6 Reports
Topics
Generating and Customizing Reports
Report Descriptions
6.1 About the Reports in Audit Vault and Database Firewall
The Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall reports are automatically generated reports that reflect audit data collected from secured targets, as well as data monitored by any Database Firewalls you have configured. You can save or schedule reports in either PDF or Excel format. You can also view reports online and interactively adjust the online report view by filtering data. You can save these interactive views to see them online later.
The reports are organized into various categories, such as access reports and management reports. An alerts report allows you to view and respond to alerts. You can also create user-defined reports that focus on specific audit events or firewall data.
You can also produce Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), Payment Card Industry (PCI), Data Protection Act (DPA), Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) reports. To specify which of these reports are required for a secured target database, you can add the secured target to the appropriate group (such as the SOX group) from the Secured Targets tab.
Auditors can view data and modify reports for secured targets to which they have been granted access by a super auditor. However, an auditor can also send a report to other auditors for attestation regardless of the access rights of the other auditors.
You can specify email recipients for scheduled reports once they are generated, as well as create email templates for report notifications.
6.2 Browsing the Built-In Reports
From the Built-in Reports section of the Reports tab, you can browse report data online, schedule reports, and link to previously scheduled and generated reports. The report displays only records that are collected by the collector before the report execution starts.
Note:
Reports run faster if the audit data is in memory on the Audit Vault Server. If your Oracle AVDF administrator has enabled Oracle Database In-Memory, you will see a date range on the dashboard (Home tab) at the top right, as shown in Figure 6-1. Reports for this date range will run faster.
Figure 6-1 Data Range Selection and In-Memory Date Range
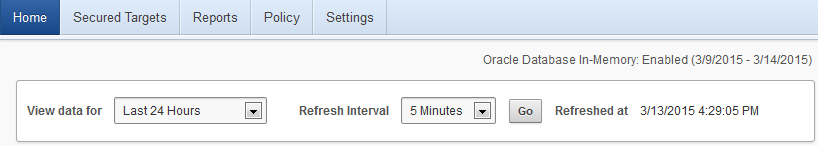
Description of "Figure 6-1 Data Range Selection and In-Memory Date Range"
To generate or browse the built-in reports:
-
Log in to the Audit Vault Server console as an auditor.
-
Click the Reports tab.
-
Click a link under the Built-in Reports menu (for example, Compliance Reports), navigate to the report you want, and then do one of the following:
-
Click the report name to view and browse the report data online. Timestamps in reports, when you browse them online, are displayed in your local browser time.
-
Click the Schedule Report icon to schedule the report in PDF or XLS format. Timestamps in a PDF or XLS report are written in the Audit Vault Server time (based on the Timezone Offset setting specified by an administrator).
-
Click the Generated Report icon to view a previously scheduled and generated report.
-
-
When browsing a report, click the Single Row View icon in the leftmost column for a row (an audit event) to view detailed information for that event.
Note:
If your Oracle AVDF administrator changes the name of a secured target, the new name does not appear on reports until the administrator restarts the Audit Vault Agent.
See Also:
-
Audit Record Fields for a description of each field in an audit record.
6.4 Customizing the Built-in Reports
Topics
6.4.1 About Customizing Built-in Reports
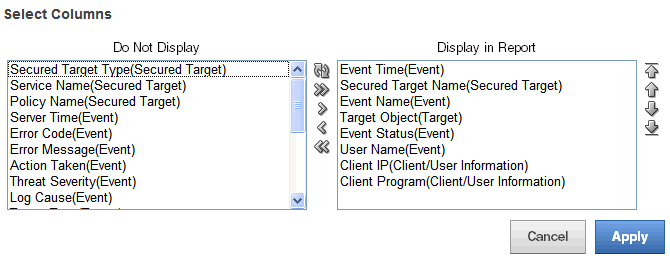
You can create customized reports based on the built-in reports and then save the new report formats. Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall provides tools to filter, group, and highlight data, and define columns displayed in the reports. You can also create a categories for your saved reports. Customized and saved reports are listed on the Saved Interactive Reports page.
While you can schedule the default built-in reports to be generated in PDF format, saved custom reports cannot be scheduled or printed in PDF format, and therefore must be viewed online.
6.4.2 Filtering and Controlling the Display of Data in a Report
Topics
6.4.2.1 About Filtering and Display Settings in Reports
You can control the display of data in a report to focus on a particular set of data. Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall automatically saves the report settings so that if you leave the page, the report settings are still in place when you return. Optionally, you can save the report as a custom report.
