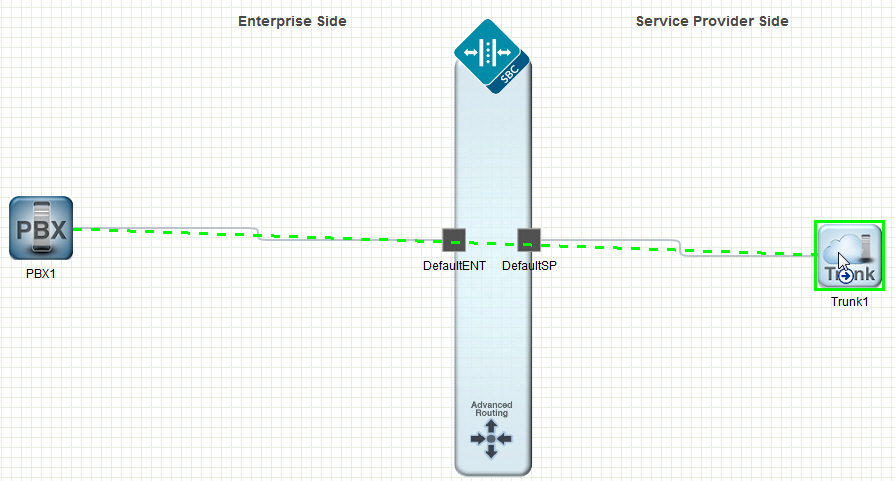
Setting Up a Typical Network
You can configure the network by dragging-and-dropping the icons from the Device tool bar onto the Basic mode workspace below the titles of Enterprise Side and Service Provider Side. After you drop the icon onto the workspace, click the icon to display the corresponding configuration dialog.
The following steps describe the process for configuring a typical network by way of the Web GUI in Basic mode.
- Drag the PBX icon to the Enterprise Side, and complete the Add PBX dialog.
- Drag the SIP Trunk icon to the Service Provider Side, and complete the Add SIP Trunk dialog.
- Click the two-way Routing icon, click the center of the PBX icon, drag to the center of the SIP Trunk icon, and complete the Add Two-Way Route Information dialog.
- Click the Network button, click Network Interface, and confirm that the Network Interface on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is correct on the Enterprise and Service Provider sides.
- Save and Activate the configuration.
Add a PBX
You can perform the minimum configuration needed to connect a PBX to the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) from the Configuration tab in Basic mode.
- Configure inbound and outbound translation rules.
- Note any System Programming Language (SPL) options that you want to add.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
Drag and drop the PBX icon from the device toolbar onto the workspace and the system displays the Add PBX dialog, where you enter the configuration parameters. After you perform the configuration and click OK in the Add PBX dialog, the PBX icon persists on the Enterprise side of the workspace. You can edit the PBX configuration any time by double-clicking the icon and modifying the configuration in the Modify PBX dialog box. Save and activate the configuration after the initial configuration and after modifying the configuration.
- Configure the Trunk.
Add a Trunk
You can perform the minimum configuration needed to make connect a SIP Trunk to the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) from the Configuration tab in Basic mode.
- Configure inbound and outbound translation rules.
- Note any System Programming Language (SPL) options that you want to add.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
Drag and drop the Trunk icon from the device toolbar onto the workspace and the system displays the Add SIP Trunk dialog, where you enter the configuration parameters. After you perform the configuration and click OK in the Add SIP Trunk dialog, the Trunk icon persists on the Service Provider side of the workspace. You can edit the Trunk configuration any time by double-clicking the icon and modifying the configuration in the Modify SIP Trunk dialog box. Save and activate the configuration after the initial configuration and after modifying the configuration.
- Configure optional network elements, such as Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), additional devices, a recording server, or remote workers.
- Configure routing policies.
Add a One-Way Local Routing Policy
You can perform the minimum configuration needed to add a one-way local routing policy to the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) from the Configuration tab in Basic mode.
- Note the IP addresses of the devices that you want to affect with this policy.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
This procedure provides an example of creating a one-way local route policy between two network devices, the PBX and the Trunk. You can perform this procedure between other elements of the network, such as other Devices and Remote Workers.
