Remote Site Survivability
Release E-C[xz]6.4.0 M2 includes a new feature called Remote Site Survivability. This feature is the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s ability of a Remote Office/Branch Office (ROBO) to detect the loss of communication over SIP-based telephony, to the Enterprise’s core call processing Data Center. When loss of communication is detected over the SIP service, the ROBO Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller dynamically switches into Survivable Mode, locally handling call processing and providing limited additional server functionality.
Note:
Remote Site Survivability supports SIP only. It does not support the H.323.The following are features of Remote Site Survivability:
- Works with or without High Availability (HA) operation.
- Configurable in real-time - no reboot required to enable this feature.
- Allows configuration of the feature via the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller Web GUI
- Maintains Historical Recording (HDR) statistics about being in survivability mode, such as:
Whether or not the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is in survivable mode using the ACLI command, show health.
Length of time the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller was in survivable mode (records number of times and amount of time in survivability mode)
Number of SIP messages handled in survivable mode
Number of SIP users registered locally in survivable mode (both existing based on cache, and separately - new registrations).
How it Works
When configured for Survivability, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) operates in either normal or survival mode. In normal mode, the IP wide area network (WAN) connection between the remote E-SBC and the data center headquarters site is operational, and endpoints at the remote site register through the SBCs to an IP-PBX or Application Server (AS) at headquarters. Similarly, the E-SBC forwards calls between endpoints to the IP-PBX or AS at headquarters. When an endpoint registers, the E-SBC inserts a registration entry for the endpoint in its local registration cache.
When the IP connection to headquarters goes down, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller operates in survival mode. In this mode, the system is able to detect any loss of connection (and subsequent re-connection) to the core data center based on a health score. When it detects a loss of connection, it enters survival mode and locally processes registrations and session traffic without routing them to the registrar. The E-SBC also handles call routing in this mode. When a subsequent re-connection is detected, the system exits survival mode and proxies all registrations and session traffic once again to the data center (normal mode).
In "Survival Mode", the ROBO E-SBC provides the following capabilities:
- Maintains SIP registrations for local SIP phones (based on existing registration cache).
- Provides local extension-to-extension calling and incoming public switched telephone network (PSTN), if available, to local extension dialing.
- Provides extension-to-PSTN calling through a media gateway (assuming a gateway is available) or alternatively, via a configured SIP trunk/route.
- Allows all new registration requests (without authentication) to be successful.
- Allows extensions to be dialed based on its multiple user identities (either identified by using P-Asserted-Identity or BroadSoft’s proprietary mechanism).
Survivability Health Score
When Survivability Mode is enabled on the E-SBC, the system is able to detect any loss of connection (and subsequent re-connection) to the Enterprise’s core data center based on a health score.
For the purpose of health monitoring, a sip-interface and one or more attached session agents can be logically grouped together by configuring a“service-tag” parameter to indicate the name of the session agent group. The service health score of the group is based upon the health status of the session agents within the group and can be configured using the session-agent-health parameter. The session-agent-health score can be a value between 0 and 100.
The determination of when to enter survival mode is determined by the session agent health score. The session-agent-health value is the amount that is deducted from the service health score when the session agent goes out of service. The sum of the service health values of all session agents assigned to a specific service tag must equal 100 to stay in normal mode. In cases where there is one session agent, the service health value is 100. For cases where there are two session agents, each session agent could have a service health of 50.
When the service health score goes down to zero the E-SBC enters survival mode. While in survival mode, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller continuously attempts to re-establish communications with the session agents. If communication is re-established, the E-SBC adds the service agent health value of the session agent to the current service health score, and survival mode is exited if the service health score is above zero.
Normal Behavior Call Process
The following illustration shows the normal call process behavior of the ROBO Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller connectivity to the Service Provider site (or headquarters site).
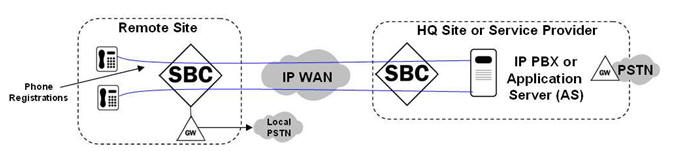
- Phones register through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to the IP PBX or Application Server (AS) at the Headquarters or Service Provider site.
- Phone-to-phone calls are proxied through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controllers to the IP PBX or AS at the Headquarters or Service Provider site.
- Phone-to-Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) calls are routed to the Headquarters or Service Provider site, or sent out a local PSTN gateway.
Remote Survivable Call Process Behavior
The following illustration shows the remote survivable call process behavior of the ROBO Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) when connectivity fails to the Service Provider site (or headquarters site).
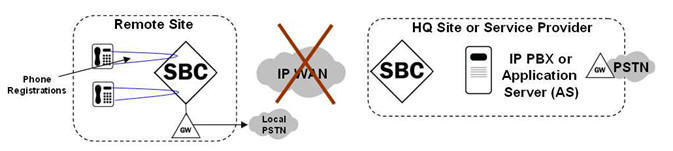
- Phones register directly on remote site E-SBC.
- Phone-to-phone calls are proxied directly on remote site E-SBC.
- Phone-to-PSTN calls are routed by remote site E-SBC to local PSTN gateway.
