A Commands
This appendix shows you the syntax and usage of LSMS commands
Introduction
You access most LSMS database administration and configuration functions through the LSMS graphical user interface (GUI). For more information about using the GUI for these functions, refer to Database Administrator's Guide, LNP Database Synchronization User's Guide, and Configuration Guide.
In addition, you can use commands to manage some LSMS functions. This appendix shows you the syntax and usage of LSMS and third-party application commands, entered at a command-line prompt, that control LSMS or third-party applications.
Overview of LSMS Application Commands Entered at the Command-Line Prompt
Table A-1 summarizes the LSMS application and third-party application commands that are entered at the command-line prompt. These commands are described in this appendix. For information about the notation used in the command descriptions, see Entering LSMS and Third-Party Application Commands.
Table A-1 LSMS Application Functions and Third-Party Commands Available at the command-line Prompt
| Function | Command |
|---|---|
|
Display, add, or delete remote locations and scheduled transfers |
|
|
Select the last change time for the specified region |
|
|
Verify that EMS Routing is set up properly |
|
|
Control an |
|
|
Import data from NPAC files into LSMS databases |
|
|
Load, delete, or display keys for NPAC associations |
|
|
Control a regional |
|
|
Obtain information about a database |
|
|
Start, stop, or show status of the SNMP Agent process |
|
|
Control the Surveillance process |
|
|
Perform mass update of SPID for LRN, NPA-NXX, and NPA-NXX-X |
|
|
Print measurement pegs to the display |
|
|
Create or remove a regional NPAC database |
|
|
Import specific files into a regional database |
|
|
Generate a report about one or more databases |
|
|
Create or remove the resynchronization database |
|
|
Control the Service Assurance agent |
|
|
Associate usernames with SPIDs |
|
|
Control the Local Services Manager and the Local Data Manager processes |
|
|
Create or remove the Supported database |
|
|
Use to send a customer-defined notification |
|
|
Detect, diagnose, or display a summary of the overall health of the LSMS |
Entering LSMS and Third-Party Application Commands
This appendix describes LSMS and certain third-party application commands used to manage the LSMS. Third-party commands identify their software source. All other commands in this appendix are LSMS commands.
All commands in this appendix are case-sensitive and are entered at the command-line prompt. After entering a command, you must press the Enter key. When the command has executed, you can enter another command.
Notation
This appendix uses the following syntax notational conventions for commands entered at the command-line prompt:
-
Keywords - identify the principal action to be performed by the system.
-
Permission - identifies the group to which the user must belong to execute the command, or for certain commands, whether the user must be logged in with a particular user name. The possible groups are
lsmsas primary group, or secondary groupslsmsadm,lsmsuser,lsmsuext,lsmsview, andlsmsall(all users defined to be a member of one of these secondary groups should havelsmsdefined as their primary group). For more information about primary and secondary group definitions, see Managing User Accounts. -
Restrictions - note restrictions or limitations applying to the use of the command.
-
Syntax - identifies the command’s keywords, options (if any), parameters, and their proper order. In syntax, the following symbols are used:
-
<xxx> indicates a variable
-
[xxx] indicates a parameter or option that is optional
-
{xxx|yyy} indicates a mandatory parameter; you must specify one of the values shown (in this case xxx or yyy)
-
-
Options - tell the operating system how to perform a command. Options are also known as switches.
-
Parameters - further define the command’s operation.
-
Sample Output - is an example of typical output produced by the command.
-
Environment - identifies any special environment variables or condition that must exist on the system for the process to execute. All commands use only default environment variables, with the exception of
start_mgui, which requires setting the $DISPLAY environment variable. -
Response Notes - identifies any pertinent command performance information.
-
Related Commands - identifies other commands or programs related to this command.
-
Files - identifies, describes, and provides the location of the configuration files required for proper execution of this command.
Command Example
The following is an example of an LSMS command entry:
$ $LSMS_DIR/resync_db_setup create
The environment variable is $LSMS_DIR, the directory containing the LSMS software. It is followed by the keyword resync_db_setup (command for creating or removing the resynchronization database). A single parameter is given for this command, create (indicates the resynchronization database is to be created). This command has no options.
autoxfercfg
Automatic File Transfers
Displays, adds, and deletes remote locations and scheduled transfers.
Keyword
autoxfercfg
Permission
The user must be defined as a member of the secondary group lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/autoxfercfg [-h]
Options
None.
Parameters
None.
Sample Output
Select one of the following menu options:
1) Display valid remote locations
2) Add new remote location
3) Remove remote location
4) Display all scheduled transfers
5) Add new scheduled transfer
6) Remove scheduled transfer
7) Exit
For more information about using this menu, see one of the following:
Caution:
The.netrc file (see “Files”) contains the ftp account login information and is readable by root.
Possible Errors
Table A-2 Error Messages: autoxfercfg
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|
The Automatic File Transfer feature is not installed. |
Contact Oracle to schedule installation and activation of the feature. |
|
2 |
|
The user that tried to run this program was not the user |
Change user to |
|
3 |
|
The |
No action necessary. |
|
4 |
|
The file permissions for |
Change permissions on the |
Files
The following files associated with the autoxfercfg command.
Table A-3 Files: autoxfercfg
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
Autologin resource file for |
|
|
List of scheduled cron jobs |
|
|
Configuration file |
|
chglct
Change Last Change Time
Manually sets the Last Change Time (LCT) for the database belonging to the specified region.
In each regional database, the LSMS updates the LCT when the LSMS receives transactions from that NPAC. When the LSMS automatically recovers from a temporary loss of association with an NPAC, it uses the LCT to determine the time range for which to request that the NPAC resend transactions.
Use this command to manually set the LCT when performing a bulk download of files from the NPAC (see “NPAC-LSMS Download Procedure”, 32
Keyword
chglct
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/chglct -h -r <region> [-d|-s <YYYYMMDDhhmmss>]
Options
-
-h - Displays help information
-
-r<region> - Display or set the LCT in Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) for the region specified by <region>. Possible values for <region> are:
-
Canada -
Midwest -
MidAtlantic -
Southeast -
Southwest -
Northeast -
Western -
WestCoast
-
-
-d - Display the current value of the LCT (in GMT) value for the specified region. The value has 14 characters in the form YYYYMMDDhhmmss which has the format shown in Table A-4.
-
-s <YYYYMMDDhhmmss> - Set the value of the last change timestamp (in GMT) value for the specified region to the value indicated by the specified character string, which has 14 characters in the form YYYYMMDDhhmmss.
Table A-4 Time Value for chglct
| Characters | Meaning | Range |
|---|---|---|
|
YYYY |
Year |
Any four digits |
|
MM |
Month |
01–12 |
|
DD |
Day |
01–31 |
|
hh |
Hour |
00–23 |
|
mm |
Minute |
00–59 |
|
ss |
Second |
00–59 |
Sample Output
Display the last changed timestamp for the Midwest region
$ chglct -d -r Midwest
Midwest last changed timestamp: 20011107113017
Local Time: 11/7/2001 6:30:17
GMT Time: 11/7/2001 11:30:17
$
Related Commands
None.
Response Notes
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-5 Error Messages: chglct
| Exit Code | Error Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
|
User entered command with incorrect syntax. |
Try the command again with correct syntax. |
|
1 |
|
Database exception. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
A user with a username other than |
Log in as |
|
3 |
|
Contact Oracle. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
Files
None.
chkfilter
Check EMS Routing Filters
Run this command to verify that EMS Routing is set up properly. This command reviews all the telephone number (TN) and number pool block (NPB) transactions that were received from NPACs in the past 24 hours and determines whether any of these TNs and NPBs were not forwarded to any EAGLE node. If any are found, a file $LSMS_DIR/../logs/trace/LsmsSubNotFwd.log.<MMDD> (where <MMDD> indicates the month and day the chkfilter command was run) is created and those TNs and NPBs are stored in this file.
Keyword
chkfilter
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/chkfilter
Options
None.
Sample Output
$ chkfilter
$
Related Commands
None.
Files
Table A-6 Files: chkfilter
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Response Notes
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-7 Error Messages: chkfilter
| Exit Code | Error Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
|
User entered command with incorrect syntax. |
Try the command again with correct syntax. |
|
1 |
|
Database exception. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
A user with a username other than |
Log in as |
|
3 |
|
The LSMS_DIR env variable is not set. |
Verify the environment variables. |
|
4 |
|
Unable to open output file, check directory and permission |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
5 |
|
Not known. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
eagle
EAGLE Agent Control
Used to start, stop, or display status of an eagleagent process.
Keyword
eagle
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/eagle <Action> <CLLI>
Options
None.
Parameters
-
Action - The function to be performed on the
eagleagentprocess. This mandatory parameter has the following values:-
start -
stop -
status
-
-
<CLLI> - Common Language Location Identifier for the network element associated with this
eagleagentprocess. This parameter is required whenActionisstartorstop. WhenActionisstatus, this parameter is optional; if not specified, the status for alleagleagentprocesses is displayed.
Sample Output
# Stop the EAGLE Agent for the network element whose CLLI is STPM1
$ $LSMS_DIR/eagle stop STPM1
eagle: Stopping...
eagle: eagleagent STPM1 stopped at Thu Mar 7 17:21:05 2002
# Verify that EAGLE Agent has stopped
$ $LSMS_DIR/eagle status STPM1
eagle: eagleagent STPM1 is not running.
