Host Routes
Host routes let you insert entries into the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller's routing table. These routes affect traffic that originates at the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s host process. Host routes are used primarily for steering management traffic to the correct network.
When traffic is destined for a network that is not explicitly defined on a Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller, the default gateway (located in the system-config) is used. If you try to route traffic to a specific destination that is not accessible through the default gateway, you need to add a host route. Host routes can be thought of as a default gateway override.
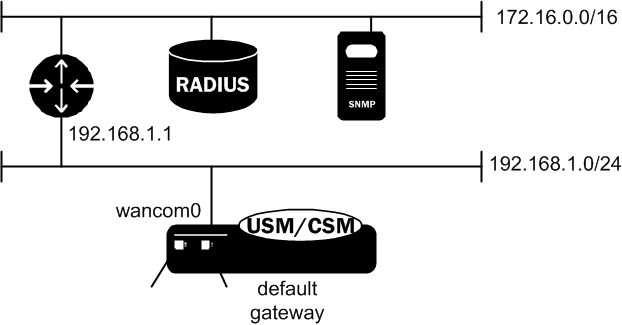
Certain SIP configurations require that the default gateway is located on a media interface. In this scenario, if management applications are located on a network connected to an administrative network, you will need to add a host route for management connectivity.
Note:
Do not configure a host-route, gateway with an address already used for any existing network-interface, gateway.Host Routes Example
When you enable SIP signaling over media interfaces, the default gateway uses an IPv4 address assigned to a media interface. Maintenance services (SNMP and Radius) are located on a network connected to, but separate from, the 192.168.1.0/24 network on wancom0. To route Radius or SNMP traffic to an NMS (labeled as SNMP in the following example), a host route entry must be a part of the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller configuration. The host route tells the host how to reach the 172.16.0.0/16 network. The actual configuration is shown in the example in the next section of this guide.