Entering Survivable Mode
Registration Behavior
When the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller enters Survivable Mode, it performs as follows for registrations:
| For endpoints already Registered... | For new Registration requests... (either new endpoints or endpoints whose registration expires when in Survivable Mode) |
|---|---|
| the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller acts as the registrar of the local SIP phones by providing 200 OK responses to subsequent REGISTER refresh messages from endpoints in the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s reg-cache for the duration of Survivable mode. This presumes that "registration-caching" has been enabled in the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller onfiguration. | the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller allows the new Registrations to be successful (without providing Authentication), incorporating them into the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller registration cache. |
| the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller lowers the "reg-expires" value to 30 seconds by default for all Registration Requests between the endpoints and the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. | the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller lowers the "reg-expires" value to 30 seconds by default for all Registration Requests between the endpoints and the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. |
In Survivable Mode, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller routes incoming INVITEs based on the lookup from the registration cache. If the entry is part of the registration cache, the INVITEs are routed depending on the contact information from the cache. If the entry is not part of the registration cache, local policy is used if there is any local policy configured on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. The prefix length in the Survivability configuration is taken into consideration when creating the extension for the phone number in the registration cache.
Call Processing Behavior
After the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller enters Survivable Mode, it performs as follows for call processing:
- Allows incoming sessions (either from an endpoint or an external PSTN gateway or alternate trunk) to be processed locally, based on its Registration cache.
- Locally handles multiple identities based on the registered P-Preferred-Identity (or via BroadSoft’s proprietary mechanism).
- For session requests coming from local endpoint destined to non-local destinations, it routes to alternate PSTN gateways or SIP trunks, if configured.
- It performs registration
cache (reg-cache) matching based on substrings of the received dialed digits
(for example, a phone registers as sip:7813284545@acmepacket.com and a local
user dials sip:4545@acmepacket.com).
Note:
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller allows extensions to be dialed based on it's multiple user identities (identified either by using P-Asserted-Identity or BroadSoft's proprietary mechanism.) For more information about Survivability when using the BroadSoft server, see Remote Site Survivability with a BroadSoft Server
Exiting Survivable Mode
Registration Behavior
When the Remote Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) exits Survivable Mode, it performs as follows for registrations:
- It forwards all registration requests (new or refreshes) to the core data center (or headquarters) site. Note: All endpoints in the registration cache associated with that Registrar are invalidated.
- "The "expires" value is no longer set to 30 seconds by default. It takes the corresponding registration-refresh value based on the
E-SBC configuration.
Note:
When the E-SBC is in Normal Mode, it routes the incoming INVITEs to the registrar if the endpoint is part of the registration cache. If the endpoint is not part of the registration cache, the INVITEs are routed using the local policy if the local policy is configured on the E-SBC. Otherwise, a 404 Not Found is returned.
Call Processing Behavior
When the Remote E-SBC exits Survivable Mode, it performs as follows for Call Processing:
- It allows incoming sessions to be sent to the core data center (or headquarters) site for processing.
- Existing sessions remain connected until a user ends the session.
Remote Site Survivability with a BroadSoft Server
The Remote Site Survivability feature can be enabled on a Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to work in a network with a BroadSoft server by installing the Survivability Session Plug-in Language (SPL) on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller called BroadsoftSurvivability.spl.
In this network configuration, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller advertises Directory Numbers (DNs), extensions, and other aliases (in XML format) in the 200 OK response to the Registrar. When the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller enters Survivability mode, an indication is sent to the BroadSoft server (as an XML object) in the 200 OK response in the REGISTER or SUBSCRIBE message. The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller then sends originations to all Shared Call Appearance (SCA) destinations via the BroadSoft server.
The following illustration shows the IP Phone sending a Register messsage through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to the BroadSoft server, and a 200 OK response returned from the BroadSoft server (containing the applicable XML info) through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to the IP Phone.

In the event that the BroadSoft server is unavailable, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller creates a location mapping entry, linking the parsed information (DNs, extensions, and aliases) to the location cache entry’s Address of Record (AOR). This allows users to dial by extension even if the BroadSoft server is unavailable.
Remote Site Survivability Configuration
You must enable remote site survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) and set the ping method for the session agent before the E-SBC can perform remote site survivability operations.
- Enable remote site survivability mode on the E-SBC.
- Configure a ping method for the session agent to use to determine when the E-SBC is not responding.
Note:
The system does not require a reboot after activating or modifying remote site survivability.Configure Remote Site Survivability
You must enable remote site survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) and set the parameters before the system can enter and exit survival mode.
- Confirm that at least one session agent is configured.
To enable remote site survivability from the ACLI command line, do the following :
- Configure a ping method for the session agent to use to determine when the E-SBC is not responding.
Configure the Ping Method for a Session Agent
Configure a ping method to confirm that the session agent is in service.
Show Survivability Command
The show survivability command displays active and total statistics about the performance of Survivability mode over a period of time and for overall lifetime. This display also provides statistics related to SIP media events that occur while the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is in Survivability mode.
Note:
The statistics that display in the output for this command are also used in the Historical Data Recording (HDR) statistics for Survivability. For more information about HDR for Survivability, see Historical Data Recording (HDR) for Survivability.The following example shows the output for the show survivability command.
