Perform the following steps to complete the installation:
· Place Files in the Installation Directories
· Generate an Encrypted Password
· Generate the Public and Private Keys
· Generate the Key Store File for Secure Batch Service
· Configure the Extract Transfer and Load_(ETL) Process
· Configure the config.sh File
· Run the FCC Studio Installer
After downloading the .zip folder, follow these steps to extract the folder contents:
1. Extract the contents of the installer archive file in the download directory using the following command:
unzip -a <FCC_Studio_Installer_Archive_File>.zip
The FCC Studio installer file is extracted and the OFS_FCCM_STUDIO directory is obtained and is referred to as <Studio_Installation_Path>.
WARNING |
Do not rename the application installer directory name after extraction from the archive. |
2. Navigate to the download directory where the installer archive is extracted and assign execute permission to the installer directory using the following command:
chmod 0755 OFS_FCCM_STUDIO -R
To place the required jars and Kerberos files in the required locations, follow these steps:
1. To place the additional jar files, follow these steps:
a. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/batchservice/user/lib directory.
b. Place the following additional jar files:
§ hive-exec-*.jar. For example, hive-exec-1.1.0.jar.
§ HiveJDBC4.jar
§ hive-metastore-*.jar. For example, hive-metastore-1.1.0.jar.
§ hive-service-*.jar. For example, hive-service-1.1.0.jar.
NOTE |
· The version of the jars is client or user-specific. These jars can be obtained from the existing jars of the Cloudera installation. · The HiveJDBC4.jar file is not available in the Cloudera setup. You must download the same from the Cloudera website. |
2. To place the Kerberos files, follow these steps:
a. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/batchservice/user/conf directory.
b. Place the following Kerberos files:
§ krb5.conf
§ keytab file name as mentioned in the config.sh file.
To generate an encrypted password, follow these steps:
1. Set the export FIC_DB_HOME path in the <Studio_Installation_Path>/ficdb directory.
2. Run the echo $FIC_DB_HOME command.
3. Go to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/ficdb/bin directory and run the ./FCCM_Studio_Base64Encoder.sh <password to be encrypted> command.
The Public and Private keys are JSON Web Tokens (JWT) that are generated for PGX Authentication from FCC Studio.
To generate the keys, follow these steps:
NOTE |
The following steps are mandatory for the first time FCC Studio installation. |
1. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/ficdb/bin directory.
2. Run the Shell Script FCCM_Studio_JWT_Keygen.sh from the directory.
The Public and Private Keys are generated and available in the <Studio_Installation_Path>/ficdb/conf directory.
3. Copy the private.key and public.key files to the following paths:
§ <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/datastudio/server/conf directory
§ <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/batchservice/conf directory
§ <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/pgx/server/conf directory
After generating the key store file and adding the batch service to the PGX trust store, configure the user mapping for GDPR and Redaction changes in the database.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy in the European Union and the European Economic Area. You can apply the GDPR changes that is required for FCC Studio.
To apply GDPR and Redaction, you must configure the following:
· Generate the Key Store File for Secure Batch Service
· Add the Batch Service (SSL) to PGX Trust Store
Generating the Key Store file for Secure Batch Service is a process of generating the key store parameters and changing the key store parameters from HTTP to HTTPS protocol.
To configure the Key Store file for Secure Batch Service, follow these steps:
1. Run the keytool -genkey -alias batchservice -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keystore <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/batchservice/conf/<Keystore file name>.jks command in the Studio Server.
When generating the keytool ensure to provide the hostname in first name. For example:
Question: What is your first and last name?
Answer: Provide the fully qualified studio server hostname.
For example, <hostname>.<domain name>
2. Specify the keystore password. The <Keystore file name>.jks file is created in the path <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/batchservice/conf directory.
3. Specify the following parameters in the config.sh file.
§ export KYESTORE_FILE_NAME=<Keystore file name>.jks
§ export KYESTORE_PASS=password
Adding the Batch Service (SSL) to PGX Trust Store facilitates you to apply redaction on the graph batch service and connect with PGX.