See Also:
6.4.2.2 Filtering Data in a Report
Topics
6.4.2.2.1 About Filtering Data in Reports
You can filter the report to show all rows based on a particular column, or a subset of rows, using an expression.
You can create multiple filters as needed. For example, if you want to filter all SYS users who are being audited for the SUPER USER LOGON event, you would create one filter to catch all SYS users, and then a second filter to catch all SUPER USER LOGON events. If two or more of the filters for a report are enabled, then the report uses both or all of them (as in an AND operation). You can toggle specific filters on or off, depending on the results that you want.
6.4.2.4 Formatting Data in a Report
Topics
6.4.2.4.4 Adding Control Breaks to a Report
You can create a break group based on selected columns. This pulls the column(s) out of the report as a main record and groups all rows with the same value for the selected column under that main record. This is useful for filtering by multiple column values.
For example, you may have an Activity Overview report that displays several columns of data. If you want to see that data broken up by the Client IP Address and Secured Target Name columns, you would add control breaks for those columns. The resulting report would have data broken up into smaller tables for each unique combination of Client IP Address and Secured Target Name.
To add a control break in a column:
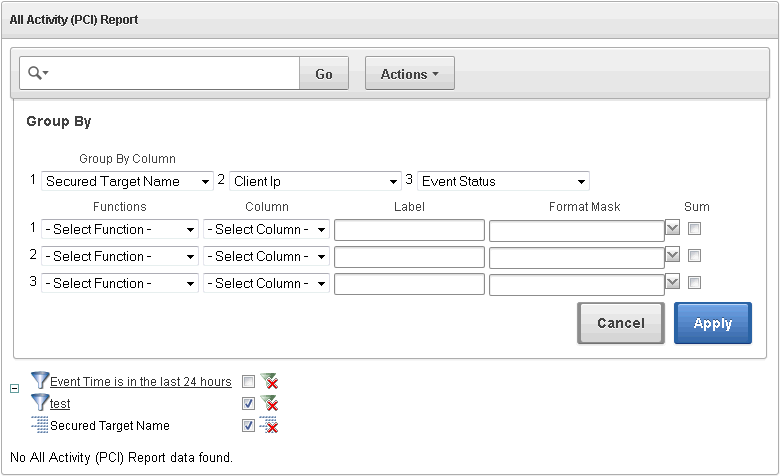
6.4.2.4.5 Using the Group By Function to Format a Report
The Group By dialog lets you group data by up to three columns in a report, and specify up to three functions to perform on any column, and display the resulting values as additional columns in the custom report.
For example, suppose you want to create a custom report to show the number of events of a certain status (for example SUCCESS or FAILURE) for each secured target and client IP address combination. Using Group By, you can create a custom report to group unique secured targets together in the first column, client IP addresses for each secured target together in the second column, and display Event Status in the third column. You then specify a function to count distinct values in the Event Status column for each secured target and client IP address combination.
The resulting custom report will contain four columns: Secured Target, Client IP, Event Status, and the final column will show the results of the function, for example, the number of events with SUCCESS status for that secured target and IP address.
To use the Group By feature:
-
Log in to the Audit Vault Server as an auditor.
-
Click the Reports tab, and then access the report that you want.
-
From the Actions menu, select Format, then Group By.
The Group By dialog is displayed, similar to the following:
-
In the Group By Column section, from the first drop-down list, select a data column for grouping data in column 1 of your custom report.
For example, if you select Secured Target Name, column 1 of your report will have secured targets grouped together. Optionally, select data groupings for columns 2 and 3 of your report.
-
Optionally, in the Functions section, specify up to three functions to operate on specific data columns:
-
Under Functions, select a function, such as Count Distinct.
-
Under Column, select any data column in the default report.
-
Optionally, under Label, enter a column heading for the new column created by the result of this function.
-
Optionally, under Format Mask, select the format of the data in the new column created by the result of this function.
-
Optionally, select the Sum check box if you want to add a Sum row to the bottom of your custom report to add the values in the new column.
-
-
Click Apply.
6.4.3 Saving your Customized Reports
When you customize a built-in report with your specified filters and display settings, you can save this customized report. Saved reports are listed in the Saved Interactive Reports page in the Reports tab. The saved reports cannot be printed in PDF format, and therefore must be viewed online.