# Restart the EAGLE Agent for the network element whose CLLI is STPM1
$ $LSMS_DIR/eagle start STPM1
eagle: Starting...
eagle: eagleagent STPM1 started at Thu Mar 7 17:17:36 2002
# Check the status of the EAGLE Agent for the network element whose CLLI is STPM1
$ $LSMS_DIR/eagle status STPM1
eagleagent:
CLLI = STPM1
Pid = 72
State = NONE_ACTIVE
Resync = NO_CONNECTION
Connection A = DOWN
Connection B = DOWN
DCM connection = NONE
EBDA = IDLE
Debug logging = OFF
Pending queue = 0 of 2000000 bytes (0%)
Keepalive timestamp = Thu Mar 7 17:19:02 EST 2002
Virtual memory = 14392 K bytes
CPU usage = 1.1 %
# Check the status of all EAGLE Agents
$ $LSMS_DIR/eagle status
CLLI Pid State Resync Conn A Conn B DCM EBDA Debug Queue Memory CPU Timestamp
STPM0 --- not running
STPM1 72 NONE_ACTIVE NO_CONNECTION DOWN DOWN NONE IDLE OFF 0 % 14 M 0.4 % 17:19:25
STPM2 449 B_ACTIVE IN_PROGRESS DOWN ACTIVE NONE RUNNING OFF 0 % 12 M 1.0 % 17:19:23
STPO3 20179 A_ACTIVE COMPLETE ACTIVE STANDBY OK IDLE OFF 0 % 14 M 0.3 % 17:19:27
Related Commands
None.
Response Notes
None.
Files
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-8 Exit Codes: eagle
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Incorrect syntax. |
Correct the syntax. |
|
2 |
Invalid command for current state. |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
Error in environment. |
Verify the environment variables. |
|
4 |
Unable to create socket. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
5 |
Unable to bind socket. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
6 |
Fatal application error. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
7 |
Operation failed. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
hastatus
Display LSMS HA Status
Allows user to display the High Availability status of the server on which the command is run.
Keyword
hastatus
Permission
The user can be logged in as any user.
Syntax
/usr/TKLC/plat/bin/hastatus
Required Flags
None.
Sample Output
$ hastatus
ACTIVE
Related Commands
None.
Response Notes
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-9 Error Messages: hastatus
| Exit Code | Error Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Success |
n/a |
n/a |
|
1 |
Failure |
Varies |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66 |
|
2 |
Query No Match |
Querying the status of a component, based on a condition, did not result in a match. Following are the most common causes, which are dependent upon the particular query. |
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
6 |
UnknownError |
Not known |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66 |
import
Upload to MySQL Database
Imports data from NPAC files into LSMS databases. This command performs all parameter checking, and validates or creates the NPAC directory if required.
Note:
Do not run theimport command while any of the following processes are also running: backups, starting a standby node (to change its state from UNINITIALIZED "INHIBITED" to STANDBY), running the lsmsdb quickaudit command, and creating query server snapshots, all of which use temporary storage space. If you try to run the import command while any of these processes are running, you may not have enough disk space to complete the process. Since backups can be run automatically, perform the procedure described in “Checking for Running Backups” to ensure that no backups are running.
Keyword
import
Permission
The user must be defined as a member of the primary group lsms.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/import [-c] [-o [-d <dir>]] <region> [<filename>...]
Provided the import command is prefaced by the $LSMS_DIR environment variable, it can be performed from any directory location.
Options
-
-c - If an error occurs, continue with the next record in the file. Errors are recorded in a file named <filename>_FAILED, where <filename> has the same value as was entered in the command.
-
-o - Generate a Response file for SV and NPB imports.
-
-d <dir> - Put the Response file(s) in the specified directory (defaults to the same directory as each SV/NPB import file).
Parameters
-
<region> - Name of the NPAC region: Midwest, MidAtlantic, Northeast, Southeast, Southwest, Western, WestCoast, Canada. This is a required parameter.
-
<filename> - The name of the NPAC downloadfile in
npacftp/<region>. This is an optional parameter. If you do not specify a<filename>, a list displays that includes all the valid import files from thenpacftp/<region>directory for the NPAC region specified (the region is a required parameter).
Note:
Filenames must adhere to the following formats:LRN.<create>.<start>.<end> NPANXX.<create>.<start>.<end> NPANXXX.<create>.<start>.<end> SPID.<create> <npanxx>-<npanxx>.<create>.<start>.<end> <npanxxx>-<npanxxx>.<create>.<start>.<end><create> is the file creation timestamp: <DD-MM-YYYYhhmmss>
<start> is the start of the time-range: <DD-MM-YYYYhhmmss>
<end> is the end of the time-range: <DD-MM-YYYYhhmmss>
Note:
For Active (not time-range) files,<start> is 00-00-0000000000 and <end> is 99-99-9999999999Note:
SPID files are always Active.Note:
Active files with filenames in the old format, with only a creation timestamp, are still supported.Example 1:
<npanxx>-<npanxx>.<create>.<start>.<end>:
303123-303125.02-11-1998133022.12-10-1998080000.13-10-1998133022
Example 2:
LRN.<create>.<start>.<end> [Active (not time-range) file]:LRN.02-10-2001102201.00-00-0000000000.99-99-9999999999Sample Output
NPAC FTP directory: /var/TKLC/lsms/free/data/npacftp/Midwest
The following NPAC download file(s) are available for import:
LRN.11-07-2001145342 NPANXX.11-07-2001145342
NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342 SPID.11-07-2001145342
000000-999999.11-07-2001145342 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
Import LRN.11-07-2001145342 (Yes/No/All/Quit)?all
The following NPAC download files have been chosen to be imported:
SPID.11-07-2001145342 NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342
NPANXX.11-07-2001145342 LRN.11-07-2001145342
000000-999999.11-07-2001145342 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
Do you want to continue (Yes/No)?yes
Beginning Delete Process for SPID.11-07-2001145342
Delete Process Completed for SPID.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for SPID.11-07-2001145342
1000 ServiceProvNetwork instance updates in MidwestDB
2000 ServiceProvNetwork instance updates in MidwestDB
2351 ServiceProvNetwork instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for SPID.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Delete Process for NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342
Delete Process Completed for NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342
1000 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
2000 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
3000 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
4000 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
30000 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
30860 ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for NPANXXX.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Delete Process for NPANXX.11-07-2001145342
Delete Process Completed for NPANXX.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for NPANXX.11-07-2001145342
90 ServiceProvNPA_NXX instance updates in MidwestDB
1090 ServiceProvNPA_NXX instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for NPANXX.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Delete Process for LRN.11-07-2001145342
Delete Process Completed for LRN.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for LRN.11-07-2001145342
1000 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
2000 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
3000 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
4000 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
4700 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
5700 ServiceProvLRN instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for LRN.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Delete Process for 000000-999999.11-07-2001145342
All Subscription Version instances deleted from Midwest
Delete Process Completed for 000000-999999.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for 000000-999999.11-07-2001145342
1000 SubscriptionVersion instance updates in MidwestDB
2000 SubscriptionVersion instance updates in MidwestDB
3000 SubscriptionVersion instance updates in MidwestDB
4000 SubscriptionVersion instance updates in MidwestDB
4500 SubscriptionVersion instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for 000000-999999.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Delete Process for 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
All Subscription Version instances deleted from Midwest
Delete Process Completed for 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
Beginning Download Process for 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
1000 NumberPoolBlock instance updates in MidwestDB
2000 NumberPoolBlock instance updates in MidwestDB
Import completed successfully.
Download Process Completed for 0000000-9999999.11-07-2001145342
Script completed.
Files
Table A-10 shows the files for the import command.
Table A-10 Files: import
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
< |
Download file |
|
|
< |
Error file, created if errors occur during import. If the -c option was not specified, the file will contain at most one entry. |
|
|
< |
Response file |
|
Error Messages
Table A-11 Error Messages: import
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
7 |
|
Delete utility failed |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
8 |
|
DNLD utility failed |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
99 |
|
Invalid number of parameters supplied |
Try the command again with correct syntax. |
|
1 |
|
Invalid NPAC region supplied |
Supply valid region name for command. |
|
2 |
LSMS_DIR environment variable is not set/defined. |
LSMS_DIR environment variable is not set |
Verify the environment variables or contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
9 |
|
NPAC directory for |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
|
NPAC FTP directory for |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
5 |
The npacagent process is currently running for the <region> region. It must be stopped prior to importing by executing the following command: |
The |
Stop the |
keyutil
Process Keys
Allows user to view security key status, load keys, or delete keys for NPAC associations.
Keyword
keyutil
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/keyutil -r <region> -k {public|private} [-d] [-l <filename>] [-x <listid>] [-s <listid>, <keyid>] [-y]
Required Flags
-
-r <region> - Perform the function specified by another option for keys for the specified region, where
<region>has one of the following values:-
Canada -
Midwest -
MidAtlantic -
Southeast -
Southwest -
Northeast -
Western -
WestCoast
-
-
-k {public|private} - Perform the function specified by another option for keys of either public type or private type.
One of the following options must be specified:
-
-d - Display all keys.