To add the Batch Service to PGX Trust Store, follow these steps:
1. Copy the <Keystore file name>.jks file to the <PGX Server path>/server/conf directory.
2. Navigate to the <PGX Server path>/server/bin directory.
3. Open the start-server file in <PGX Server path>/server/bin directory and add the following lines in export JAVA_OPTS:
§ Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=<PGX Server path>/conf/<Keystore file name>.jks
§ Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=<Keystore file password>
The code snippet shows an example of the file when the code is added:
#!/bin/bash
export HADOOP_EXTRA_CLASSPATH="$APP_HOME/hdfs-libs/*:$APP_HOME/conf/hadoop_cluster"
export CLASSPATH="$APP_HOME/shared-lib/common/*:$APP_HOME/shared-lib/server/*:$APP_HOME/shared-lib/embedded/*:$APP_HOME/shared-lib/third-party/*:$APP_HOME/conf:$APP_HOME/shared-memory/server/*:$APP_HOME/shared-memory/common/*:$APP_HOME/shared-memory/third-party/*:$HADOOP_EXTRA_CLASSPATH"
export JAVA_OPTS="-Dpgx.max_off_heap_size=$PGX_SERVER_OFF_HEAP_MB -Xmx${PGX_SERVER_ON_HEAP_MB}m -Xms${PGX_SERVER_ON_HEAP_MB}m -XX:MaxNewSize=${PGX_SERVER_YOUNG_SPACE_MB}m -XX:NewSize=${PGX_SERVER_YOUNG_SPACE_MB}m -Dsun.security.krb5.debug=false -Djavax.security.auth.useSubjectCredsOnly=false -Djava.security.krb5.conf=$APP_HOME/conf/kerberos/krb5.conf -Dpgx_conf=$APP_HOME/conf/pgx.conf -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=/scratch/fccstudio/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/pgx/server /conf/keystore.jks -Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=password"
java -cp "$CLASSPATH" -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 $JAVA_OPTS oracle.pgx.server.Main $APP_HOME/shared-memory/server/pgx-webapp-*.war $APP_HOME/conf/server.conf
After generating the key store file and adding the batch service to PGX trust store, in the database you must configure the user mapping for the changes made. For more information about how to configure user mapping, see the FCC Studio Administration Guide.
Extract Transfer and Load (ETL) is the procedure of copying data from one or more sources into a destination system which represents the data differently from the source or in a different context than the source. Data movement and graph loading is performed using ETL.
NOTE |
In case you have 8.0.7.4.0 installed and the spark cluster has both batchservice-8.0.7.*.0.jar and elasticsearch-spark-20_2.11-7.* jar files installed, you must remove them from the spark class path. |
To configure the Data Movement and Graph Load, copy the applicable FCCM_Studio_SqoopJob.sh files from the <Studio_Installation_Path>/ficdb/bin directory and add in the <FIC_HOME of OFSAA_Installed_Path>/ficdb/bin directory. For information on performing Data Movement and Graph Load, see the Data Movement and Graph Loading for Big Data Environment section in the OFS Crime and Compliance Studio Administration Guide.
NOTE |
Before you run the sqoop job, ensure that the serverconfig.properties file from the <Studio_Installed_Path>/ batchservice/conf directory has the correct values. |
To configure the config.sh file for installing FCC Studio, follow these steps:
1. Login to the server as a non-root user.
2. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/bin/ directory.