Example
ORACLE# show survivability 12:44:48-109 SIP Status -- Period -- -------- Lifetime -------- Active High Total Total PerMax High Sessions 0 0 0 0 0 0 Subscriptions 0 0 0 0 0 0 Dialogs 0 0 0 0 0 0 CallID Map 0 0 0 0 0 0 Rejections - - 0 0 0 ReINVITEs - - 0 0 0 ReINV Suppress - - 0 0 0 Media Sessions 0 0 0 0 0 0 Media Pending 0 0 0 0 0 0 Client Trans 1 1 1 718 2 1 Server Trans 0 0 0 0 0 0 Resp Contexts 0 0 0 0 0 0 Saved Contexts 0 0 0 0 0 0 Sockets 2 2 0 2 2 2 Req Dropped - - 0 0 0 DNS Trans 0 0 0 0 0 0 DNS Sockets 0 0 0 0 0 0 DNS Results 0 0 0 0 0 0 Rejected Msgs 0 0 0 0 0 0
If Survivability mode was never initiated, the output shows values of zero (0) in all columns.
Output
The following table provides a description of this output.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Sessions | Number of sessions established by INVITE and SUBSCRIBE messages during Survivability. |
| Subscriptions | Number of sessions established by SUBSCRIPTION during Survivability. |
| Dialogs | Number of end-to-end SIP signaling connections during Survivability. |
| CallID Map | Number of successful session header Call ID mappings during Survivability. |
| Rejections | Number of rejected INVITEs during Survivability. |
| ReINVITEs | Number of ReINVITEs during Survivability. |
| ReINV Suppress | Number of ReINVITEs that were suppressed during Survivability. |
| Media Sessions | Number of successful media sessions during Survivability. |
| Media Pending | Number of media sessions waiting to be established during Survivability. |
| Client Trans | Number of client transactions during Survivability. |
| Server Trans | Number of server transactions that have taken place on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller during Survivability. |
| Resp Contexts | Number of response contexts during Survivability. |
| Saved Contexts | Number of saved contexts during Survivability. |
| Sockets | Number of SIP sockets during Survivability. |
| Req Dropped | Number of dropped requests during Survivability. |
| DNS Trans | Number of Domain Name System (DNS) transactions during Survivability. |
| DNS Sockets | Number of Domain Name System (DNS) sockets during Survivability. |
| DNS Results | Number of Domain Name System (DNS) results during Survivability. |
| Rejected Msgs | Number of rejected messages during Survivability. |
Show Command for Survivability Status
The show survivability status command allows you to display the current status of Survivability mode on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC). This command displays whether or not Survivability mode is enabled on an interface, and the date and time that Survivability mode was enabled.
The following is an example output of the show survivability status command.
Example
ORACLE# show survivability status Survivability sip-interface service-tag state start time end time --------------------------------------------------------------------- net192 test enabled Aug 15 12:53:01 - net172 none n/a n/a n/a
The following table describes the output for the above command.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| sip-interface | Interface currently configured on the E-SBC. |
| service-tag | Service tag that indicates the Session Agent Group (SAG) assigned to the interface on the E-SBC. |
| state | Current Survivability state on the interface.
Valid values are:
enabled - Survivability is enabled on the interface disabled - Survivability is disabled on the interface n/a - Survivability does not configured on this interface. |
| start time | The date (MM:DD) and time (HH:MM:SS) that Survivability Mode became in-service on the interface. |
| end time | The date (MM:DD) and time (HH:MM:SS) that Survivability Mode became out-of-service on the interface. A - indicates that Survivability Mode is currently in-service and has not yet ended. |
You can also display the current status of Survivability mode on a specific interface using the command, show survivability status <interface> where <interface> is the SIP interface name.
The following is an example output of the show survivability status <interface> command.
ORACLE# show survivability status net192 Survivability sip-interface service-tag state start time end time --------------------------------------------------------------------- net192 test enabled Aug 15 12:53:01 -
Show Commands for Survivability
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller allows you to use specific show commands to display statisitcal data about Survivability mode. Survivability mode data consists of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Request method statistics. You can initiate the show commands whether or not the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is in Survivability mode. However, if you initiate the commands when the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is in Normal mode, and Survivability mode was never initiated, the statistics display as zero (0).
This section describes the various show ACLI commands you can use to display statistics about the performance of Survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller.
Show Commands for Request Methods
The show survivability<method_name> command for SIP Request methods allow you to display specific statistical information about Request events that pass between the User Agent Server (UAS) and User Agent Client (UAC). Specific Request methods include:
| SIP Request Method | Description |
|---|---|
| INVITE | Method used to request a session. |
| REGISTER | Method used to register the client with the server according to the address in the To header field. |
| BYE | Method used to terminate an established media session. |
| ACK | Method is used to acknowledge final responses to INVITE requests. |
| CANCEL | Method is used to terminate pending requests. |
| OPTIONS | Method used to query a user agent or server about its capabilities and discover its current availability. |
| REFER | Method used by a user agent to request another user agent to access a URI or URL resource. |
| SUBSCRIBE | Method used by a user agent to subscribe the device for the purpose of receiving notifications (via the NOTIFY method) about a particular event. |
| NOTIFY | Method used by a user agent to convey information about the occurrence of a particular event. A NOTIFY is always sent within a dialog, when a subscription exists between the subscriber and the notifier. |
| UPDATE | Method used to modify the state of a session without changing the state of the dialog, |
| PRACK | Method used to acknowledge receipt of reliably transported provisional responses. This is generated by a UAC. |
| MESSAGE | Method used to transport instant messages (IM) using SIP. |
| INFO | Method used to send information in the middle of a session that doesn't modify the session's state. |
| PUBLISH | Method used to publish an event state to the server. |
| OTHER | Method used |
The following is an example of the show command output for an ACK Request.