-
-l <filename> - Load keys from the specified
<filename>. -
-x <listid> - Delete keys in the specified list.
-
-s <listid>, <keyid> - Set the active key. All private keys for the specified region that occur in the specified list before the specified key are expired; all private keys for that region that occur in the specified list after the specified key are made valid.
Sample Output
$ keyutil -r Midwest -k public -l ../../TKLC.1.public.key
Customer ID: TKLC
List ID: 1
Ok to make changes? y
$
Related Commands
None.
Response Notes
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-12 Error Messages: keyutil
| Exit Code | Error Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
|
The command was entered with incorrect syntax. |
Try the command again with correct syntax. |
|
1 |
|
The key file to be opened could not be found. |
Verify the file path. If necessary, correct the path and try the command again. If the problem persists, contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
User answered no when prompted for changes. |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
|
User specified keys to delete, but those keys were not found. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
4 |
|
Database exception occurred; contact Oracle. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
5 |
|
A user who is not |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
6 |
|
Not known. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
lsms
NPAC Agent Control
Lets you start, stop, or display status of an instance of the NPAC Agent for a particular region.
Keyword
lsms
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Restrictions
Do not start an NPAC agent unless you have already created a regional database for it (see “npac_db_setup”).
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/lsms <Action> <Region>
Options
None.
Parameters
-
Action - Function to perform on
npacagentprocess. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:-
start -
stop -
status
-
-
Region - NPAC region associated with this
npacagentprocess. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:-
Canada -
Midwest -
MidAtlantic -
Southeast -
Southwest -
Northeast -
Western -
WestCoast
-
Sample Output
# Stop the NPAC Agent for the Canada NPAC
$ $LSMS_DIR/lsms stop Canada
Checking if npacagent is running....Yes.
Stopping npacagent....
OK.
npacagent stopped: Wed Nov 30 16:28:26 2005
Command complete.
$
# Verify that NPAC Agent has terminated
$ $LSMS_DIR/lsms status Canada
Checking if npacagent is running. .. .No.
Command Complete.
# Restart the NPAC Agent for the Canada NPAC
>
$ $LSMS_DIR/lsms start Canada
Checking if npacagent is already running....No
Starting npacagent....
Verifying....OK.
npacagent started: Wed Nov 30 16:29:45 2005
Command complete.
Possible Errors
Table A-13 Error Messages: lsms
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|
Operator tried to start |
No action necessary. |
|
1 |
|
Operator tried to stop |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
|
Attempt to bind UDP socket failed. errornumber is the error returned by bind. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
|
Attempt to exec |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Execution of |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Attempt to stop |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
LSMS_DIR environment variable is not set |
Verify the environment variables. |
|
3 |
|
Attempt to send command to agent failed. errornumber is the error returned by send. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
|
Attempt to open UDP socket failed. errornumber is the error returned by socket. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
Operator does not have permission to execute this command or executable could not be found. The operator must be an |
Change user to |
|
2 |
Unknown region ==>< region name > must be one of the following:
|
Invalid NPAC region specified |
Try the command again with a valid region name. |
|
2 |
|
Invalid action specified |
Try the command again with correct syntax. |
lsmsdb
Database Maintenance Utility
The LSMS Database Command-Line Utility (a MySQL client), $LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb, provides the capability of obtaining information and performing maintenance operations on the LSMS database. Additionally, the lsmsdb command is used to provide information and perform operations to configure query servers.
The syntax for lsmsdb as used within this document is as follows:
Keyword
lsmsdb
Permission
The user can be root or be defined as a member of the primary group lsms.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c <command> [-b <basedir>] [-d <database>] [-h <hostname>] [-p <password>] [-u <username>]
-c <command> Options
-
adduser - Creates TPD and MySQL users, both with the same password. Must be run as root.When the
addusercommand option is specified, the-u <username>option is required. -
addrepluser - Sets up a special replication user at the LSMS with privileges and permission that a query server can use to access the LSMS and perform database replication. When the
addreplusercommand option is specified, the-h <hostname>and-p <password>options are required. SECURITY NOTE: The combination of username and password is unique to replication use and only provides read access to the resynchronization binary log on the LSMS system. Additionally, access to this user account is restricted to the hostname specified. If the maximum number of EAGLE nodes supported would be exceeded, the command terminates with the following error:"Failed: The maximum number of eagles supported has been reached." -
chguserpw - Allows modification of the TPD and MySQL passwords. Can be run as root, or as the user who wants to change the password. When the
chguserpwcommand option is specified, the-u <username>option is required.Note:
Thelsmsdb - c chguserpw - u <username>command must be run on both the primary and the secondary servers to completely change the password. -
counts - Displays counts of records in specified database.
-
dblist - Displays list of databases (if the
-doption is specified, it is ignored). -
features - Displays current settings of all optional features.
-
users - Lists all defined LSMS GUI users.
-
masterstatus - Displays status information (log name and position) on the binary log of the master server (LSMS).
-
ping - Pings the
mysqldaemon. -
queryservers - Displays the connection status of all query servers that are directly connected to the LSMS. The connection status for each query server (denoted by hostname and IP address) is displayed as
Connected,Disconnected,Not Reachable, orHostname not associated with IP address. For this command to show correct connection status between LSMS and a query server, a new user must be created on the query server. For information about how to create this user to check replication status from LSMS, see the Query Server Installation and Upgrade Instructions. -
quickaudit - Performs a quick comparison of the number of rows in all of the database tables on both the active and standby servers. It returns "0" if the comparison on the active and standby servers results in a match; it returns various error numbers and error messages if the comparison does not produce a match or if a problem was encountered.
Note:
Do not specify this option when the LSMS is performing bulk download. In addition, do not specify this option when any of the following processes are running, due to the possibility of disk space shortage: backups, starting a standby node (to change its state from UNINITIALIZED "INHIBITED" to STANDBY), running theimportcommand, and creating query server snapshots. Since backups can be run automatically, perform the procedure described in Checking for Running Backups to ensure that no backups are running.This option:- Takes about 5 seconds to run.
- Must be run from the active server.
- Checks first to see if the standby server is more than 5 seconds behind the active server; if it is, an error message is generated and quickaudit does not proceed.
-
rmrepluser - Removes a replication user at the LSMS. When the
rmreplusercommand option is specified, the-h <hostname>option is required. -
rmuser - Deletes TPD and MySQL users. Must be run as root. When the
rmusercommand option is specified, the-u <username>option is required. -
shutdown - Stops
mysql(if the-doption is specified, it is ignored). -
snapshot - Creates a snapshot of the LSMSLNP database to be used to setup query servers and/or for disaster recovery.When the
snapshotcommand option is specified, the-b <basedir>option is optional.During the creation of a snapshot of the LSMS LNP database, the following occurs:
-
A read lock will be obtained
-
Table information is flushed
-
Binary logs (if already existing) are removed and a new one started (with log numbered 1)
-
MySQL server performs a shutdown
-
All LSMS database tables are archived as compressed files,
mysql-snapshot-supDB.tar.gzandmysql-snapshot-<regionDB>.tar.gz(by default in/var/TKLC/lsms/db, although the-boption changes this base directory) -
MySQL server is restarted
-
The read lock is released
-
-
start - Starts
mysql(if the-doption is specified, it is ignored). -
syspwexp - Modifies the system level defaul password timeout interval.
-
usrpwexp - Modifies the user level defaul password timeout interval, the
-u <username>option is required.
Options
-
-b basedir - Base directory for storing snapshots.
-
-d database - Run the command on the database specified by this option. If the
-doption is not specified, the command is run on all databases. -
-h hostname - Name of the host.
-
-p password - User’s password.
-
-u username - LSMS user’s username.
Note:
The -c flag is required.
Sample Input and Output
$ ./lsmsdb -c features
Y AFT
Y EDR
Y ENHANCED_FILTERS
Y HTTP
Y HTTPS
16 MAX_EAGLES
32 MAX_SPIDS
8 MAX_USERS
Y QUERY_SERVER
Y REPORT_GEN
0 REPORT_GEN_QUERY_ACTIVE
Y SNMP
Y SPID_SECURITY
Y WSMSC
N WSMSC_TO_EAGLE
$ ./lsmsdb -c counts -d NortheastDB
1 ............. NortheastDB.NumberPoolBlock
1 ............. NortheastDB.ServiceProvLRN
0 ............. NortheastDB.ServiceProvNPA_NXX
0 ............. NortheastDB.ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X
1 ............. NortheastDB.ServiceProvNetwork
39,756 ........ NortheastDB.SubscriptionVersion
$ $LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c addrepluser -h queryserver1 -p password
$ $LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c masterstatus
Lsmspri-bin.001 73
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c queryservers
queryserver1 (10.25.60.28) Connected
queryserver2 (10.25.60.45) Disconnected
queryserver3 (10.25.60.31) Not Reachable
queryserver4 (Unknown) Hostname not associated with IP address
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c rmrepluser -h queryserver1 -p password
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/lsmsdb -c snapshot
WARNING: For the duration of this command, traffic being sent from the NPAC to connected network elements and local LSMS provisioning will be INTERRUPTED.
Do you want to continue? [Y/N] Y
lsmsSNMP
SNMP Agent Process Control
Lets you start, stop, or show status of the SNMP Agent process. For more information about the SNMP agent process, see “Understanding the SNMP Agent Process”.