3. Configure the applicable config.sh attributes shown in the following table.
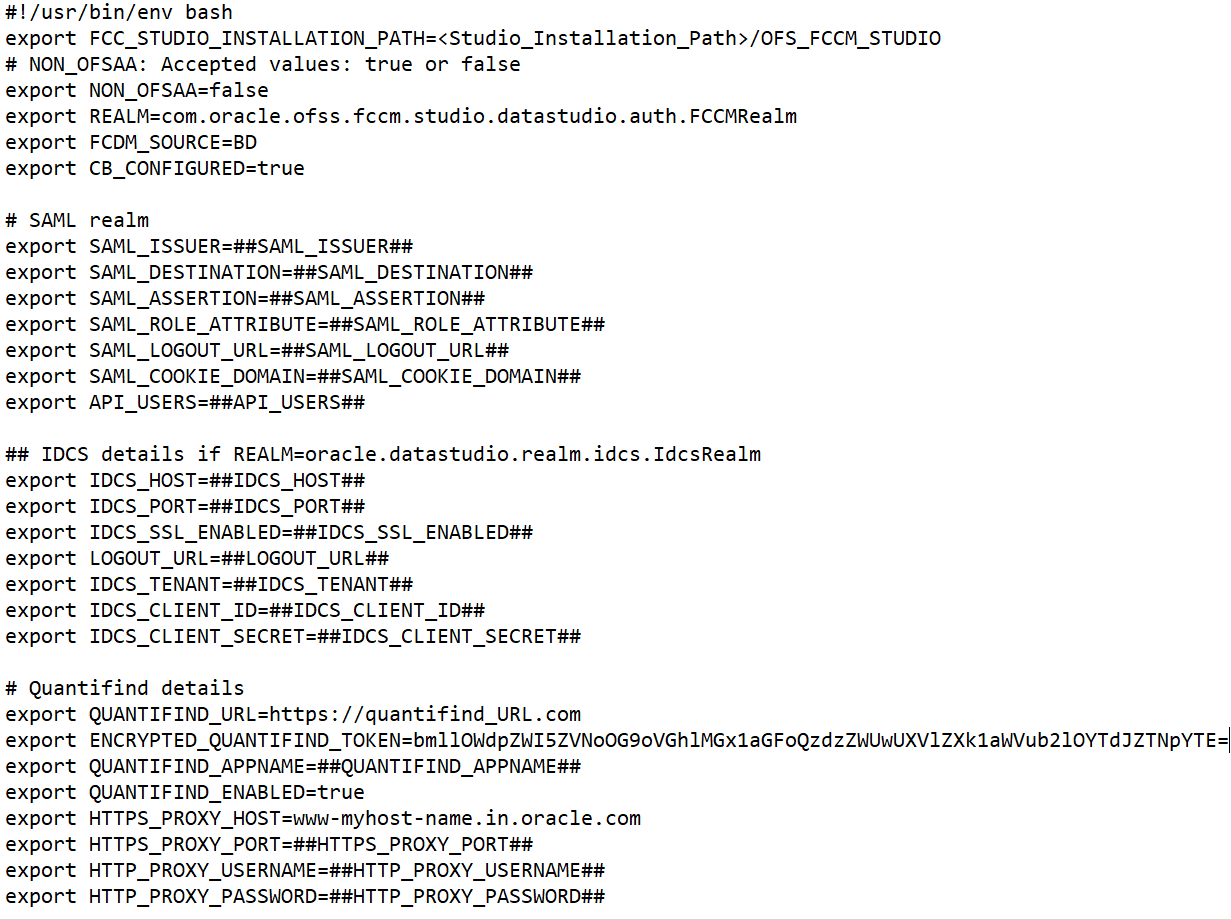
A sample config.sh file is shown:
Figure 5: Sample Config.sh File

WARNING |
· After you complete the applicable configurations, perform a backup of the config.sh file. · Do not alter the parameter values that are already set in the config.sh file |
NOTE |
· You must manually set the parameter value in the config.sh file. If a value is not applicable, enter NA and ensure that the value is not entered as NULL. · Depending on the installation architecture, ensure to provide the correct hostname for URL of PGX service in the config.sh file. · When you upgrade FCC Studio with OFSAA, ensure to provide the same BD database, Studio schema, Hive schema, wallet related information that you used during the installation of the existing instance FCC Studio. · When you upgrade FCC Studio without OFSAA, ensure to provide the same Studio schema and wallet related information that you used during the installation of the existing instance of FCC Studio. |
Table 12: config.sh file
Parameter |
Significance |
Installing with OFSAA (Mandatory) |
Upgrading with OFSAA (Mandatory) |
Installing without OFSAA (Mandatory) |
Upgrading without OFSAA (Mandatory) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
FCC_STUDIO_INSTALLATION_PATH |
Indicates the path where the FCC Studio installer file is extracted. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
NON_OFSAA |
· To install FCC Studio with OFSAA, enter "false" · To install FCC Studio without OFSAA, enter "true" |
Enter false |
Enter false |
Enter true |
Enter true |
REALM |
Realm indicates functional grouping of database schemas and roles that must be secured for an application. Realms protect data from access through system privileges; realms do not give additional privileges to its owner or participants. FCC Studio uses realm based authorization and authentication for its users. For more information, see the Realm Based Authorization for FCC Studio section in the OFS Crime and Compliance Studio Administration Guide. The FCC Studio application can be accessed using the following realms: · FCCMRealm Value=com.oracle.ofss.fccm.studio.datastudio.auth.FCCMRealm · IdcsRealm Value=oracle.datastudio.realm.idcs.IdcsRealm · DemoRealm Value=com.oracle.ofss.fccm.studio.datastudio.auth.DemoRealm 1 FCCSamlRealm Value=com.oracle.ofss.fccm.studio.datastudio.auth.FCCSamlRealm NOTE: The DemoRealm is used only for demo purpose and is not recommended for usage. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
FCDM_SOURCE |
Indicates the source database for FCC Studio. The available options are ECM and BD. NOTE: · FCC Studio can use either the BD or ECM schema as the source of FCDM data for the graph. · Ensure to enter the value as ECM whenever ECM integration is required with Investigation Hub. Here, ECM schema is used as the source of the FCDM data to load the case information into the graph. |
Enter BD or ECM |
Enter BD or ECM |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
CB_CONFIGURED |
Indicates the setting of the graph edges. When the corresponding edges of the graph is needed, set the value to true. |
Enter true or false | Enter true or false | Enter NA |
Enter NA |
IDCS The IDCS related parameters are applicable only if IdcsRealm is used in the Realm parameter. |
|
|
|
|
|
IDCS_HOST |
Indicates the server of the Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) instance. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IDCS_PORT |
Indicates the port number of the IDCS instance. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IDCS_SSL_ENABLED |
Indicates if SSL is enabled for the IDCS application. Default value: true |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
LOGOUT_URL |
Indicates the URL to redirect after logout from FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IDCS_TENANT |
Indicates the IDCS tenant provided by the IDCS Administrator while creating the IDCS application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IDCS_CLIENT_ID |
Indicates the IDCS client identifier provided by the IDCS Administrator while creating the IDCS application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IDCS_CLIENT_SECRET |
Indicates the IDCS client secret provided by the IDCS Administrator while creating the IDCS application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML The SAML related parameters are applicable only if SAMLRealm is used in the Realm parameter. |
1. In case of SAML Realm, the certificate from IDP (key.cert file) is required. 2. The certificate that is obtained from the IDP must be renamed to key.cert and placed in the <Studio_Installation_Path>/OFS_FCCM_STUDIO/datastudio/server/conf directory. 3. This certificate is used to identify the trust of the SAML response from the Identity Provider. 4. Specify the Role Attribute name from IDP, in which the User Roles are present in the SAML response. |