Drag and drop the one-way routing icon from the device toolbar onto the PBX icon and connect it to the Trunk icon. The system displays the Add One-Way Route Information dialog, where you enter the local routing policy parameters. After you perform the configuration and click OK in the Add One-Way Route Information dialog. The one-way route icon persists on the workspace. You can edit the local policy configuration any time by double-clicking the icon and modifying the configuration in the Modify One-Way Route Information dialog box. Save and activate the configuration after the initial configuration and after modifying the configuration.
Add a Two-Way Local Routing Policy
You can perform the minimum configuration needed to add a two-way local routing policy to the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) from the Configuration tab in Basic mode.
- Note the IP addresses of the devices that you want to affect with this policy.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
This procedure provides an example of creating a two-way local route policy between two network devices, the PBX and the Trunk. You can perform this procedure between other elements of the network, such as other Devices and Remote Workers.
Drag and drop the two-way routing icon from the device toolbar onto the PBX icon and connect it to the Trunk icon. The system displays the Add Two-Way Route Information dialog, where you enter the local routing policy parameters. After you perform the configuration and click OK in the Add Two-Way Route Information dialog. The two-way route icon persists on the workspace. You can edit the local policy configuration any time by double-clicking the icon and modifying the configuration in the Modify Two-Way Route Information dialog box. Save and activate the configuration after the initial configuration and after modifying the configuration.
Configure Advanced Local Routing Policy
After adding a one-way or two-way local policy route, you can configure the polices with advanced parameters from the Web GUI in Basic mode.
- Configure at least one local routing policy.
- Note the name of the local routing server.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
In the Advanced Routing dialog, configure the advanced routing parameters that you want and add the corresponding LDAP configuration.
- Configure LDAP.
- Save the configuration.
Configure LDAP
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) uses Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) for interaction between an LDAP client and an LDAP server. Use the ldap-config tab in the Advanced routing dialog in Basic mode to create and enable an LDAP configuration on the E-SBC.
- Confirm that one or more authentication modes exist.
- Confirm that one or more Transport Layer Security (TLS) profiles exist.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
In the following procedure, you configure the LDAP server, filters, security, and local policy.
Time Division Multiplexing
Oracle® designed the Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) functionality for companies planning to migrate from TDM to SIP trunks by using a hybrid TDM-SIP infrastructure, rather than adopting VoIP-SIP as their sole means of voice communications. The TDM interface on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) provides switchover for egress audio calls, when the primary SIP trunk becomes unavailable. You can use TDM with legacy PBXs and other TDM devices.
- Only the Acme Packet 1100 and the Acme Packet 3900 platforms support TDM, which requires the optional TDM card.
- TDM supports bidirectional calls as well as unidirectional calls.
- TDM operations require the configuration of tdm-config and tdm-profile, as well as local policies for inbound and outbound traffic.
- The software upgrade procedure supports the TDM configuration.
- Options for the Acme Packet 1100 and the Acme Packet 3900 platforms include Calling-Line Identification Presentation (CLIP) and Connected-Line Identification Presentation (COLP).
- Options for the Acme Packet 1100 platform include the four-port Primary Rate Interface (PRI), the Euro ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI), and the Foreign Exchange Office-Foreign Subscriber Office (FXO-FXS) card.
Interface Requirements
PRI—Digium1TE133F single-port or Digium 1TE435BF four-port card.
BRI—Digium 1B433LF four-port card
FXS—Digium 1A8B04F eight-port card, green module (ports 1-4)
FXO—Diguim 1A8B04F eight-port card, red module (ports 5-8)
Notes
When you deploy either the Acme Packet 1100 or the Acme Packet 3900 in a High Availability (HA) pair, the active system cannot replicate calls between SIP and TDM to the standby system.
The Acme Packet 1100 does not support HA for the PRI, BRI, and FXO-FXS interfaces.
Time Division Multiplexing Configuration
To perform Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) operations on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC), you must enable TDM, specify the parameters for the interface in use, run the TDM configuration wizard, and create local policies for routing TDM traffic.
