After source data has been loaded into your implementation, you may need to perform some manipulations.
The goal of this step is to create source records with the correct set of source properties, before any mapping occurs.
You can use a Perl manipulator component in your pipeline to add, edit, and remove source properties from your records during data processing. Using a Perl manipulator, you can perform a number of tasks, including (but not limited to) the following:
This section of the Developer Studio Help provides basic information on implementing Perl manipulators. Detailed Perl manipulator information can be found in the Forge API Guide for Perl, which is available from Help menu in Developer Studio. The Forge API Guide for Perl provides descriptions for the classes and methods you can incorporate in a Perl manipulator. It also provides sample code for the most common Perl manipulator tasks.
Note
Because Perl manipulators only deal with source properties, they must always come before property mappers in a pipeline's data flow.
The Record Manipulator editor contains a unique name for this record manipulator.
The Record Manipulator editor contains the following tabs:
The Sources tab contains the following options:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Record source |
Required. A choice of the record servers in the project. |
|
Dimension source |
A choice of the dimension adapters and dimension servers in the project. If any expressions require dimensions, or the record manipulator's record index uses dimensions, then the manipulator must contain a dimension source. |
Optional. The Record Index tab allows you to add or remove dimensions or properties used in a component's record index, and to change their order. Record indexes support join functionality. See Join sources must have matching join keys and record indexes for more details.
The Record Index tab contains the following fields:
You can change source properties by writing the code in the Perl Manipulator editor, or by pointing to an external Perl file or Perl class from the Perl Manipulator editor.
A Perl manipulator component uses Perl to efficiently manipulate source records as part of Forge's data processing.
You can provide individual Perl methods to the Perl manipulator in either of the following ways:
Write the code in the Perl Manipulator editor. This approach is useful for simpler data manipulation and cases where you want to keep the Perl code in the Developer Studio project.
Specify the code in a Perl file (.pl) external to your project, and identify the file's URL in the Perl Manipulator editor. This approach is useful if you want to maintain the Perl code outside the Developer Studio project, reuse the code by calling the file from more than one pipeline, or if you simply prefer to work in an external editor.
Alternatively, if you want to write an entire Perl manipulator, you can specify the code in a Perl class external to your project, and identify the file in the 'Use this Perl class' setting in the Perl Manipulator editor. This approach is useful in cases where the amount of Perl code is large or complex.
Note
You can use a Perl manipulator to add, remove, and reformat properties, join record sources, and so on. If your pipeline contains a property mapper, the Perl manipulator is placed upstream of it.
A Perl manipulator is a pipeline component that uses Perl to efficiently manipulate source records and Endeca records as part of data processing performed in the Endeca Information Transformation Layer. This section describes the procedure for adding a Perl manipulator to your Endeca pipeline.
To add a Perl manipulator to your pipeline:
In the Pipeline Diagram editor, click New, and then choose Perl Manipulator.
The Perl Manipulator editor appears.
In the Name text box, type a unique name for this Perl manipulator. Perl manipulator names cannot contain spaces.
Click the Sources tab and do the following to specify the Perl manipulator's record sources:
To add a record source:
To remove a record source:
Do one of the following to add or point to the necessary Perl code:
In the Perl Manipulator editor, click OK to return to the Pipeline Diagram editor.
The Perl Manipulator editor contains a unique name for this Perl manipulator.
The Perl Manipulator editor contains the following tabs:
The General tab contains the following options:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Override these methods |
If you are using your own external Perl file (.pl) or want to write in-line Perl code, select 'Override these methods,' check one of the methods, and then click the method's Edit button to open the Method Override editor. |
|
Use this Perl class |
If you are using your own external Perl class , select "Use this Perl class" and then type the module's URL. |
(Optional) The Record Index tab allows you to add or remove dimensions or properties used in a component's record index, and to change their order. Record indexes support join functionality. See Join sources must have matching join keys and record indexes for more details.
The Record Index tab contains the following field:
Each Perl manipulator in your pipeline is an instance of the Forge
Execution Framework's
EDF::Manipulator class and can contain up to four
methods that Forge executes to perform data retrieval and manipulation:
This topic assumes you understand the basic concepts behind record retrieval and manipulation as implemented by the Forge Execution Framework's four core classes. Oracle strongly recommends that you read Understanding record data flow for a basic discussion of these concepts before attempting to implement a Perl manipulator.
EDF::Manipulator::prepare—The Forge Execution Framework calls this method before individual record processing begins. Thepreparemethod performs set up and initialization tasks.EDF::Manipulator::finish—Similar toprepare, the Forge Execution Framework calls this method after all record processing is complete. Typically, afinishmethod performs clean up or logging tasks.—A Perl manipulator's
next_recordmethod accomplishes three tasks:
EDF::Manipulator::get_records—Similar to next_record, a Perl manipulator's get_records accomplishes these tasks:The
get_recordsmethod callsnext_recordon its upstream component multiple times to retrieve all of the records from the upstream component.Get_recordsthen calculates which records out of the total collection match the specified key, and returns those records to the downstream component, via the Forge Execution Framework.
All record server components (record adapter, record cache, and so on)
have native implementations of these four methods. With the exception of the
Perl manipulator, however, the methods are internal and not accessible to
developers. The Perl manipulator's native implementations of these methods do
nothing. You must write your own implementations for a minimum of one of these
methods, either
next_record or
get_records. The native implementations delegate
responsibility for the tasks to your custom implementations. Your custom
implementations use methods and classes in the EDF namespace such as
EDF::Record, EDF::PVal, EDF::DVal, and so on, to accomplish their tasks. See
the
Forge API Guide for Perl for information about the methods
and classes available in the EDF namespace.