When you save a custom report, you can save it under a specific category that you select or create as you save the report. You can also make the custom report private or share it with other users as a public report.
To create and save a custom report starting from a built-in report:
6.5 Scheduling and Generating PDF or XLS Reports
Topics
6.5.1 About Scheduling and Creating PDF or XLS Reports
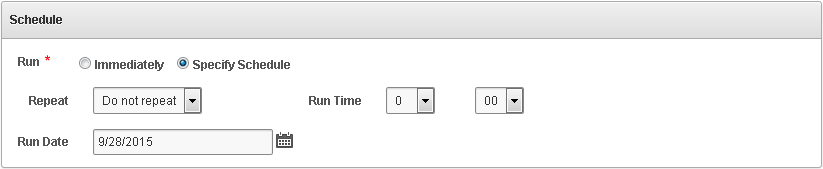
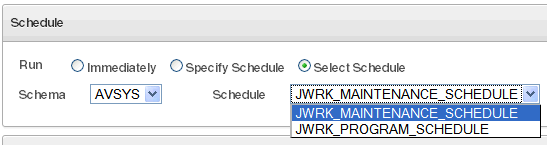
You can schedule reports to be sent to other users in PDF or XLS format. You can run the report immediately, or you can create or select a schedule to run the report at a later time. You can specify a list of users who receive notifications of the report, or who need to attest to the report.
Note:
The saved interactive reports (saved reports you created by customizing built-in reports) cannot be scheduled.
See Also:
The timestamp shown in scheduled reports is based on the Timezone Offset setting specified by the administrator in the Audit Vault Server. See Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall Administrator's Guide for more information.
6.5.3 Viewing or Modifying Report Schedules
To view or modify report schedules, in the Report Workflow menu, click Report Schedules. To modify a report schedule, click the name of the report.
See Also:
Creating a Report Schedule for details on report schedule fields.
6.5.4 Downloading Generated Reports in PDF or XLS Format
When scheduled reports are generated you can download them to your computer in PDF or XLS format (depending on the format you selected in your report schedule). You can also notify other users by sending a link to the report, or attaching the report in an email.
You can download an unscheduled report in HTML or CSV format, while browsing it online.
To list and download generated PDF or XLS reports you have scheduled:
6.6 Annotating and Attesting Reports
After a report has been generated, auditors can annotate and attest to the report. This enables you to create a record of all notes and attestations for the report in one place, with the most recent note and attestation listed first. If you delete the report, its associated annotation and attestations are removed as well.
To annotate and attest to a report:
6.7 Creating and Uploading Your Own Custom Reports
You can add your own custom reports by using Oracle BI Publisher, or another report authoring tool from a third party. You will need a report definition file (XML format) and a report template (RTF format), which you can download from Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall. This section describes how to download these files from an existing Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall report and use them for your own report.
The audit event appendices in this guide contain data that may help you in creating your own reports.
To add a report starting from an existing report definition and template file:
-
Log in to the Audit Vault Server console as an auditor.
-
Click the Reports tab, and under Custom Reports, click PDF/XLS Reports.
The PDF/XLS Reports page is displayed, listing any previously uploaded custom reports, and built-in reports in the Built-in Reports section.
-
Find a built-in report to use as a starting point for your new custom report.
-
Download the report definition and template files for the report you want:
-
Click the Download Report Template icon and save the RTF file.
-
Click the Download Report Definition icon and save the XML file.
-
-
Customize the report definition and template files using either Oracle BI Publisher or another tool, as necessary.
-
Click Upload.
-
In the Report Template file field, enter the name or browse for your customized report template (RTF) file.
-
In the Report Definition file field, enter the name or browse for your customized report definition (XML) file.
-
Click Save.
The new report is listed under PDF/XLS Reports.
6.8 Activity Reports
Topics
6.8.1 About the Activity Reports
You can access Activity Reports from the Reports tab by clicking Activity Reports. There are six groups of Activity Reports:
-
Activity Reports
-
Alert Reports
-
Correlation Reports
-
Database Firewall Reports
-
Entitlement Reports
-
Stored Procedure Audit Reports
This section contains information about Activity, Alert, and Stored Procedure Reports.
See Also:
6.8.2 Activity Reports
Topics
6.8.2.1 About the Activity Reports
You can access Activity Reports from the Reports tab by clicking Activity Reports.
