12Siebel Assignment Manager Load Splitter Configuration
Siebel Assignment Manager Load Splitter Configuration
This chapter describes Siebel Assignment Manager load splitter configuration. It includes the following topics:
How Load Splitter Configuration Works
Using load splitter configuration for Siebel Assignment Manager (AM in the following image), you can run multiple Siebel Servers concurrently on separate computers within the Siebel Enterprise, as shown in the following image. This deployment option can enhance assignment throughput by reducing the amount of time required to complete assignment requests.

This figure shows that, when a batch request is submitted, the load splitter divides the objects into multiple assignment requests across multiple computers. Assignment Manager then executes according to the predefined load splitter configurations and outputs to the database server. In this way, Assignment Manager balances job load when processing a large number of object rows.
Load splitter configuration is especially useful for batch assignment or when you must reassign large amounts of data, launch new product lines, change territory coverage or routing definitions, and so on. This feature is a useful tool for processing major reassignments, because load splitter configuration can automatically determine the load and share it evenly across multiple servers.
Load splitter configuration works in two modes, write mode and read mode, depending on where it finds the object row IDs to process. For more information about these modes, see Distribute Data Method.
Scenarios for Load Splitter Configuration
This topic provides scenarios for how you might use load splitter configuration for Siebel Assignment Manager, and how you can use threshold and batch size to manage your tasks. You might use this feature differently, depending on your business model.
You can use load splitter configuration when you perform:
Bulk import of accounts, contacts, or other data from a legacy system or data feeds
A software company periodically imports several thousands of accounts, contacts, and other data (for example, assets, products, and so on) from a legacy system. The company uses load splitter configuration to make sure that this newly imported information is visible to the correct people using the Siebel Business Applications. In this case, the assignment administrator is spared the responsibility of load balancing because load splitter configuration automatically identifies how to distribute the imported data evenly among the available Siebel Servers.
Periodic assignment rule changes
A consumer goods company periodically makes changes to assignment rules. The company uses load splitter configuration to make sure that all accounts and contacts are reassigned in optimal time. In this case, the assignment administrator is spared the time-consuming responsibility of planning and determining what resources are available for the realignment.
Setting Up Load Splitter Configuration
To set up load splitter configuration
Navigate to the Administration - Assignment screen, and then the Load Splitter Configuration view.
In the Load Splitter Configuration list, click New to add a new record.
The Configuration ID field automatically populates.
In the new record, enter values for the relevant information.
In the Name field, type the name of the configuration.
In the Threshold field, click the calculator button to enter a number. This field identifies the maximum number after which the splitting will occur.
In the Minimum Batch Size field, click the calculator button to enter a positive number. This field determines the minimum number of rows processed within a single task.
In the Server Configuration list, click New to add a new record.
In the Priority field, click the calculator button to enter a number.
This field determines which server is picked up first for processing over others. The priority is determined in ascending order, that is, 1 is a higher priority than 2. For example, assume that you have dedicated Assignment Manager servers that require a higher priority than another server running Siebel EIM. In this case, you would set a higher priority for the Assignment Manager servers than for the Siebel EIM server.Tip: It is recommended to set your first priority number fairly high, such as to 100, and to provide sufficient gaps between priority numbers. Doing this can be helpful in case new servers are added for processing load splitting tasks, because you will not have to reset your entire priority arrangement. For example, if you start with two servers, then set one priority at 100, and the other at 200. If you add a third server, then you could set its priority to 150 if its priority is between that of the other two values.In the Server Name field, enter the name of the Siebel Server.
In the Number of Tasks field, click the calculator button to enter a positive number. This field determines the number of tasks that can be executed on that particular server.
