Table of Contents
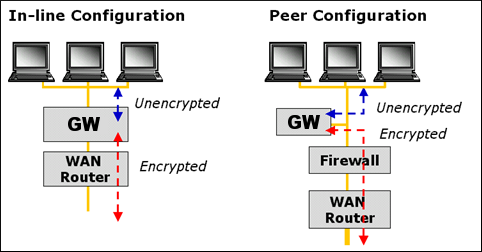
There are two basic network configurations for a Corente Cloud Services Exchange Gateway: on a single-Ethernet connection to a LAN (peer configuration), and on a dual-Ethernet connection between a LAN and a WAN (in-line configuration). See Figure 3.1, “Gateway Network Configurations”.
The two basic configurations support a range of customer LAN environments and security methods, some of which are described in this chapter.
A Corente Services Gateway in the peer configuration is a secure device with a single Ethernet card that sits on the same network as the machines that will be participating in the VPN.
A Corente Services Gateway in the in-line configuration is a secure device with two Ethernet cards: one Ethernet card is connected to the internal trusted network, while the other card is connected to the external untrusted network.
Both configurations can provide services such as a VPN Gateway, router, backhaul client/server, DHCP client/server, stateful inspection firewall, DNS, and Internet connection sharing (ICS) device.
When deploying a VPN, each location must select the best position in the network to meet security needs. A Corente Services Gateway can be deployed at demarcation point between WAN and LAN, or behind the network firewall on the trusted LAN. The following sections describe the benefits and risks of each of these designs.