|
|
|
|
SAML_ISSUER |
Indicates the SAML entity ID (Studio URL) configured in the IDP. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML_DESTINATION |
Indicates the SAML IDP URL that is provided by the Identity Provider after creating the SAML Application. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML_ASSERTION |
Indicates the SAML consume URL (Studio/URL/saml/consume) that is configured in IDP. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML_ROLE_ATTRIBUTE |
Indicates the SAML client identifier provided by the SAML Administrator for the Role and Attributes information, while creating the SAML application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML_LOGOUT_URL |
Indicates the SAML client identifier provided by the SAML Administrator for the Logout URL information, while creating the SAML application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SAML_COOKIE_DOMAIN |
Indicates the SAML client identifier provided by the SAML Administrator for the Logout URL information, while creating the SAML application for FCC Studio. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
API_USER |
Indicates the API users. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
External Services |
|
|
|
|
|
OFSAA_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the URL of the OFSAA instance. Do not enter ’/’ at the end of the URL. NOTE: For OFSAAI, the value must be set in the following format: https://<HostName>:<PortNo>/<ContextName>/rest-api |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
PGX_SERVER_URL |
Indicates the URL of the PGX server. Example: http://<HostName>:<PortNo>/ Here, default <PortNo> is 7007. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
LIVY_HOST_URL |
Indicates the URL of the Livy application. Example: http://<HostName>:<PortNo> NOTE: This parameter is applicable only if the fcc-spark-sql, fcc-spark-scala and (or) fcc-pyspark interpreters are to be used. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Internal Services |
|
|
|
|
|
AUTH_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the AUTH service URL that gets activated after the fcc-studio.sh file runs. Example: http://<HostName>:7041/authservice |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
BATCH_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the batch service URL that gets activated after the fcc-studio.sh file runs. Example: https://<HostName>:7043/batchservice |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
META_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the metaservice URL that gets activated after the fcc-studio.sh file runs. Example: http://<HostName>:7045/metaservice |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SESSION_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the session service URL that gets activated after the fcc-studio.sh file runs. Example: http://<HostName>:7047/sessionservice |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
FCC_STUDIO_URL |
Indicates the FCC Studio URL. Example: http://<HostName>:7008 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ORE Interpreter Settings This section is applicable only if ORE interpreter is to be used. |
|
|
|
|
|
RSERVE_USERNAME |
Indicates the RServe username. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
RSERVE_PASSWORD |
Indicates the RServe password. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
HTTP_PROXY |
Indicates the proxy for the host where FCC Studio is installed. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
HTTPS_PROXY |
Indicates the proxy for the host where FCC Studio is installed. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
REPO_CRAN_URL |
Indicates the URL from where the R packages are obtained. The format for the REPO_CRAN_URL is as follows: |
No |
No |
No |
No |
USERS_LIB_PATH |
Indicates the path where the R packages are installed. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
RSERVE_CONF_PATH |
Indicates the path where the Rserve.conf file is present. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
DB Details for Studio Schema You must be logged in as SYSDBA to perform these configurations. |
|
|
|
|
|
STUDIO_DB_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the hostname of the database where Studio schema is created. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_PORT |
Indicates the port number where Studio schema is created. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_SERVICE_NAME |
Indicates the service name of the database where Studio schema is created. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_SID |
Indicates the SID of the database where Studio schema is created. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_USERNAME |
Indicates the username of the Studio Schema (newly created Oracle Schema). |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_PASSWORD |