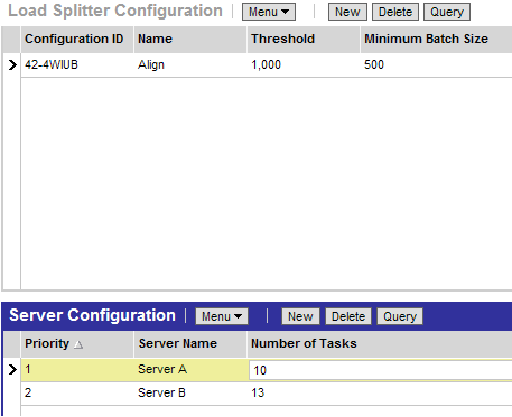
The following figure shows a sample Align configuration that uses two servers, Server A and Server B, to process multiple tasks. In this configuration, Server A has a higher priority than Server B.
Examples for Administering the Load Splitter
The following three examples show how the assignment administrator might use threshold, batch size, and load splitter configuration to split a batch request into multiple, manageable tasks. You might use this feature differently, depending on your business model for Siebel Assignment Manager.
Example 1: Load Splitter Less Than Threshold
In this example, the load splitter receives 900 row IDs for the account assignment object. Because this is less than the threshold, which is 1000, no load splitting occurs. All rows are passed to the server with the lowest priority number.
Example 2: Load Splitter Using Minimum Batch Size
In this example, the load splitter receives 1001 row IDs for the account assignment object, which is greater than the threshold of 1000. The total number of tasks is 10, and minimum batch size is 500. The load splitter tries to split the rows into even tasks. The default calculation for batch size calculates 1001 divided by 10, or about 100 rows, as the batch size. Due to the ramp-up time for different server components, this processing is actually more inefficient than just running two separates batches of 500 and 501 row IDs. Therefore, the load splitter takes the minimum batch size of 500 into account and splits the rows into two tasks of 500 and 501.
Example 3: Load Splitter When Batch Size Is Greater Than Minimum Batch Size
In this example, the load splitter receives 6023 row IDs for the Account assignment object. Because this is greater than the threshold of 1000, the load splitter tries to split the rows into batches. The default calculation for batch size calculates 6023 divided by 10, or about 600 rows, as the batch size. Because this is greater than the minimum batch size of 500, the load splitter splits the rows into 8 tasks of 600 and one task of 623.
Load Splitter Operating Modes
Load splitter configuration for Siebel Assignment Manager uses the Configuration ID parameter to query for the threshold, minimum batch size, list of servers, the server task numbers, and the maximum number of tasks. However, if certain conditions exist, then load splitter configuration passes all the objects as one batch onto the server component. Those conditions are:
If there is no configuration data
If configuration is incorrect
If the server cannot be found
There are two operating modes for load splitter configuration, write mode and read mode, depending on where load splitter configuration finds the object row IDs to process. Write mode writes to the S_ASGN_LB_DATA table, whereas read mode expects the data to already be loaded into the table.
Write Mode. By default, load splitter configuration runs in write mode. This mode takes a property set of WHERE clauses (one for each object type), inserts the rows into the S_ASGN_LB_DATA table, and then groups the object row IDs into several tasks and passes them to Assignment Manager.
In write mode, the Load Splitter Service business service takes two types of input to identify the records that must be assigned: the object to be assigned and the search specification (in SQL format).
Based on load splitter configuration parameters, the load splitter splits the data, computes the resources available, and then distributes the assignment load among the configured Siebel Servers.
Read Mode. Load splitter configuration runs in read mode based on a request ID. If the Mode input argument is Read, then load splitter configuration separates the object rows into separate tasks and submits a request to a server component job to the appropriate server or servers.
In read mode, the assignment administrator (AA) determines the records that must be assigned in the S_ASGN_LB_DATA staging table, and then invokes the load splitter in read mode. The Load Splitter Service business service bypasses the identifying phase and reads the predetermined set of records that must be assigned.
Based on load splitter configuration parameters, the load splitter computes the resources available (as in write mode), and then distributes the assignment load among the configured Siebel Servers.
For information about invoking the load splitter, see Distribute Data Method.
