| User Data Repository Diameter User's Guide Release 12.4 E92984-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
MME/SGSN Topology Hiding is concerned with hiding the identity of a Protected Home Network's MME/SGSNs and the number of MME/SGSNs in the network, when it exchanges messages with Untrusted Networks. A MME/SGSN's identity is embedded in the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs sent in Request messages and in the Origin-Host AVP sent in Answer messages. MME/SGSN Topology Hiding is associated with the Diameter S6a/S6d application message set defined in 3GPP TS 29.272, Mobility Management Entity (MME) and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) related interfaces based on Diameter protocol.
MME/SGSN Topology Hiding determines which entity (HSS or MME/SGSN) initiated an S6a/S6d message based on the Command Code in the message.
MME/SGSN identities are hidden by replacing the Actual Hostname portion of the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs (Session-ID format: <host name><implementation portion>) with an MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostname. The Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs can have different MME/SGSN Hostnames. A unique Pseudo Hostname must be created for each MME/SGSN in a Protected Network. When the MME/SGSN initiates a transaction to the HSS, the HSS saves the MME/SGSN's identity for use in subsequent HSS-to-MME/SGSN transactions. This MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostname must not only be unique, but the DEA must be able to convert the MME/SGSN's Pseudo Hostname to an Actual MME/SGSN Hostname for these subsequent HSS-to-MME/SGSN transactions.
To hide the number of MME/SGSNs in a network, each MME/SGSN is assigned either a random or fixed number of Pseudo Hostnames. A maximum number is defined by the Count in the Pseudo Hostname Generation attribute of the MME/SGSN Topology Hiding Configuration Set. The Randomize Count creates a random number of Pseudo Hostnames, between 1 and the Count value, that are associated with an Actual Hostname. This procedure of creating randomized MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostnames and assigning them to an Actual Pseudo Hostname is performed by the GUI, then used by the Diameter Routing Function. The created MME/SGSN TH Hostnames allow the Diameter Routing Function to map a Protected-MME/SGSN Actual Hostname to a set of MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostnames, and to map a MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostname received from an Untrusted-HSS to a Protected-MME/SGSN Actual Hostname.
Table 10-16 shows an example of MME/SGSN TH Host Names configuration for a Protected Network with a maximum of 3 randomly created Pseudo Hostnames.
Table 10-16 Example of Configuration of MME/SGSN TH Hostnames for a Protected Network
| MME/SGSN TH Configuration Set Name | MME/SGSN Actual Hostname | MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostnames |
|---|---|---|
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.westregion.example.com | mme042.example.com mme821.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.westregion.example.com | mme123.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme2.westregion.example.com | mme533.example.com mme773.example.com mme092.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.eastregion.example.com | mme922.example.com mme729.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme2.eastregion.example.com | mme411.example.com mme002.example.com mme655.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme2.eastregion.example.com | mme218.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme2.eastregion.example.com | mme331.example.com mme249.example.com mme447.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.texasregion.example.com | mme776.example.com mme077.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.texasregion.example.com | mme295.example.com mme622.example.com mme861.example.com |
| Protected Network-1 MME/SGSN Config | mme1.texasregion.example.com | mme333.example.com |
Protected-MME/SGSN to Untrusted-HSS Transactions
Note:
Although the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs both have MME/SGSN Actual Hostnames, the names could be different. Because the HSS associates the MME/SGSN's location based on the Origin-Host AVP content, it is the MME/SGSN Actual Hostname in the Origin-Host AVP that must be used for selecting a MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostname. This MME/SGSN Pseudo Hostname can be used to replace both of the Hostname fields in the forwarded Request message.This Hostname restoral procedure is not required for Answers initiated by diameter internal nodes (the Diameter Routing Function and applications) as these Answer responses are based upon the original Request message content.
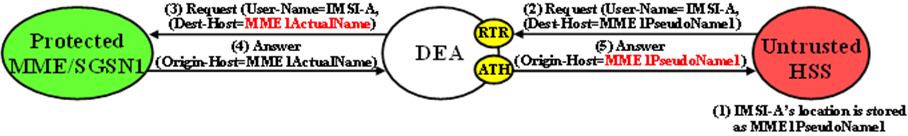
An example of a Protected-MME/SGSN to Untrusted-HSS Diameter transaction is shown in Figure 10-15.
Figure 10-15 MME/SGSN TH Protected-MME/SGSN to Untrusted HSS Transaction
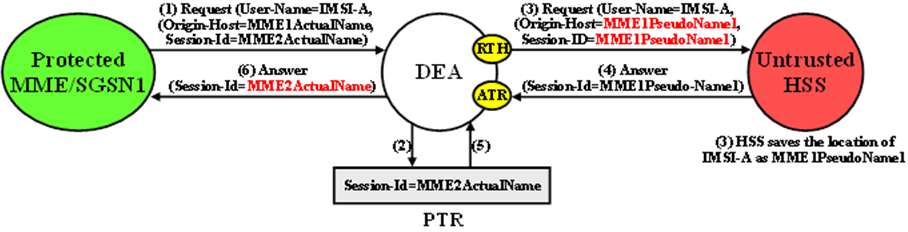
It is not necessary to extract the IMSI portion from the User-Name AVP value. The User-Name AVP value content is the same in all transactions associated with subscriber.
Untrusted-HSS to Protected-MME/SGSN Transactions
Note:
For local nodes, CEAs are sent in response to erroneous CERs.An example of an Untrusted-HSS to Protected-MME/SGSN Diameter transaction is shown in Figure 10-16.
Figure 10-16 MME/SGSN TH Untrusted-HSS to Protected MME/SGSN Transaction