|
Configuring Siebel Business Applications > Configuring a Siebel Application > Using Development Tools and Setting Up the Development Environment >
Creating Scripts to Configure Siebel CRM
This topic describes how you can use Siebel Visual Basic, Siebel eScript, and browser script to write scripts that configure Siebel CRM. It includes the following information:
A script is associated with an object and event in the Siebel Event Model. Scripts That You Write for the Server
Siebel Tools includes the following scripting languages:
- Siebel Visual Basic. Similar to Microsoft Visual Basic. It supports scripting only on the Windows operating system.
- Siebel eScript. Compatible with JavaScript. It supports scripting in Windows and other operating systems, such as UNIX.
You can use Siebel Visual Basic and Siebel eScript to do the following work:
- Integrate Siebel CRM with a third-party application.
- Configure the base functionality of the screens and business components in Siebel CRM.
- Develop a data validation routine to enforce rules before or after Siebel CRM manipulates records. Siebel CRM does validation routines before the user updates or inserts a record. This configuration makes sure that the user does not enter data into the database that is not logical or is not complete.
- Develop a data manipulation or computational routine to modify or analyze data.
- Develop a data transport routine to import and export small volumes of data between Siebel CRM and a third-party application.
- Develop a routine that opens an external application on the Siebel Server in reply to a Siebel event or to send start-up parameters. This capability is valid for browser script only.
You use the Script Editor, Debugger, and Compiler to develop and test Siebel Visual Basic script, Siebel eScript script, or browser script. Siebel CRM integrates this capability with the Applet Layout Editor. You can attach a script to a control that Siebel CRM displays in the Siebel client, such as a field. You can associate a server script with the following object types:
- Web Applet
- Business Component
- Business Service
- Application
For more information about:
- Scripting, see Siebel eScript Language Reference and Siebel VB Language Reference.
- Redeploying a script written for a prior release of Siebel CRM in the Siebel client, see Siebel Database Upgrade Guide.
Simultaneous Use of Siebel Visual Basic Script and Siebel eScript
To respond to various client events, you can use Siebel Visual Basic and Siebel eScript simultaneously in the same environment but not in the same object. It is recommended that you use Siebel eScript only because it works on UNIX and Windows servers. When you initially add a script to an object, Siebel Tools prompts you to choose the scripting type. Scripts That You Write for the Browser
Browser script allows you to use JavaScript, which is an interpreted language that runs in many Web browsers. A browser script responds to an event on a browser Java object. This browser object works with the corresponding object that runs in the object manager. The set of events that you can script with a Browser object type is different from the set of events that you can script with a server script:
- For Siebel CRM, you can script a wide variety of events that the browser supports. An HTML control does not support the OnClick event. For more information, see Siebel eScript Language Reference.
- For a Siebel employee application, you can only script on the OnBlur or OnFocus events.
You use Siebel Tools to write a browser script. You can associate a browser script with the following object types:
- Applet
- Business Component
- Business Service
- Application
NOTE: A browser script on a business component is appropriate only if Siebel CRM displays the Siebel object that the script references in the Siebel client.
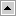
Hierarchy of Object Types That Siebel CRM Uses With a Script
Figure 40 describes the hierarchy of relationships between object types that Siebel CRM can use with a script. To script a browser event, you use a child object type of the parent. You can use these object types with their server counterparts in Siebel Visual Basic, JavaScript, or Java.
Figure 40. Hierarchy of Relationships Between Object Types That Siebel CRM Uses with a Script
|
Figure 41 includes an example of how you can use a browser script to validate the field in a form that Siebel CRM displays in the Siebel client. This example uses browser script on the BusComp_PreSetFieldValue event handler in the Account business component.
Figure 41. Example of Browser Script to Validate a Field
|
Creating and Deploying a Browser Script
You can create and deploy a JavaScript file (.js). To create and deploy a browser script
- Use one of the following configurations to create the browser script:
- In Siebel Tools, create or open a workspace.
- Create required browser scripts and then deliver the workspace that will publish the changes to runtime repository.
If you compile objects to a runtime repository, then Siebel Tools only creates browser scripts for compiled objects. Siebel Tools places them in the directory that you define in the Scripting tab of the Development Tools Options dialog box. To view this dialog box, choose the View menu, and then the Options menu item.
If you do not create a directory, then Siebel Tools stores the browser script in the following directory:
SIEBEL_TOOLS_ROOT\public\language_code\srf_timestamp\bscripts\all
where:
genbscript config_file destination_directory language_code
where:
- config_file is the name of the configuration file.
- destination_directory is the destination directory where genbscript stores the script files.
- language_code is the language code, such as ENU. The language code parameter is optional for ENU, but you must define it for other languages.
For example:
genbscript c:\siebel\client\bin\enu\uagent.cfg c:\siebel\client\public\enu enu
- Deploy the browser script to the following directory on the Siebel Application Interface:
SAI_ROOT\applicationcontainer\webapps\siebel\language_code
- Deploy the browser script to the following directory on the Siebel Mobile Web Client, as necessary:
SIEBEL_CLIENT_ROOT\public\language_code
- If you migrate scripts from one location to another location, then you must copy the following directories to the correct location (from
SIEBEL_TOOLS_ROOT\public\language_code, for example):
srf_timestamp\bscripts\all
If you create a browser script, then the Siebel software creates a directory path and names it according to the version of the Siebel runtime repository. The system appends it to the path that you create as the destination directory. For example, after you compile or migrate browser scripts to the Siebel Application Interface, the Siebel software uses the following path to the browser script files:
SAI_ROOT\applicationcontainer\webapps\siebel\language_code\srf_timestamp\bscript\all
- If you compile on a Siebel Server that runs in the Windows operating system, and then migrate browser scripts to a Siebel Server that runs on an Oracle Solaris or AIX operating system, then you must FTP the directories to the correct location on the Oracle Solaris or AIX computer.
|