Indicates the password of the Studio schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_DB_ENCRYPTED_PASSWORD |
Indicates the encrypted password that is provided for the Studio schema. For example, cGFzc3dvcmQ. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_HADOOP_CREDENTIAL_ALIAS |
Indicated the alias password saved in Hadoop. For example, studio.password.alias |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_HADOOP_CREDENTIAL_PATH |
Indicates the credentials path. For example, <Studio Installed Path>oracle.password.jceks |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Studio DB Wallet Details For information on creating a wallet, see Setup Password Stores with Oracle Wallet. |
|
|
|
|
|
STUDIO_ALIAS_NAME |
Indicates the Studio alias name. NOTE: Enter the alias name that was created during wallet creation. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_WALLET_LOCATION |
Indicates the Studio wallet location. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
STUDIO_TNS_ADMIN_PATH |
Indicates the path of the tnsnames.ora file where an entry for the STUDIO_ALIAS_NAME is present. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
DB Details for BD Config Schema |
|
|
|
|
|
BD_CONFIG_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the hostname of the database where BD or ECM config schema is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_PORT |
Indicates the port of the database where BD or ECM config schema is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_SERVICE_NAME |
Indicates the service name of the database where BD or ECM config schema is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_SID |
Indicates the SID of the database where BD or ECM config schema is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_USERNAME |
Indicates the username for the BD or ECM config schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_PASSWORD |
Indicates the password for the BD or ECM config schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD Config Wallet Details For information on creating a wallet, see Setup Password Stores with Oracle Wallet. |
|
|
|
|
|
BD_CONFIG_ALIAS_NAME |
Indicates the BD or ECM config alias name. NOTE: Enter the alias name that was created during wallet creation. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_WALLET_LOCATION |
Indicates the BD or ECM config wallet location. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_CONFIG_TNS_ADMIN_PATH |
Indicates the path of the tnsnames.ora file where an entry for the BD_CONFIG_ALIAS_NAME is present. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
DB Details for BD Atomic Schema |
|
|
|
|
|
BD_ATOMIC_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic schema hostname. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_PORT |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic schema port number. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_SERVICE_NAME |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic schema service name. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_SID |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic schema SID. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_USERNAME |
Indicates the username of the BD or ECM atomic schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_PASSWORD |
Indicates the password of the BD or ECM atomic schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD Atomic Wallet Details For information on creating a wallet, see Setup Password Stores with Oracle Wallet. |
|
|
|
|
|
BD_ATOMIC_ALIAS_NAME |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic alias name. NOTE: Enter the alias name that was created during wallet creation. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_WALLET_LOCATION |
Indicates the BD or ECM atomic wallet location. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
BD_ATOMIC_TNS_ADMIN_PATH |
Indicates the path of the tnsnames.ora file where an entry for the BD_ATOMIC_ALIAS_NAME is present. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQL Scripts |
|
|
|
|
|
FSINFODOM |
Indicates the name of the BD or ECM Infodom. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
FSSEGMENT |
Indicates the name of the BD or ECM segment. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
DATAMOVEMENT_LINK_NAME |
· If the Studio schema is in a different database host, you must create a DB link and provide the same link in this parameter. · If no DB link is present, provide the BD or ECM Atomic schema name in this parameter. · If the Studio schema is in the same database host, the value for this parameter is the user name of the BD or ECM Atomic schema. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
DATAMOVEMENT_LINK_TYPE |
If the DB link is used, enter DBLINK in this field. If the DB link is not used, enter SCHEMA in this field. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