- Configure the
tdm-config element and its corresponding sub-elements. The
tdm-config element, located under
system, contains the parameters that are common to all TDM configurations. The sub-elements contain the particular parameters for the interface that the system detects in use on the
E-SBC. The system displays the sub-elements, as follows:
- When the E-SBC detects either the Primary Rate Interface (PRI) or the Basic Rate Interface (BRI) interface, tdm-config displays the tdm-profile sub-element with the parameters that correspond to the interface. See "Primary Rate Interface Support" and "Basic Rate Interface Support."
- When the E-SBC detects the Analog interface, tdm-config displays both the fxo-profile and the fxs-profile sub-elements with the parameters that correspond to the interface. See "Foreign Exchange Office-Foreign Exchange Subscriber Support."
- Run the TDM configuration wizard to complete the configuration. The wizard creates the realm, SIP interface, steering pools, and other necessary configuration elements including the network interface and the phy-interface for SIP call routing. With SRTP enabled (default), the wizard also creates the
media-sec-policy object, enables the
secured-network attribute for the
sip-interface
object, and configures the
media-sec-policy attribute for
realm-config. You can run the wizard from either the Web GUI (Set TDM Configuration) or the ACLI (setup tdm).
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) requires running the TDM configuration wizard only after the initial TDM configuration. The system does not require you to run the wizard after you make changes to the existing configuration.
Note:
When the Oracle Session Delivery Manager (SDM) manages the E-SBC, you configure TDM from the SDM and you do not need to run the TDM configuration wizard. See "Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Settings on the Session Delivery Manager (SDM)" for the required settings. - Configure the local policy for routing traffic through the TDM interface. For unidirectional TDM call routing, the system requires a local policy only for the call direction that you want. For example, inbound-only or outbound-only. For bi-directional TDM call routing, create both inbound and outbound local policies. See "Local Policy Configuration for Time Division Multiplexing."
- ACLI—Use the tdm-config, tdm-profile, fxo-profile, and fxs-profile elements located under system.
- Web GUI—Basic mode. Double-click the TDM icon in the network diagram to display the TDM configuration dialog.
- Web GUI—Expert mode. Use the tdm-config, tdm-profile, fxo-profile, and fxs-profile elements located under system.
- Session Delivery Manager (SDM)—Launch the Web GUI from SDM and use the tdm-config, tdm-profile, fxo-profile, and fxs-profile elements located under system.
Configure TDM
To perform Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) operations, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) requires a profile that specifies the TDM interface.
- Confirm that the E-SBC contains the optional TDM card.
- If you want to enable TDM logging in this procedure, you must enable system logging before you begin.
In the following procedure, the line mode that you specify dictates certain corresponding settings, as noted. For example, when you select the T1 line mode, you must specify ESF for the Framing Value. Do not specify an E1 value for the T1 line mode or a T1 value for the E1 line mode.
Configure the inbound and outbound TDM local policies.
Configure Outbound Local Policy with TDM Backup
To complete the Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) configuration for redundancy, you must configure the outbound TDM local routing policy.
- Confirm that a TDM configuration exists.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
In the following procedure, you must draw the outbound local routing policy arrow from the PBX icon to the Trunk icon because the system supports TDM operations only from the PBX to the Trunk. If you draw the outbound local routing policy arrow from the Trunk icon to the PBX icon, you cannot configure this policy for TDM.
Configure Bidirectional Local Policy with TDM Backup
To complete the Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) configuration for redundancy, you must configure the TDM local routing policy.
- Confirm that a TDM configuration exists.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
The following procedure assumes drawing the bidirectional local routing policy arrow from the PBX to the Trunk.
Configure Outbound TDM Local Policy - Basic
To complete the configuration for outbound Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) operations, you must configure the TDM local routing policy.
- Confirm that a TDM configuration exists.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
In the following procedure, you must draw the outbound local routing policy arrow from the TDM icon to the Trunk icon. If you draw the outbound local routing policy arrow from the Trunk icon to the TDM icon, you cannot configure this policy for TDM.
Configure Bidirectional TDM Local Policy
To complete the configuration for inbound and outbound Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) operations, you must configure the TDM local routing policy.
- Confirm that a TDM configuration exists.
- Confirm that the system displays the Basic mode.
The following procedure assumes drawing the bidirectional local routing policy arrow from the TDM to the Trunk.