The default activity reports track general database access activities such as audited SQL statements, application access activities, and user login activities. These reports display the following kinds of information: secured target name, secured target type, host name for the secured target, version of the secured target, IP address of the secured target, audit time, the event itself (such as LOGIN statements), current and previous values of the event, user and host client information, the event status (such as failure), and the time the event took place.
6.8.2.2 Activity Overview Report
The Activity Overview page provides a summary of all audited and monitored events.
This includes information about all monitored and audited events. Events appear based on their audit event time in descending order (newest record first). This report can be very large, but you can create a user-defined version that filters specific audit data. By default, 15 audit records are displayed on each page.
If you suspect that the Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall data warehouse is not being refreshed with the latest audit data, then check the Activity Overview Report. If you find that the audit data that you want is not listed in this report, then ask your Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall administrator to check the server-side log files (alert and trace logs) for errors. If there are errors, then contact Oracle Support.
Note:
Apply filters based on date and time. Access the audit interactive reports. For example, Activity Overview report. Click on Actions, and then select Filter. Choose Row as the Filter Type.
Enter a name for the filter you are creating. In the Filter Expression field, enter the query as follows:
<event_time> BETWEEN ‘MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS PM/AM’ and ‘MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS PM/AM’
For example:
BZ BETWEEN ‘8/20/2018 2:30:50 PM’ and ‘8/20/2018 2:40:50 PM’
6.8.2.3 All Activity Report
The All Activity Report displays details of all captured audit events for a specified period of time.
6.8.2.4 Audit Settings Changes Report
The Audit Settings Changes Report displays details of observed user activity targeting audit settings for a specified period of time.
6.8.2.5 Data Access Report
The Data Access Report displays details of read access events.
See Also:
Related Event Data Appendices for related data access audit events in a specific secured target type.
6.8.2.6 Data Modification Report
The Data Modification Report displays events that lead to data modification.
6.8.2.7 Data Modification Before-After Values Report
The Data Modification Before-After Values Report displays data modification events with before and after values in an Oracle database.
Data for this report comes from the TRANSACTION LOG audit trails written by databases. Be sure that an Oracle AVDF administrator has configured and started a TRANSACTION LOG audit trail for the secured target you want to monitor. This report then pulls data from database transaction (REDO) logs.
The user can filter the Data Modification Before-After Values report. To apply the filter on a Column Name, Before Value, and After Value, select Like as the Operator.
Note:
-
The Transaction Log collector uses Streams to collect the Audit Trail. When Transaction Log trail is added, it creates the capture process on the secured target. When the capture process begins, it creates a Logminer dictionary in an archive log. From then onwards, only the Before and After records from the archive logs is captured. It is not possible to acquire the Before and After values prior to the creation of Logminer dictionary. So Transaction Log trail cannot capture the old data. This is a limitation.
-
While setting up REDO collector, no role should be granted to the source user other than DV_STREAMS_ADMIN. To set up
DVSYS.AUDIT_TRAIL$table trail, first set up the REDO collector with DV_STREAMS_ADMIN role granted to the source user. Once REDO collector is up and running, grant DV_SECANALYST role to the source user. -
The
Equal To(=) operator does not work while applying filter on Column Name, Before Value, and After Value columns. -
To check the change in column value of a particular table, add filter on Target Object. The filter can be something like, Target Object Equal to (=) table name and
Column Namein the Column field. For example, if the Address column of employee table is changed, the filter should be Target Object = EMPLOYEE and Column Name like %ADDRESS%.
6.8.2.8 Database Schema Changes Report
The Database Schema Changes Report displays information about changes in the database schema.
6.8.2.9 Entitlements Changes Report
The Entitlements Changes Report displays information about changes in grants of database privileges and roles.
6.8.2.10 Failed Logins Report
The Failed Logins Report displays information about failed authentication attempts.
6.8.2.11 User Login and Logout Report
The Login and Logout Report displays information about all successful login and logout events.
6.8.3 Alert Reports
Alert reports are accessed from the Reports tab, by clicking Activity Reports.
The alert reports track critical and warning alerts. An alert is raised when data in audit records matches a predefined alert rule condition. Alerts are grouped by associated secured target, by event category, and by the severity level of the alert (either warning or critical).
There are three alert reports:
-
All Alerts Report - This report shows all alerts, both critical and warning alerts, that were raised by raised by Audit Vault Server.