You can provide Perl methods using in-line code, or by providing a Perl file retrievable via URL. Alternatively, you can write your own class that provides these methods and point to it in the Perl Manipulator editor.
Include in-line Perl code in your pipeline using the Method Override editor.
To include in-line Perl code in your pipeline:
In the Perl Manipulator editor's General tab, select Override these methods.
Check the methods you want to override.
The Method Override editor appears.
Type or paste the method into the text box.
Consult the Forge API Guide for Perl (available on the Developer Studio Help menu) for syntax details and examples.
Detailed Perl manipulator information can be found in the Forge API Guide for Perl, which is available from Help menu in Developer Studio. The Forge API Guide for Perl provides descriptions for the classes and methods you can incorporate in a Perl manipulator. It also provides sample code for the most common Perl manipulator tasks.
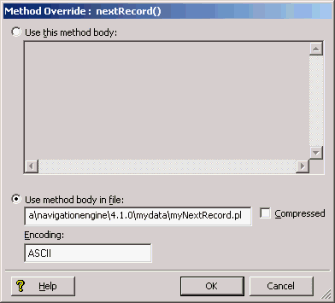
Use the method body of an external Perl file to override methods in a Perl Manipulator.
You must create a Perl manipulator. See "Adding a Perl manipulator" for details on this procedure.
To use an external Perl file to override a method:
In the Perl Manipulator editor's General tab, select Override These Methods.
Check at least one of the methods.
The Method Override editor appears.
Type the URL to the Perl file.
In the Encoding text box, type the encoding of the input data.
(Optional) If the Perl file being accessed is compressed, check Compressed.
Note
This instructs Forge to decompress the file before processing.
Note
Detailed Perl manipulator information can be found in the Forge API Guide for Perl, which is available from Help menu in Developer Studio. The Forge API Guide for Perl provides descriptions for the classes and methods you can incorporate in a Perl manipulator. It also provides sample code for the most common Perl manipulator tasks.
Use an external Perl class to call a method.
To use an external Perl class:
This section describes the Perl class requirements for use with the Endeca software.
The
Perl class must be located on the machine running Forge. It is convenient to
locate the .pm file in the same location as other Perl modules for Endeca
(ENDECA_ROOT\lib\perl). Placing your .pm file in
ENDECA_ROOT\lib\perl does not require any
additional configuration for Forge to locate it. However, if you upgrade Forge,
you will need to copy the file to the new location.
If you place the file in another location, you must modify Perl's
library search path to include the path to the .pm file. You can modify the
path by either modifying your PERLLIB environment variable or by running Forge
with the
--perllib command line option and providing the
path as an argument. In this case, you will not need to copy the file if you
upgrade Forge.
Note
Detailed Perl manipulator information can be found in the Forge API Guide for Perl, which is available from Help menu in Developer Studio. The Forge API Guide for Perl provides descriptions for the classes and methods you can incorporate in a Perl manipulator. It also provides sample code for the most common Perl manipulator tasks.
You can override methods in two ways: by writing in-line code, or by referencing an external Perl file. Both of these actions are performed in the Method Override editor.
The Method Override editor contains the following fields:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Use this method body |
Provides a text box where you can type or paste your custom Perl code. The Forge API Guide for Perl , which can be accessed from the Developer Studio Help menu, provides information for the class and method descriptions that can be used in the Perl manipulator component. |
|
Use method body in file |
The URL of a Perl file that contains your custom Perl code. |
|
Compressed |
If checked, indicates that the file referenced in "Use method body in file" is compressed. In this case, Forge will uncompress it before processing. |
|
Encoding |
Optional. Defines the encoding of the input data. Several hundred encodings are supported; the following are typical examples: If Encoding is not set, it is assumed to be UTF-8. |
A Java manipulator is your own code in Java that takes records from any number of pipeline components in Forge or, optionally, your source data, and changes it according to your processing requirements.
A Java manipulator can then write any records you choose to its output. For example, a Java manipulator can write the "transformed" records into its output, so that the records can be passed to the next pipeline component in Forge.
Java manipulators are the most generic way of modifying your data and records in the pipeline. In other words, content adapters represent a specific case of Java manipulators. For more information about writing and implementing Java manipulators, refer to the Endeca Content Adapter Developer's Guide .
The Java Manipulator editor contains a unique name for this Java manipulator.
In addition, it contains the following tabs:
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Java home |
Optional. Specifies the location of the Java runtime engine (JRE). If you do not specify this value, Forge first uses the value of the --javaHome flag. If the flag is not specified, Forge uses ENDECA_ROOT\j2sdk and lastly uses the JAVA_HOME environment variable. |
|
Class |
Required. Specifies the name of the class used by the component. |
|
Class path |
Optional. Specifies the path to a .jar file containing the class used by the manipulator. If you do not specify this value, the component checks for the class in the default class path of ENDECA_ROOT/lib/java.
NoteWhen running your pipeline, you can override the Java home and Class path settings using command-line options. See Overriding Java home and class path settings.
|
Optional. The Pass Throughs tab passes additional information to Forge. The tab contains text boxes where you can add, modify, or delete key/value pairs.