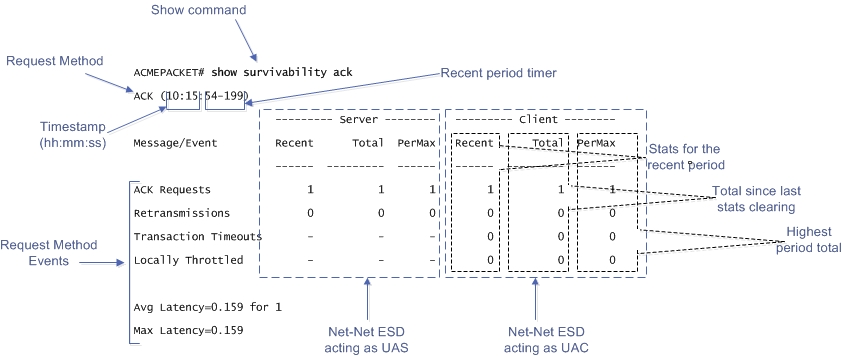
The example above provides a description for each area of the output. The Request method displays on the line directly under the command prompt (ACK in the above example), followed by the time stamp (hour:minute:second format), and then the recent period timer. The User Agent Server (UAS) data (when the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is acting as a server) is listed in the middle of the display, and the User Agent Client (UAC) data (when the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is acting as a client) is listed on the right side.
For both the UAS and UAC, the Recent column represents statistics for the recent period (the current period plus the last period). The Total column represents the total for a particular metric since the last stats clearing. Statistics are cleared either through the re-issue of the show survivability <method_name> command or on a reboot. The PerMax column represents the maximum for a given metric seen in any given individual (current) period.
Note:
The “Recent” column represents the recent period, which includes statistics from the current and the last period, which is why that number may be higher than what displays in the PerMax column.Recent Period Timer Operation
The Current period timer counts from 100 to 200 in one second increments as shown in the following illustration.
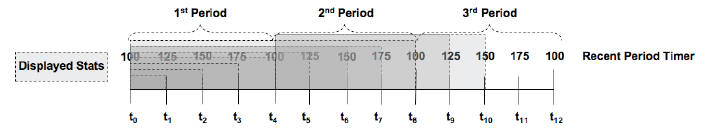
The statistics that display in the Recent column for any show survivability command reflects the appropriate behaviors for the associated value within the current period PLUS the last period (which constitutes a 100-200 second Recent period). This prevents the statistics from zeroing out between period transitions. So at time t4, in the display above, the statistics that display represent the last 100 seconds worth of behaviors (from the first period). The Recent Period statistics at time t6 represent the last 150 seconds of statistics (including 100 period 1). The Recent Period statistics at time t8 represent the last 100 seconds of statistics (including 100 from period 2).
The Recent period is the sum of the Active (current) period and the previous period.
SIP Request Method Examples
The following are examples of the show survivability <method_name> command. This command displays the recent and total Request events passed between the server and client when Survivability mode was enabled on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. This output also displays the maximum number of Request events that occurred during a current time period window of 100 seconds, when Survivability mode was enabled.
You can specify any SIP Request method for the <method_name>. The following example uses the INVITE SIP Request name.
Example 1
ORACLE# show survivability invite INVITE (10:15:44-189) --------- Server -------- --------- Client -------- Message/Event Recent Total PerMax Recent Total PerMax ------ --------- ------ ------ --------- ------ INVITE Requests 1 1 1 1 1 1 Retransmissions 0 0 0 0 0 0 100 Trying 1 1 1 0 0 0 180 Ringing 1 1 1 1 1 1 200 OK 1 1 1 1 1 1 Response Retrans 0 0 0 0 0 0 Transaction Timeouts - - - 0 0 0 Locally Throttled - - - 0 0 0 Avg Latency=0.130 for 1 Max Latency=0.130
Example 2
The following example uses the REGISTER SIP Request name.
ORACLE# show survivability register REGISTER (09:55:26-150) --------- Server -------- --------- Client -------- Message/Event Recent Total PerMax Recent Total PerMax ------ --------- ------ ------ --------- ------ REGISTER Requests 4 4 4 4 4 4 Retransmissions 0 0 0 0 0 0 200 OK 2 2 2 2 2 2 401 Unauthorized 2 2 2 2 2 2 Transaction Timeouts - - - 0 0 0 Locally Throttled - - - 0 0 0 Avg Latency=0.139 for 4 Max Latency=0.158
If Survivability mode was never initiated, the outputs show values of zero (0) in all columns.
show survivability commands
The following table describes the output for the “show survivability <method_name> command.
