.
- Select the Configuration tab in the center pane.
- Select EC Manager in the drop-down list.
- Select
audit.dateformatin the list of properties. - Edit the value field to specify the format of the date and time. Use a specification that is supported by Java’s SimpleDateFormat class.
- Click the Save button.
- Wait at least 10 minutes for the change to take effect and view the current audit log to confirm.
Example of an Audit Log
Sample audit log.
Example 1-1 shows the contents of an audit log for the following operations:
Example 1-1 Example of an Audit Log
5/23/14 3:06 PM LOGIN rmi://127.0.0.1 root 13 5/23/14 3:06 PM REMOTE_INFO rmi://127.0.0.1 root 13, Remote Info: User root Session ID:c2870004d5308069ffbf367fde6b connected from 192.0.2.1:45338 / JMX Session: com.sun.cacao.session^Armi://127.0.0.1:2 com.sun.cacao.user^Aroot 5/23/14 3:12 PM USER_ADD rmi://127.0.0.1 root 13, Remote Info: User root connected from Session ID:c2870004d5308069ffbf367fde6b 192.0.2.1:45338 / JMX Session: com.sun.cacao.session^Armi://127.0.0.1:2 com.sun.cacao.user^Aroot Add user stanfield: SUCCESS 5/23/14 3:12 PM ROLES ASSIGN rmi://127.0.0.1 root 13 Roles [OPS_CENTER_ADMIN] granted to user stanfield 5/23/14 3:12 PM DISCONNECT rmi://127.0.0.1 root 13 5/23/14 3:12 PM LOGIN rmi://127.0.0.1 stanfield 18 5/23/14 3:12 PM REMOTE_INFO rmi://127.0.0.1 stanfield 18, Remote Info: User stanfield Session ID:c2870004d5308069ffbf367fde6d connected from 192.0.2.1:45351 / JMX Session: com.sun.cacao.session^Armi://127.0.0.1:3 com.sun.cacao.user^Astanfield 5/23/14 3:13 PM JOB_STARTED rmi://127.0.0.1 stanfield 18 sm4170m2-11-n172.27.immediate - DHCP Server Configuration on sm4170m2-11-n172 5/23/14 3:13 PM JOB_END Job sm4170m2-11-n172.27 Completed with Status: SUCCESS 5/23/14 3:13 PM DISCONNECT rmi://127.0.0.1 stanfield 18
Activity Log Files for Components
Lists the type of event and the type of information about the event that is logged.
The following log files contain detailed information about the same events as the audit log files except for login information. They include the interactions between components of the product software.
-
On Oracle Solaris:
/var/cacao/instances/oem-ec/audits/ -
On Linux:
/var/opt/sun/cacao/instances/oem-ec/audits/
The following log files are specialized for specific events:
-
Messages from operating system such as Info and Warning:
/var/adm/messages* -
Login and connection information:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/audit-logs* -
Events in the user interface component:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/emoc.log -
Events between controllers and agents:
-
On an Oracle Solaris Enterprise Controller:
/var/cacao/instances/oem-ec/logs/cacao.n -
On a Linux Enterprise Controller:
/var/opt/sun/cacao/instances/oem-ec/logs/cacao.n -
On each Oracle Solaris Proxy Controller:
/var/cacao/instances/scn-proxy/logs/cacao.n -
On each Linux Proxy Controller:
/var/opt/sun/cacao/instances/scn-proxy/logs/cacao.n -
On each Oracle Solaris agent:
/var/cacao/instances/scn-agent/logs/cacao.n -
On each Oracle Linux agent:
/var/opt/sun/cacao/instances/scn-agent/logs/cacao.n
-
High Availability
Lists the Clusterware activity log.
In a High Availability configuration, each Enterprise Controller is a Clusterware node. The Clusterware resource activity is logged each time the active Enterprise Controller's resource action script's check() function is executed. The default interval is 60 seconds.
On Oracle Solaris: /var/opt/sun/xvm/ha/EnterpriseController.log
Software Updates
Lists the events for software updates.
The Software Update component has its own server with its own logs. The following logs provide information on the activity for this server:
-
Audit Log
-
On Oracle Solaris:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/uce/var.opt/server/logs/audit.log -
On Linux:
/usr/local/uce/server/logs/audit.log
-
-
Errors
-
On Oracle Solaris:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/uce/var.opt/server/logs/error.log -
On Linux:
/usr/local/uce/server/logs/error.log -
Download jobs:
/opt/SUNWuce/server/logs/SERVICE_CHANNEL/error.log
-
-
Job Log
-
On Oracle Solaris:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/uce/var.opt/server/logs/job.log -
On Linux:
/usr/local/uce/server/logs/job.log
-
Agents
Lists the type of event and the type of information about the event that is logged
-
/var/scn/update-agent/logsdirectory. -
/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs
Local Database
Lists the log files for database activity.
-
On the Enterprise Controller:
-
For installation events:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/cfgtoollogs/dbca/OCDB/*/var/tmp/opscenter/installer.log.latest -
For operational events reported by the
ecadm sqlplusutility:/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/diag/rdbms/ocdb/OCDB/alert/log.xml.*/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/diag/rdbms/ocdb/OCDB/trace/alert_OCDB.log.*/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/<hostname>/oclistener/alert/log.xml.*/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/<hostname>/oclistener/trace/listener.log.* -
For schema changes:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/log/satadmsqlplus.log/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/alter_oracle_schema.out/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/alter_oracle_storage.out -
For backup, restore, and migrate operations:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/sat-backup-date-time.log/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/sat-restore-date-time.log/var/opt/sun/xvm/logs/migrate.log
-
-
For data files:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/oradata/OCDB -
For redo log files:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/oradata/OCDB.If you used OCDoctor to prepare a zpool directory with Oracle OS user permission, the log files are in:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/oracle/oradata/OCDB/REDO/ -
On the Proxy Controller:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/proxydb/* -
On each agent:
/var/opt/sun/xvm/agentdb/*