Keyword
lsmsSNMP
Permission
Any user who belongs to the lsmsadm permission group.
Restrictions
The LSMS_DIR environment variable must be set.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/lsmsSNMP <Action>
Options
None.
Parameters
Sample Output
#Stop the SNMP Agent
> $LSMS_DIR/lsmsSNMP stop
LSMS SNMP Agent stopped: Fri Mar 10 09:50:47 2000 #Start the SNMP Agent
> $LSMS_DIR/lsmsSNMP start
LSMS SNMP Agent started: Fri Mar 10 10:50:47 2000 #Determine the SNMP Agent status
> $LSMS_DIR/lsmsSNMP status
LSMS SNMP AGENT PROCESS STATUS:
TOTAL SUCCESSFUL TRAP REQUEST= 12
TOTAL FAILED TRAP REQUEST = 2
== IP-ADDRESS == == STATUS ====
177.88.34.7 Failed
198.77.39.2 SNMP Session EstablishedFiles
Table A-14 shows the files for the lsmsSNMP command.
Table A-14 Files: lsmsSNMP
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Configuration file |
|
Possible Errors
Table A-15 Exit Codes: lsmsSNMP
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Failed operation. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
Operation not required. |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
Usage error. |
Correct the syntax. |
|
4 |
Fatal application error |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
5 |
Server not active. |
Execute the command on the active server. |
|
6 |
LSMS software not running. |
Start the LSMS. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
lsmssurv
Surveillance Monitor Control
Starts, stops, and retrieves the status of the Surveillance Monitor.
The notification output from the Surveillance Monitor is written to Serial Port 3 on each server. The non-active server, whether its state is STANDBY or UNINITIALIZED "INHIBITED", sends surveillance notifications only for platform events that it detects on itself. It also forwards those notifications to the active server.
-
The active server sends surveillance notifications for:
-
All platform events that the active server detects on itself
-
All platform notifications received from the non-active server (the active server inserts the hostname of the non-active server before the event text for these notifications)
-
Some applications events (not all application events generate surveillance notifications; for more information, see Automatic Monitoring of Events).
-
By default, all notification output that is sent to Serial Port 3 on a given server is written also to the log file on that server, /var/TKLC/lsms/logs/survlog.log. (See “Files”.)
Keyword
lsmssurv
Permission
The user must be root to specify the start or stop for <Action>.
Syntax
# $LSMS_DIR/lsmssurv <Action>
Options
None.
Parameters
Sample Output
# Start LSMS Surveillance Process
#
$LSMS_DIR/lsmssurv start
LSMS Surveillance feature started
# Request LSMS Surveillance Process status
#
$LSMS_DIR/lsmssurv status
LSMS Surveillance feature is currently started
# Stop LSMS Surveillance Process
#
$LSMS_DIR/lsmssurv stop
LSMS Surveillance feature stopped
# Return LSMS Surveillance Process to last valid state. The following
# output indicates that the process had been running prior to termination
#
$LSMS_DIR/lsmssurv last
LSMS Surveillance feature started
#
Files
Table A-16 shows the files for the lsmssurv command.
Table A-16 Files: lsmssurv
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Error/Debug log file |
|
|
|
Notification log file |
|
Response Notes
The designated response will not occur for five to ten seconds after execution.
Possible Errors
Table A-17 Error Messages: lsmssurv
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|
LSMS Surveillance feature is running |
No action necessary. |
|
1 |
|
LSMS Surveillance feature is not running |
No action necessary. |
|
1 |
|
Socket communication problems, hang on opening of console/serial ports |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
User ID must be root to start the LSMS Surveillance feature |
Change user to |
massupdate
SPID Mass Update
The optional mass update utility provides the ability to migrate subscription version, number pool block, and network data from one Service Provider ID (SPID) to another based on an input file downloaded from the NPAC. The mass update utility reads SIC-SMURF files for LRN, NPA-NXX, and NPA-NXX-X, performs the required database updates and, in the case of LRN data, forwards an appropriate Update Override GTT message to the EAGLE.
Keyword
massupdate
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/massupdate [-v] [-p] [-n <npacRegion>] <filename>
Note:
Stop thenpacagent process for the region in question when the -n option is used. It is not necessary to stop the npacagent processes for all eight regions when the -n option is used.
Optional flags:
Parameters
-
<npacRegion> - The name of the region to perform the mass update for.
-
<filename> - The name of the SIC-SMURF file to process.
Note:
The filename must be in the following format:SIC-SMURF-[LRN|NPANXX|NPANXXX].OldSpid.NewSpid.DD-MM-YYYYHH24MISS
Example: SIC-SMURF-NPANXX.0001.0002.25-12-1996081122
Sample Output
$ $LSMS_DIR/massupdate SIC-SMURF-LRN.1234.9876.15-03-2002121530
One or more npacagents processes are currently running. They must be
Stopped prior to mass spid updates by executing the following command:
/lsms stop <region>
Massupdate: exiting.
$ $LSMS_DIR/massupdate SIC-SMURF-LRN.1234.9876.15-03-2002121530
WARNING: The supman, lsman or an eagleagent process is currently running. It is recommended that all of these processes be stopped prior to mass spid updates to prevent modifications of GTT data during execution of this command.
Do you wish to continue [N]?
Massupdate: exiting.
$ $LSMS_DIR/massupdate -v SIC-SMURF-LRN.1234.9876.15-03-2002121530
Using SIC-SMURF File: SIC-SMURF-LRN.1234.9876.15-03-2002121530
Performing Mass Update of SPIDs for LRN data...
Updating LRN 2223334000 from SPID 1234 to SPID 9876...
5 OverrideGtt object(s) updated in supported database
1 ServiceProvLRN object(s) updated in Southeast region
4 NumberPoolBlock object(s) updated in Southeast region
Updating LRN 2224441000 from SPID 1234 to SPID 9876...
0 OverrideGtt object(s) updated
1 ServiceProvLRN object(s) updated in Southeast region
10 NumberPoolBlock object(s) updated in Southeast region
Updating LRN 2225550000 from SPID 1234 to SPID 9876...
4 OverrideGtt object(s) updated
0 ServiceProvLRN object(s) updated in Southeast region
4 NumberPoolBlock object(s) updated in Southeast region
Updating SubscriptionVersion tables (this may take a while)...
790 SubscriptionVersion object(s) updated in Southeast region
Command stats
-------------
Lines processed: 3
Successful: 3
Failed: 0
Command complete.
$
$ $LSMS_DIR/massupdate -p SIC-SMURF-LRN.TKLC.SP05.06-30-2004101010
WARNING: The supman, lsman or an eagleagent process is currently running. It is recommended that all of these processes be stopped prior to mass spid updates to prevent modifications of GTT data during execution of this command.
Do you wish to continue [N]? Y
START Mass update command: Thu Nov 8 13:41:57 EST 2007
Precheck mode: Makes NO CHANGES, but reports everything as if updating.
Executing mass update for all regions...
{Precheck only}
Reading SIC-SMURF File: SIC-SMURF-LRN.TKLC.SP05.06-30-2004101010
Performing Mass Update of SPIDs for LRN data... {Precheck only}
Command stats {Precheck only}
-------------
Lines processed: 1
Successful: 1
Failed: 0
Mass update command complete: Thu Nov 8 13:41:57 EST 2007massupdate for the various SIC-SMURF files.
For each table/field that is affected, the field that is checked for a match is listed under the appropriate SIC-SMURF filename. Under the Table/Field column, the database containing the object to be updated (for example, SupDB), the table to be updated (for example, OverrideGTT), and the field to be updated (for example, spid) are listed.
Under each SIC-SMURF file type, the field to be used for the match (for example, lrn) is listed for each Table/Field impacted by the update. For example, for LRN SIC-SMURF files, the SupDB OverrideGTT table's spid is updated if the lrn is matched.
Table A-18 Tables/Fields Affected By SIC-SMURF Processing
| Table/Field | LRN SIC-SMURF | NPA-NXX SIC-SMURF | NPA-NXX-X SIC-SMURF |
|---|---|---|---|
|
supDB.OverrideGtt.spid |
lrn |
||
|
supDB.LsmsServiceProvider.spid (create if required) |
spid |
||
|
supDB.GttGroupSpid.spid (create if required) |
spid |
||
|
<regionDB>.ServiceProvLRN.serviceProviderId |
lrn |
||
|
<regionDB>.ServiceProvNPA_NXX.serviceProvId |
npanxx |
||
|
<regionDB>.ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X.service-ProvId |
npanxx_x |
||
|
<regionDB>.ServiceProvNetwork.serviceProvId (create if required) |
spid |
spid |
spid |
|
<regionDB>.SubscriptionVersion.newCurrentSp |
lrn |
||
|
<regionDB>.NumberPoolBlock.newCurrentSp |
lrn |
If an Override GTT entry is modified and there is no LSMS Service Provider with the NewSpid, then one is created. If that LSMS Service Provider SPID is not a member of the GTT group for a modified Override GTT, then that membership is added by creating a GTT Group SPID table entry.
If a ServiceProvLRN, ServiceProvNPA_NXX, or ServiceProvNPA_NXX_X object is modified and there is no ServiceProvNetwork object with the NewSpid, then one is created.
