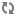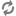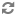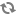Each of these examples shows the HTTP request and the response from the Call Setup API in each of the scenarios.
Example 1: End a call that is in progress
HTTP Request | DELETE /call/2.0/1TfU02Xfme2GMuzfUh0rkdgvz4 |
The response should be:
Response Status | 200 OK |
|---|---|
Response Body | {“callState”:”ended”} |
Example 2: End a call that is already ending or has already ended
HTTP Request | DELETE /call/2.0/1TfU02Xfme2GMuzfUh0rkdgvz4 |
The response should be:
Response Status | 403 Forbidden |
|---|---|
Response Body | The call has already ended. |
Example 3: End a call that does not exist
HTTP Request | DELETE /call/2.0/1TfU02Xfme2GMuzfUh0rkdgvz4 |
The response should be:
Response Status | 404 Not Found |
|---|---|
Response Body | Attempt to end the call failed. |
Example 4: Request with an invalid URI path
In this example, the Get Call Status request is missing part of the URI.
HTTP Request | DELETE /call/2.0/1TfU02Xfme2GMuzfUh0rkdgvz4 |
The response should be:
Response Status | 404 Bad Request |
Example 5: Invalid HTTP method
This table is described in surrounding text.
In this example, the wrong HTTP method is used in the Get Call Status request.
HTTP Request | PUT /call/2.0/1TfU02Xfme2GMuzfUh0rkdgvz4/status |
The response should be:
Response Status | 405 Method Not Allowed |