PGX Setup Details |
|
|
|
|
|
PGX_INSTALATION_PATH |
Indicates the installation path of the PGX server. Example: <STUDIO_INSTALLATION_PATH> |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
PGX_PGB_PATH |
Indicates the path where you want to obtain the output graph PGB file. Example for Hive Installation: hdfs:/user/ofsaa Example for Oracle DB Installation: /scratch/ofsaa |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Cloudera Setup Details Contact your System Administrator to obtain the required details for these parameters. |
|
|
|
|
|
HADOOP_CREDENTIAL_PROVIDER_PATH |
Indicates the path where Hadoop credential is stored. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
HADOOP_PASSWORD_ALIAS |
Indicates the Hadoop alias given when creating the Hadoop credentials. For information on creating credential keystore, see Create the Credential Keystore. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
Hive_Host_Name |
Indicates the Hive hostname. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
Hive_Port_number |
Indicates the Hive port number. Contact your Studio Administrator to obtain the port number. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
HIVE_PRINCIPAL |
Indicates the Hive Principal. Contact your Studio Administrator to obtain the HIVE_PRINCIPAL value. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
HIVE_SCHEMA |
Indicates to create a schema in HIVE. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
JAAS_CONF_FILE_PATH |
Created for future use. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
Krb_Host_FQDN_Name |
Indicates the Kerberos host FQDN name. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
Krb_Realm_Name |
Indicates the Kerberos realm name. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
Krb_Service_Name |
Indicates the Kerberos service name. Example: Hive |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
KRB5_CONF_FILE_PATH |
Created for future use. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
security_krb5_kdc_server |
Created for future use. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
security_krb5_realm |
Created for future use. |
No |
No |
No |
No |
server_kerberos_keytab_file |
Indicates the Kerberos keytab file. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
server_kerberos_principal |
Indicates the Kerberos Principal. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQOOP_HOSTMACHINE_USER_NAME |
Indicates the user name of the Host machine where sqoop will run. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQOOP_PARAMFILE_PATH |
1. Create a file with the name sqoop.properties in the Big Data server and add the following entry: oracle.jdbc.mapDateToTimestamp=false 2. Enter the location of the sqoop.properties file as the value for this parameter. Example: /scratch/ofsaa/ NOTE: Ensure that the location name ends with a ’/’. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQOOP_PARTITION_COL |
Indicates the column in which the HIVE table is partitioned. The value must be SNAPSHOT_DT. |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQOOP_TRG_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the hostname of the Big Data server where SQOOP will run. Example: <HostName> |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
SQOOP_WORKDIR_HDFS |
Indicates the Sqoop working directory in HDFS. Example: /user/ofsaa |
Yes |
Yes |
Enter NA |
Enter NA |
Keystore file and pass details for batch service |
|
|
|
|
|
KEYSTORE_FILE_NAME |
Indicates the keystore file name that is used for secure batch service. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
KEYSTORE_PASS |
Indicates the keystore password details for the secure batch service. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Elastic Search Cluster details |
|
|
|
|
|
ELASTIC_SEARCH_PORT |
Indicates the port number where the elastic search service is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ELASTIC_SEARCH_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the hostname of the database where the elastic search service is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Quantifind Details In case of Quantifind, the generated Quantifind token must be encoded. Use the <Fic_DB_path>/FCCM_Studio_Base64Encoder.sh file for encoding Quantifind token. |
|
|
|
|
|
QUANTIFIND_URL |
Indicates the URL of the Quantifind. For example, https://api-test.quantifind.com |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ENCRYPTED_QUANTIFIND_TOKEN |
Indicates the token that is generated when integrating with Quantifind. For example, c2FtcGxlX2VuY3J5cHRlZF9xdWFudGlmaW5kX3Rva2Vu |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
QUANTIFIND_APPNAME |
Indicates the Quantifind App Name. For example, OracleIntegrationTest |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
QUANTIFIND_ENABLED |
Indicates that Quantifind is enabled. Options are True or False. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