-
Critical Alerts Report - This report shows critical alerts that were raised by raised by Audit Vault Server.
-
Warning Alerts Report - This report shows warning alerts that were raised by raised by Audit Vault Server.
See Also:
-
Creating Alerts and Writing Alert Conditions for information about creating and configuring alerts.
-
Responding to an Alert for information about responding to an alert.
6.8.4 Correlation Reports
The Linux SU SUDO Transition Report provides details of database events that are correlated with the Linux operating system user before su or sudo transition. It is specific to Oracle Database secured targets running on Linux. This report uses the OS and Database audit trails to correlate su and sudo activity on the Linux OS with Oracle Database audit events. This lets auditors see the original OS user in cases where this user runs a shell or executes a command as another user by using su or sudo.
For example, suppose the Linux OS user, user_01, logs in to a Linux terminal, and then performs su or sudo activity to another Linux user, user_02. Then user_01 connects as the Oracle Database user user_db locally and then remotely, and performs some database activities.The Linux SU SUDO Transition report displays the Oracle Database audit events with the additional columns OS User Transition, Transition Type, and Database Connection Type. These columns provide information about the correlation that occurred before the Oracle Database operations. For example:
| Column Name | Data |
|---|---|
|
OS User Transition |
user_01 > user_02 |
|
Transition Type |
su (for a sudo operation, it would list sudo) |
|
Database Connection Type |
Local (for a remote database connection, it would be remote) |
|
Database User Name |
user_db |
Similarly, the Linux SU SUDO Transition Report displays data for local and remote database connections and for SYS and non-SYS users.
In order to generate information for this report, you must have audit trails configured and running for both the Oracle Database and for the Linux OS on which the database runs. The Linux OS audit trail must be registered with a host name, and not an IP address. See Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall Administrator's Guide for instructions on how to configure audit trails in Oracle AVDF.
Be aware that if there is a slippage in Linux events, then the report does not show the correct correlation data.
Table 6-1 shows the currently available correlation reports.
Table 6-1 su/sudo Correlation Reports
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Linux SU SUDO Transition |
Details of database events correlated with the Linux operating system user before |
6.8.5 Database Firewall Reports
Database Firewall Reports contain data that is collected if a secured target is monitored by the Database Firewall (using a firewall policy).
Data collected by the Database Firewall includes:
-
Database Firewall action and threat level
-
Database user name
-
OS user name
-
Statement type (data definition, procedural, data manipulation, etc.)
-
Client application name and IP address
-
SQL request ID
-
Database Firewall cluster ID
Table 6-2 lists the Database Firewall reports.
Table 6-2 Database Firewall Policy Reports
| Report Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Database Traffic Analysis by Client IP |
Database Firewall events grouped by client IP and database |
|
Database Traffic Analysis by OS User |
Database Firewall events grouped by operating system user and database |
|
Database Traffic Analysis by User Blocked Statements |
SQL statements blocked by the Database Firewall |
|
Database Traffic Analysis by User Warned Statements |
SQL statements marked as WARN by the Database Firewall |
|
Database Traffic Analysis by User Invalid Statements |
SQL statements marked as INVALID by the Database Firewall |
6.8.7 Stored Procedure Auditing Reports
You can access Stored Procedure Auditing reports from the Reports tab by clicking Activity Reports.
Stored procedure auditing reports allow you to audit changes to stored procedures on secured target databases. Oracle AVDF connects to the secured target database at scheduled intervals and discovers any changes or additions that have been made to stored procedures.
Table 6-3 lists the Stored Procedure Auditing reports.
Table 6-3 Stored Procedure Auditing Reports
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Stored Procedure Activity Overview |
Summary of stored procedure activity |
|
Created Stored Procedures |
Creation history of stored procedures |
|
Deleted Stored Procedures |
Deletion history of stored procedures |
|
New Stored Procedures |
Recently created stored procedures |
|
Stored Procedure Modification History |
Modifications of stored procedures |
6.9 Summary Reports
6.9.1 Trend Charts
The Trend Charts report shows the event trends (total events) in the last n days.
Table 6-4 shows the available event trend reports.
Table 6-4 Trend Charts
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Event Trend |
Trend of all events |
|
Event Trend By Secured Target |
Trend of events by secured target |
|
Event Trend By Client IP |
Trend of events by client IP |
|
Event Trend By OS User |
Trend of events by OS user |
6.9.2 Anomaly Reports
The Anomaly Reports report shows new and dormant user and client IP anomalies (total anomalies) in the last n days.