| Message/Event | Description |
|---|---|
| INVITE Requests | Number of INVITE Request events that occurred between the server and client during Survivability mode. |
| Retransmissions | Number of retransmission of INVITE Request events that occurred during Survivability. |
| <Response Code> | Type and number of responses that occurred between the Client and Server during Surviability. |
| Transaction Timeouts | Number of INVITE Request event timeouts that occurred during Survivability. |
| Locally Throttled | Number of INVITE Request events that were locally throttled during Survivability. This is the number of INVITE Request events that were transmitted during the regulation (slowing down) of network traffic by the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to minimize bandwidth congestion. |
| Avg Latency | Average amount of time for INVITE Request events to travel in the time period window with the amount of events specified. |
| Max Latency | Maximum amount of time it took for INVITE Request events to travel in the time period window. |
Show Commands for Session Agents Interfaces and Realms
The following show commands for Session Agents, interfaces and realms allow you to display recent and total statistics about the SIP methods used during Survivability mode:
- show survivability agents <hostname><method_name>
- show survivability interface <realm-id><method_name>
- show survivability realms <realm-id><method_name>
- BYE
- UPDATE
- CANCEL
- ACK
- INVITE
- PRACK
- REFER
- OTHER
- OPTIONS
- SUBSCRIBE
- NOTIFY
- INFO
- MESSAGE
- PUBLISH
- REGISTER
The output for these commands display recent and total number of SIP Requests that occurred for a session agent, interface, or realm during a current time period window of 100 seconds, when Survivability mode was enabled.
Note:
To view the method names available, press the tab key after entering the command as shown in the following example.ORACLE# show survivability agents net192<tab>
ack bye cancel info invite message
notify options other prack publish refer
register subscribe update
The following examples show the output of the show survivability commands for agents, interface, and realms.
If Survivability mode was never initiated, the outputs show values of zero (0) in all columns.
Session Agents
ORACLE# show survivability agents net192 refer REFER (13:15:35-117) --------- Server -------- --------- Client -------- Message/Event Recent Total PerMax Recent Total PerMax ------ --------- ------ ------ --------- ------ REFER Requests 0 2 2 0 2 2 Retransmissions 0 0 0 0 0 0 202 Accepted 0 2 2 0 2 2 Transaction Timeouts - - - 0 0 0 Locally Throttled - - - 0 0 0 Avg Latency=0.000 for 0 Max Latency=0.000
Interface
ORACLE# show survivability interface net192 refer REFER (13:15:35-117) --------- Server -------- --------- Client -------- Message/Event Recent Total PerMax Recent Total PerMax ------ --------- ------ ------ --------- ------ REFER Requests 0 2 2 0 2 2 Retransmissions 0 0 0 0 0 0 202 Accepted 0 2 2 0 2 2 Transaction Timeouts - - - 0 0 0 Locally Throttled - - - 0 0 0 Avg Latency=0.000 for 0 Max Latency=0.000
Realms
ORACLE# show survivability realms net192 refer REFER (13:15:35-117) --------- Server -------- --------- Client -------- Message/Event Recent Total PerMax Recent Total PerMax ------ --------- ------ ------ --------- ------ REFER Requests 0 2 2 0 2 2 Retransmissions 0 0 0 0 0 0 202 Accepted 0 2 2 0 2 2 Transaction Timeouts - - - 0 0 0 Locally Throttled - - - 0 0 0 Avg Latency=0.000 for 0 Max Latency=0.000
Output
The following table describes the output for the above commands.
| Message/Event | Description |
|---|---|
| <method_name> Requests | Number of the specified Request events that occurred between the server and client during Survivability mode. |
| Retransmissions | Number of retransmissions of specified Request message that occurred during Survivability. |
| <Response Code> | Type and number of responses that occurred between the Client and Server during Surviability. |
| Transaction Timeouts | Number of the specified Request event timeouts that occurred during Survivability. |
| Locally Throttled | Number of the specified Request events that were locally throttled during Survivability. This is the number of ACK Request events that were transmitted during the regulation (slowing down) of network traffic by the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to minimize bandwidth congestion. |
| Avg Latency | Average amount of time for the specified Request events to travel in the time period window of 100 seconds, for the amount of events specified, during Survivability. |
| Max Latency | Maximum amount of time it took for the specified Request events to travel in the time period window of 100 seconds during Survivability. |
Historical Data Recording (HDR) for Survivability
If the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is configured to collect Historical Data Recording (HDR) statistics, statistics are collected on Survivability whether or not it is in-service.
HDR data consists of a “Group” with associated Group Statistics that apply to each group. HDR data comes from two sources:
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Management Information Bases (MIBs)
- Oracle’s Command Line Interface (ACLI)
The Survivability data in the HDR outputs are taken from the ACLI. The following are the HDR Groups for survivability:
- survivability-sip-status
- survivability-sip-invites
- survivability-sip-register
- survivability-sip-errors
When the collector on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is enabled, these Groups and associated Group Statistics are included in the collection of data.
The following paragraphs provide a description of each Survivability Group and Group Statistic. Each Group table identifies the ACLI Show command for which it is associated.