LsmsServiceProvider Limit
The mass update utility creates LsmsServiceProvider objects, if needed, even if creating them exceeds the maximum number of SPIDs supported (as recorded in the MAX_SPIDS field in the DbConfig entry.) However, the fact that the limit has been exceeded is recorded in the log file and the limit remains in force otherwise.
Mass Update Log File
To record information or errors during the mass update or the precheck, the mass update utility appends to a log file named massupdate.log.MMDD, located in the $LSMS_DIR/../logs/massupdate directory. The .MMDD suffix is the month and day the massupdate excution begins. If the massupdate runs past midnight, it will keep all output from one massupdate execution in one file, so the file will not be split across days but continue in the same file it started in. The following information is written to the log file by the mass update utility:
-
The path name of the mass update input file being used
-
The time and date for the start and stop of utility execution
-
Identifying information for all automatically created objects, whether ServiceProvNetwork or LsmsServiceProvider, including the adding of a (possibly already existing) LsmsServiceProvider to a GttGroup and noting if a newly created LsmsServiceProvider is over the MAX_SPIDS limit
-
Identifying information for any LsmsServiceProvider objects that are no longer used in any OverrideGtt as a result of the mass update and therefore could be removed
-
Output from the precheck
-
Any kind of processing problem or error
-
A summary showing the number of lines actually processed successfully for each invocation of the utility (not needed for precheck mode)
Error Codes
Table A-19 Error Codes: massupdate
| Error Code | Cause | Suggested Corrective Action |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Success |
None required. |
|
1 |
Command syntax error |
Rerun the command with the proper syntax. |
|
2 |
Feature not enabled |
Enable optional feature. |
|
3 |
SIC-SMURF file not found |
Verify path and filename for SIC-SMURF file. |
|
4 |
Unable to open SIC-SMURF file |
Verify permissions on SIC-SMURF file. |
|
5 |
Incorrect file format |
Supply valid SIC-SMURF file for processing. |
|
6 |
massupdate already running |
Do not attempt to execute more than one massupdate process at the same time. |
|
7 |
npacmassupdate executable not found |
Define environment variable LSMS_DIR or contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
8 |
Database error |
Make sure the database server is running. |
|
9 |
User chose to stop |
None needed. |
|
10 |
|
If massupdate is run for all regions, stop all |
|
11 |
Unable to write |
Remove |
|
12 |
Invalid user |
Rerun as user |
measdump
Print Measurement Information
Lets you print measurement information (contained in databases) to the display.
Keyword
measdump
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name in the lsmsuser, lsmsuext, lsmsview, or lsmsall, group.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/measdump {-r <region>|-c <CLLI> [-n]
Required Flags
Specify one of the following flags:
-
-r <region> - NPAC region associated with this
npacagentprocess. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:-
Canada -
Midwest -
MidAtlantic -
Southeast -
Southwest -
Northeast -
Western -
WestCoast
-
-
-c <CLLI> - Common Language Location Identifier for the network element for which you wish to display measurements.
Optional Flags
Optionally specify one of the following flags:
-
-l - Lets you create measurement logs (a
<region>.meas.<MMDD>file for each NPAC region and a<clli>.meas.<MMDD>file for each network elements) for compatibility with previous releases of the LSMS. -
-n - Number of days before current day for which measurements are to be displayed, where
ncan have one of the values shown in Table A-20 (if this option is not specified, the default value is 0):
Table A-20 Measurement Pegs Date
| Value | Print Measurement Pegs for the Date of: |
|---|---|
|
0 |
Today |
|
1 |
Yesterday |
|
2 |
Two days before current date |
|
3 |
Three days before current date |
|
4 |
Four days before current date |
|
5 |
Five days before current date |
|
6 |
Six days before current date |
Sample Output
$ measdump -r Midwest -2
measdump: There is no measurement data available for the requested day.
$ measdump -r Midwest
Hour Binds SuccessOps FailedOps
0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0
2 0 0 0
3 0 0 0
4 0 0 0
5 0 0 0
6 0 0 0
7 0 0 0
8 0 0 0
9 0 0 0
10 1 0 0
11 0 0 0
12 0 0 0
13 0 0 0
14 0 0 0
15 0 0 0
16 0 0 0
17 0 0 0
18 0 0 0
19 0 0 0
20 0 0 0
21 0 0 0
22 0 0 0
23 0 0 0
Possible Errors
Table A-21 Error Messages: measdump
| Exit Code | Error Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
|
User entered command with incorrect syntax. |
Try the command again with the correct syntax. |
|
1 |
|
Database exception. Contact Oracle. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
The LSMS_DIR env variable is not set. |
Verify the environment variables. |
|
3 |
|
No measurement data available for the specified day (the agent was never started) |
No action necessary. |
|
4 |
|
Not known. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
npac_db_setup
NPAC Database Maintenance
Creates or removes the regional NPAC database.
Keyword
npac_db_setup
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Restrictions
-
This command must be run on each server.
-
If a database is in use by a regional LSMS agent, it cannot be removed.
-
If a regional database has already been created, it must be removed before it can be created again.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/npac_db_setup <Action> <Region>
This command must be run from the $LSMS_DIR directory and run only from the primary server.
Options
None.
Parameters
-
Action - Specifies the action to be performed on the database. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:
-
create -
remove
-
-
Region - NPAC region associated with this
npacagent. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:-
Canada -
Midwest -
MidAtlantic -
Southeast -
Southwest -
Northeast -
Western -
WestCoast
-
Sample Output
# Create NPAC database for Canada region for the first time
> $LSMS_DIR/npac_db_setup create Canada
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Npac Region Database Setup Script
The Region Database Name is CanadaDB
Initializing regional database...CanadaDB
The regional database CanadaDB was created successfully.
>
> $LSMS_DIR/npac_db_setup remove Northeast
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
Npac Region Database Setup Script
The Region Database Name is NortheastDB
Warning: NPAC region database CanadaDB is about to be removed.
All data in the database will be lost.
Do you want to continue? [Y/N]Y
Removing regional database...CanadaDB
>
Response Notes
This command takes approximately 35 to 40 seconds to execute.
Possible Errors
Table A-22 Error Messages: npac_db_setup
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Syntax was incorrect |
Use correct syntax. |
|
2 |
MySQL command failed |
Contact Oracle. |
|
7 |
User attempted to create a database that already exists |
None needed. |
|
9 |
User attempted to remove a database that is in use |
Stop indicated processes before attempting to remove the database. |
|
10 |
The root user cannot execute this command |
Change users to |
|
12 |
User attempted to remove database for an active region |
Make region inactive and retry command. |
npacimport
Import Specific Files into a Regional Database
Allows user to import specific files into the regional NPAC database.
Keyword
npacimport
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Restrictions
This command must be run from the $LSMS_DIR directory and run only from the primary server.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/npacimport [-h] -r <region> -i <type> [-u] [-y] [-t <number>] [-c <number>] <filename>
Required Flags
-
-r <region> - Specifies the region whose database the imported files are intended for. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:
-
Canada -
MidAtlantic -
Midwest -
Northeast -
Southeast -
Southwest -
WestCoast -
Western
-
-
-i <type> - Specifies the type of the file to be imported into the database. This is a mandatory parameter with the following values:
-
SubscriptionVersion -
NumberPoolBlock -
ServiceProvNetwork -
ServiceProvLRN -
ServiceProvNPA-NXX -
ServiceProvNPA-NXX-X
-
Optional Flags
-
-h - Display Help text and quit.
-
-u - Time-range update: May modify or delete and does not purge object range first. Not valid for ServiceProvNetwork.
-
-y - Continue on if a record update fails.
-
-t - Specify number of threads to use (maximum number is 10).
-
-c - Specify number of records in each batch to a thread (default is 1000).
Exit Codes
Table A-23 lists the exit codes generated by the npacimport command.
Table A-23 Exit Codes: npacimport
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
Invalid syntax |
Correct the syntax. |
|
1 |
Database error |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
File access error |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
Invalid record in the input file |
Correct the file entry or contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
4 |
Invalid user |
Change user to |
|
5 |
Unknown error |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
report
Report Generation
Generates reports for regional NPAC databases and supplemental databases.
Keyword
report
Permission
The user must be defined as a member of the primary group lsms.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/report <OutputFile> <ReportType> [<SP>|<LRN>|<DPC>|<Region>|<SplitStatus>] [<StartTN>] [<EndTN>] [<StartNPB>] [<EndNPB>]
Options
None.