Table 6-5 shows the available anomaly reports.
Table 6-5 Anomaly Reports
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
New or Dormant User Activity |
Activity by newly created or dormant users |
|
New or Dormant Client IP Activity |
Activity from newly seen or dormant client IPs |
6.9.3 Summary Reports
The Summary Reports report shows summaries of client and operating system user activities, DDL and DML activities, and failed logins in the last n days.
Table 6-6 shows the available summary reports.
Table 6-6 Summary Reports
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Activity Summary by Client IP and OS User |
Events grouped by user and client IP |
|
Activity Summary by Secured Target |
Events grouped by secured target |
|
DDL Activity Summary by Secured Target |
Schema changes grouped by secured target |
|
DML Activity Summary by Secured Target |
Data modifications grouped by secured target |
|
Failed Logins Summary by Secured Target |
Failed authentication attempts grouped by secured target |
6.10 Compliance Reports
6.10.1 About the Compliance Reports
The compliance reports provide out-of-the-box reports to help you meet regulations associated with credit card, financial, data protection, and health care related data. They track activities that are typically required to meet standard compliance regulations, such as changes to the database structure or its objects, failed logins, administrator activities, system events, and user logins or logoffs.
The following compliance report categories are available:
-
Data Privacy Reports
-
Payment Card Industry (PCI) Reports
-
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) Reports
-
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Reports
-
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) Reports
-
Data Protection Act (DPA) Reports
-
Reports based on IRS Publication 1075
To access the compliance reports, click the Reports tab, then from the Built-in Reports menu, select Compliance Reports.
6.10.2 Associating Secured Targets with Compliance Report Categories
In order to generate compliance reports for a secured target, you must add it to a compliance report category.
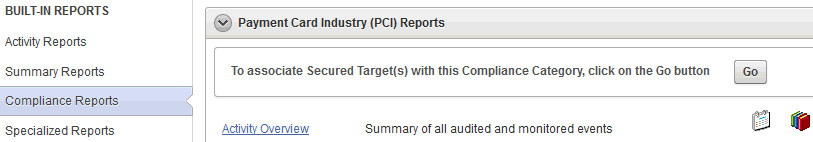
To associate secured targets with compliance report categories from the Compliance Reports page, click the Go button for a compliance category, as shown in Figure 6-2.
Figure 6-2 Associating Secured Targets With Compliance Report Categories
This takes you to the Groups page under the Secured Targets tab, and allows you to add a secured target as a member of a compliance group in Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall.
See Also:
Managing Compliance for Secured Target Databases for detailed instructions on assigning secured targets to compliance groups.
6.10.3 Reports Based on IRS Publication 1075
Table 6-7 lists reports that help you meet the reporting requirements of IRS Publication 1075.
Table 6-7 Reports Based on IRS Publication 1075
| Report Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Password Change |
Password change events in operating systems |
|
User Switch |
Switch user events for Windows and Linux operating systems |
|
Permissions and Privileges Change |
Privilege changes in operating systems |
|
Startup and Shutdown of Audit Functions |
Start and stop of auditing functionality in the database |
6.11 Specialized Reports
6.11.2 Oracle Database Reports - Database Vault Activity
Oracle Database Vault may be enabled in an Oracle Database secured target to provide greater security by restricting access to sensitive areas of the database. For example, you can restrict administrative access to employee salaries, customer medical records, or other sensitive information.
If your Oracle Database secured targets have Database Vault enabled, then the Database Vault Activity report shows the details of Oracle Database Vault activity, such as Database Vault events that capture policy or rule violations, unauthorized access attempts, and so on.
You can check if Oracle Database Vault is enabled in a target by running the following SQL query in SQL*Plus:
SELECT PARAMETER, VALUE FROM V$OPTION WHERE PARAMETER = 'Oracle Database Vault';
Remember that the PARAMETER column value is case sensitive.