Group survivability-sip-status
| Description | Consists of statistics pertaining to the status of Survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. |
|---|---|
| Group Statistics | Sessions Subscriptions Dialogs CallID Maps Rejections ReINVITEs Media Sessions Media Pending Client Trans Server Trans Resp Contexts Saved Contexts Sockets Req Drops DNS Trans DNS Sockets DNS Results Session Rate Load Rate Active Subscriptions SubscriptionsPerMax Subscriptions High |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Group Statistics
Active Subscriptions
| Description | Specifies the current global count of active SIP subscriptions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command show sipd realms <realm_name> in the E-SBC Historical Data Recording Resource Guide. |
CallID Maps
| Description | Total number of successful session header Call ID mappings during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Client Trans
| Description | Total number of client transactions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
DNS Results
| Description | Total number of Domain Name System (DNS) results during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
DNS Sockets
| Description | Total number of Domain Name System (DNS) sockets during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
DNS Trans
| Description | Total number of Domain Name System (DNS) transactions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Dialogs
| Description | Total number of end-to-end SIP signaling connections during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Load Rate
| Description | Average Central Processing Unit (CPU) utilization of the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller during the current window period, and during Survivability. The average is computed every 10 seconds unless the load-limit is configured in the SIPConfig record, in which case it is 5 seconds. |
|---|---|
| Type | period |
| Timer Value (seconds) | 30 |
| Range | 0% to 100% |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Media Pending
| Description | Total number of media sessions waiting to be established during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Media Sessions
| Description | Total number of successful media sessions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
ReINVITEs
| Description | Total number of ReINVITEs during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Rejections
| Description | Total number of rejected INVITEs during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Req Drops
| Description | Total number of dropped requests during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Resp Contexts
| Description | Total number of response contexts during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Saved Contexts
| Description | Total number of saved contexts during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Server Trans
| Description | Total number of server transactions that have taken place on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Sessions
| Description | Total number of sessions established by INVITE and SUBSCRIBE messages during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Session Rate
| Description | The rate, per second, of SIP invites allowed to or from the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller during the sliding window period, and during Survivability. The rate is computed every 10 seconds . |
|---|---|
| Type | period |
| Timer Value (seconds) | 30 |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Sockets
| Description | Total number of SIP sockets during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Subscriptions
| Description | Total number of sessions established by SUBSCRIPTION during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the table at Show Survivability Command . |
Subscriptions High
| Description | Specifies the maximum global count of active SIP subscriptions since the last SBC re-boot, and during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command show sipd realms <realm_name> in the E-SBC Historical Data Recording Resource Guide. |
SubscriptionsPerMax
| Description | Specifies the maximum global count of SIP subscriptions initiated during any 100 second period since the last E-SBC re-boot, and during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command show sipd realms <realm_name> in the E-SBC Historical Data Recording Resource Guide. |
Group survivability-sip-invites
| Description | Consists of response statistics pertaining to INVITES during Survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. |
|---|---|
| Group Statistics | INVITE Requests Retransmissions Response Codes Each response code is next printed to the HDR file on a separate line. The format is <timestamp> <3-digit-code Description> <Total count> <Client total count>. See the above link to the Response Codes description table. Response Retrans Transaction Timeouts Locally Throttled |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Group Statistics
INVITE Requests
| Description | Total number of INVITE requests during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Locally Throttled
| Description | Total number of INVITE requests locally throttled during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Response Codes
| Description | Total number of a specific INVITE response codes that occurred during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Description | Each of the response codes are as follows:
1xx --Informational: 100 Trying: This response is used to indicate the next node receives the request and stop the retransmission. This response is sent if there is delay in sending the final response more the 200ms. 180 Ringing: The response is generated if UA receives the INVITE and started the ringing. It may used to initiate local ring back. 181 Call is being Forwarded: This response is indication of call is being forwarded to different destination. 182 Call Queued: The called server is overloaded or temporary unavailable. the server sends this status code to queue the call. When server ready to take the call, it initiates appropriate final response. 183 Call Progress: This response may be used to send extra information for a call which is still being set up. 2xx—Successful Responses 200 OK: Indicates the request was successful. 202 Accepted: Indicates that the request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. 3xx—Redirection Response 301 Moved Permanently: The original Request-URI is no longer valid, the new address is given in the Contact header field, and the client should update any records of the original Request-URI with the new value. 302 Moved Temporarily: The client should try at the address in the Contact field. If an Expires field is present, the client may cache the result for that period of time. 305 Use Proxy: The Contact field details a proxy that must be used to access the requested destination. 380 Alternative Service: The call failed, but alternatives are detailed in the message body. 4xx—Client Failure Responses 400 Bad Request: The request could not be understood due to malformed syntax. 401 Unauthorized: The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by UASs and registrars. 403 Forbidden: The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it 404 Not Found: The server has definitive information that the user does not exist at the domain specified in the Request-URI. This status is also returned if the domain in the Request-URI does not match any of the domains handled by the recipient of the request. 405 Method Not Allowed: The method specified in the Request-Line is understood, but not allowed for the address identified by the Request-URI. 406 Not Acceptable: The resource identified by the request is only capable of generating response entities that have content characteristics but not acceptable according to the Accept header field sent in the request. 407 Proxy Authentication Required: The request requires user authentication. This response is issued by proxys 4xx—Client Failure Responses (continued)408 Request Timed Out: Couldn't find the user in time. 415 Unsupported Media Type: Request body in a format not supported. 420 Bad Extension: Bad SIP Protocol Extension used, not understood by the server. 421 Extension Required: The server needs a specific extension not listed in the Supported header. 422 Session Interval Too Small: The received request contains a Session-Expires header field with a duration below the minimum timer. 423 Interval Too Brief: Expiration time of the resource is too short. 480 Temporarily Unavailable: Callee currently unavailable. 481 Call/Transaction Does Not Exist: Server received a request that does not match any dialog or transaction. 482 Loop Detected: Server has detected a loop. 483 Too Many Hops: Max-Forwards header has reached the value '0'. 484 Address Incomplete: Request-URI incomplete. 485 Ambiguous: Request-URI is ambiguous. 486 Busy Here: Callee is busy. 487 Request Terminated: Request has terminated by bye or cancel. 488 Not Acceptable Here: Some aspects of the session description of the Request-URI is not acceptable. 