Distribute Data Method
The Distribute Data business service method is part of the Load Splitter Service business service, which allows you to configure Siebel Assignment Manager to run on multiple Siebel Servers concurrently within the Siebel Enterprise. This method consists of a complex hierarchical input property set.
This topic documents the arguments, usage, and invocation context for the Distribute Data method, and provides example code for invoking load splitter configuration.
Arguments
The following table lists the arguments supported for the Distribute Data method.
Argument |
Description |
|---|---|
Configuration Id |
The load splitter uses the configuration ID to get the configuration for the servers, threshold, minimum batch size, list of servers to run on, and so on. |
Mode |
Determines whether the load splitter runs in write or read mode. Read mode is the default. |
Object Types |
A property set that identifies the types of objects in a run and a child property set that contains a WHERE clause and the table name of each object type. For example: Object Type = Contact WHERE Clause = Specialty LIKE Cardiology TableName = S_PARTY |
Request Id |
Identifies the rows in the S_ASGN_LB_DATA table for a specific assignment request. |
Server Component |
Identifies the server component that the load splitter uses to pass the object rows for subsequent processing. The component is either Assignment Manager (AsgnSrvr) or Batch Assignment (AsgnBatch). This parameter also contains a child property set that has the input arguments used by a particular server component. For example: AsgnSrvr can take in the following input arguments based on underlying component parameters: AsgnKey, CopyPersonSpecData, and so on. |
Component Parameters |
The property set that contains all the parameters for the specified server component. This property set must be added as a child of each (previous) Object Type property set.
Note: It is not possible to pass parameters such as Assignment Key, Regular Assign, and Reporting Mode using the Load Splitter Service business service. If you specify any of these values to be passed by the load splitter as property name and value pairs, then they are ignored. For example, the Assignment Key is ignored and Batch Assignment chooses the default All AM Rule Set component parameter rather than the particular rule group that you want to execute.
|
Set Server Component Object Type Parameter |
Indicates which parameter to populate with the object type. |
Set Server Component SQL Parameter |
Indicates which parameter to populate with the load-balanced SQL statement. |
Usage
Input for load splitter configuration comes from any service that intends to use it, for example Target Object Selector (TOS), a business service. Load splitter configuration splits the objects that need processing into separate batches and submits those batches to a the server component, such as Assignment Manager (AsgnSrvr) in the example that follows.
Invoked From
You can invoke the load splitter using a workflow process, business service, scripting, and so on.
Example
The following is sample code for invoking load splitter configuration using a business service.
function LoadSplitterCreateInputs()
{
var psInputArgs;
var psOutputArgs;
var psObjTypes;
var psSrvrCompParams;
var pService;
psInputArgs = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Request Id", "LoadSplitterTest");
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Configuration Id", "42-4VPGT");
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Mode", "Write");
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Server Component", "AsgnSrvr");
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Set Server Component Object Type Parameter",
"AsgnObjName");
psInputArgs.SetProperty ("Set Server Component SQL Parameter", "ObjRowSqlStmt");
psObjTypes = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
psObjTypes.SetType ("Object Type");
psObjTypes.SetValue ("Account");
psObjTypes.SetProperty("SQL", "SELECT ROW_ID FROM SIEBEL.S_ORG_EXT WHERE NAME LIKE
'K%TEST%'");
psInputArgs.AddChild (psObjTypes);
psObjTypes = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
psObjTypes.SetType ("Object Type");
psObjTypes.SetValue ("Opportunity");
psObjTypes.SetProperty ("SQL", "SELECT ROW_ID FROM SIEBEL.S_OPTY WHERE NAME LIKE
'K%TEST%'");
psInputArgs.AddChild (psObjTypes);
psSrvrCompParams = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
psSrvrCompParams.SetType ("Component Parameters");
psInputArgs.AddChild (psSrvrCompParams); psOutputArgs = TheApplication().NewPropertySet();
pService = TheApplication().GetService("Load Splitter Service");
pService.InvokeMethod ("DistributeData", psInputArgs, psOutputArgs);
}