If Oracle Database Vault is enabled, the following output appears:
PARAMETER VALUE ----------------------------- ----------------------- Oracle Database Vault TRUE
6.12 Data Privacy Reports
Topics
Overview
Data privacy is also known as information privacy or data protection. It is concerned with the relationship between collection and dissemination of data and technology, the public perception, expectation of privacy, the legal regulation, and political issues surrounding that data. The details and implementation of data protection vary depending on the region, the context, the methods, and the extent to which it is regulated.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a regulation in European Union (EU) law on data protection and privacy for all individuals within the European Union. It addresses the export of personal data outside the EU. GDPR is an overhaul of the existing European Commission data protection legislation. It harmonizes data privacy laws, aims to strengthen, and unify these laws for EU citizens. GDPR is about individuals having autonomy and control over their data. It primarily aims to give control back to citizens and residents over their personal data and to simplify the regulatory environment for international business by unifying the regulation within the EU. It is important for organizations to protect information they possess about individuals to prevent others from accessing or misusing their personal information.
GDPR is applicable in case the following are based in the European Union:
-
Data controller
-
Data processor
-
Data subject or the person
-
Data recipient
-
Authority supervising and auditing data
-
An organization that collects data from EU residents
-
An organization that processes data on behalf of data controller like the service providers
-
An organization based outside the EU that collects or processes personal data of individuals located inside the EU
According to the European Commission, personal data is any information relating to an individual. This information can be private, professional, or public life of the individual. It includes, but is not limited to, a name, a home address, a photo, an email address, bank details, posts on social networking websites, medical information, or an IP address.
In order to comply with GDPR, the data controller must implement measures, which meet the principles of data protection by design, and data protection by default. It is the responsibility and the liability of the data controller to implement effective measures and to demonstrate the compliance of processing activities. This includes if the processing is performed by an external data processor on behalf of the controller.
GDPR considers encryption as one of the components in the security strategy, and mandates that organizations need to consider assessment, preventive, and detective controls based upon the sensitivity of the personal data in their possession.
Articles 30 and 33 of GDPR, mandate that organizations must maintain a record of its processing activities. This can only be achieved by constantly monitoring and auditing activities on personal data. This data can be used to timely notify authorities in case of a breach. In addition to mandating auditing and timely alerts, GDPR also requires that organizations must keep the audit records under their control. A centralized control of audit records prevents attackers or malicious users to cover the tracks of their suspicious activity by deleting the local audit records. There are four reports under Data Protection. They primarily focus on access to sensitive data by regular or privileged users and also privilege settings on objects.
6.12.1 Implementation In Oracle Audit Vault And Database Firewall
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall complies with data protection directives and regulations by offering services like centralized auditing, monitoring, reporting, and alerting of anomalous activity on the database. It reports any access to sensitive data stored in the database.
The report relates to sensitive data, as identified and received from the sensitive data discovery processes. It contains information regarding activity on sensitive data by all users including privileged users.
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall complies with data protection at source by centralizing control and administration. It stores and manages the data for processing in a centralized location. It monitors and sends timely alerts of suspicious behavior. It can centrally manage millions of audit records, or different types of security policies, by simplifying the administration related tasks. This is managed using Oracle Enterprise Manager that has a unified web based GUI.
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall centrally collects and manages audit records. It monitors, alerts, reports, and blocks suspicious behavior.
Note:
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall helps in complying with data privacy regulations such as GDPR.
6.12.2 Importing Sensitive Data Into Repository
Information about sensitive data is imported and stored in the AVDF repository. You can import a data file in .csv and .xml format. These data files are sourced from Oracle Enterprise Manager and Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool by running data discovery job to search for sensitive data in specific Oracle Database secured targets.
Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool generates the file in .csv format and Oracle Enterprise Manager generates the file in .xml format. The data file extracted contains a list of sensitive columns that is imported into the AVDF repository. It is viewed in the Audit Vault Server GUI using Data Privacy Reports.
Note:
Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall supports 13.1; 13.2; and 13.3 versions of Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
See Also:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager Lifecycle Management Administrator's Guide to run data discovery job and search for sensitive data for specific targets using Oracle Enterprise Manager.
-
Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool User Guide to run a discovery job using Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool.
-
Oracle Data Masking and Subsetting Guide for more information on Application Data Modeling that stores the list of applications, tables, and relationships between table columns and maintains sensitive data types.
6.12.3 Accessing Data Privacy Reports
The sensitive data file is imported into the AVDF repository. Once the sensitive data definitions are imported into the repository, the Audit Vault Server GUI is used to view related Data Privacy Reports. This section contains information on how to access the reports that contain sensitive data.
Prerequisite
Ensure the appropriate entitlement data is available for the secured target. See Retrieving User Entitlement Data for Oracle Database Secured Targets for complete information.