Parameters
-
OutputFile - The filename for the file in which to store the report. This is a mandatory parameter whose value is the filename. The filename is appended with the value specified for
<ReportType>and the file is stored in the directory where the command is run. -
ReportType - The type of report to create. This is a mandatory parameter; use one of the following values:
SPA- Service Provider Administrative Report
SPN- Service Provider Network Report
EMR- Element Management Report
6DT- Six Digit Translation Report
10DT- Ten Digit Translation Report
SPL- NPA Split Data by Status Report
SBL- Subscription Report by LRN
SBS- Subscription Report by Service Provider ID
SBT- Subscription Report by TN
NBL- Number Pool Block Report by LRN
NBS- Number Pool Block Report by Service Provider ID
NBN- Number Pool Block Report by NPA-NXX-X
SPD- Service Provider Data Report
-
SP - Four-character alphanumeric string to specify Service Provider ID. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSBSorNBS; optional when<ReportType>is set to6DT,10DT,EMR, orSPN; otherwise not allowed. -
LRN - Ten-digit string (values 0000000000–9999999999) to specify Location Routing Number. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSBLorNBL; otherwise not allowed. -
DPC - Eleven-character string of format xxx-xxx-xxx (where each xxx can have a value 000 to 256) to specify Destination Point Code. This is an optional parameter when
<ReportType>is set to6DTor10DT; otherwise not allowed. -
Region - NPAC region. This is an optional parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSPL; otherwise not allowed. Use one of the following values:-
MidAtlantic
-
Midwest -
Northeast
-
Southeast
-
Southwest
-
Western
-
Westcoast
-
Canada
-
-
SplitStatus - NPA-NXX split status. This is an optional parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSPL; otherwise not allowed. Use one of the following values:-
Active
-
Pending
-
Error
-
-
StartTN - Starting telephone number in a range of telephone numbers. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSBT. Valid values are 10 digits from 0000000000 to 9999999999. -
EndTN - Ending telephone number in a range of telephone numbers. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toSBT. Valid values are 10 digits from 0000000000 to 9999999999. -
StartNPB - Starting value in a range of number pool blocks. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toNBN. Valid values are 7 digits from 0000000 to 9999999. -
EndNPB - Ending value in a range of number pool blocks. This is a mandatory parameter when
<ReportType>is set toNBN. Valid values are 7 digits from 0000000 to 9999999.
Sample Commands
# Generate SPA report for MidAtlantic NPAC
$ $LSMS_DIR/report MidAtlanticDB supDB report.output SPA
# Generate SBL report for MidAtlantic NPAC for LRN 9194605500
$ $LSMS_DIR/report MidAtlanticDB supDB report.output SBL 9194605500
# Generate SPL report
> $LSMS_DIR/report MidAtlanticDB supDB report.out SPL
# Generate SBS report for Midwest NPAC for all Subscriptions having a service provider of TKLC and a TN in the range of 9194600000 to 9195600000
$ $LSMS_DIR/report MidwestDB supDB report.out SBS TKLC 9194600000 9195600000
# Generate SBT report for Western NPAC for all Subscriptions having a TN in the range of 9194600000 to 9195600000
$ $LSMS_DIR/report WesternDB supDB report.out SBT 9194600000 9195600000
Files
Table A-24 shows the files for the report command.
Table A-24 Files: report
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Report Output File |
Directory where command is run |
Response Notes
The report command can process approximately 300-500 records per second, depending upon the type of report.
To view the report, change directory to the directory where the command was run and use any text editor to open the file named in the command. If you run the command from the $HOME/LSMSreports directory, you can also view the report through the graphical user interface; for information, refer to the Database Administrator's Guide.
Possible Errors
Table A-25 Error Messages: report
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
|
Specified database could not be found |
Verify that the database exists and try the command again. |
|
1 |
|
Attempt to check available disk space failed |
Remove unnecessary reports from disk. |
|
1 |
|
The start TN is greater than the end TN in the range of TNs to generate an LSMS subscription report |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
Insufficient disk space to save report |
Remove unnecessary reports from disk. |
|
1 |
|
The last TN in the range of TNs to generate an LSMS subscription report is out of range. The valid range of values for a telephone number is 0000000000...9999999999. |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
The value specified for the ReportType parameter is not valid. |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
The first TN in the range of TNs to generate an LSMS subscription report is out of range. The valid range of values for a telephone number is 0000000000...9999999999. |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
LRN argument is required for SBL/NBL report
|
If <ReportType> parameter is specified as SBL or NBL, the <LRN> parameter must also be specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
3 |
|
An <LRN> parameter that had less than 10 digits, more than 10 digits, or non-numeric characters was specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
The command was specified with an insufficient number of arguments. |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
Requesting operator does not have access rights to the database |
Change user to a username that has access rights to the database. |
|
4 |
|
The <SP> parameter was specified with more than 4 characters |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
If <ReportType> parameter is specified as SBS or NBS, the <SP> parameter must also be specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
If <ReportType> parameter is specified as NBN, the <StartNPB> parameter must also be specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
If <ReportType> parameter is specified as SBT, the <StartTN> parameter must also be specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
Report could not be stored in home directory of user |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Could not open the file in which to save the report |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Operator did not supply the correct number of arguments |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
|
1 |
|
The <ReportType> parameter was specified as SPLA or SPLR, but the wrong number of parameters was specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax and supplying all required arguments. |
resync_db_setup
Resynchronization Database Maintenance
Creates or removes the resynchronization database.
Keyword
resync_db_setup
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Restrictions
-
This command must be run on each server.
-
If the resynchronization database has already been created, it must be removed before it can be created again.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/resync_db_setup <Action>
This command must be run from the $LSMS_DIR directory and run only from the primary server.
Options
None.
Parameters
Response Notes
This command takes approximately 35 to 40 seconds to execute.
Files
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-26 Exit Codes: resync_db_setup
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Missing arguments. |
Use the correct syntax and supply all required arguments. |
|
3 |
Executing command from wrong directory. |
Change directory to $LSMS_DIR. |
|
6 |
Invalid action argument. |
Use the correct syntax and supply a valid action argument. |
|
7 |
Database already exists. |
No action necessary. |
|
8 |
Database exists on another host. |
No action necessary. |
|
9 |
Database in use by process. |
Stop the process that is using the database. |
|
10 |
User is not authorized to use this command. |
Change user to |
|
11 |
Command executed on secondary server. |
Execute command on the primary server. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
SAagent
Service Assurance Agent Control
Starts, stops, inhibits automatic restart, allows automatic restart, and retrieves the status of the Service Assurance Agent.
The SA Agent can be prevented from starting by inhibiting the process. This action allows you to control whether or not the Surveillance feature automatically starts the agent when it detects that it is not running.
NOTE: If the SA agent is running, the inhibit action does not take effect until the agent has stopped.
Keyword
SAagent
Permission
The user must be defined as a member of the secondary group lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/SAagent <Action>
Options
None.
Parameters
Sample Output
# Start the process
$ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent start
Checking if SA Agent is already running...No Starting SA Agent...Started...Verifying... SAagent started: 1997 Sept 04 12:13:14 EST # Stop the process, allow Surveillance to restart it.
$ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent stop
Checking if SA Agent is already running...Yes Stopping SA Agent... SAagent stopped: 1997 Sept 04 12:13:24 EST # Stop the process but keep Surveillance or the user from starting it. # This case assumes it was stopped.
$ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent inhibit
Saagent inhibited: 1997 Sept 04 12:13:34 EST # Now restart the process after it had be inhibited.
$ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent allow
Saagent allowed: 1997 Sept 04 12:13:44 EST $ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent start Checking if SA Agent is already running...No Starting SA Agent...Started...Verifying... SAagent started: 1997 Sept 04 12:13:45 EST # Request status
$ $LSMS_DIR/SAagent status
Checking if SA Agent is already running...Yes
SA Agent: GPL=012-000-000 : mem= 5176 kbytes : pcpu = 0.0 % TOTAL QUERIES=0 : TOTAL TNs=0
THERE ARE CURRENTLY NO SERVICE ASSURANCE ASSOCIATIONS
Files
Table A-27 shows the files for the SAagent command.
Table A-27 Files: SAagent
| Filename | Type | Location |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Configuration file |
|
Command Usage
Table A-28 gives several examples of typical command usage sequence.
Table A-28 SAagent Command Usage
| Case | Action | Command Sequence |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Start the process. |
|
|
2 |
Stop the process, allow Surveillance to restart it. |
$LSMS_DIR/SAagent stop
|
|
3 |
Stop the process but keep Surveillance or the user from starting it. This case assumes it was already started. |
|
|
4 |
Start the process after it was stopped as in Case #3. |
$LSMS_DIR/SAagent allow
|
Understanding Status Output
The association status shows each association established for that pairing. The association is designated with a number (1..4) in the left-most column. The number is a tag to coordinate with the statistics that precede the association status.
Figure A-1 shows an example in which there are three active associations. The first is handling 10 TNs per query, the second is associated but no traffic has been sent across the interface, and the third is handling an average of 3.5 TNs per query.