489 Bad Event: The server did not understand an event package specified in an Event header field. 491 Request Pending: Server has some pending request from the same dialog. 5xx—Server Failure Responses500 Server Internal Error: The server could not fulfill the request due to some unexpected condition. 501 Not Implemented: The server does not have the ability to fulfill the request, such as because it does not recognize the request method. (Compare with 405 Method Not Allowed, where the server recognizes the method but does not allow or support it.) 502 Bad Gateway: The server is acting as a gateway or proxy, and received an invalid response from a downstream server while attempting to fulfill the request. 503 Service Unavailable: The server is undergoing maintenance or is temporarily overloaded and so cannot process the request. A "Retry-After" header field may specify when the client may re attempt its request. 504 Server Time-out: The server attempted to access another server in attempting to process the request, and did not receive a prompt response. 513 Message Too Large: The request message length is longer than the server can process. 580 Precondition Failure: The server is unable or unwilling to meet some constraints specified in the offer. 6xx—Global Failure Responses 600 Busy Everywhere: All possible destinations are busy. Unlike the 486 response, this response indicates the destination knows there are no alternative destinations (such as a voicemail server) able to accept the call. 603 Decline: The destination does not wish to participate in the call, or cannot do so, and additionally the client knows there are no alternative destinations (such as a voicemail server) willing to accept the call. 604 Does Not Exist Anywhere: The server has authoritative information that the requested user does not exist anywhere. 606 Not Acceptable: The user's agent was contacted successfully but some aspects of the session description such as the requested media, bandwidth, or addressing style were not acceptable. |
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Response Retrans
| Description | Total number of INVITE response retransmissions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Retransmissions
| Description | Total number of retransmissions of INVITEs during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Transaction Timeouts
| Description | Total number of INVITE request transaction timeouts during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Group survivability-sip-register
| Description | Consists of response statistics pertaining to REGISTRATIONS during Survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. |
|---|---|
| Group Statistics | REGISTRATION Requests Retransmissions Response Retrans Transaction Timeouts Locally Throttled |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability register” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Group Statistics
Locally Throttled
| Description | Total number of Register requests locally throttled during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
REGISTRATION Requests
| Description | Total number of Register requests sent between the client and server during Surivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability register” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Response Retrans
| Description | Total number of Register response retransmissions during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Retransmissions
| Description | Total number of Register retransmissions that ocurred during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability register |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability register” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Transaction Timeouts
| Description | Total number of Register request transaction timeouts during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability invite |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability invite” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Group survivability-sip-errors
| Description | Consists of response statistics pertaining to REGISTRATIONS during Survivability on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. |
|---|---|
| Group Statistics | SDP Offer Errors SDP Answer Errors Drop Media Errors Transaction Errors Application Errors Media Exp Events Early Media Exps Exp Media Drops Expired Sessions Multiple OK Drops Multiple OK Terms Media Failure Drops Non-ACK 2xx Drops Invalid Requests Invalid Responses Invalid Messages CAC Session Drop CAC BW Drop |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Group Statistics
Application Errors
| Description | Total number of miscellaneous errors in the SIP application that are otherwise uncategorized during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples. |
CAC BW Drop
| Description | Total number of call admission control (CAC) session setup failures due to insufficient bandwidth (BW) during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
CAC Session Drop
| Description | Total number of call admission control (CAC) session setup failures during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Drop Media Errors
| Description | Total number of errors encountered during Survivability |
|---|---|
| Description | Total number of errors encountered during
Survivability, in tearing down the media for a dialog or session that is being
terminated due to:
a) non-successful response to an INVITE transaction, or b) a BYE transaction received from one of the participants in a dialog/session, or c) a BYE initiated by the E-SBC due to a timeout notification from the Middlebox Control Daemon (MBCD). |
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Early Media Exps
| Description | Total number of flow timer expiration notifications received for media sessions that were not completely set up due to an incomplete or pending INVITE transaction during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Expired Sessions
| Description | Total number of sessions terminated due to the session timer expiring during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Exp Media Drops
| Description | Total number of flow timer expiration notifications from the Middlebox Control Daemon (MBCD) that resulted in the termination of the dialog/session by the SIP application during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Invalid Messages
| Description | Total number of messages dropped due to parse failure during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Invalid Requests
| Description | Total number of invalid requests (for example, an unsupported header was received) during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Invalid Responses
| Description | Total number of invalid responses (for example, no Via header in response) during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Media Exp Events
| Description | Total number of flow timer expiration notifications received from the Middlebox Control Daemon (MBCD) during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Media Failure Drops
| Description | Total number of dialogs terminated due to a failure in establishing the media session during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Multiple OK Drops
| Description | Total number of dialogs terminated upon reception of a 200 OK response from multiple User Agent Servers (UASs) for a given INVITE transaction that was forked by a downstream proxy during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Multiple OK Terms
| Description | Total number of dialogs terminated upon reception of a 200 OK response that conflicts with an existing established dialog on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
Non-ACK 2xx Drops
| Description | Total number of sessions terminated because an ACK was not received for a 2xx response during Survivability. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
SDP Answer Errors
| Description | Total number of errors encountered during Survivability, in setting up the media session for a session description in a SIP request or response which is a Session Description Protocol (SDP) Answer in the Offer/Answer model (RFC 3264) |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
SDP Offer Errors
| Description | Total number of errors encountered during Survivability, in setting up the media session for a session description in a SIP request or response which is a Session Description Protocol (SDP) Offer in the Offer/Answer model (RFC 3264) |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |
SNMP Trap for Survivability
An Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) MIB contains objects of management data, and also information about Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) traps, which enable an agent to notify the management station of significant events by way of an unsolicited SNMP message. When an element sends a TRAP packet, it can include an Object Identifier (OID) and value information (bindings) to clarify the event. For more information about SNMP on the E-SBC, see the MIB Reference Guide.