HTTPS_PROXY_HOST |
Indicates the proxy host that is used. For example, www-proxy-idc.in.oracle.com |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
HTTPS_PROXY_PORT |
Indicates the proxy port that is used. For example, 80 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
HTTPS_PROXY_USERNAME |
Indicates the proxy username used if there is any. For example, ##HTTP_PROXY_USERNAME## |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
HTTPS_PROXY_PASSWORD |
Indicates the proxy password used if there is any. For example, ##HTTP_PROXY_PASSWORD## |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Matching Service |
|
|
|
|
|
MATCHING_SERVICE_HOSTNAME |
Indicates the host name where the matching service is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
MATCHING_SERVICE_PORT |
Indicates the port number where the matching service is installed. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
EXECUTOR_THREADS |
Indicates the number of threads to run in parallel during one scroll. For example: 10 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ELASTICRESPONSE_BUFFERLIMIT_BYTE |
Indicates the buffer size of the response obtained from the elastic search service. For example: 200 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SCROLL_TIME |
Indicates the duration for which the scroll_size output is active. For example: 5 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
SCROLL_SIZE |
Indicates the amount of data that must be obtained in one attempt when a query is fired on an index in the elastic search service. For example: 1000 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
BULK_RESULT_SIZE |
Indicates the amount of data that can be loaded in bulk. For example: 100 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
REAL_TIME_RESULT_SIZE |
Indicates the result size in real time. For example: 100 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
GROUP_THRESHOLD |
Indicates the lowest threshold value for the rule sets. |
|
|
|
|
Entity Resolution |
|
|
|
|
|
ER_SERVICE_PORT |
Indicates the port number where the entity resolution service is installed. Default Value: 7051 NOTE: This value is already set. Do not change the value. |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ER_SERVICE_URL |
Indicates the URL of the entity resolution service. For example: http://<HostName>:7051 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
ETL |
|
|
|
|
|
HDFS_GRAPH_FILES_PATH |
Indicates the filepath in the HDFS where the graph.json is formed. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
GRAPH_FILES_PATH |
Indicates the directory in the Big Data server for graph files. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
GRAPH_NAME |
Indicates the name you want to assign to the global graph at the end of ETL. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
ETL_PROCESSING_RANGE |
Indicates the duration for which the data would be moved from Oracle to Hive. For example: If the ETL_PROCESSING_RANGE = 2Y, 3M, 10D, that is, 2 years, 3 months, and 10 days, and the present date is 20200814, then the data movement occurs for the range 20180504 to 20200814. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
OLD_GRAPH_SESSION_DURATION |
Indicates the session older than this specified duration will be removed from the PGX server. If unsure, you can set this value for a week (7D). |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
REMOVE_TRNXS_EDGE_AFTER_DURATION |
Indicates the date range for which transaction edges will be maintained in graph. For example: 6Y, 3M, 10D, which means 6 years, 3 months and 15 days. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
CONNECTOR_CHANGESET_SIZE |
Indicates the number of nodes or edges you want to process during an update of graph. If unsure, you can set it to 10000. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
PGX_SERVER_URLS |
Indicates the comma ‘,’ separated values of PGX URLs. If you have only one PGX URL, then the value is http://<server1>:7007. |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
To run the FCC Studio installer, follow these steps:
WARNING |
Do not run the install.sh command until you verify the configurations made in the config.sh file. |
1. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/bin/ directory.
2. Execute the following command in the console:
./install.sh
NOTE |
Execution of the install.sh command does not generate any log file. |
3. Execute the following command in the console:
./fcc-studio.sh
Congratulations! Your installation is complete.
The FCC Studio application is installed with or without OFSAA depending on the configuration provided in the config.sh file. The FCC Studio application and all the interpreters are started.
After the successful completion of the FCC Studio installation, the script displays a URL that can be used to access the FCC Studio Application.