Figure A-1 Example of SA Agent Status Output
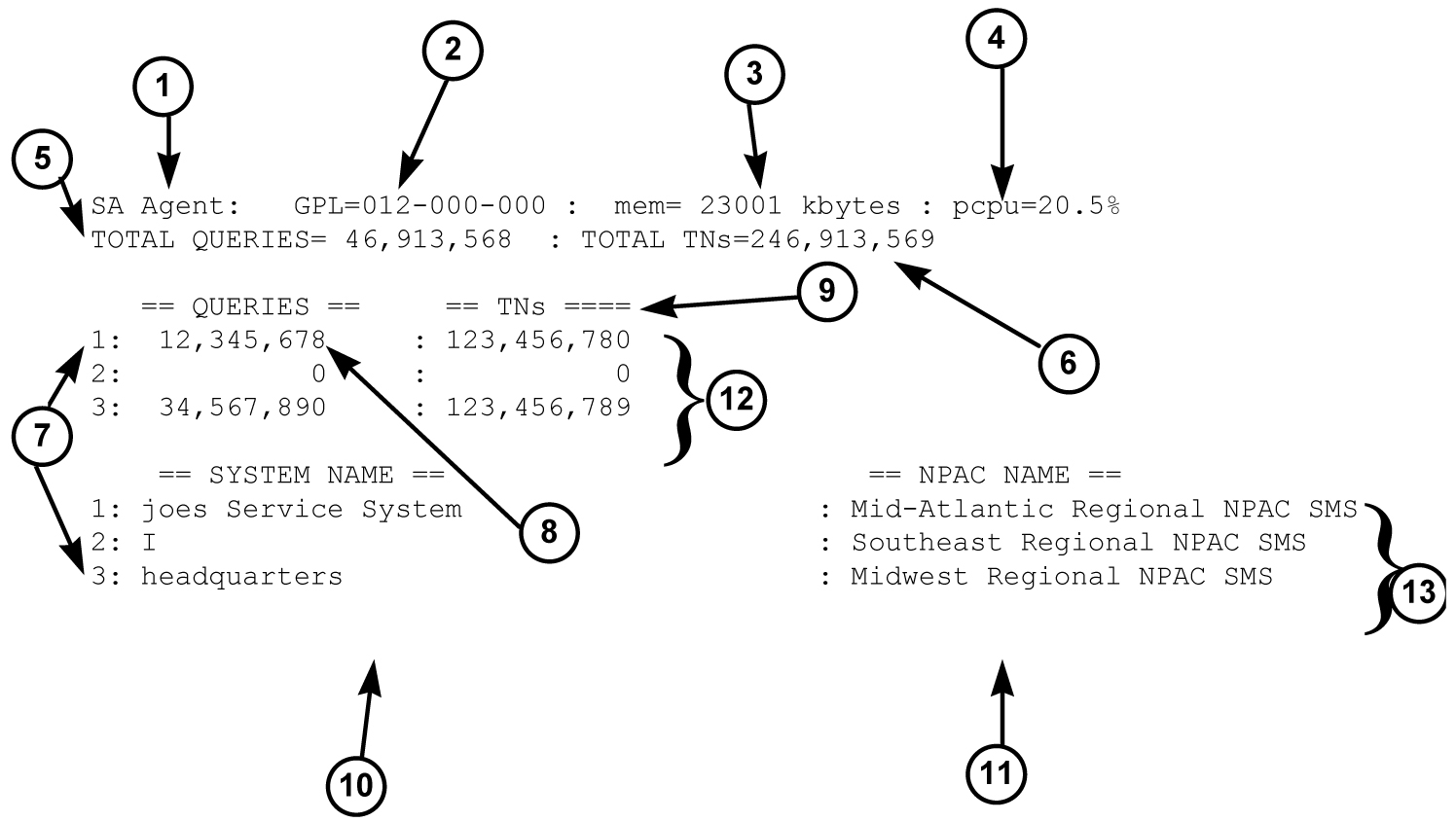
The following numbered items correspond to the numbers in Figure A-1:
-
Name of the process (SA Agent)
-
GPL number of the SA Agent process
-
Number of bytes used by the SA Agent process, in kilobytes as decimal number
-
Ratio of the CPU time used by the SA Agent to the CPU time available during the same time period
-
Total number of queries received by the SA Agent since it was last started
-
Total number of TNs in the queries
-
Tag that correlates the association statistics to the System Name and the NPAC database to which it is connected. Only the systems that are currently associated are shown
-
Total number of queries received by the SA Agent on that association since the association was established
-
Total number of TNs received by the SA Agent on that association since the association was established
-
SystemName of SA Manager
-
lnpNPAC-SMS-Name
-
Association statistics block. Values of zero indicate that no queries or TNs have been sent across the association.
-
Association status
The examples below show the status as the user sees it when the SA Agent is in various conditions. Figure A-2 shows the SA Agent running without any associations.
Figure A-2 Example -- No Associations Status Output
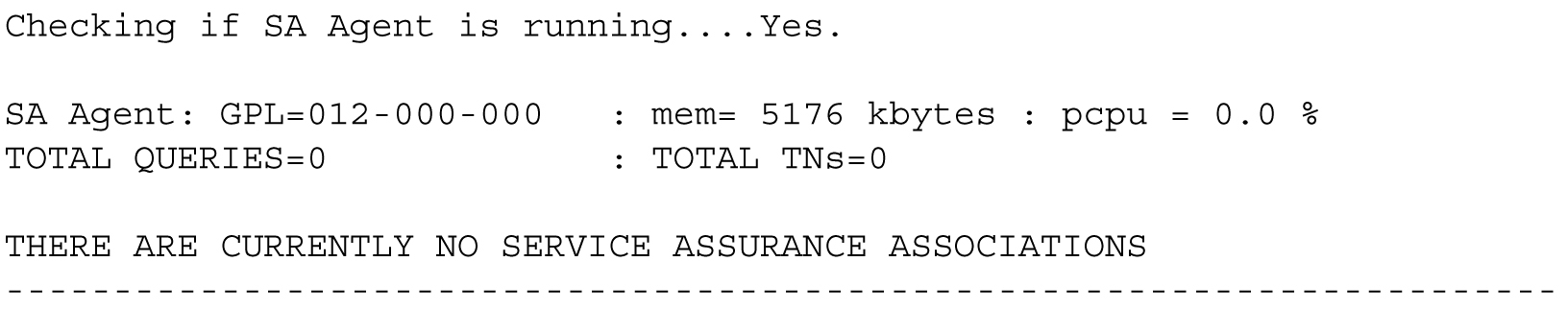
Figure A-3 shows example output that indicates that the SA Agent was inhibited after it was started.
Figure A-3 Example -- Marked Inhibited Status Output

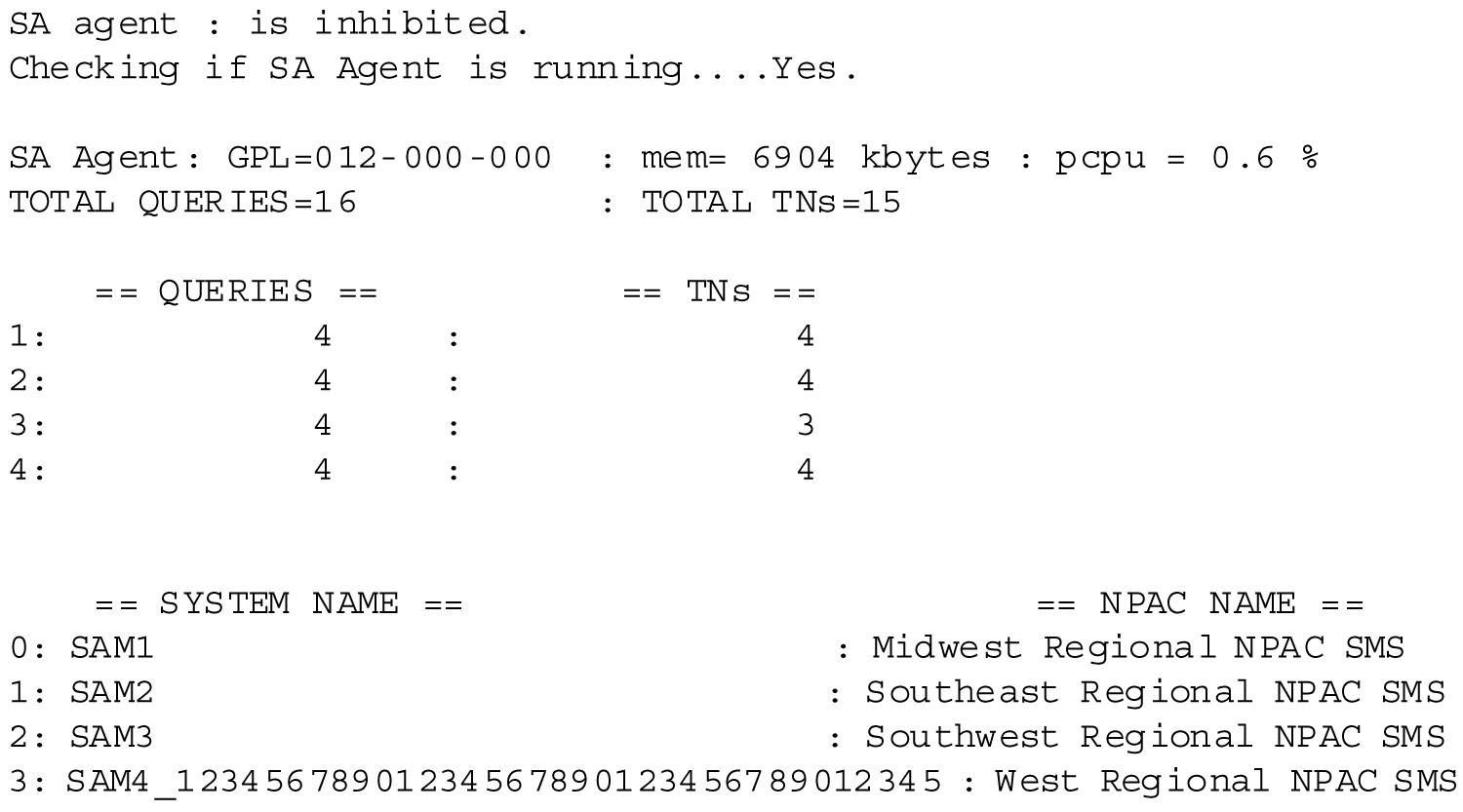
Figure A-4 shows example output that indicates that the SA Agent is inhibited and has active associations.