The E-SBC triggers an Enterprise SNMP trap when a SIP interface goes in or out of Survivability mode. This trap is called:
- snmp_survivability_mode_trap_send
This trap has been added to the SIP application MIB called ap-sip.mib. The trap information is as follows in this MIB:
apSipSurvivabilityNotif OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { apSipNotificationObjects 2 }
apSipSurvivabilityNotifObjects OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { apSipSurvivabilityNotif 1 }
apSipSurvivabilityNotifPrefix OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { apSipSurvivabilityNotif 2 }
apSipSurvivabilityNotifications OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { apSipSurvivabilityNotifPrefix 0 }
apSipSurvivabilityModeEnter NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { apSysMgmtSipInterfaceRealmName, apSysMgmtSipInterfaceIP }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
" The trap will be generated when SIP interface enters Survivability Mode."
::= { apSipSurvivabilityNotifications 1 }
apSipSurvivabilityModeExit NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { apSysMgmtSipInterfaceRealmName,
apSysMgmtSipInterfaceIP }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
" The trap will be generated when SIP interface exits Survivability Mode and resumes normal operation."
::= { apSipSurvivabilityNotifications 2 }
apSipSurvivabilityNotificationsGroup NOTIFICATION-GROUP
NOTIFICATIONS {apSipSurvivabilityModeEnter,
apSipSurvivabilityModeExit }
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"Traps to monitor SIP interface Survivability feature."
::= { apSipNotificationGroups 2 }
Note:
The apSysMgmtSipInterfaceRealmName and apSysMgmtSipInterfaceIP objects are imported strings defined in ap-smgmt.mib.- realmname—Realm name of the SIP interface
- ipaddr—IP address of the SIP interface
- mode—Specifies whether or
not the SIP interface is in survivability mode. Values included with the trap
are:
- 0 - SIP interface is OK. It is not in Survivability mode.
- 1 - SIP interface is in Survivability mode.
The following table identifies the Survivability OBJECT IDENTIFIERS in the Oracle MIB that the E-SBC supports.
| Trap Name: OID Number | Description |
|---|---|
| apSipSurvivabilityNotificationsGroupCap:
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.2.1.21.3 |
Specifies the capability of the E-SBC to notify the Agent regarding Survivability on the SIP interface. |
| apSipSurvivabilityNotif
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2 |
N/A |
| apSipSurvivabilityNotifObjects
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2.1 |
N/A |
| apSipSurvivabilityNotifPrefix
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2.2 |
N/A |
| apSipSurvivabilityNotifications
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2.2.0 |
N/A |
| apSipSurvivabilityModeEnter
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2.2.0.1 |
Specifies that the SIP interface has entered Survivability mode. |
| apSipSurvivabilityModeExit
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.2.2.2.0.2 |
Specifies that the SIP interface has exited Survivability mode and resumed normal operation. |
| apSipSurvivabilityNotificationsGroup
1.3.6.1.4.1.9148.3.15.3.2.2 |
Specifies the notification from the E-SBC to the Agent regarding Survivability on the SIP interface. |
Survivability Alarms and Logging
All survivability debug information and messages are logged to the serviceHealth.log. When a SIP interface enters Survivability Mode, a MAJOR alarm is raised. The alarm message contains the SIP interface’s IP address and realm ID on which it resides. The following is an example of the alarm.
Survivability Alarm Example
ID Task Severity First Occurred Last Occurred 3145745 776175088 4 2013-08-20 10:19:35 2013-08-20 10:19:35 Count Description 1 SIP interface ip=172.16.38.17 realm-id=core running in Survivability Mode
Transaction Errors
| Description | Total number of errors encountered during Survivability when processing SIP client transactions associated with setting up or tearing down of the media session. |
|---|---|
| Type | counter |
| Timer Value (seconds) | N/A |
| Range | 0 to 4294967295 |
| ACLI Show Command | show survivability errors |
| ACLI Parameter Mapping | For ACLI parameter mappings, see the command “show survivability errors” at SIP Request Method Examples . |