NOTE |
PGX service can be installed on the same server where FCC Studio is installed or on a different server. |
To install PGX service, follow these steps:
1. Navigate to the <Studio_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/ directory.
2. Perform the following:
§ If PGX service is to be installed on the same server where FCC Studio is installed, extract the pgx-distribution-20.1.1.1-server.zip file.
§ If PGX service is to be installed on a different server, follow these steps:
i. Copy the pgx-distribution-20.1.1.1-server.zip file to the PGX server.
ii. Extract the pgx-distribution-20.1.1.1-server.zip file.
NOTE |
The path where the pgx-distribution-20.1.1.1-server.zip file is unzipped is referred to as <PGX_Installation_Path>. |
3. Navigate to the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/conf directory.
NOTE |
Configure the following properties if applicable: · In the server.conf file, configure the following properties: enable_tls: false, enable_client_authentication: false · In the pgx.conf file, configure the following properties: allow_local_filesystem: true By default, the property value is true, which means that the SSL certificate is enabled, and is the recommended value. Change to false only if you do not the SSL certificate enabled. To enable the SSL certificate, see the steps in <security guide>. |
4. Replace the following Kerberos Files in the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/conf/kerberos directory:
§ krb5.conf
§ keytab file name as mentioned in the config.sh file.
5. Replace the following Hadoop configuration files in the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/conf/hadoop_cluster directory:
§ core-site.xml
§ hadoop-env.sh
§ hdfs-site.xml
§ log4j.properties
§ ssl-client.xml
§ topology.map
§ topology.py
Contact your administrator to get the files.
6. Navigate to the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/bin directory and configure the config.sh file as described in the following table:
Table 13: config.sh Parameters
Interaction Variable Name |
Significance |
|---|---|
KERBEROS_TICKET_RENEWAL_PERIOD |
For example: 7200 would mean every 2 hours |
KERBEROS_PRINCIPAL |
For example: USER@PRINCIPAL |
KERBEROS_KEYTAB_FILENAME |
For example: fccstudio.keytab |
KRB5_CONFIG_FILENAME |
For example: krb5.conf |
PGX_SERVER_OFF_HEAP_MB |
Indicates the maximum off-heap memory size in megabytes (mainly used for storing graphs except for their string properties) that PGX tries to respect. Recommended Value: 42% of the container's memory limit size above. For example: 10240 |
PGX_SERVER_ON_HEAP_MB |
Indicates the maximum and minimum heap memory size (mainly used for storing graphs' string properties) for the Java process of PGX. Recommended Value: 58% of the container's memory limit size above. For example: 10240 |
PGX_SERVER_YOUNG_SPACE_MB |
Indicates the amount of young space (new space) configured for the java heap. |
URL_GLOBAL_GRAPH_CONFIG_JSON |
Indicates the URL of the global graph to be pre-loaded. The value can be on HDFS. For example: hdfs:///user/fccstudio/graph.json |
PGX_GLOBAL_GRAPH_NAME |
Indicates the name that the pre-loaded global graph is published with and the FCC Studio users can use to reference the global graph. For example: GlobalGraphIH |
HDFS_GRAPH_FILES_PATH |
Indicates the path of the graph files. For example: hdfs:///user/fccstudio/hive_808_test_BD_19aug |
7. Navigate to the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/bin directory and run the following command:
./install.sh
8. Start the PGX service.
To start the PGX service, follow these steps:
a. Navigate to the path where PGX service is installed.
b. Navigate to the following directory where the start service for PGX is located:
<PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/bin
c. Run the following command:
nohup ./start-pgx.sh &
NOTE |
· You must run at least one successful ETL batch to start the PGX service with the graph.json file located in the URL_GLOBAL_GRAPH_CONFIG_JSON path is present. For more information, see the Data Movement and Graph Loading for Big Data Environment section in the OFS Crime and Compliance Studio Administration Guide. · In case the PGX service or the ETL graph is unresponsive after installation, you must restart the PGX service. To do this, go the <PGX_Installation_Path>/pgx/server/bin directory and then run the following commands in order: ./stop-script.sh nohup ./start-pgx.sh &
|
After the PGX service runs successfully, run the ./FCCM_Studio_ETL_BulkSimilarityEdgeGeneration.sh job.