Figure A-4 Example -- Active Associations Status Output
Response Notes
It takes 15 seconds to start the SA agent. If the SA agent is not running, the results of a status request will not appear for at least five seconds.
Possible Errors
Table A-29 Error Messages: SAagent
| Exit Code | Message | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
|
4 |
|
The bind command failed. errormsgis the error message. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
|
sacw executable could not be found |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Start action failed |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
1 |
|
Stop action failed |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
|
Allow action failed since SA Agent is already in Allow state |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
|
Inhibit action failed because the SA Agent is already inhibited |
No action necessary. |
|
2 |
|
Could not start SA Agent since it is already executing |
No action necessary. |
|
2 |
|
Status or stop performed when SA Agent was not running |
No action necessary. |
|
3 |
SA Agent: log directory $logdir does not exist |
Logfile directory does not exist |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
|
LSMS_DIR environment variable not set |
Verify the environment variables. |
|
3 |
|
Cannot start SA Agent because it has been inhibited |
Perform |
|
4 |
|
The socket command failed. errormsg is the error message. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
|
Invalid action specified |
Try the command again using the correct syntax. |
savelogs
Save logs
Enables you to capture LSMS system logs for debugging purposes.
When this command is issued on the LSMS console, an alarm (event number 8110) is raised on the LSMS GUI, followed by alarm/event number 8111 after the logs are successfully captured. Savelogs files are generated in bz format in the savelogs directory, which is in the LSMS free directory.
Keyword
savelogs
Permission
The user must be root.
Syntax
savelogs -n days {-f} {-x [activity]:[cmip]:[ems]:[npac]}
service mysql status
Check MySQL Status
Enables you to check the status of the MySQL database.
Keyword
service mysql status
Permission
The user must be root.
Syntax
# service mysql status
Options
None.
Sample Output
[lsmsadm@lsmspri etc]$ su - root
Password:
[root@lsmspri ~]#
[root@lsmspri ~]#
[root@lsmspri ~]# service mysql status
MySQL running (5089) [ OK ]
[root@lsmspri ~]#
spidsec
Authorize Users to Access SPIDs
When the SPID Security feature is enabled, this command allows a user logged in as lsmsadm to associate specified users to access data belonging to specified Service Provider ID (SPID).
Keyword
spidsec
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_TOOLS_DIR/spidsec [-h] [-a -r -d] -u <user> -s{<spid>|GOLDEN}
Required Flags
-
-u <user> - Specify a username that has already been defined on the LSMS (see Managing User Accounts).
-
-s {<spid>|GOLDEN} - Specify a SPID that has been defined (for more information, refer to the Configuration Guide) or specify
GOLDENto apply to all defined SPIDs.
One of the following options must be specified:
Sample Output
# Display the SPID security for the username lsmsadm
$ spidsec -d -u lsmsadm
lsmsadm GOLDEN
# Authorize the username thomas to access the SPID TKLC
$ spidsec -a -u thomas -s TKLC
No output is displayed.
# Display the SPID security for all usernames
$ spidsec -d
lsmsadm GOLDEN
lsmsall GOLDEN
lsmsuser GOLDEN
lsmsuext GOLDEN
lsmsview GOLDEN
thomas TKLC
Related Commands
None.
Possible Errors
Table A-30 Exit Codes: spidsec
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
-1 |
Usage error. |
Correct the syntax. |
|
1 |
File access error. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
Database error. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
3 |
Invalid user. |
Change user to |
|
4 |
Unknown error. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
sup
Control of Local Services Manager and Local Data Manager
Used to start, stop, or display status of the Local Services Manager (lsman) and Local Data Manager (supman).
Keyword
sup
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/sup <Action>
Options
None.
Parameters
Sample Output
# Stop the lsman and supman currently running
$ $LSMS_DIR/sup stop
supman stopped
lsman stopped
# Restart the lsman and supman
$ $LSMS_DIR/sup start
This command has no output.
# Check the status of the lsman and supman
$ $LSMS_DIR/sup status
0 reports in progress
0 LNP database synchronization operations in progress
6 GUIs connected
lsman: mem= 23480 kbytes : pcpu = 0.1 %
supman: mem= 41216 kbytes : pcpu = 0.2 %
reportma: mem= 14072 kbytes : pcpu = 0.1 %
Possible Errors
Table A-31 Exit Codes: sup
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Usage error. |
Correct the syntax. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
sup_db_setup
Supplemental Database Setup
Creates or removes the supplemental database.
Note:
See “Special Procedure to Remove EMSs from Shared Memory” for information about removing EMSs from shared memory when removing supDB.
Keyword
sup_db_setup
Permission
The user must be logged in with the user name lsmsadm.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/sup_db_setup <Action>
This command must be executed from the $LSMS_DIR and must be run on the both servers. The operator must respond to a prompt to verify removal or creation of the database when a version already exists.
Options
None.
Parameters
Sample Output
To create a new Supplemental Database:
$ $LSMS_DIR/sup_db_setup create
------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplemental Database Setup Script The Supplemental Database name is supDB
Initializing Supplemental Database...supDB
The supplemental database supDB was created successfully.
To remove the current Supplemental Database
$ $LSMS_DIR/sup_db_setup remove
------------------------------------------------------------------
Supplemental Database Setup Script
WARNING: Supplemental Database supDB is about to be removed.
All data in this database will be lost.
Do you want to continue? [Y/N] Y
Removing Supplemental Database...supDB
$
Response Notes
The create action requires 20 or more seconds to create the database and respond.
Possible Errors
Table A-32 Error Messages: sup_db_setup
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Syntax was incorrect |
Use correct syntax. |
|
2 |
MySQL command failed |
Contact Oracle. |
|
7 |
User attempted to create a database that already exists |
None needed. |
|
9 |
User attempted to remove a database that is in use |
Stop indicated processes before attempting to remove the database. |
|
10 |
The root user cannot execute this command |
Change users to |
Special Procedure to Remove EMSs from Shared Memory
Note:
Beginning with LSMS Release 6.0, Sentry information for LSMS processes is stored in shared memory, not the database. As a result, use of the sup_db_setup command to remove the supDB leaves Sentry in the state that it still monitors/restarts EagleAgents for EMS that were previously defined in the supDB. Therefore, Sentry will continually attempt to restart the EagleAgents for these EMS’s and will continue to display their status. To eliminate this problem, perform the following procedure:
Procedure:
-
Delete all EMS Components using the LSMS GUI. (For more information, refer to the Configuration Guide, Chapter 3, "Deleting an EMS Configuration Component.")
-
Deactivate all NPAC Regions using the LSMS GUI. (For more information, refer to the Configuration Guide, Chapter 3, "Modifying LSMS Configuration Components.")
-
Shutdown the LSMS using Sentry. Log in to the active server as
root, and execute thesentry shutdowncommand:# sentry shutdown -
Delete the supDB. Log in to the active server as
lsmsadm, and execute thesup_db_setup removecommand:$ $LSMS_DIR/sup_db_setup remove
You have now completed this procedure.
survNotify
Surveillance Notification Command
Use this command to send a customer-defined notification.
Keyword
survNotify
Permission
The user must be defined as a member of the primary group lsms.
Syntax
$LSMS_DIR/survNotify <MsgNo> SET <Text>
Options
None.
Parameters
-
MsgNo - Unique identifier for a customer-defined message. When the
Actionparameter has the valueSET, this parameter is mandatory and must have a value in the range 9000-9999. When theActionparameter has any value other thanSET, this parameter is not allowed. -
SET - Send a surveillance notification which has the number specified by the
MsgNoparameter and the text specified byTextparameter. -
Text - The message text for a customer-defined notification. This parameter can contain up to 39 characters. If the text contains spaces, the text should begin and end with a double quote character. This parameter is optional.
Sample Output
# Notify the Surveillance Monitor that a new customer-defined event has occurred
$ $LSMS_DIR/survNotify 9001 SET "Job completed"
Response Notes
This command has no output other than the prompt.
Possible Errors
Table A-33 Exit Codes: survNotify
| Exit Code | Cause | Suggested Recovery |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Socket open error. |
Contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66. |
|
2 |
Usage error. |
Correct the syntax. |
|
3 |
Unknown operation argument. |
Supply a valid operation argument. |
|
This command is usually run by scripts; scripts should search for exit codes. When the command is run from the command line, the output indicates suggested recovery. |
||
syscheck
Check System Health
Detects, diagnoses, and displays a summary of the overall health of the LSMS.
Keyword
syscheck
Permission
The user must be root.
Syntax
The syscheck command resides in the /usr/TKLC/plat/bin directory. Use only the syntax specified in procedures in this manual. For all other uses, contact the unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-646F2C79-C167-4B5A-A8DF-7ED0EAA9AD66.
Additional Information
For additional information about the syscheck command, access the man page from the LSMS by typing the following:
man syscheck